Identification and Characterization of Quorum-Quenching Activity of N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. AHL-Degrading Activities in CNS Strains
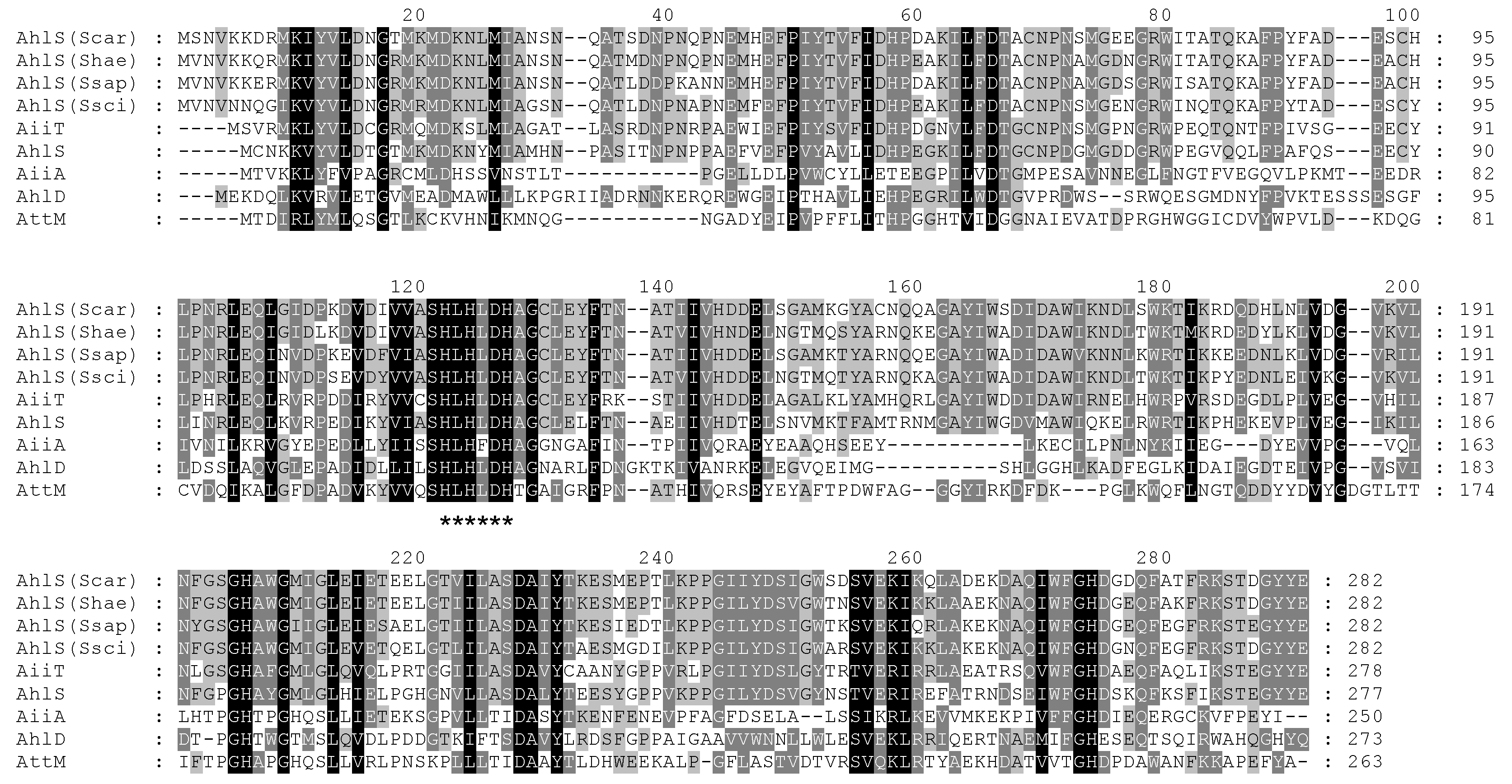
2.2. AiiA-Type AHL Lactonase Gene Is Present in the CNS Strains
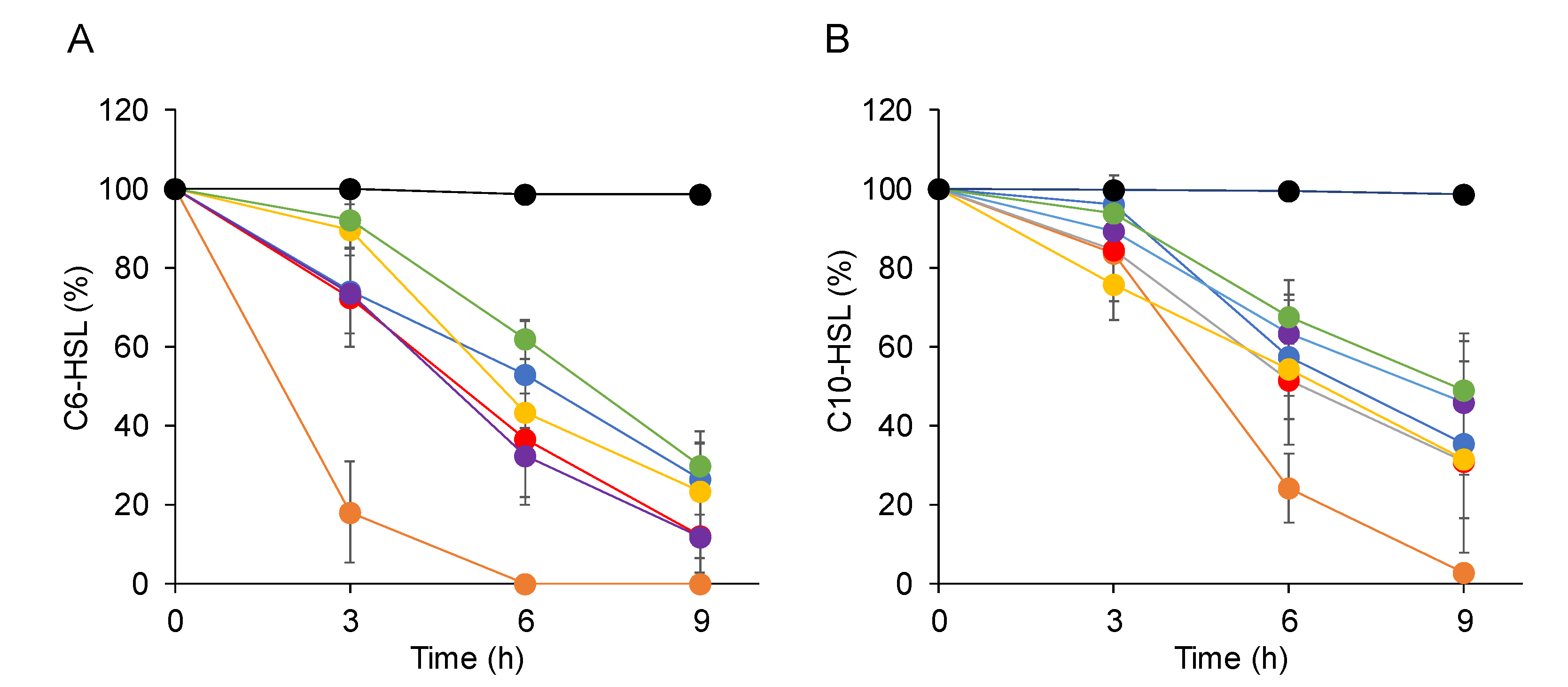
2.3. Characterization of the AHL-Degrading Activity of AhlS from the CNS Strains
2.4. AhlS Inhibits the Quorum-Sensing Phenotypes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains, Compounds, and Incubation Conditions
3.2. Amplification and Sequencing of the ahlS Gene from S. sciuri
3.3. Cloning of the ahlS Gene from the CNS Strains
3.4. Assessment of AHL-Degrading Activities
3.5. AHL Restoration Assay
3.6. Purification of AhlS as an MBP Fusion
3.7. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing by MBP-AhlS in P. aeruginosa
3.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: A signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8789–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kievit, T.R.; Iglewski, B.H. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4839–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bodman, S.B.; Bauer, W.D.; Coplin, D.L. Quorum sensing in plant-pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 41, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uroz, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Oger, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: The yin and yang of bacterial communication. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, L.H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Someya, N.; Ikeda, T. Complete genome sequence and characterization of the N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading gene of the potato leaf-associated Solibacillus silvestris. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, L.H. Genetic control of quorum-sensing signal turnover in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4638–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, T.K.; Oh, J.W.; Koo, B.T.; Yum, D.Y.; Lee, J.K. AhlD, an N-acylhomoserine lactonase in Arthrobacter sp., and predicted homologues in other bacteria. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Morohoshi, T.; Someya, N.; Ikeda, T. AidC, a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the potato root-associated Cytophaga-Flavobacteria-Bacteroides (CFB) group bacterium Chryseobacterium sp. strain StRB126. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7985–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Someya, N.; Ikeda, T. Characterization of a novel thermostable N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the thermophilic bacterium Thermaerobacter marianensis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, J.; Goldmann, D.A. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: Role as pathogens. Annu. Rev. Med. 1999, 50, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, T.; Kato, M.; Fukamachi, K.; Kato, N.; Ikeda, T. N-acylhomoserine lactone regulates violacein production in Chromobacterium violaceum type strain ATCC 12472. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyaz, L.; Karki, A.B.; Fakhr, M.K. Draft genome sequence of megaplasmid-bearing Staphylococcus sciuri strain B9-58B, isolated from retail pork. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01419–e01474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, T.; Someya, N.; Ikeda, T. Novel N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria isolated from the leaf surface of Solanum tuberosum and their quorum-quenching properties. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 2124–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbaugh, K.P.; Griswold, J.A.; Iglewski, B.H.; Hamood, A.N. Contribution of quorum sensing to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vurn wound infections. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5854–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyaja, P.; Jayesh, P.; Philip, R.; Bright Singh, I.S. Pyocyanin induced in vitro oxidative damage and its toxicity level in human, fish and insect cell lines for its selective biological applications. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Fischer, U. Description of a new species of the genus Staphylococcus: Staphylococcus carnosus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1982, 32, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Kloos, W.E. Isolation and characterization of Staphylococci from human skin I. amended descriptions of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus and descriptions of three new species: Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus xylosus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1975, 25, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kloos, W.E.; Schleifer, K.H.; Smith, R.F. Characterization of Staphylococcus sciuri sp. nov. and its subspecies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1976, 26, 22–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual/Joseph Sambrook, David, W. Russell; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, S.R.; Harty, C.; Hooi, D.S.; Daykin, M.; Williams, P.; Telford, G.; Pritchard, D.I.; Bycroft, B.W. Synthetic analogues of the bacterial signal (quorum sensing) molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone as immune modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kovach, M.E.; Elzer, P.H.; Hill, D.S.; Robertson, G.T.; Farris, M.A.; Roop, R.M., 2nd; Peterson, K.M. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 1995, 166, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, S.; Yasumoto, S.; Morohoshi, T.; Ikeda, T. AmiE, a novel N-acylhomoserine lactone acylase belonging to the amidase family, from the activated-sludge isolate Acinetobacter sp. strain Ooi24. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6919–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, S.; Morohoshi, T.; Kurabeishi, A.; Shinozaki, M.; Fujita, H.; Sawada, I.; Ikeda, T. Production and degradation of N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signal molecules in bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2436–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, B.W.; Krishnapillai, V.; Morgan, A.F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol. Rev. 1979, 43, 73–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, M.; Lee, K.M.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification of genes controlled by quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13904–13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Ikeda, T.; Takiguchi, N.; Kuroda, A.; Ohtake, H.; Kato, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by N-acyl cyclopentylamides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3183–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihl, M.; Chávez de Paz, L.E.; Schmidtchen, A.; Svensäter, G.; Davies, J.R. Effects of clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihl, M.; Arvidsson, A.; Skepö, M.; Nilsson, M.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Svensäter, G.; Davies, J.R. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis on peritoneal dialysis catheters and the effects of extracellular products from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kievit, T.R. Quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morohoshi, T.; Kamimura, Y.; Someya, N. Identification and Characterization of Quorum-Quenching Activity of N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080483
Morohoshi T, Kamimura Y, Someya N. Identification and Characterization of Quorum-Quenching Activity of N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(8):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080483
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorohoshi, Tomohiro, Yaoki Kamimura, and Nobutaka Someya. 2020. "Identification and Characterization of Quorum-Quenching Activity of N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci" Antibiotics 9, no. 8: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080483
APA StyleMorohoshi, T., Kamimura, Y., & Someya, N. (2020). Identification and Characterization of Quorum-Quenching Activity of N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Antibiotics, 9(8), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080483




