Synthesis and Anti-Saprolegnia Activity of New 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
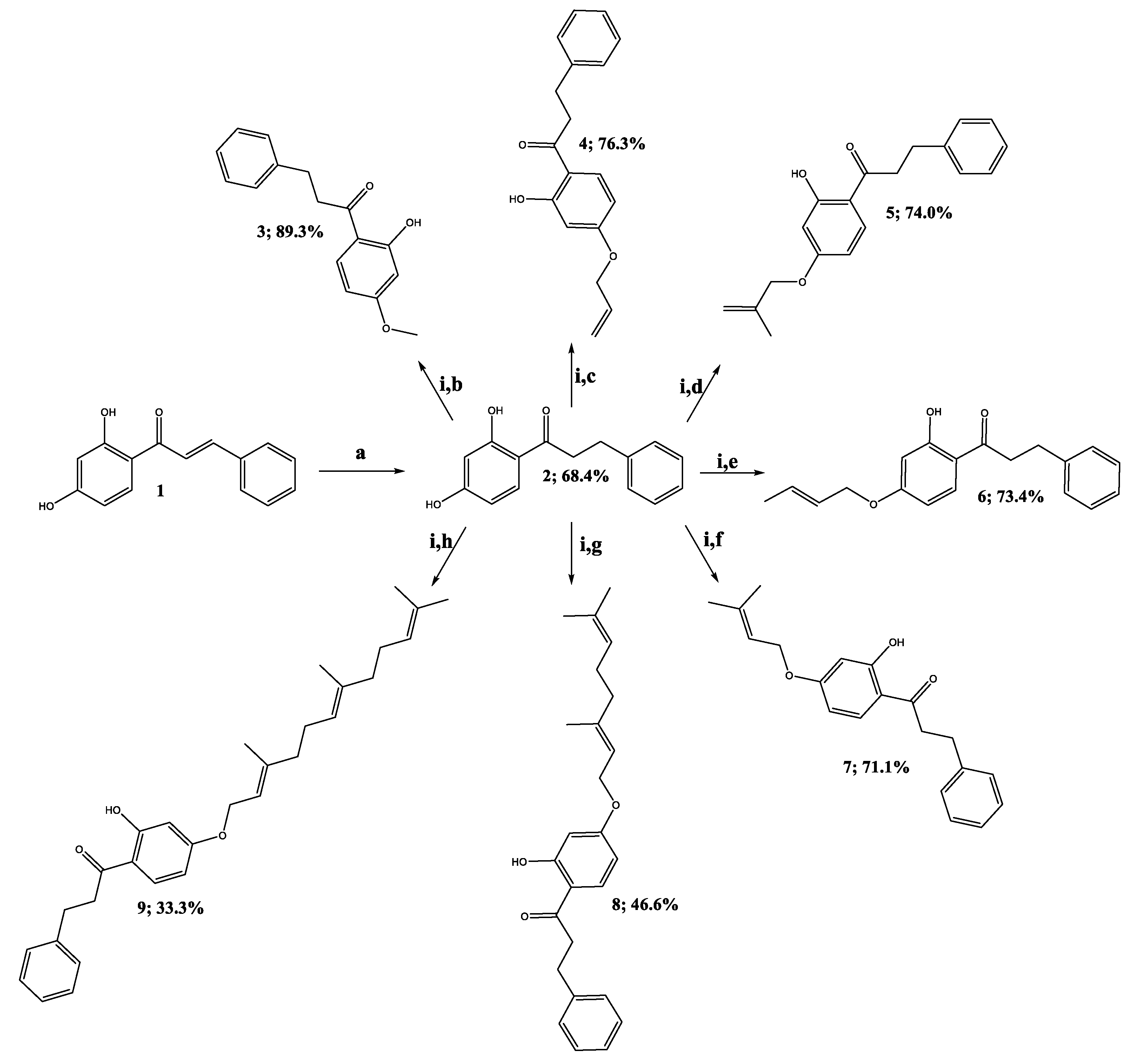
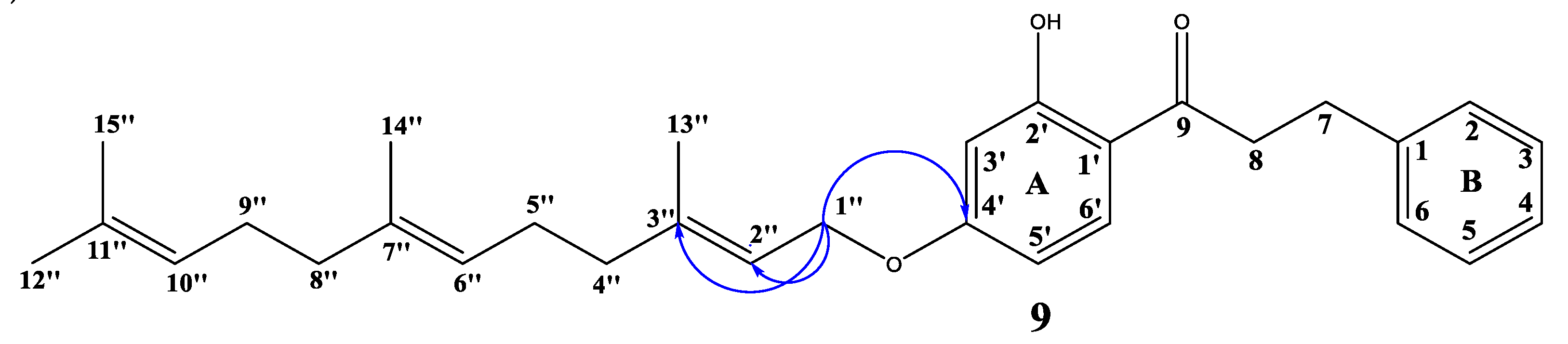
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Anti-Saprolegnia Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone (2)
3.3. Synthesis of Oxyalkylated Derivatives (3–9)
3.4. Determination of MIC and MOC
3.5. Membrane Damage
3.6. Statistical Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bostock, J.; McAndrew, B.; Richards, R.; Jauncey, K.; Telfer, T.; Lorenzen, K.; Little, D.; Ross, L.; Handisyde, N.; Gatward, I.; et al. Aquaculture: Global status and trends. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfield, M.J.; Kamoun, S. Hooked and Cooked: A Fish Killer Genome Exposed. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van West, P. Saprolegnia parasitica, an oomycete pathogen with a fishy appetite: New challenges for an old problem. Mycologist 2006, 20, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torto-Alalibo, T.; Tian, M.; Gajendran, K.; Waugh, M.E.; van West, P.; Kamoun, S. Expressed sequence tags form the oomycete fish pathogen Saprolegnia parasitica reveal putative virulence factors. BMC Microbial. 2005, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, T.M.; Rach, J.J.; Howe, G.E. Efficacy of formalin, hydrogen peroxide, and sodium chloride on fungal-infected rainbow trout eggs. Aquaculture 1996, 140, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.A.; Wada, S.; Hatai, K.; Yamamoto, A. Antimycotic activity of eugenol against selected water molds. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, S.; Yoon, G.H.; Freeman, M.A.; Mackie, J.A.; Shinn, A.P. The efficacy of selected plant extracts and bioflavonoids in controlling infections of Saprolegnia australis (Saprolegniales; Oomycetes). Aquaculture 2012, 358–359, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piamsomboon, P.; Lukkana, M.; Wongtavatchai, J. Safety and Toxicity Evaluation of Bronopol in Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Thai. J. Vet. Med. 2013, 43, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Detsi, A.; Majdalani, M.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Kefalas, P. Natural and synthetic 2’-hydroxy-chalcones and aurones: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of the antioxidant and soybean lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 8073–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, G.; Mascolo, N.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, F. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stompor, M.; Broda, D.; Bajek-Bil, A. Dihydrochalcones: Methods of acquisition and pharmacological properties—a first systematic review. Molecules 2019, 24, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koorbanally, N.; Randrianarivelojosia, M.; Mulholland, D.; Quarles van Ufford, L.; van den Berg, A. Chalcones from the seed of Cedrelopsis grevei (Ptaeroxylaceae). Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheenpracha, S.; Karalai, C.; Ponglimanont, C.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Tewtrakul, S. Anti-HIV-1 protease activity of compounds from Boesenbergia pandurata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassan, A.M.; Abdullahi, M.I.; Uba, A.; Umar, A. Prenylation of aromatic secondary metabolites: A new frontier for development of novel drugs. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, S.L.; Pan, C.; Guan, L.P.; Sun, X.Y. Synthesis of 2′-hydroxy-4′-isoprenyloxychalcone Derivatives with Potential Antidepressant-like Activity. Med. Chem. 2014, 10, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquina, S.; Maldonado-Santiagoa, M.; Sánchez-Carranza, J.N.; Antúnez-Mojica, M.; González-Maya, L.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Alvarez, L. Design, synthesis and QSAR study of 2′-hydroxy-4′-alkoxy chalcone derivatives that exert cytotoxic activity by the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, I.; Madrid, A. Synthesis of dihydroisorcordoin derivatives and their in vitro anti-oomycete activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, D.; Grover, S.K. Facile reduction of chalcones to dihydrochalcones with NaBH4 /Ni2+ system. Synth. Commun. 1992, 22, 2405–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenweber, E.; Seigler, D.S. Flavonoids from the exudate of Acacia neovernicosa. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Q.; Bao, W.; Ao, W. Structure elucidation and NMR assignments of a new dihydrochalcone from Empetrum nigrum subsp. asiaticum (Nakai ex H.Ito) Kuvaev. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa-Susłow, E.; Dymarska, M.; Guzik, U.; Wojcieszyńska, D.; Janeczko, T. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A Gram-Negative Bacterium Useful for Transformations of Flavanone and Chalcone. Molecules 2017, 22, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnov, E.A.; Ermilova, E.V.; Kadyrova, T.V.; Raldugin, V.A.; Bagryanskaya, I.Y.; Gatilov, Y.V.; Druganov, A.G.; Semenov, A.A.; Tolstikov, G.A. Phenolic components of Empetrum extract and the crystal structure of one of them. Chem Nat Comp. 2000, 36, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.; Dringl, J.V.; Herring, C. Phenolics in Lonchocarpus (Leguminosae), a review with some new findings. Kew Bull 2007, 62, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, M.S.; Blaney, W.M.; Delle Monache, F.; Marini Bettolo, G.B. Insect Antifeedant Activity Associated With Compounds Isolated From Species of Lonchocarpus and Tephrosia. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, I.; Muñoz, O.; Villena, J.; Werner, E.; Mellado, M.; Ramírez, I.; Caro, N.; Flores, S.; Madrid, A. Structure-Activity Relationship of Dialkoxychalcones to Combat Fish Pathogen Saprolegnia australis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, S.; Montenegro, I.; Villena, J.; Cuellar, M.; Werner, E.; Godoy, P.; Madrid, A. Synthesis and Evaluation of novel oxyalkylated derivatives of 2′,4′-dihydroxychalcone as anti-oomycete agents against bronopol resistant strains of Saprolegnia sp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngaini, Z.; Fadzillah, S.M.H.; Hussain, H. Synthesis and antimicrobial studies of hydroxylated chalcone derivatives with variable chain length. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, D.; Ibrahim, R. Isoprenylated flavonoids—A survey. Phytochemistry 1996, 43, 921–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | MIC a (µg/mL) | MOC b (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. parasitica | S. australis | S. diclina | S. parasitica | S. australis | S. diclina | |
| 2 | 225 | 200 | 150 | 225 | 175 | 175 |
| 3 | >250 | 250 | 250 | >250 | >250 | >250 |
| 4 | >250 | 250 | 225 | >250 | >250 | >250 |
| 5 | >250 | 225 | 200 | >250 | 250 | 225 |
| 6 | >250 | 250 | 225 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| 7 | >250 | 225 | 175 | >250 | 250 | 200 |
| 8 | 200 | 175 | 125 | 225 | 175 | 150 |
| 9 | 175 | 150 | 100 | 200 | 150 | 100 |
| Bronopol | 225 | 200 | 150 | 250 | 200 | 150 |
| Fluconazole | >250 | 250 | 200 | >250 | >250 | 250 |
| Compound (150 µg/mL) | % Membrane Lysis a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. parasitica | S. australis | S. diclina | |
| 2 | 21.0 ± 0.1 | 25.0 ± 0.3 | 35.0 ± 0.2 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 16.0 ± 0.1 |
| 8 | 23.0 ± 0.3 | 27.0 ± 0.5 | 30.0 ± 0.2 |
| 9 | 30.0 ± 0.2 | 35.0 ± 0.4 | 43.0 ± 0.3 |
| Bronopol | 20.0 ± 0.4 | 25.0 ± 0.3 | 28.0 ± 0.2 |
| Fluconazole | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SDS | 100 | 100 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Werner, E.; Montenegro, I.; Said, B.; Godoy, P.; Besoain, X.; Caro, N.; Madrid, A. Synthesis and Anti-Saprolegnia Activity of New 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone Derivatives. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060317
Werner E, Montenegro I, Said B, Godoy P, Besoain X, Caro N, Madrid A. Synthesis and Anti-Saprolegnia Activity of New 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone Derivatives. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(6):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060317
Chicago/Turabian StyleWerner, Enrique, Iván Montenegro, Bastian Said, Patricio Godoy, Ximena Besoain, Nelson Caro, and Alejandro Madrid. 2020. "Synthesis and Anti-Saprolegnia Activity of New 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone Derivatives" Antibiotics 9, no. 6: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060317
APA StyleWerner, E., Montenegro, I., Said, B., Godoy, P., Besoain, X., Caro, N., & Madrid, A. (2020). Synthesis and Anti-Saprolegnia Activity of New 2’,4’-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone Derivatives. Antibiotics, 9(6), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060317





