Trematocine, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Antarctic Fish Trematomus bernacchii: Identification and Biological Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Trematocine: A Piscidin
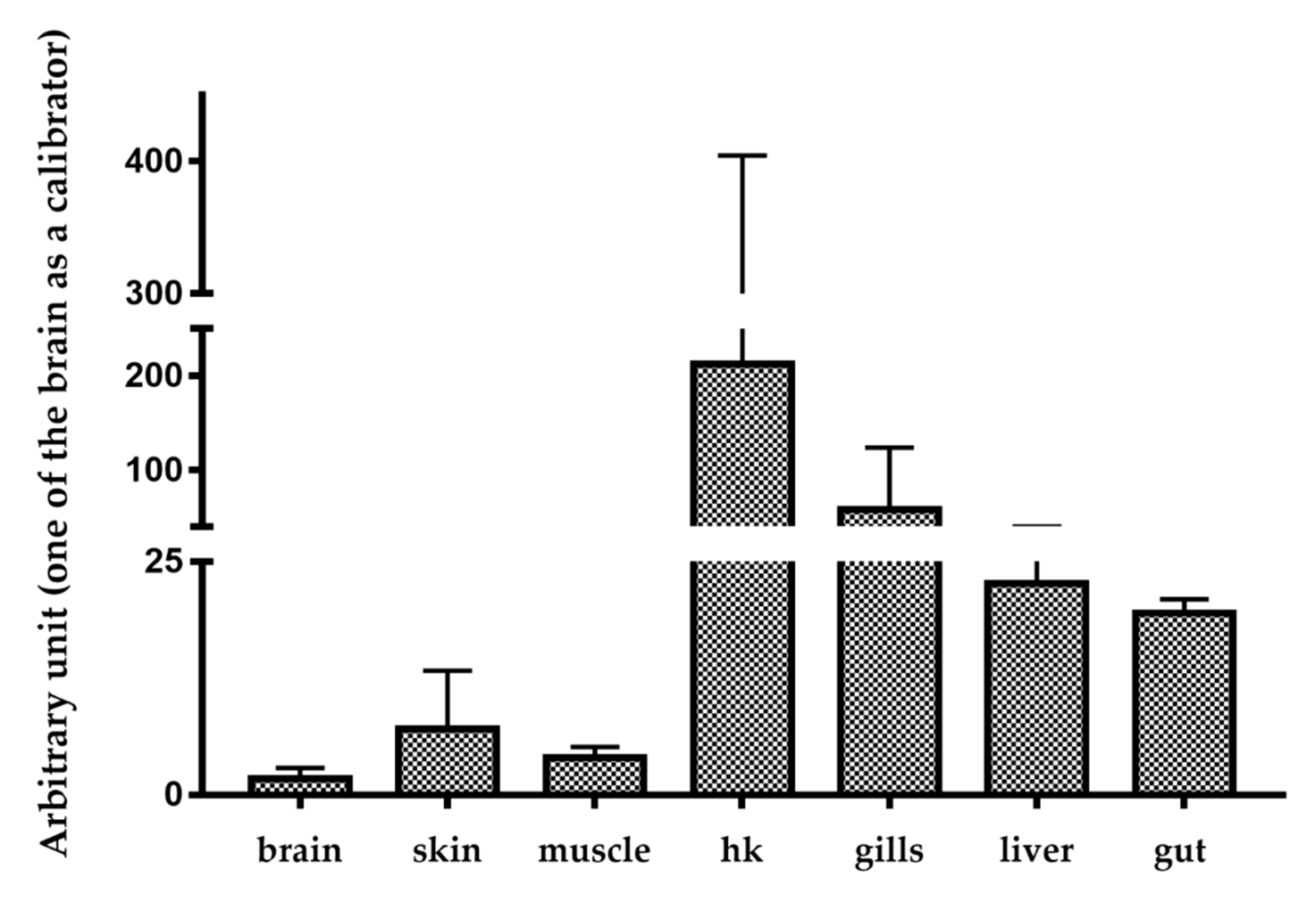
2.2. Basal and Stimulated Expression in Different Tissues
2.3. Trematocine Mature Peptide Structure
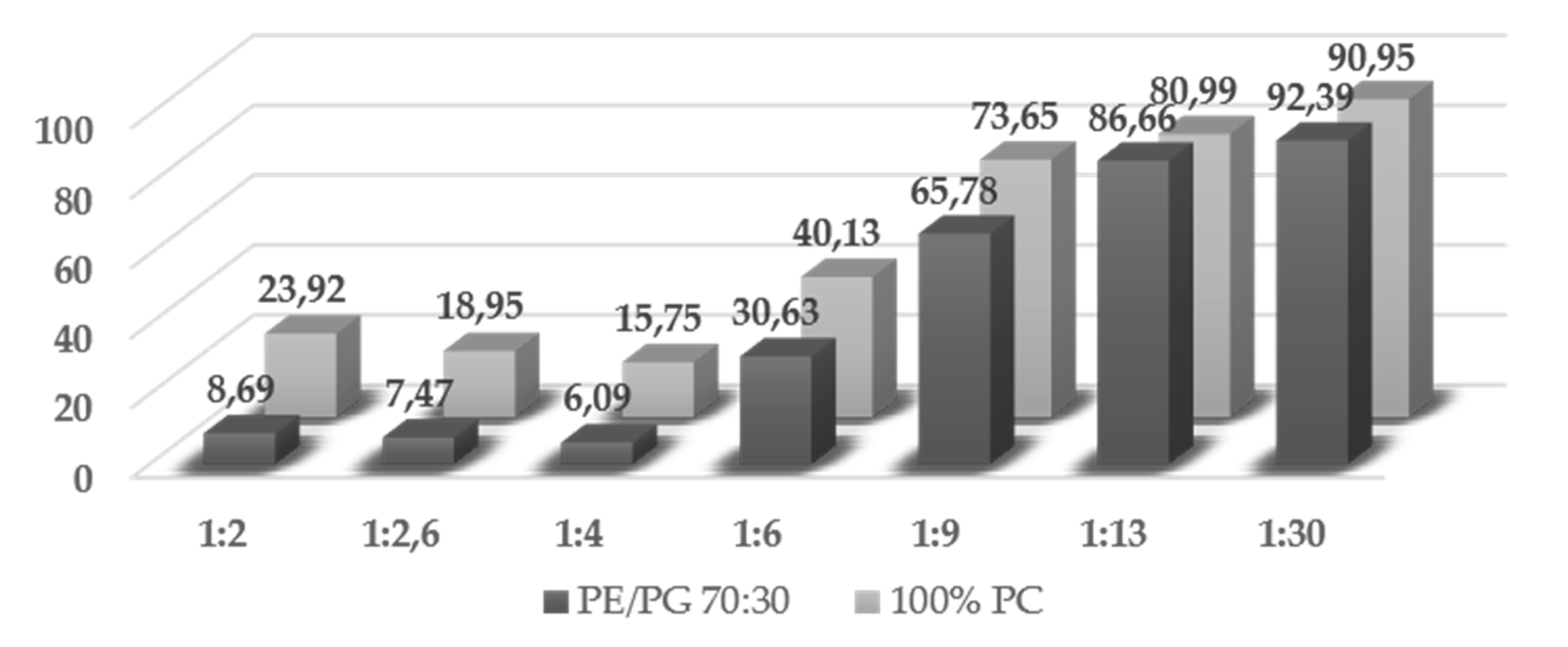
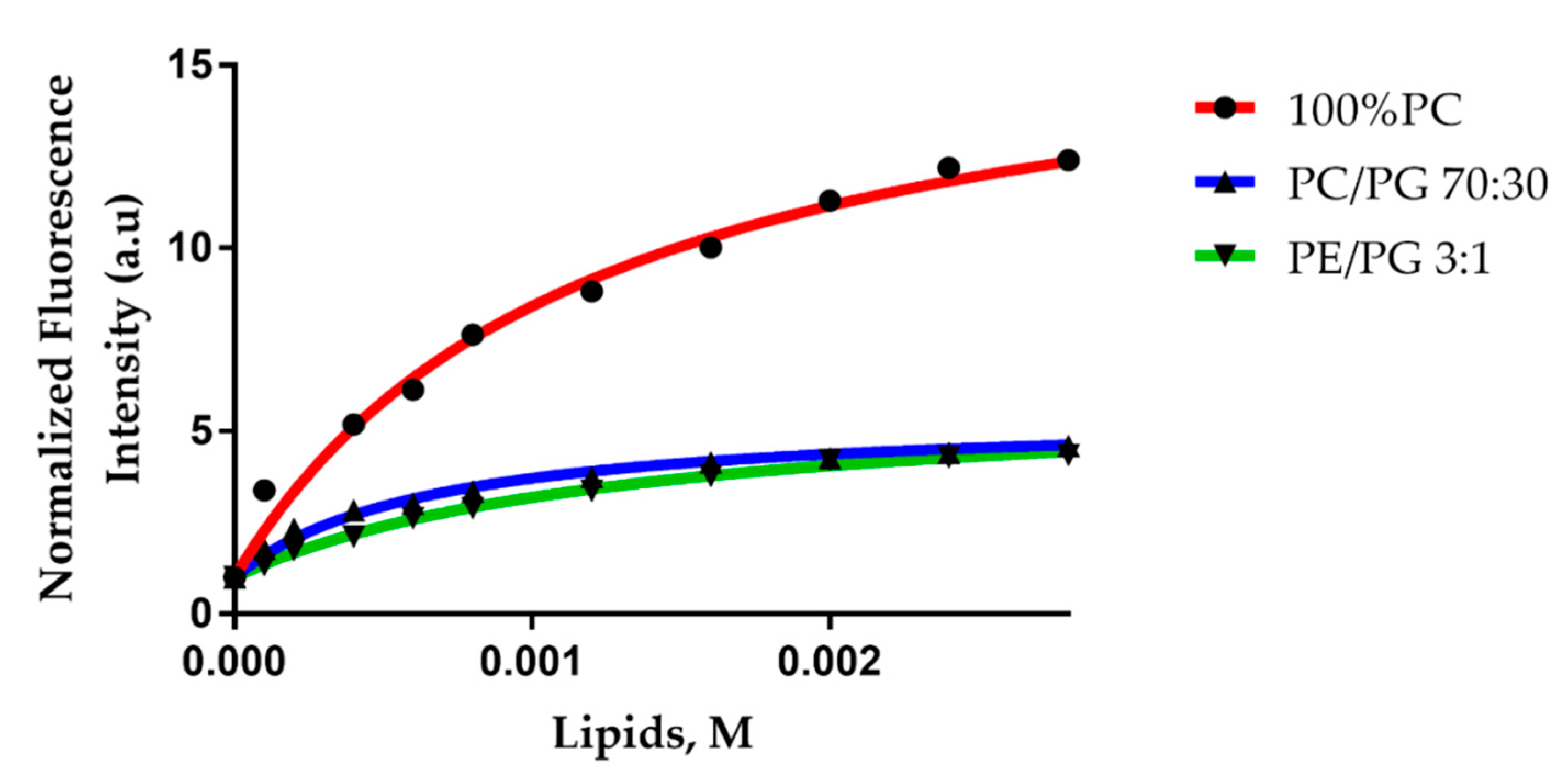
2.4. Trematocine Model Membranes Interaction
2.5. Trematocine Crosses Outer Membrane and Interacts with Inner Membrane
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity
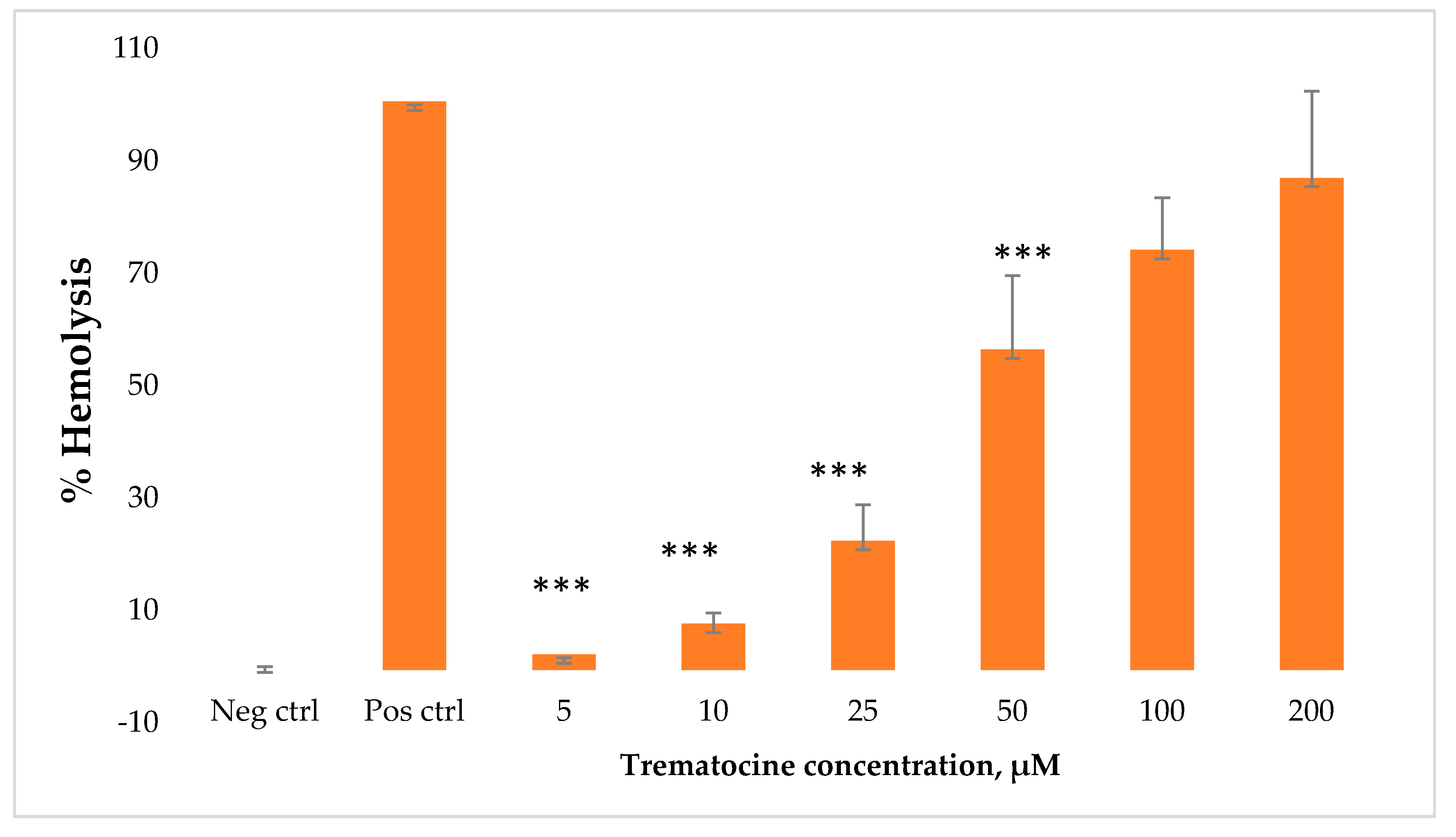
2.7. Haemolytic and Cytotoxic Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of an AMP from T. bernacchii
4.2. Basal Expression of Trematocine
4.3. Expression after In Vivo Immunization with Psychrobacter sp. TAD1
4.4. Peptides and LUVs Preparation
4.5. Circular Dichroism Studies
4.6. Steady-State Fluorescence Studies
4.6.1. Partition Studies
4.6.2. Intrinsic Fluorescence Quenching Studies
4.6.3. Outer Membrane Permeability Essay
4.6.4. Inner Membrane Depolarization Essay
4.6.5. Fluorescence Anisotropy Studies
4.7. Antimicrobial Activity of Trematocine
4.8. Haemolytic Activity Assay
4.9. Cytotoxicity Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMP | antimicrobial peptide |
| DPH | 1,6-diphenil-exatrien |
| OM | outer membrane |
| IM | inner membrane |
| PC | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| PG | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol |
| PE | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine |
| MIC | minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MBC | minimum bactericidal concentration |
| MFC | minimum fungicidal concentration |
| CFU | colony forming units |
| LUV | large unilamellar vesicle |
| DEPC | diethyl pyrocarbonate |
| ROX | 6-carboxy-X-rhodamine |
| EDTA | ethylenediamin tetraacetic acid |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| OD | optical density |
| ANS | 1-aminonaphtalene-8-sulfonic acid |
References
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulet, P.; Stöcklin, R.; Menin, L. Anti-microbial peptides: From invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulet, P.; Hetru, C.; Dimarcq, J.L.; Hoffmann, D. Antimicrobial peptides in insects; structure and function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leippe, M. Antimicrobial and cytolytic polypeptides of amoeboid protozoa—Effector molecules of primitive phagocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Olmedo, F.; Molina, A.; Alamillo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Palenzuéla, P. Plant defense peptides. Biopolymers 1998, 47, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotz, H.U.; Waller, F.; Wang, K. Innate immunity in plants: The role of antimicrobial peptides. In Antimicrobial Peptides and Innate Immunity; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 29–51. ISBN 9783034805414. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.; Cheung, R.; Wong, J.; Ye, X. Antimicrobial Activity of Defensins and Defensin-Like Peptides with Special Emphasis on those from Fungi and Invertebrate Animals. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygind, P.H.; Fischer, R.L.; Schnorr, K.M.; Hansen, M.T.; Sönksen, C.P.; Ludvigsen, S.; Raventós, D.; Buskov, S.; Christensen, B.; De Maria, L.; et al. Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 2005, 437, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Kafatos, F.C.; Janeway, C.A.; Ezekowitz, R.A.B. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 1999, 284, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Hooper, L.V. Antimicrobial defense of the intestine. Immunity 2015, 42, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Antimicrobial peptides: Key components of the innate immune system. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.V.R.; Yedery, R.D.; Aranha, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Premises and promises. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagna, S.; Saint, N.; Molle, G.; Aumelas, A. Structure and mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide piscidin. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shai, Y. Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by α-helical antimicrobial and cell non-selective membrane-lytic peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1999, 1462, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, F.; Picchietti, S.; Porcelli, F.; Della Pelle, G.; Olivieri, C.; Poerio, E.; Bugli, F.; Menchinelli, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Bresciani, A.; et al. Fish-derived antimicrobial peptides: Activity of a chionodracine mutant against bacterial models and human bacterial pathogens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, F.; Verardi, R.; Shi, L.; Henzler-Wildman, K.A.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Veglia, G. NMR structure of the cathelicidin-derived human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 in dodecylphosphocholine micelles. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talandashti, R.; Mahdiuni, H.; Jafari, M.; Mehrnejad, F. Molecular Basis for Membrane Selectivity of Antimicrobial Peptide Pleurocidin in the Presence of Different Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Model Membranes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3262–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, M.D.; Birembaut, F.; Clifton, L.A.; Frazier, R.A.; Webster, J.R.P.; Green, R.J. Antimicrobial peptide-lipid binding interactions and binding selectivity. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.F.; Pokorny, A. Mechanisms of antimicrobial, cytolytic, and cell-penetrating peptides: From kinetics to thermodynamics. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 8083–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Martins, M.C.L. Clinical application of AMPs. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1117, pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Mader, J.S.; Hoskin, D.W. Cationic antimicrobial peptides as novel cytotoxic agents for cancer treatment. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 15, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tharmalingam, N.; Liu, Q.; Jayamani, E.; Kim, W.; Fuchs, B.B.; Zhang, R.; Vilcinskas, A.; Mylonakis, E. Synergistic efficacy of Aedes aegypti antimicrobial peptide cecropin A2 and tetracycline against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.D.; Won, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Mishig-Ochir, T.; Lee, B.J. Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: A review. Molecules 2012, 17, 12276–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noga, E.J.; Silphaduang, U. Piscidins: A novel family of peptide antibiotics from fish. Drug News Perspect. 2003, 16, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.C.; Ahn, I.H.; Ahn, D.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.-W.; Park, H. Characterization of Two Antimicrobial Peptides from Antarctic Fishes (Notothenia coriiceps and Parachaenichthys charcoti). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Olivieri, C.; Buonocore, F.; Picchietti, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Bernini, C.; Scapigliati, G.; Dicke, A.A.; Vostrikov, V.V.; Veglia, G.; Porcelli, F. Structure and membrane interactions of chionodracine, a piscidin-like antimicrobial peptide from the icefish Chionodraco hamatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, C.; Bugli, F.; Menchinelli, G.; Veglia, G.; Buonocore, F.; Scapigliati, G.; Stocchi, V.; Ceccacci, F.; Papi, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. Design and characterization of chionodracine-derived antimicrobial peptides with enhanced activity against drug-resistant human pathogens. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41331–41346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, A. Near UV Protein CD. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 1694. [Google Scholar]
- Louis-Jeune, C.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Perez-Iratxeta, C. Prediction of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism using theoretically derived spectra. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2012, 80, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimley, W.C.; White, S.H. Membrane Partitioning: Distinguishing Bilayer Effects from the Hydrophobic Effect. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 6307–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, K.; Chaudhary, N. Interaction of MreB-derived antimicrobial peptides with membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzyn, K.; Róg, T.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Phosphatidylethanolamine-phosphatidylglycerol bilayer as a model of the inner bacterial membrane. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Diamond, G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Buonocore, F.; Scapigliati, G.; Pallavicini, A. Analysis and characterization of the head kidney transcriptome from the Antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii (Teleostea, Notothenioidea): A source for immune relevant genes. Mar. Genomics 2015, 20, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, G.; Parrinello, N.; Roch, P.; Cammarata, M. cDNA sequence and tissue expression of an antimicrobial peptide, dicentracin; a new component of the moronecidin family isolated from head kidney leukocytes of sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 146, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, J.; Vilcinskas, A. Antimicrobial peptides: The ancient arm of the human immune system. Virulence 2010, 1, 440–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geven, E.J.W.; Klaren, P.H.M. The teleost head kidney: Integrating thyroid and immune signalling. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 66, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, C.; Folch, H.; Enriquez, R.; Moran, G. Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: A review. Vet. Med. (Praha) 2011, 56, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Cheng, Y.S.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Ni, I.H.; Sheen, J.F.; Pan, Y.L.; Kuo, C.M. Gene expression and localization of the epinecidin-1 antimicrobial peptide in the grouper (Epinephelus coioides), and its role in protecting fish against pathogenic infection. DNA Cell Biol. 2007, 26, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebran, N.; Julien, S.; Orange, N.; Saglio, P.; Lemaître, C.; Molle, G. Pore-forming properties and antibacterial activity of proteins extracted from epidermal mucus of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1999, 122, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Ross, N.W.; MacKinnon, S.L. Comparison of antimicrobial activity in the epidermal mucus extracts of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 150, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Mcintosh, D. Natural antibacterial compounds on the surface of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. Fish Dis. 1988, 11, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakers, S.; Niklasson, L.; Steinhagen, D.; Kruse, C.; Schauber, J.; Sundell, K.; Paus, R. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) from fish epidermis: Perspectives for investigative dermatology. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. The antimicrobial peptide hepcidin exerts an important role in the innate immunity against bacteria in the bony fish gilthead seabream. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.G.; Silphaduang, U.; Moon, H.S.; Seo, J.K.; Corrales, J.; Noga, E.J. Structure-Activity Relationships of Piscidin 4, a Piscine Antimicrobial Peptide. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3288–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.J.; Feng, C.Y.; Booth, V.; Rise, M.L. Characterization and expression studies of Gaduscidin-1 and Gaduscidin-2; paralogous antimicrobial peptide-like transcripts from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reite, O.B. Mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells of teleostean fish: A review focusing on staining properties and functional responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1998, 8, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathe, M.; Wieprecht, T. Structural features of helical antimicrobial peptides: Their potential to modulate activity on model membranes and biological cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1999, 1462, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mant, C.T.; Farmer, S.W.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Vasil, M.L.; Hodges, R.S. Rational design of α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced activities and specificity/therapeutic index. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12316–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.J.; Marquette, A.; Bechinger, B. Zwitterionic phospholipids and sterols modulate antimicrobial peptide-induced membrane destabilization. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 4289–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jastimi, R.; Edwards, K.; Lafleur, M. Characterization of permeability and morphological perturbations induced by nisin on phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, P.S.; Sousa, V.K.; Donato, M.; Itri, R.; Beltramini, L.M.; Araujo, A.P.U.; Buerck, J.; Wallace, B.A.; Lopes, J.L.S. Unveiling the binding and orientation of the antimicrobial peptide Plantaricin 149 in zwitterionic and negatively charged membranes. Eur. Biophys. J. 2019, 48, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensterseifer, I.C.M.; Felício, M.R.; Alves, E.S.F.; Cardoso, M.H.; Torres, M.D.T.; Matos, C.O.; Silva, O.N.; Lu, T.K.; Freire, M.V.; Neves, N.C.; et al. Selective antibacterial activity of the cationic peptide PaDBS1R6 against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.M.; Verly, R.M.; Piló-Veloso, D.; De Maria, M.; De Carvalho, M.A.R.; Cisalpino, P.S.; Soares, B.M.; Diniz, C.G.; Farias, L.M.; Moreira, D.F.F.; et al. LyeTx I, a potent antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the spider Lycosa erythrognatha. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poojari, C.; Wilkosz, N.; Lira, R.B.; Dimova, R.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Petka, R.; Kepczynski, M.; Róg, T. Behavior of the DPH fluorescence probe in membranes perturbed by drugs. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Lee, D.G.; Jang, S.H.; Woo, E.R.; Jeong, H.G.; Choi, C.H.; Hahm, K.S. A Leu-Lys-rich antimicrobial peptide: Activity and mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteomics 2003, 1645, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, B.M.; Vu, M.P.; McLemore, C.O.; Lund, M.S.; Gibbons, E.; Brueseke, T.J.; Wilson-Ashworth, H.A.; Bell, J.D. Use of fluorescence to determine the effects of cholesterol on lipid behavior in sphingomyelin liposomes and erythrocyte membranes. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armengol, E.; Domenech, O.; Fusté, E.; Pérez-Guillén, I.; Borrell, J.H.; Sierra, J.M.; Vinas, M. Efficacy of combinations of colistin with other antimicrobials involves membrane fluidity and efflux machinery. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patiño-Márquez, I.A.; Manrique-Moreno, M.; Patiño-González, E.; Jemioła-Rzemińska, M.; Strzałka, K. Effect of antimicrobial peptides from Galleria mellonella on molecular models of Leishmania membrane. Thermotropic and fluorescence anisotropy study. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2018, 71, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, P.I.; Park, Y.; Woo, E.R.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, C.H.; Hahm, K.S. Design of novel peptide analogs with potent fungicidal activity, based on PMAP-23 antimicrobial peptide isolated from porcine myeloid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasniewski, J.; Cailliez-Grimal, C.; Younsi, M.; Millière, J.B.; Revol-Junelles, A.M. Fluorescence anisotropy analysis of the mechanism of action of mesenterocin 52A: Speculations on antimicrobial mechanism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaehnig, F.; Vogel, H.; Best, L. Unifying description of the effect of membrane proteins on lipid order. Verification for the melittin/dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine system. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 6790–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, Z.; Shai, Y. Mode of action of linear amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers 1998, 47, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.F.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Su, Y.Q.; Wang, J. Characterization of a novel piscidin-like antimicrobial peptide from Pseudosciaena crocea and its immune response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladokhin, A.S.; Jayasinghe, S.; White, S.H. How to measure and analyze tryptophan fluorescence in membranes properly, and why bother? Anal. Biochem. 2000, 285, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinakumar, R.; Wimley, W.C. Biomolecular engineering by combinatorial design and high-throughput screening: Small, soluble peptides that permeabilize membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9849–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladokhin, A.S. Fluorescence spectroscopy in thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of pH-dependent membrane protein insertion. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 466, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Vidal, M.; White, S.H.; Ladokhin, A.S. Membrane partitioning: “classical” and “nonclassical” hydrophobic effects. J. Membr. Biol. 2011, 239, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domadia, P.N.; Bhunia, A.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Bhattacharjya, S. Structure, interactions, and antibacterial activities of MSI-594 derived mutant peptide MSI-594F5A in lipopolysaccharide micelles: Role of the helical hairpin conformation in outer-membrane permeabilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18417–18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.C.; Yoon, M.Y.; Hahm, K.S.; Park, Y. C-terminal amidation of PMAP-23: Translocation to the inner membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Canto, A.M.T.M.; Robalo, J.R.; Santos, P.D.; Carvalho, A.J.P.; Ramalho, J.P.P.; Loura, L.M.S. Diphenylhexatriene membrane probes DPH and TMA-DPH: A comparative molecular dynamics simulation study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2647–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belokoneva, O.S.; Villegas, E.; Corzo, G.; Dai, L.; Nakajima, T. The hemolytic activity of six arachnid cationic peptides is affected by the phosphatidylcholine-to-sphingomyelin ratio in lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2003, 1617, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| LUV Composition | Kx (1 × 104) | r2 |
|---|---|---|
| PC/PG (70:30) | 8.84 ± 1.5 | 0.99 |
| 100% PC | 4.7 ± 0.6 | 0.99 |
| PE/PG (3:1) | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 0.99 |
| LUV Composition | KSV | NAF(1) |
|---|---|---|
| PC/PG (70:30) | 1.33 ± 0.05 | 0.063 |
| 100% PC | 1.31 ± 0.03 | 0.062 |
| PE/PG (3:1) | 0.94 ± 0.06 | 0.044 |
| Buffer | 21.16 ± 0.08 | 1 |
| Microrganism | MIC | MBC/MFC |
|---|---|---|
| Trematocine (μM) | ||
| Escherichia coli | 25 | 25 |
| Bacillus pumilus | 10 | 25 |
| Psychrobacter sp. (TAD1) | 2.5 | 10 |
| Candida boidinii | 50 | 100 |
| Gene | Primers Sequence 5′-3′ (Forward, FW, and Reverse, RV) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | ATGTACGTTGCCATCC (FW) GAGATGCCACGCTCTC (RV) | AJ493428 |
| Trematocine | GTGCACCATCGTCTTTCTGGTGC (FW, complete sequence) GGCAAACGCTCGCTCTCGGTC (RV, complete sequence) | MH325166 |
| Trematocine | GTGCACCATCGTCTTTCTGGTGC (FW, real-time) GGCAAACGCTCGCTCTCGGTC (RV, real-time) | MH325166 |
| 18 S ribosomal RNA | CCAACGAGCTGCTGACC (FW, real-time PCR) CCGTTACCCGTGGTCC (RV, real-time PCR) | AY831388 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Della Pelle, G.; Perà, G.; Belardinelli, M.C.; Gerdol, M.; Felli, M.; Crognale, S.; Scapigliati, G.; Ceccacci, F.; Buonocore, F.; Porcelli, F. Trematocine, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Antarctic Fish Trematomus bernacchii: Identification and Biological Activity. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020066
Della Pelle G, Perà G, Belardinelli MC, Gerdol M, Felli M, Crognale S, Scapigliati G, Ceccacci F, Buonocore F, Porcelli F. Trematocine, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Antarctic Fish Trematomus bernacchii: Identification and Biological Activity. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(2):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020066
Chicago/Turabian StyleDella Pelle, Giulia, Giulia Perà, Maria Cristina Belardinelli, Marco Gerdol, Martina Felli, Silvia Crognale, Giuseppe Scapigliati, Francesca Ceccacci, Francesco Buonocore, and Fernando Porcelli. 2020. "Trematocine, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Antarctic Fish Trematomus bernacchii: Identification and Biological Activity" Antibiotics 9, no. 2: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020066
APA StyleDella Pelle, G., Perà, G., Belardinelli, M. C., Gerdol, M., Felli, M., Crognale, S., Scapigliati, G., Ceccacci, F., Buonocore, F., & Porcelli, F. (2020). Trematocine, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Antarctic Fish Trematomus bernacchii: Identification and Biological Activity. Antibiotics, 9(2), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020066








