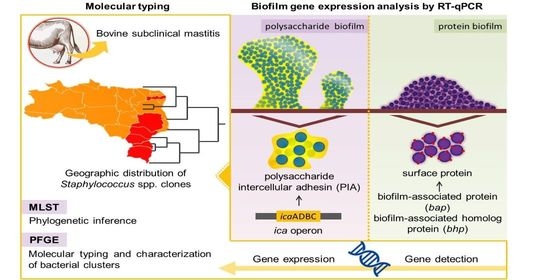
Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Regions of Brazil: Molecular Typing and Biofilm Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Detection of Genes Involved in Biofilm Formation
2.2. Expression Analysis of Genes of the Ica ADBC Operon by RT-qPCR
2.3. Interpretation of Susceptibility to Oxacillin and Vancomycin by the E-Test
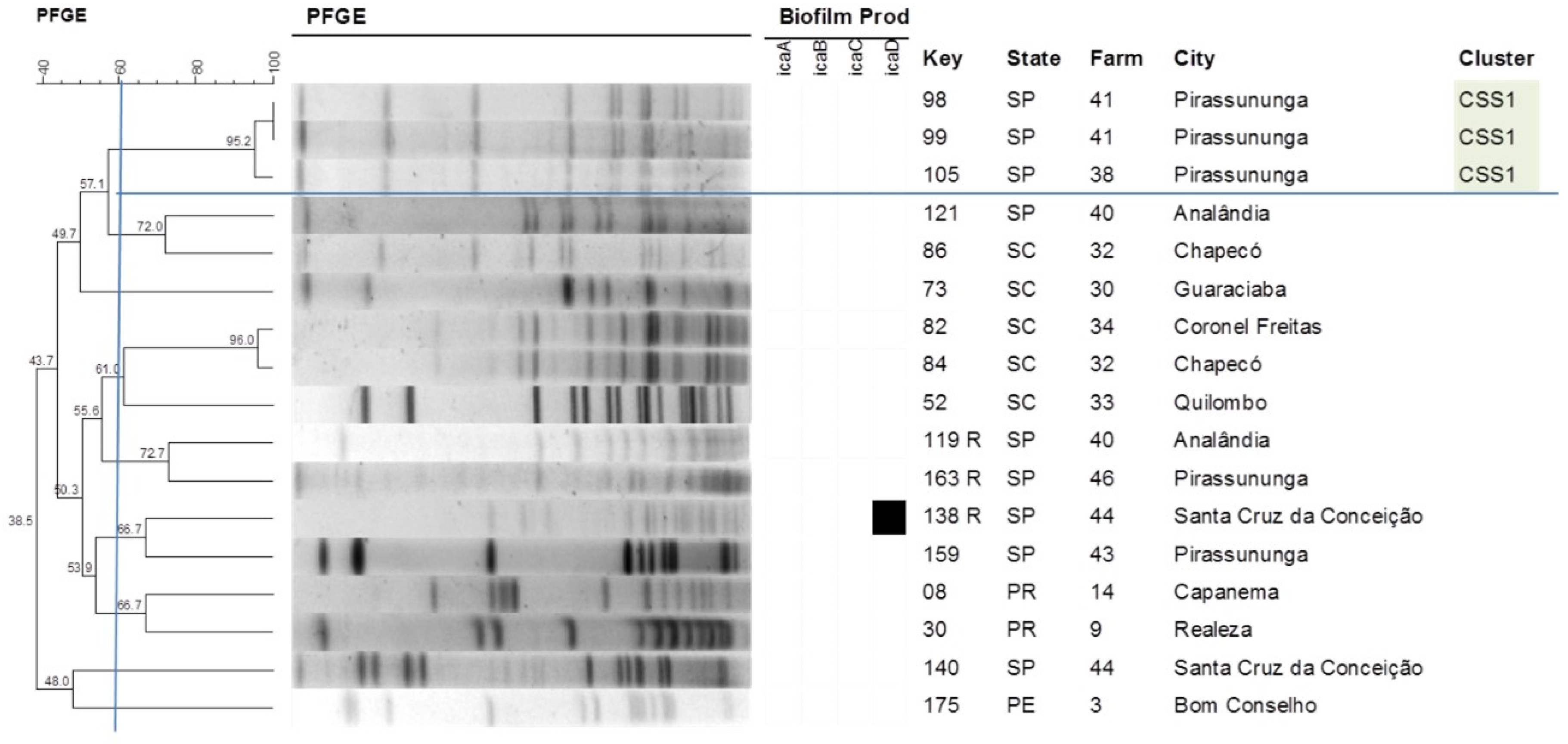
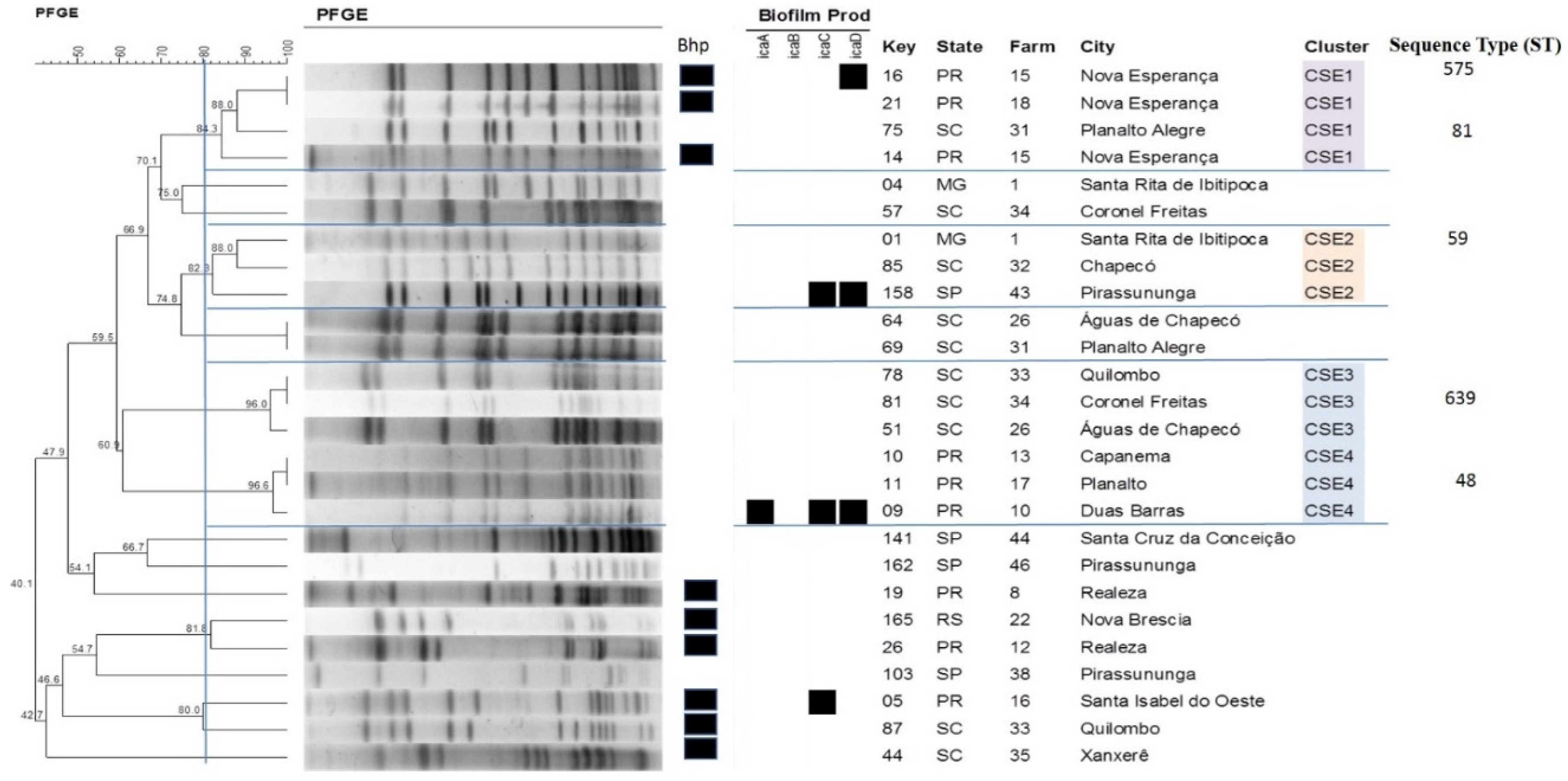
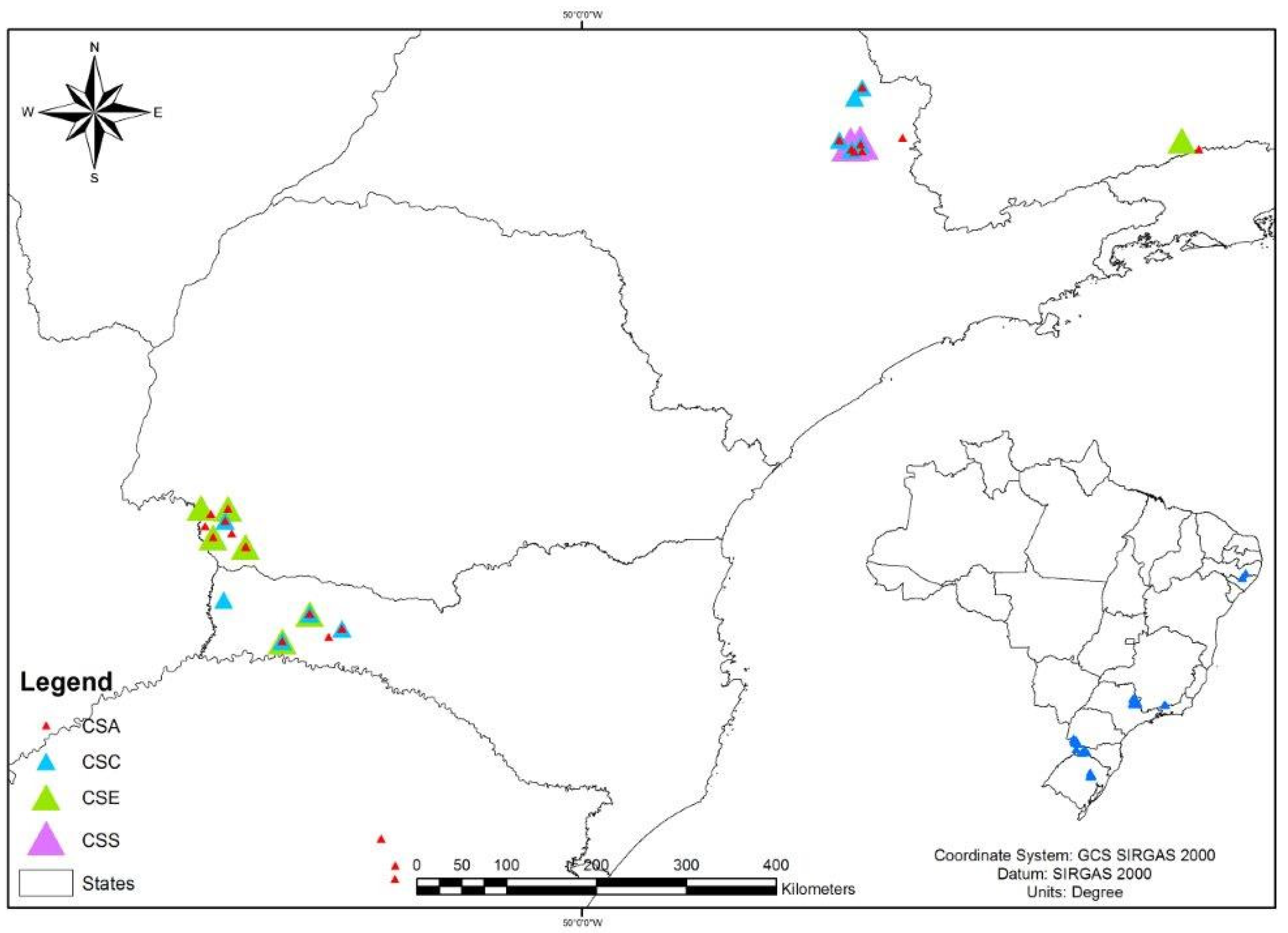
2.4. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Multilocus Sequence Typing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Herds and Sampling
4.2. Samples Included in the Study
4.3. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
4.4. Detection of the Genes Involved in Biofilm Formation
4.5. Expression Analysis of the Genes of the icaADBC Operon by RT-qPCR
4.5.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.5.2. Standardization of the Reaction and Primers
4.5.3. Relative Standard Curve
4.5.4. Analysis of Gene Expression in the Isolates
4.6. Determination of Oxacillin and Vancomycin Inhibitory Concentrations by the E-Test
4.7. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
4.8. Geographic Distribution of Staphylococcus spp. Clones
4.9. Multilocus Sequence Typing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottardi, C.P.T.; Muricy, R.F.; Cardoso, M.; Schmidt, V. Qualidade higiênica do leite caprino por contagem de coliformes e estafilococos. Ciência Rural 2008, 38, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasal, T.; Huijpsl, K.; Osterds, O.; Hogeveen, H. Economic effects of bovine mastitis and mastitis management: A review. Vet. Q. 2007, 29, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.B.C.; Zanardo, L.G.; Galvão, N.N.; Carvalho, I.A.; Nero, L.A.; Moreira, M.A.S. Escherichia coli from clinical mastitis: Serotypes and virulence factors. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.; Saavedra, M.J.; Henriques, M. Bovine mastitis disease/pathogenicity: Evidence of the potential role of microbial biofilms. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busanello, M.; Rossi, R.S.; Cassoli, L.D.; Pantoja, J.C.F.; Machado, P.F. Estimation of prevalence and incidence of subclinical mastitis in a large population of Brazilian dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6545–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANUÁRIO leite 2018: Indicadores, Tendências e Oportunidades Para Quem Vive no Setor Leiteiro; Embrapa Gado de Leite: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018; p. 114.
- Radostitis, O.M.; Gay, C.C.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Constable, P.D. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Disease of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs and Goats, 10th ed.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; p. 2156. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.W. Intramammary infections produced by various strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Micrococcus. Cornell Vet. 1973, 63, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.W.; Scherer, R.K. Classification of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Micrococcus strains isolated from bovine milk. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 39, 767. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.J.; Jones, G.W. The distribution and characteristics of coagulase-negative staphylococci of the bovine udder. J. Dairy Res. 1966, 33, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.S.; White, D.G.; Pankey, J.W. Effects of teat dipping on intramammary infections by staphylococci other than Staphylococcus aureus. J. Dairy Sci. 1987, 70, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazi, T.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Barreiro, J.R.; Arcari, M.A.; Santos, M.V. Bovine subclinical intramammary infection caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci increases somatic cell count but has no effect on milk yield or composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3071–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, B.; Amorena, B.; Iturralde, M. Effect of slime on adherence of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine and ovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 78, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L.K.; Zadoks, R.N.; Gaskins, C.T. Biofilm production by Staphylococcus aureus associated with intramammary infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 107, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S. Theoretical aspects of antibiotic diffusion into microbial biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, G.; Kaplan, H.B.; Kolter, R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, C.; Tormo, M.A.; Úbeda, C.; Trotonda, M.P.; Monzón, M.; Peris, C.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Role of biofilm-associated protein bap in the pathogenesis of bovine Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.C.; Saffran, W.; Welsh, J.; Haas, R.; Goldenberg, M.; Cantor, C.R. New Techniques for Purifying Large DNAs and Studying Their Properties and Packaging. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1983, 47, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russel, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhow, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing: A portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, K.B.; Ismail, J.; Campbell, J.; Mulvey, M.R.; Bourgault, A.M.; Messier, S.; Zhao, X. Regional profiling for determination of genotype diversity of mastitis-specific Staphylococcus aureus lineage in Canada by use of clumping factor a, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and spa typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, H.J.M.; Boumedine, K.S.; Nesme, X.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular tools for the characterization of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Vet. Res. 2001, 32, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute-CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, Approved Standard-Tenth ed.; CLSI Document M07-A10; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McDougal, L.K.; Steward, C.D.; Killgore, G.E.; Chaitram, J.M.; McAllister, S.K.; Tenover, F.C. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: Establishing a national database. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5113–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, P.; Nair, M.K.; Annamalai, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K.S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of bovine mastitis isolates of Staphylococcus aureus for biofilm formation. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 92, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewer, C.C.; Amanso, E.S.; Gouveia, G.V.; Souza, R.L.; Costa, M.M.; Mota, R.A. Resistance to antimicrobials and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from bovine mastitis in the Northeast of Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, M.T.; Langsrud, S.; Holck, A.; Moretro, T. Different patterns of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus under food-related stress conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 116, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, B.; Sytykiewicz, H.; Sprawka, I. Expression of the Biofilm-Associated Genes in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Biofilm and Planktonic Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akshatha, B.M.; Isloor, S.; Sundareshan, S.; Veeresh, B.H.; Nuthanalakshmi, V.; Sinha, A.Y.; Rathnamma, D.; Veeregowda, B.M.; Upendra, H.A.; Bhat, A.S.; et al. Biofilm production, antibiotic resistance and the presence of ica, bap, agr and blaz genes in bovine mastitis-associated Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Karnataka. Indian J. Comp. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 41, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, M.A.; Knecht, E.; Gotz, F.; Lasa, I.; Penade, J.R. Bap-dependent biofilm formation by pathogenic species of Staphylococcus: Evidence of horizontal gene transfer? Microbiology 2005, 151, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, R.; Albizu, I.; De La Cruz, M.; Del Cacho, E.; Barberan, M.; Amorena, B. Phase variation of slime production in Staphylococcus aureus: Implications in colonization and virulence. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, R.; van Leeuwen, W.; Barkema, H.; Sampimon, O.; Verbrugh, H.; Schukken, Y.H.; van Belkum, A. Application of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and binary typing as tools in veterinary clinical microbiology and molecular epidemiologic analysis of bovine and human Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akineden, O.; Annemüller, C.; Hassan, A.A.; Lämmler, C.; Wolter, W.; Zschöck, M. Toxin genes and other characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from milk of cows with mastitis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, E.C.; Guimarães, M.C.; Henriques, J.A.; Ayub, M.A. Assessing and analysing contamination of a dairy products processing plant by Staphylococcus aureus using antibiotic resistance and PFGE. Can. J. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzola, F.R.; Quelle, L.; Gomez, M.I.; Catalano, M.; Steele-Moore, L.; Berg, D.; Gentilini, E.; Denamiel, G.; Sordelli, D.O. Genotypic analysis of Staphylococcus aureus from milk of dairy cows with mastitis in Argentina. Epidemiol. Infect. 2001, 126, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, L.M.D.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Cunha, M.L.R.S.C.; Zafalon, L.F. Fatores de Virulência e Genes Regulatórios agr de Staphylococcus aureus e Outras Espécies Coagulase Positivas Isoladas de Mastites Bovina e Ovina. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo—USP, São Pulo, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivoni, A.M.; Diep, B.A.; De Gouveia Magalhães, A.C.; Santos, K.R.; Riley, L.W.; Sensabaugh, G.F.; Moreira, B.M. Clonal composition of Staphylococcus aureus isolates at a Brazilian university hospital: Identification of international circulating lineages. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, N.H.; Park, K.T.; Moon, J.S.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, S.K.; Koo, H.C.; Joo, Y.S.; Park, Y.O. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) characterization and molecular analysis for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and novel SCCmec subtype IVg isolated from bovine milk in Korea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rabello, R.F.; Moreira, B.M.; Lopes, R.M.M.; Teixeira, L.M.; Riley, L.W.; Castro, A.C.D. Multilocus sequence typing of Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from cows with mastitis in Brazilian dairy herds. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Castiglioni, V.; Gelain, M.E.; Scanziani, E.; Lorenzi, V.; Anjum, M.; Piccinini, R. Long-term study of MRSA ST1, t127 mastitis in a dairy cow. Vet. Record. 2012, 170, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadoks, R.N.; Middleton, J.R.; McDougall, S.; Katholm, J.; Schukken, Y.H. Molecular epidemiology of mastitis pathogens of dairy cattle and comparative relevance to humans. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2011, 16, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, B.F.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Castilho, I.G.; Dantas, S.T.A.; Salina, A.; Langoni, H.; Pantoja, J.C.F.; Budri, P.E.; Fitzgerald-Hughes, D.; Júnior, A.F.; et al. Genotyping of long term persistent Staphylococcus aureus in bovine subclinical mastitis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.M.; Green, L.E.; Medley, G.F.; Bird, H.E.; Fox, L.K.; Schukken, Y.H.; Kruze, J.V.; Bradley, A.J.; Zadoks, R.N.; Dowson, C.G. Multilocus sequence typing of intercontinental bovine Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, R.; Cosandey, A.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Subtyping, evolution, and zoonotic transfer. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneman, E.W.; Allen, S.D.; Janda, W.M.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; Winn, W.C., Jr. Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 5th ed.; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M.L.R.S.; Sinzato, Y.K.; Silveira, L.V.A. Comparison of methods for identification of coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2004, 99, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, I.; Pereira, S.; Miragaia, M.; Sanches, I.S.; Lencastre, H. Identification of clinical staphylococcal isolates from humans by Internal Transcribed Spacer PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3099–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciola, C.R.; Gamberini, S.; Campoccia, D.; Visai, L.; Speziale, P.; Baldassari, L.; Montanaro, L. A multiplex PCR method for the detection of all five individual genes of ica locus in Staphylococcus epidermidis. A survey on 400 clinical isolates from prosthesis-associated infections. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2005, 75, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J.; Ou, Y.; Molin, S.; Qu, D. Formation and properties of in vitro biofilms of ica-negative Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecasteele, S.J.; Peetermans, W.E.; Merckx, R.; Van Eldere, J. Expression of biofilm-associated genes in Staphylococcus epidermidis during in vitro and in vivo foreign body infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 1, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, D.; Wallet, F.; Kacet, S.; Courcol, R.J. Involvement of adherence and adhesion Staphylococcus epidermidis genes in pacemaker lead-associated infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3348–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Peng, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, S.; Tang, T. The use of quaternised chitosan-loaded PMMA to inhibit biofilm formation and downregulate the virulence-associated gene expression of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S.; Reed, A.; Chen, F.; Stewart, C.N., Jr. Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.J.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin- resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
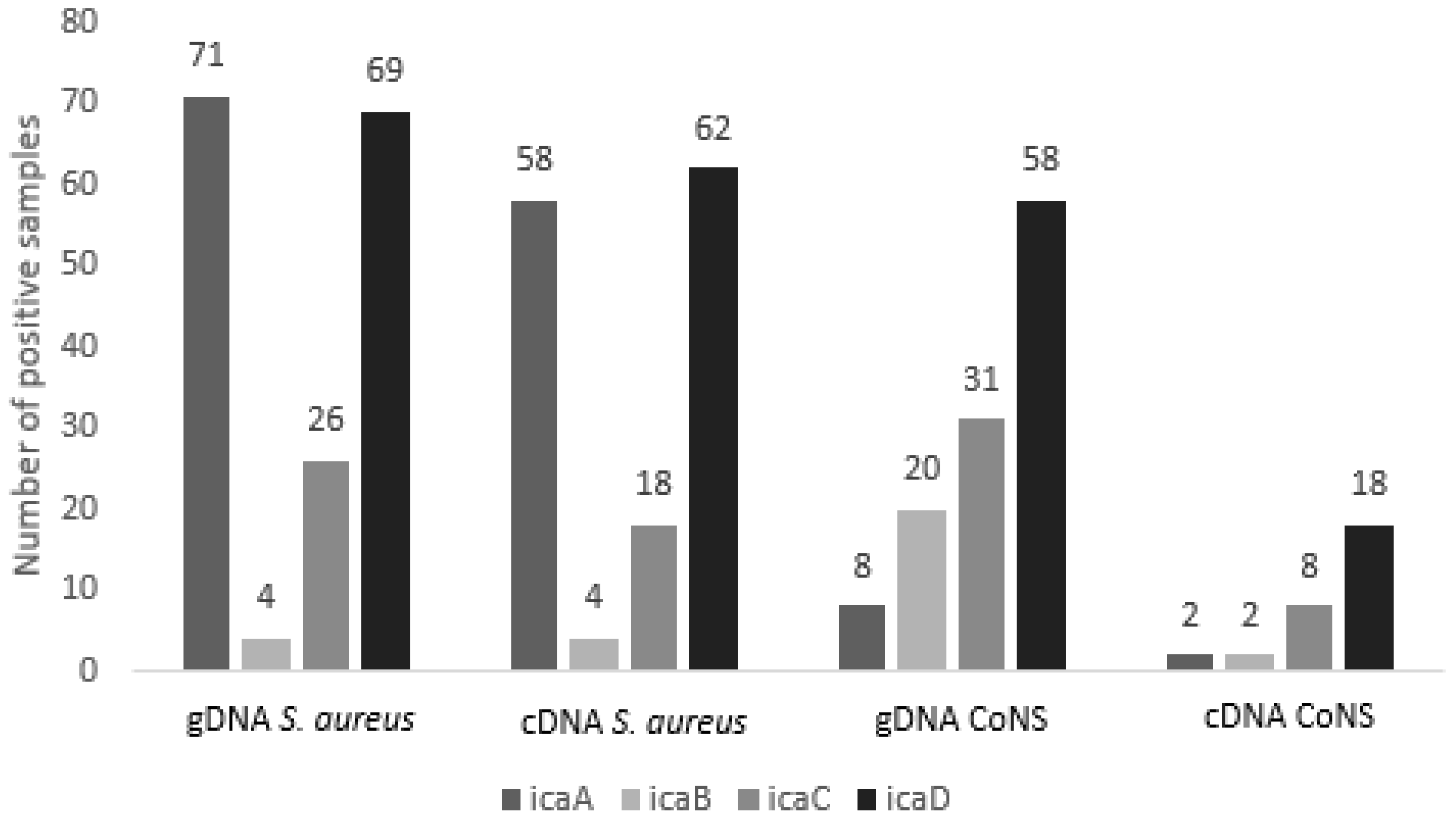




| Species (N) | gDNA 1 icaA | cDNA 2 icaA | gDNA icaB | cDNA icaB | gDNA icaC | cDNA icaC | gDNA icaD | cDNA icaD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (82) | 71 | 58 | 4 | 4 | 26 | 18 | 69 | 62 |
| S. chromogenes (27) | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 12 | 4 |
| S. epidermidis (26) | 5 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 12 | 3 | 17 | 3 |
| S. saprophyticus (17) | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| S. haemolyticus (6) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| S. simulans (6) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| S. warneri (6) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| S. hyicus (5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
| S. hominis (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| S. xylosus (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Total (181) | 79 | 60 | 24 | 6 | 57 | 24 | 127 | 80 |
| Antimicrobial | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxacillin | Vancomycin | |||||
| Species | MIC50 | MIC90 | Resistant | MIC50 | MIC90 | Resistant |
| S. aureus | 0.094 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.50 | 1.0 | 0 |
| CoNS | 0.25 | 1.5 | 32 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Species | Cluster | No. of Isolates | Expression of icaADBC Genes | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | CSA1 | 31 | icaA (23); icaB (0); icaC (4); icaD (23) | SP; MG |
| CSA2 | 3 | icaA (1); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (1) | SP; RS | |
| CSA3 | 7 | icaA (5); icaB (2); icaC (5); icaD (7) | PR | |
| CSA4 | 5 | icaA (3); icaB (0); icaC (2); icaD (4) | PR; SC; SP | |
| CSA5 | 6 | icaA (5); icaB (0); icaC (1); icaD (5) | SC | |
| CSA6 | 5 | icaA (4); icaB (0); icaC (2); icaD (5) | SC | |
| CSA7 | 3 | icaA (2); icaB (0); icaC (2); icaD (2) | RS; SC; SP | |
| CSA8 | 4 | icaA (3); icaB (1); icaC (0); icaD (3) | SC | |
| S. chromogenes | CSC1 | 11 | icaA (0); icaB (1); icaC (0); icaD (2) | SC; SP |
| CSC2 | 4 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (0) | SC; SP | |
| CSC3 | 6 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (2) | PR; SC; SP | |
| S. epidermidis | CSE1 | 4 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (1) | PR; SC |
| CSE2 | 3 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (1); icaD (1) | MG; SC; SP | |
| CSE3 | 3 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (0) | SC | |
| CSE4 | 3 | icaA (1); icaB (0); icaC (1); icaD (1) | PR | |
| S. saprophyticus | CSS1 | 3 | icaA (0); icaB (0); icaC (0); icaD (0) | SP |
| S. simulans | CSI1 | 3 | icaA (0); icaB (1); icaC (0); icaD (0) | RS; SC |
| Origin | PFGE Cluster | Isolates | Alleles | ST | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arcC | aroE | glpF | gmk | pta | tpi | yqiL | ||||
| MG | CSA1 | 2 | 3 | 68 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 40 | 126 |
| SP | CSA1 | 91 | 3 | 68 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 40 | 126 |
| SP | CSA2 | 88 | 3 | 68 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 40 | 126 |
| PR | CSA3 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PR | CSA3 | 178 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SC | CSA4 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SC | CSA5 | 54 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 188 |
| SC | CSA6 | 43 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 92 | 746 |
| RS | CSA6 | 170 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 92 | 746 |
| PR | CSA7 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SC | CSA8 | 71 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 8 |
| Origin | PFGE Cluster | Isolates | Alleles | ST | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arcC | aroE | gtr | mut | pyr | tpi | yqiL | ||||
| PR | CSE1 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 575 |
| SC | CSE1 | 75 | 2 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 81 |
| MG | CSE2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 59 |
| SC | CSE3 | 81 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 639 |
| PR | CSE4 | 11 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 48 |
| Species | Strain | ST | Oxacillin | Vancomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. epidermidis | 1 | 59 | R | S |
| S. aureus | 2 | 126 | S | S |
| S. epidermidis | 11 | 48 | R | S |
| S. epidermidis | 16 | 575 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 18 | 1 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 24 | 1 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 43 | 746 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 54 | 188 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 71 | 8 | S | S |
| S. epidermidis | 75 | 81 | R | S |
| S. epidermidis | 81 | 639 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 88 | 126 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 91 | 126 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 170 | 746 | S | S |
| S. aureus | 178 | 1 | S | S |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mello, P.L.; Riboli, D.F.M.; Martins, L.d.A.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; Victória, C.; Calixto Romero, L.; Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M.d.L. Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Regions of Brazil: Molecular Typing and Biofilm Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120888
Mello PL, Riboli DFM, Martins LdA, Brito MAVP, Victória C, Calixto Romero L, Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha MdL. Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Regions of Brazil: Molecular Typing and Biofilm Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMello, Priscila Luiza, Danilo Flávio Moraes Riboli, Lisiane de Almeida Martins, Maria Aparecida Vasconcelos Paiva Brito, Cassiano Victória, Letícia Calixto Romero, and Maria de Lourdes Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha. 2020. "Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Regions of Brazil: Molecular Typing and Biofilm Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120888
APA StyleMello, P. L., Riboli, D. F. M., Martins, L. d. A., Brito, M. A. V. P., Victória, C., Calixto Romero, L., & Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M. d. L. (2020). Staphylococcus spp. Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Regions of Brazil: Molecular Typing and Biofilm Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR. Antibiotics, 9(12), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120888