Single Cell Analysis of Drug Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus during Macrophage Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
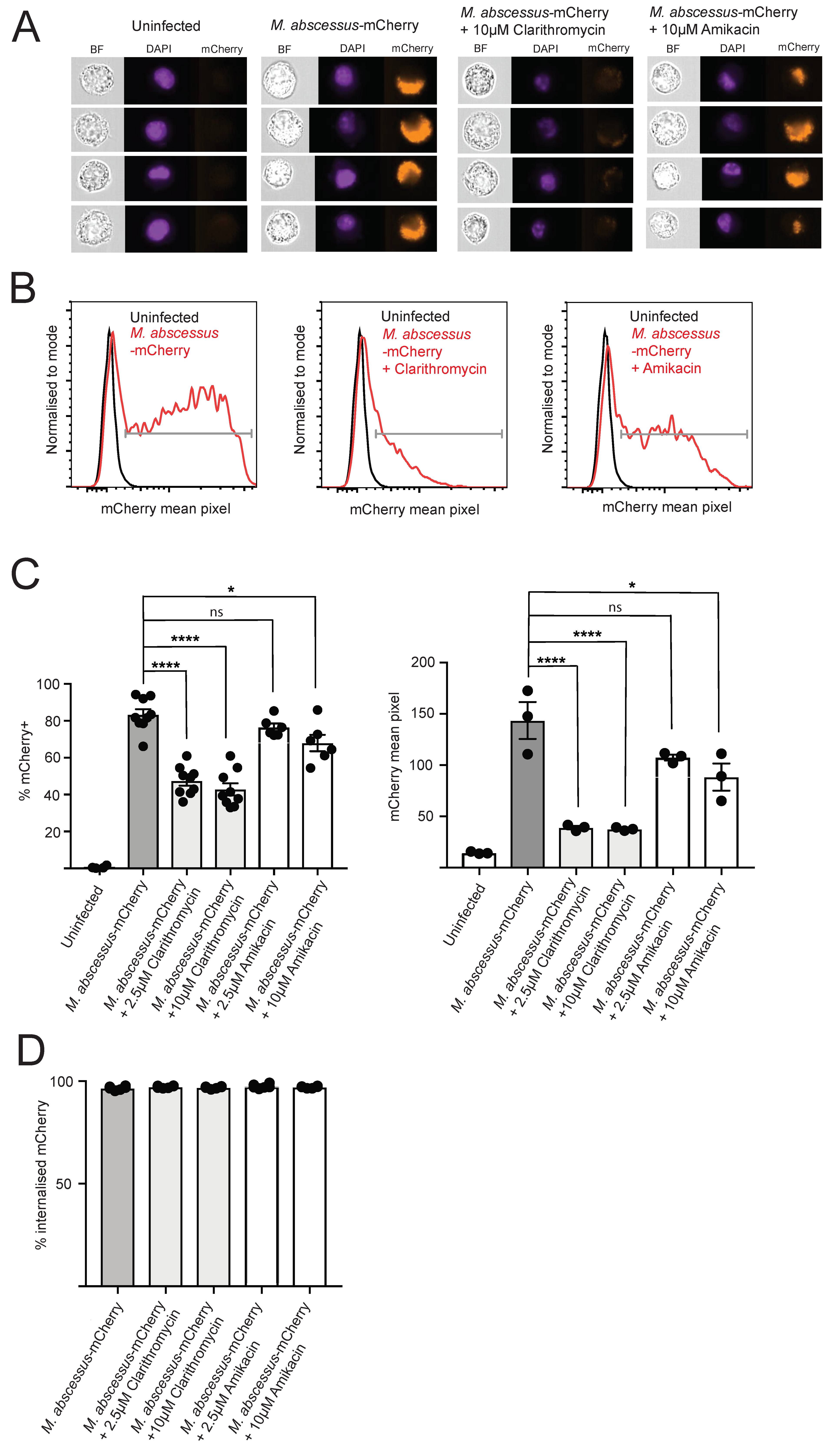
2.1. Fluorescent M. abscessus Reporter System in Macrophage Infections
2.2. Clarithromycin and Amikacin Treatment Reduce Intracellular M. abscessus Bacterial Load
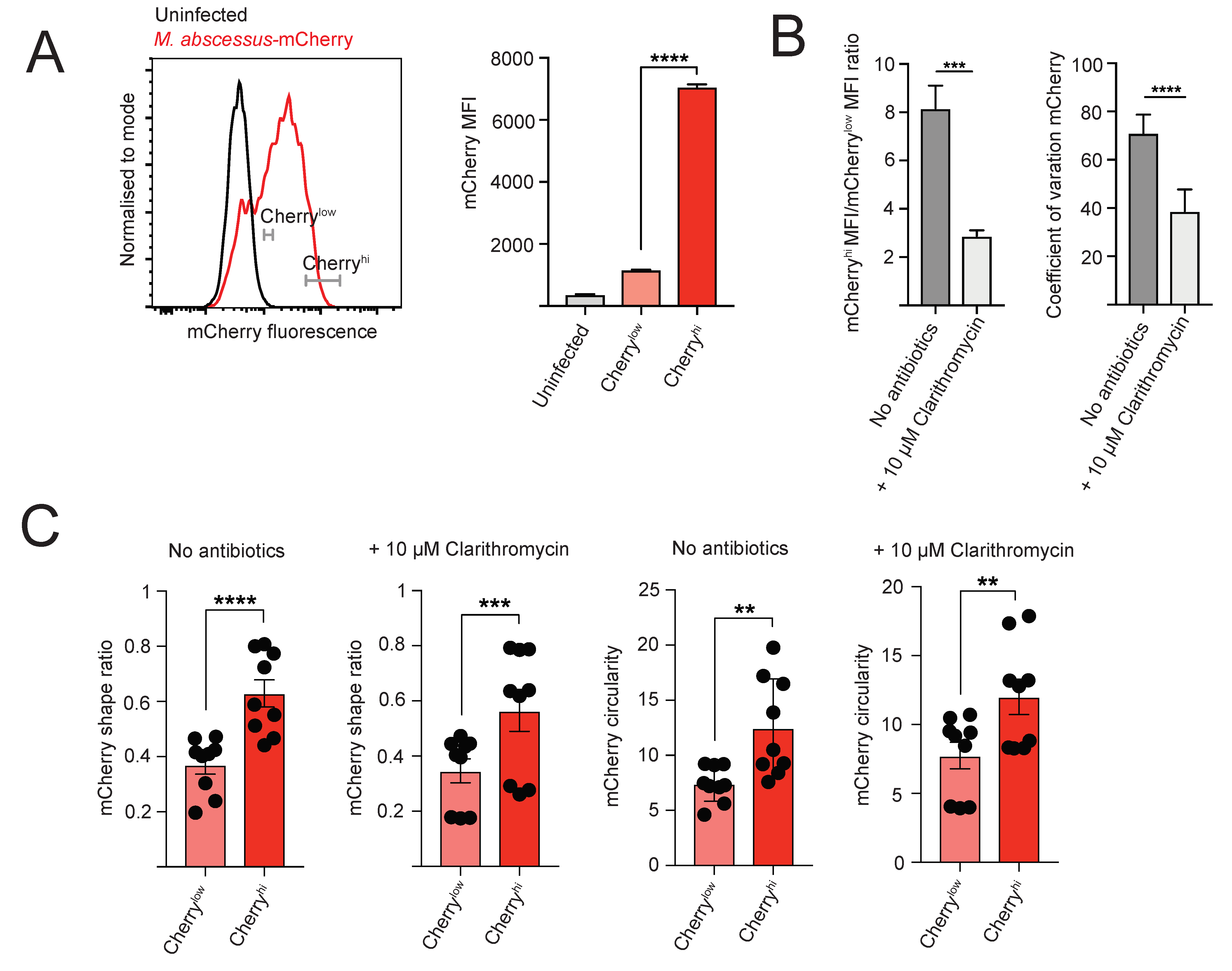
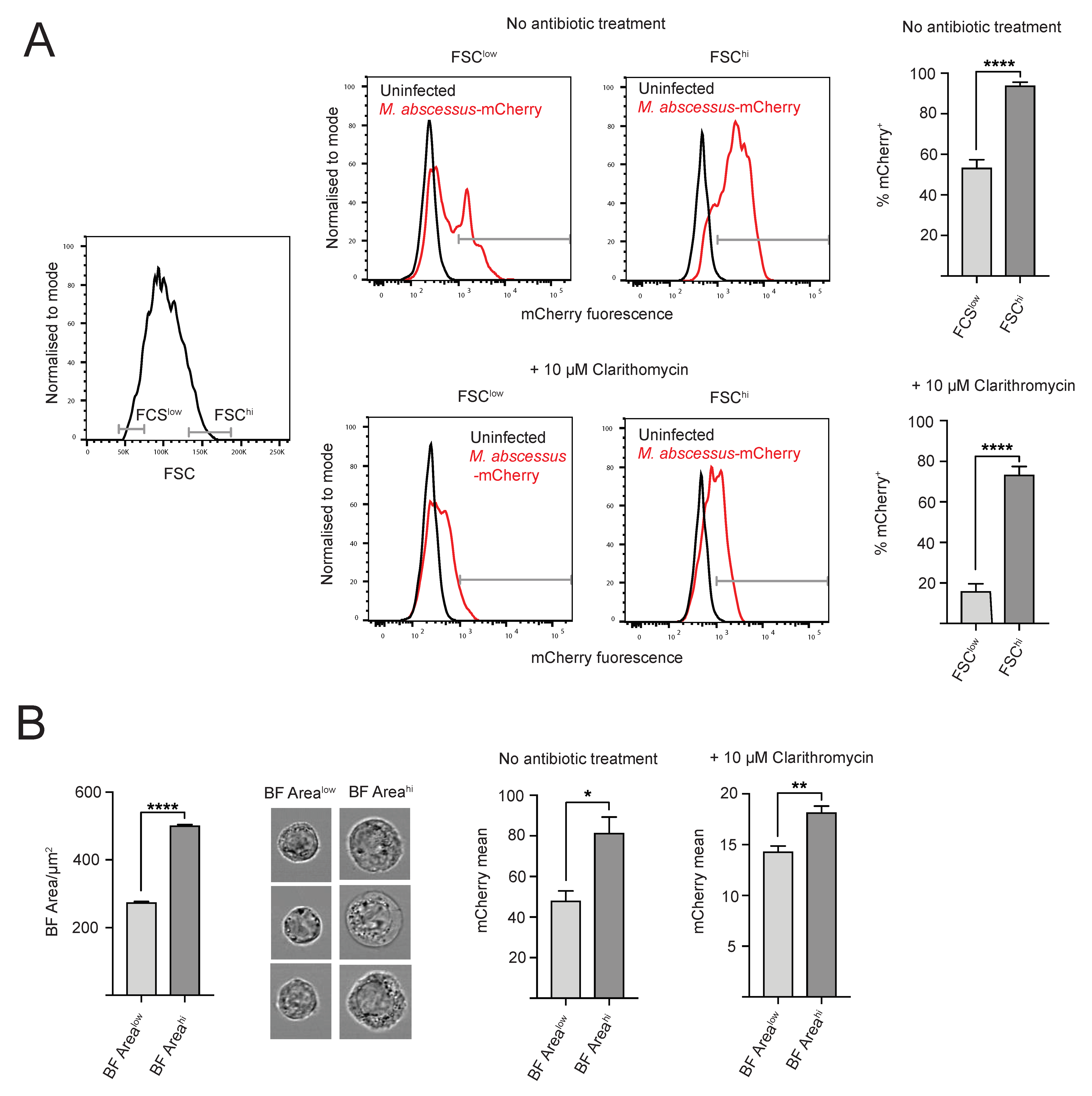
2.3. Heterogeneity of Intracellular M. abscessus Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Generation of M. abscessus-mCherry
4.3. M. abscessus Infection of J774 and THP-1 Cells
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Imaging Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopeman, R.C.; Harrison, J.; Desai, M.; Cox, J.A.G. Mycobacterium abscessus: Environmental bacterium turned clinical nightmare. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.; Byrd, T.F. Mycobacterium abscessus: Shapeshifter of the mycobacterial world. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umrao, J.; Singh, D.; Zia, A.; Saxena, S.; Sarsaiya, S.; Singh, S.; Khatoon, J.; Dhole, T.N. Prevalence and species spectrum of both pulmonary and extrapulmonary nontuberculous Mycobacteria isolates at a tertiary care center. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, H.; Kinjo, T.; Nei, Y.; Yamashiro, S.; Fujita, J.; Kishaba, T. Causative species of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease and comparative investigation on clinical features of Mycobacterium abscessus complex disease: A retrospective analysis for two major hospitals in a subtropical region of Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.Y.H.; Chotirmall, S.H.; Fok, E.T.K.; Verma, A.; De, P.P.; Goh, S.K.; Puah, S.H.; Goh, D.E.L.; Abisheganaden, J.A. Profiling non-tuberculous Mycobacteria in an Asian setting: Characteristics and clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients in Singapore. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Cherng, B.P.Z.; Sng, L.H.; Tan, Y.E. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of non-tuberculous Mycobacteria diseases in Singapore with a focus on pulmonary disease, 2012–2016. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.M.; Grogono, D.M.; Greaves, D.; Foweraker, J.; Roddick, I.; Inns, T.; Reacher, M.; Haworth, C.S.; Curran, M.D.; Harris, S.R.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing to identify transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus between patients with cystic fibrosis: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2013, 381, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.M.; Grogono, D.M.; Rodriguez-Rincon, D.; Everall, I.; Brown, K.P.; Moreno, P.; Verma, D.; Hill, E.; Drijkoningen, J.; Gilligan, P.; et al. Emergence and spread of a human-transmissible multidrug-resistant nontuberculous. Mycobacterium. Sci. 2016, 354, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Singh, S. Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria in TB-endemic countries: Are we neglecting the danger? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Rominski, A.; Sander, P. The role of antibiotic-target-modifying and antibiotic-modifying enzymes in Mycobacterium abscessus drug resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessar, R.; Cambau, E.; Reyrat, J.M.; Murray, A.; Gicquel, B. Mycobacterium abscessus: A new antibiotic nightmare. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benwill, J.L.; Wallace, R.J., Jr. Mycobacterium abscessus: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Mao, Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Chu, H. Clinical efficacy and adverse effects of antibiotics used to treat Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease. Front. Microb. 2019, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.L.; Aziz, D.B.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. NTM drug discovery: Status, gaps and the way forward. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1502–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Matsuyama, K.; Hutson, C.; Madrid, P. Identification of antimicrobial activity among FDA-approved drugs for combating Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium chelonae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.L.; Wu, M.L.; Aziz, D.B.; Laleu, B.; Dick, T. Screening of TB actives for activity against nontuberculous Mycobacteria delivers high hit rates. Front. Microb. 2017, 8, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lian, L.L.; Wan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Liu, H.; Wan, K. Antimicrobial susceptibility of standard strains of nontuberculous Mycobacteria by microplate alamar blue assay. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Netherton, M.; Byrd, T.F.; Rohde, K.H. Reporter-based assays for high-throughput drug screening against Mycobacterium abscessus. Front. Microb. 2017, 8, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Strauch, A.; Chao, J.; Ko, M.; Av-Gay, Y. Screening of preselected libraries targeting Mycobacterium abscessus for drug discovery. Antimicrob. Agents and Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Castro, L.; Russell, D.; Ovechkina, Y.; Parish, T. Novel screen to assess bactericidal activity of compounds against non-replicating Mycobacterium abscessus. Front. Microb. 2018, 9, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernut, A.; Herrmann, J.L.; Ordway, D.; Kremer, L. The diverse cellular and animal models to decipher the physiopathological traits of Mycobacterium abscessus infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obregon-Henao, A.; Arnett, K.A.; Henao-Tamayo, M.; Massoudi, L.; Creissen, E.; Andries, K.; Lenaerts, A.J.; Ordway, D.J. Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus to antimycobacterial drugs in preclinical models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6904–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernut, A.; Le Moigne, V.; Lesne, T.; Lutfalla, G.; Herrmann, J.L.; Kremer, L. In vivo assessment of drug efficacy against Mycobacterium abscessus using the embryonic zebrafish test system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4054–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.T.; Moon, C.; Park, O.K.; Kwon, S.H.; Jang, J. Novel drug combination for Mycobacterium abscessus disease therapy identified in a Drosophila infection model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.B.; Trapnell, C.; Bloom, J.D. Extreme heterogeneity of influenza virus infection in single cells. eLife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helaine, S.; Thompson, J.A.; Watson, K.G.; Liu, M.; Boyle, C.; Holden, D.W. Dynamics of intracellular bacterial replication at the single cell level. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3746–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.M.; Helaine, S.; Holden, D.W.; Sampson, S.L. Elucidating population-wide mycobacterial replication dynamics at the single-cell level. Microbiology 2016, 162, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.; Avraham, R. Breaking the population barrier by single cell analysis: One host against one pathogen. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 36, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu, N.; Zelmer, A.; Fletcher, T.; Elkington, P.T.; Ward, T.H.; Ripoll, J.; Parish, T.; Bancroft, G.J.; Schaible, U.; Robertson, B.D.; et al. Optimisation of bioluminescent reporters for use with Mycobacteria. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, M.; Klinzing, D.; Wei, J.R.; Gengenbacher, M.; Rubin, E.J.; Dick, T. Draft genome sequence of Mycobacterium abscessus Bamboo. Genome Announc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, Y.K.; Alvarez, N.; Go, M.L.; Dick, T. Extreme drug tolerance of Mycobacterium abscessus “persisters”. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togami, K.; Chono, S.; Morimoto, K. Distribution characteristics of clarithromycin and azithromycin, macrolide antimicrobial agents used for treatment of respiratory infections, in lung epithelial lining fluid and alveolar macrophages. Biopharm. Drug Disposition 2011, 32, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heins, A.L.; Johanson, T.; Han, S.; Lundin, L.; Carlquist, M.; Gernaey, K.V.; Sørensen, S.J.; Eliasson Lantz, A. Quantitative flow cytometry to understand population heterogeneity in response to changes in substrate availability in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae chemostats. Front. Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helaine, S.; Holden, D.W. Heterogeneity of intracellular replication of bacterial pathogens. Current Opinion Microbiol. 2013, 16, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yongky, A.; Yin, J. Growth of an RNA virus in single cells reveals a broad fitness distribution. Virology 2009, 385, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldt, F.S.; Kupke, S.Y.; Dorl, S.; Reichl, U.; Frensing, T. Single-cell analysis and stochastic modelling unveil large cell-to-cell variability in Influenza A virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, A.L.; Viljoen, A.; Bah, A.; Simeone, R.; Bernut, A.; Laencina, L.; Deramaudt, T.; Rottman, M.; Gaillard, J.L.; Majlessi, L.; et al. The distinct fate of smooth and rough Mycobacterium abscessus variants inside macrophages. Open Biol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brzostek, J.; Fatin, A.; Chua, W.H.; Tan, H.Y.; Dick, T.; Gascoigne, N.R.J. Single Cell Analysis of Drug Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus during Macrophage Infection. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100711
Brzostek J, Fatin A, Chua WH, Tan HY, Dick T, Gascoigne NRJ. Single Cell Analysis of Drug Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus during Macrophage Infection. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(10):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100711
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrzostek, Joanna, Amierah Fatin, Wen Hui Chua, Hui Yi Tan, Thomas Dick, and Nicholas R. J. Gascoigne. 2020. "Single Cell Analysis of Drug Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus during Macrophage Infection" Antibiotics 9, no. 10: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100711
APA StyleBrzostek, J., Fatin, A., Chua, W. H., Tan, H. Y., Dick, T., & Gascoigne, N. R. J. (2020). Single Cell Analysis of Drug Susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus during Macrophage Infection. Antibiotics, 9(10), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100711





