The Structure Features and Improving Effects of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of Astragalus Polysaccharide
2.3. Physiochemical Analysis of WAP
2.4. Animals and Treatment
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Measurement of SCFAs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
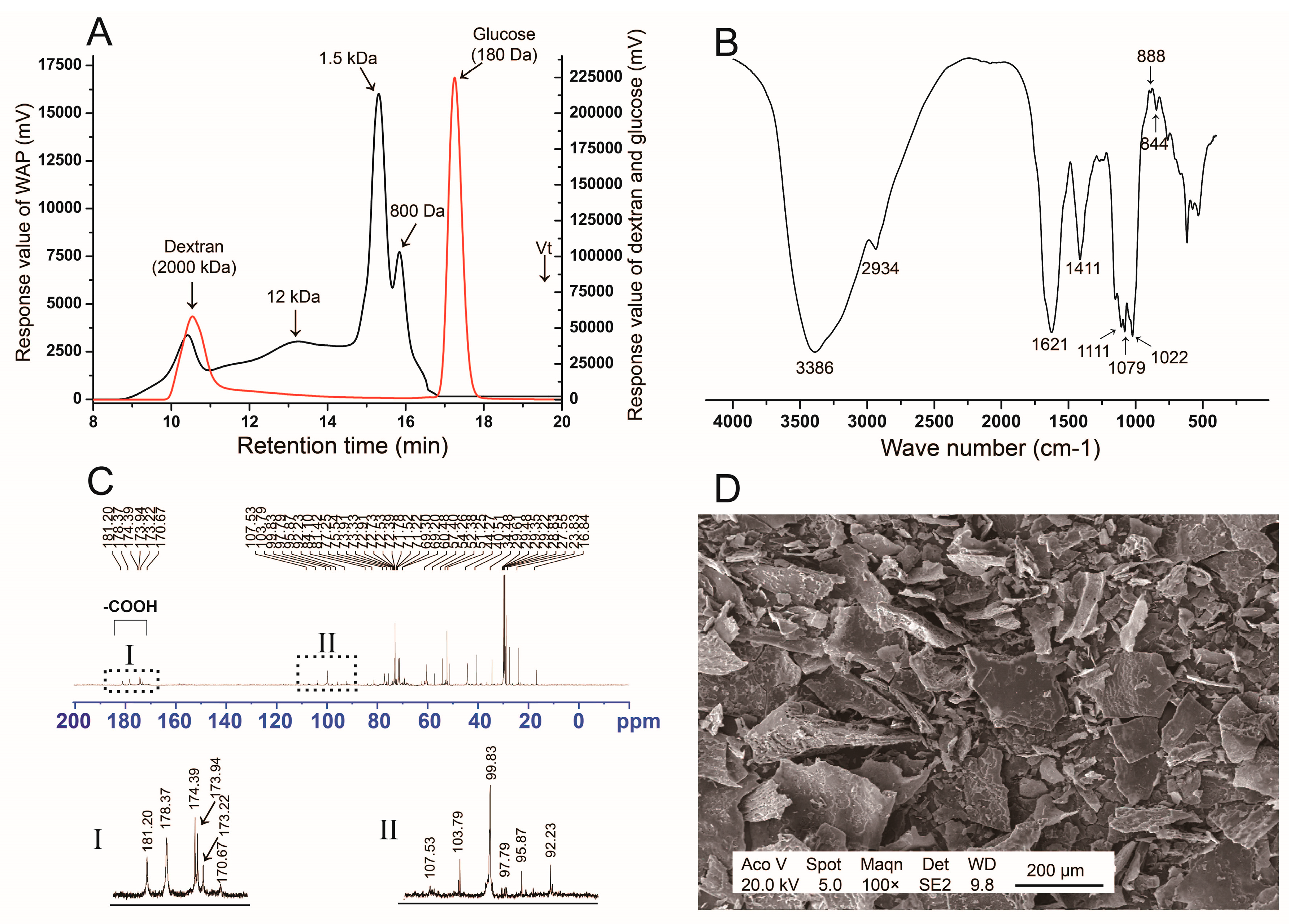
3.1. Structure Analysis of WAP
3.1.1. Monosaccharide Composition and Molecular Distribution
3.1.2. FT-IR Spectrum
3.1.3. 13C NMR Analysis
3.1.4. SEM Analysis
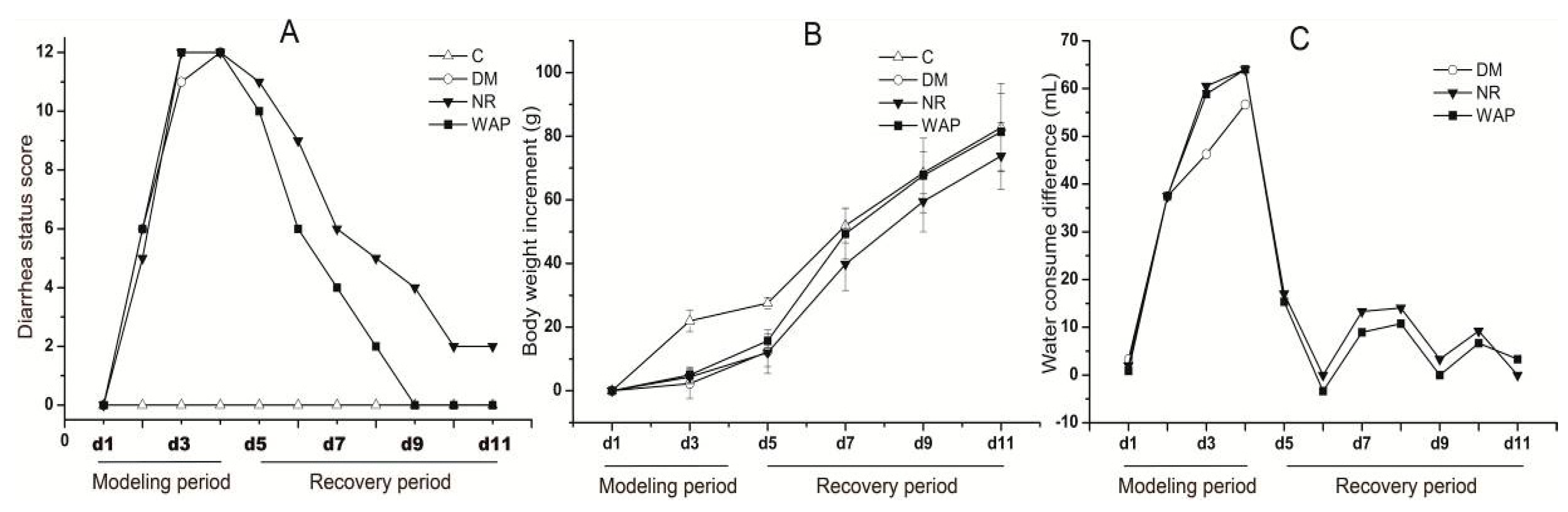
3.2. Normal Status of Rats
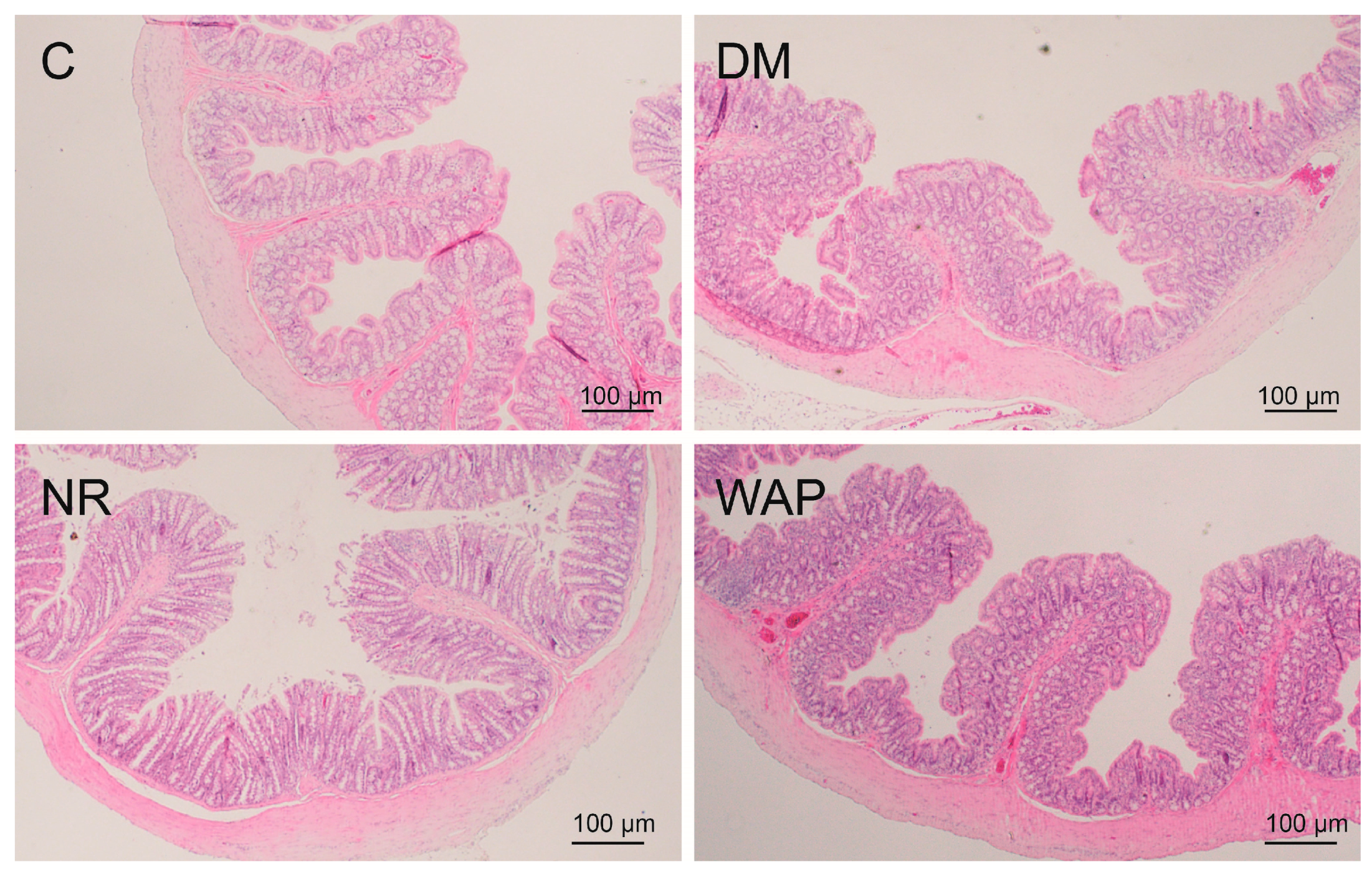
3.3. Effects of WAP on Colon Morphology
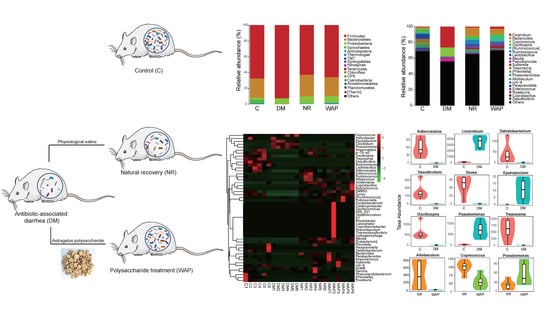
3.4. Effects of WAP on Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
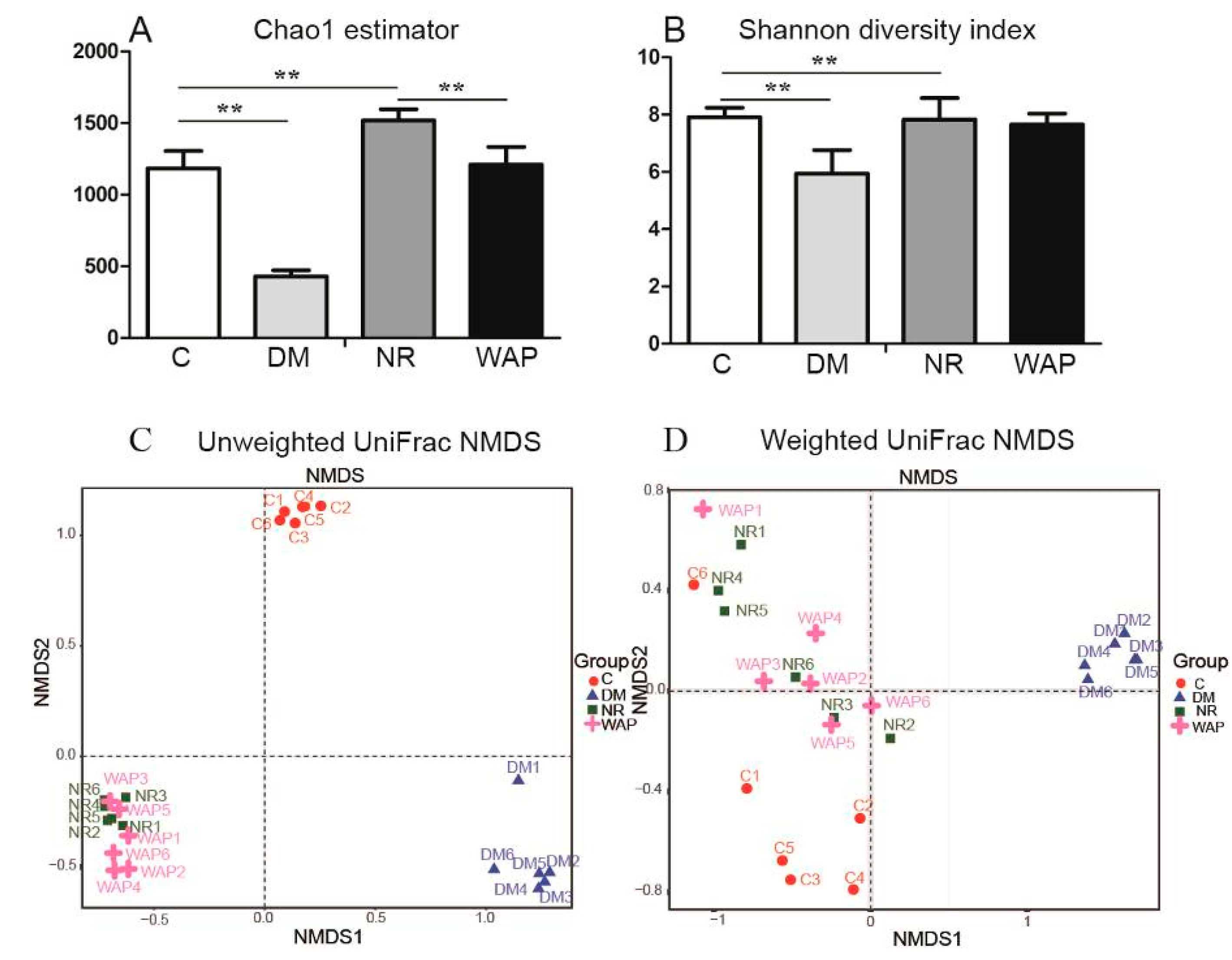
3.4.1. α and β Diversity Analysis
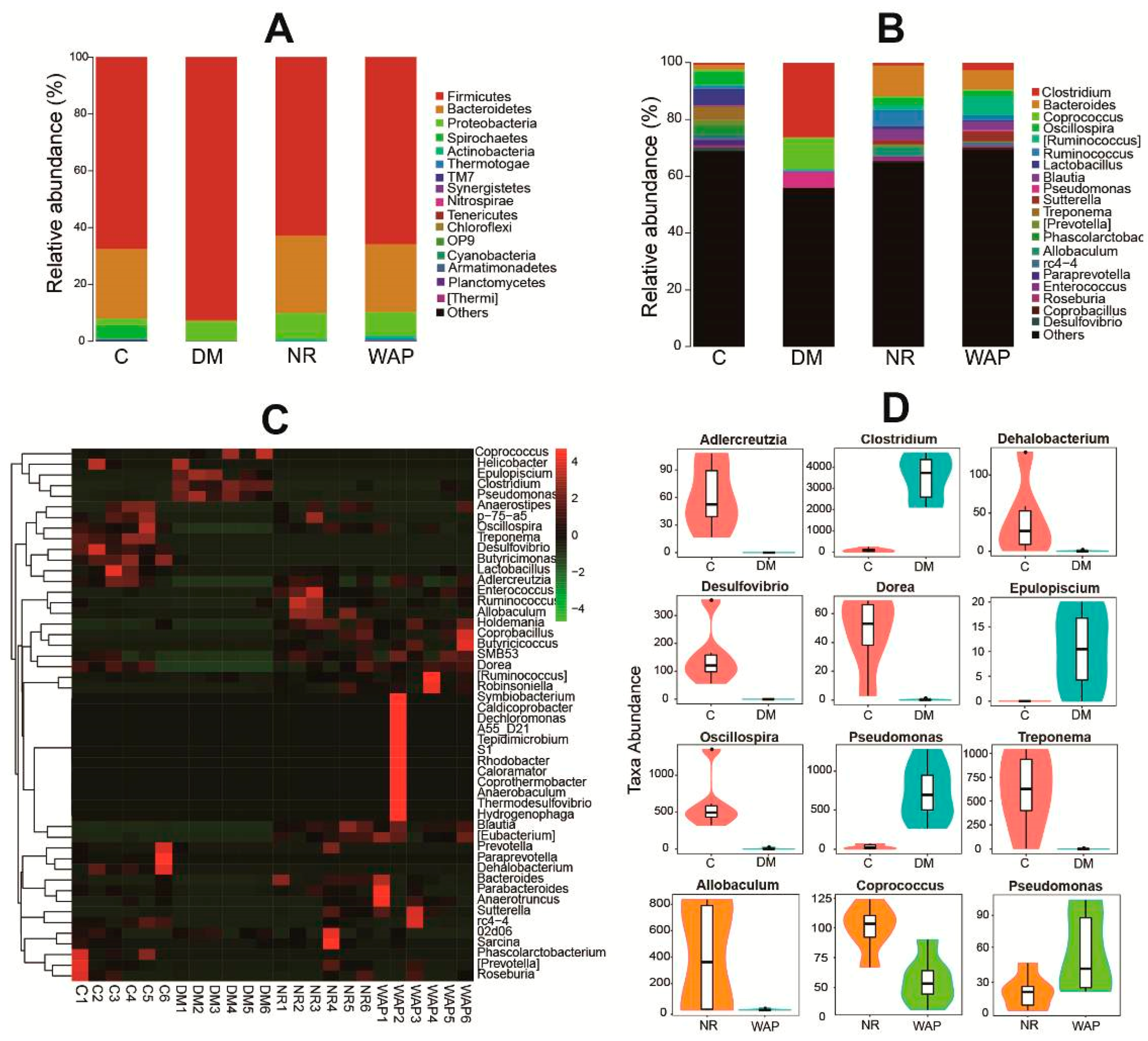
3.4.2. Composition Shifts of Key Microbial Phylotypes
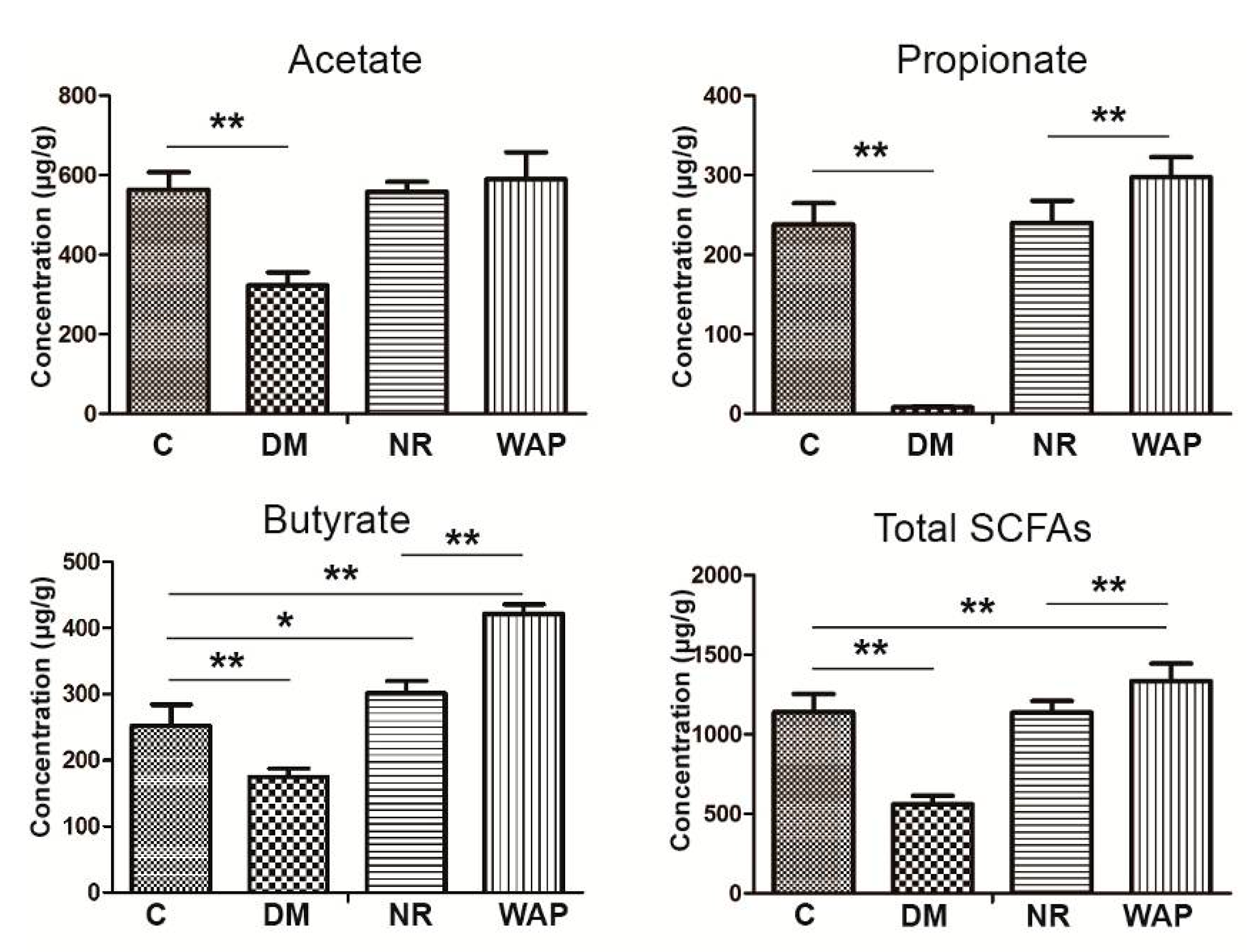
3.5. Impact of WAP on SCFA Production
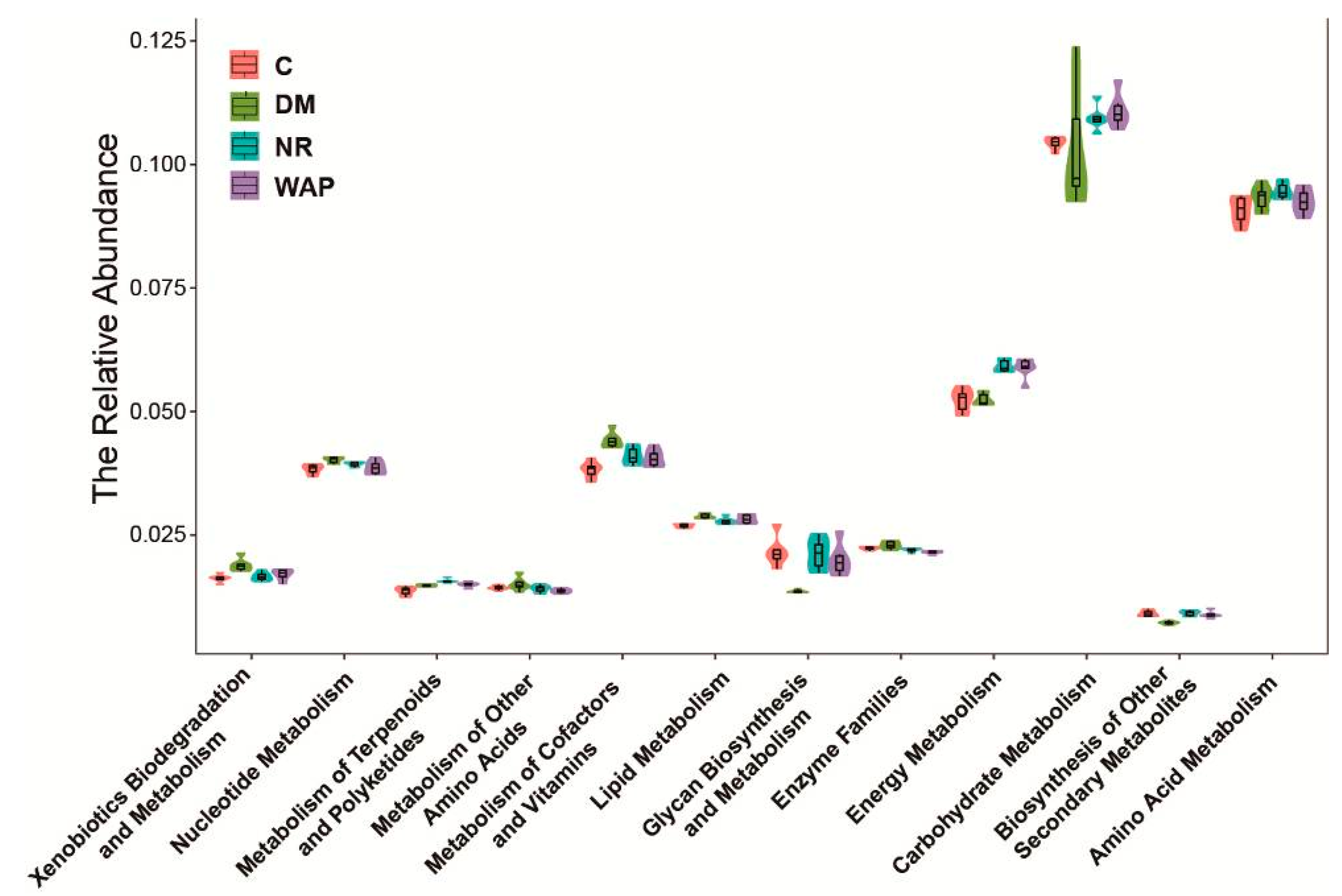
3.6. Effect of WAP on the Functional Prediction of Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, S.; Santullo, P.; Hirani, S.P.; Kumar, N.; Chowdhury, J.R.; Garcíaforcada, A.; Recio, M.; Paz, F.; Zobina, I.; Kolli, S. Use of antibiotics and the prevalence of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in patients with spinal cord injuries: An international, multicentre centre study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 97, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Xiao, B.; Sun, T.Y. Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Lei, X.Y.; Yin, Z.C.; Guo, W.; Wu, S.R.; Yang, X.J. Transgenerational effects of paternal dietary Astragalus polysaccharides on spleen immunity of broilers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.Y.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Z.Q.; Liu, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P.Y. Astragalus polysaccharides protect against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting NF-κB activation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Zhang, Y.Q. Characterization and renal protective effect of a polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus. Carbohyd. Polym. 2009, 78, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.K.; Gao, R.R.; Wu, S.J. Preparation, characterization and hypolipidaemic activity of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Wang, M.J.; Huang, W.H.; Yao, W.B.; Gao, X.D. A polysaccharide extracted from Astragalus membranaceus residue improves cognitive dysfunction by altering gut microbiota in diabetic mice. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 205, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, W.C.; Wang, W.P.; Tian, W.Y.; Zhang, X.G. Extraction, characterization of Astragalus polysaccharides and its immune modulating activities in rats with gastric cancer. Carbohyd. Polym. 2009, 78, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhua, Z.Y.; Liu, R.Q.; Si, C.L.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Y.X.; Ding, L.N.; Jing, C.; Liu, A.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Structural analysis and anti-tumor activity comparison of polysaccharides from Astragalus. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 85, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M.; Leclerc, E.; Simsek, S. Arabinoxylans, gut microbiota and immunity. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 139, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Foster, K.R.; Comstock, L.E. The evolution of cooperation within the gut microbiota. Nature 2016, 533, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative deter-mination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmark, J.J.; Grossberg, S.E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 79, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Yang, G.; Yan, J.M.; Wu, D.; Hou, Y.; Diao, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.F. Polysaccharide structure and immunological relationships of RG-I pectin from the bee pollen of Nelumbo nucifera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.J.; Liu, C.; Ye, C.X.; Sun, J.Q.; Tan, X.W.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Q.; Shi, D.Y.; Guo, S.N. Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of antibiotic-associated diarrhea with herbal formula. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Chen, L.X.; Gao, K.; Shao, Z.J.; Huo, X.H.; Hua, M.; Liu, S.X.; Sun, Y.S.; Li, S.S. Effects of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on rats with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.; Mann, J.; Chapman, T.; Thomas, F.; Whitton, C.; Floyd, R.; Abebe, E. Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data. Philos. Trans. R. Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Van Belle, G.; Simberloff, D. Explicit calculation of the rarefaction diversity measurement and the determination of sufficient sample size. Ecology 1975, 56, 1459–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.F.; Aller, J.Y. Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: What 16S rDNA libraries can tell us. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramette, A. Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical Methods for Detecting Differentially Abundant Features in Clinical Metagenomic Samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J. Traditional medicine—A culture in the balance. Nature 2007, 448, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, G.B.; Liu, P.; Song, J.H.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.J.; Xu, F.; Wang, B.S.; Mao, J.H.; Shen, Z.X.; et al. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4826–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Long, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Li, Q.A.; Wu, H.J.; Guo, Z.J.; Li, Y.H.; Niu, Y.B.; Li, C.; et al. Evidence for the complementary and synergistic effects of the three-alkaloid combination regimen containing berberine, hypaconitine and skimmianine on the ulcerative colitis rats induced by trinitrobenzene-sulfonic acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 651, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Shimada, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kaneko, A.; Oomiya, Y.; Kubota, K.; Kase, Y.; Lee, K.; Uezono, Y. Complementary and synergistic therapeutic effects of compounds found in Kampo medicine: Analysis of daikenchuto. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wen, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, H.L.; Tan, Y.F.; Li, Y.H.; Zeng, N.K. Could the gut microbiota reconcile the oral bioavailability conundrum of traditional herbs? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.K.; Zhou, M.M.; Zhao, A.H.; Jia, W. Traditional Chinese medicine: Balancing the gut ecosystem. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.H.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Zhao, C.H. Beneficial effect of intestinal fermentation of natural polysaccharides. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Zhuo, C.; Teng, C.Y.; Yu, S.M.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ren, G.M.; Yu, M.; Qu, J.J. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on chronic pancreatitisand intestinal microbiota in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S.; Qi, Y.L.; Chen, L.X.; Qu, D.; Li, Z.M.; Gao, K.; Chen, J.B.; Sun, Y.S. Effects of Panax ginseng polysaccharides on the gut microbiota in mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadia, K.; Thomson, P.J.; Lawrence, O.; Ren, X.M.; Li, M.Q.; Xin, Y. A polysaccharide isolated from Dictyophora indusiata promotes recovery from antibiotic-driven intestinal dysbiosis and improves gut epithelial barrier function in a mouse model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Datchary, P.K.; Backhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Gutiérrez-Del-Río, I.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Colon microbiota fermentation of dietary prebiotics towards short-chain fatty acids and their roles as anti-inflammatory and antitumour agents: A review. J. Funct. Food 2016, 25, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Van, B.E.; Wagenaar, G.; Garssen, J.; Folkerts, G.; Henricks, P. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 831, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulangé, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumas, M.E. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.L.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.F.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.J.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scores | Diarrhea Status |
|---|---|
| 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Loose, light color, and nonstick perianal stool status; general mental state |
| 2 | Adhesion stool in the anus, mental depression, no appetite for food, weight loss |
| Relative Abundance (%) | Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | DM | NR | WAP | |
| Firmicutes | 78.7 ± 11.2 a | 92.4 ± 3.4 b | 62.8 ± 14.9 a | 65.8 ± 12.4 a |
| Bacteroidetes | 24.5 ± 14.4 a | 0.5 ± 0.7 b | 27.2 ± 13.7 a | 23.9 ± 13.6 a |
| Proteobacteria | 2.5 ± 1.0 b | 7.0 ± 3.5 a | 9.1 ± 3.1 a | 8.4 ± 4.1 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Ren, D.; Qu, D.; Sun, Y. The Structure Features and Improving Effects of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010008
Li S, Qi Y, Ren D, Qu D, Sun Y. The Structure Features and Improving Effects of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shanshan, Yuli Qi, Duoduo Ren, Di Qu, and Yinshi Sun. 2020. "The Structure Features and Improving Effects of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea" Antibiotics 9, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010008
APA StyleLi, S., Qi, Y., Ren, D., Qu, D., & Sun, Y. (2020). The Structure Features and Improving Effects of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Antibiotics, 9(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010008