The Effect of Different Antibiotic Regimens on Bacterial Resistance: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
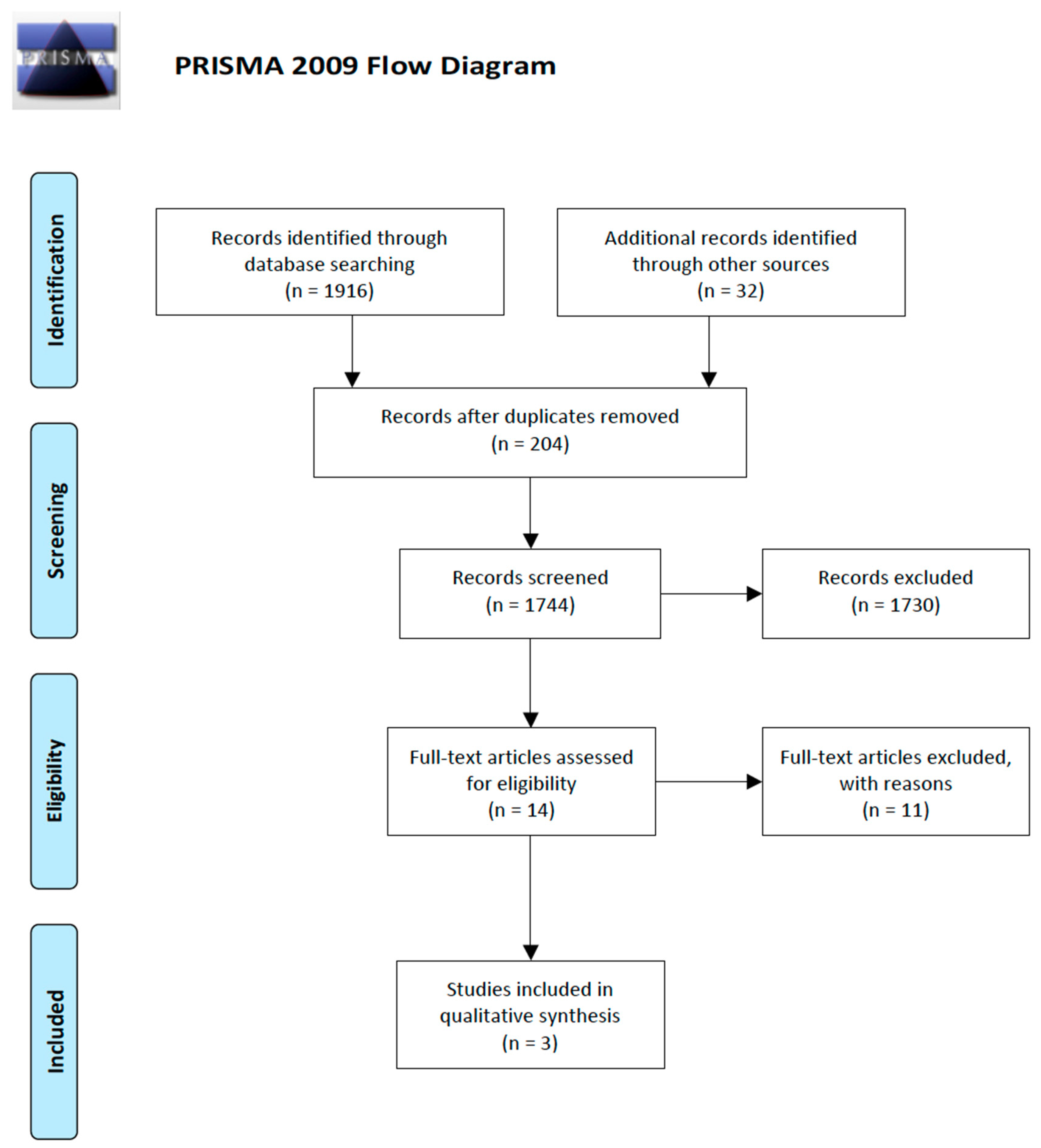
2.1. Results of the Search
2.2. Exclusion of Studies
2.3. Included Studies
2.4. Characteristics of Participants
2.5. Characteristics of Interventions
2.6. Characteristics of Outcome Measures
2.7. Risk of Bias in Included Studies and Strength of Evidence
2.8. Effects of Interventions
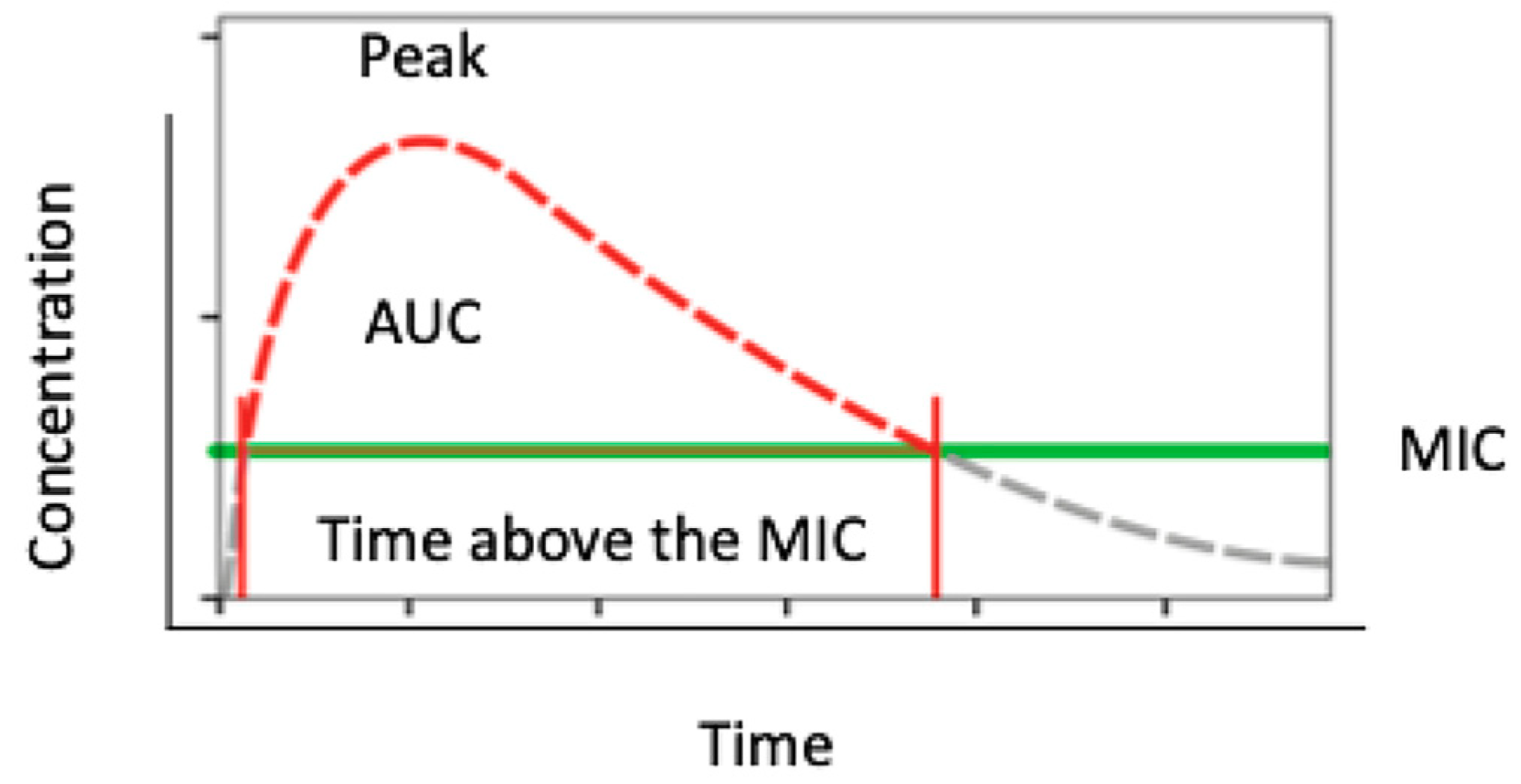
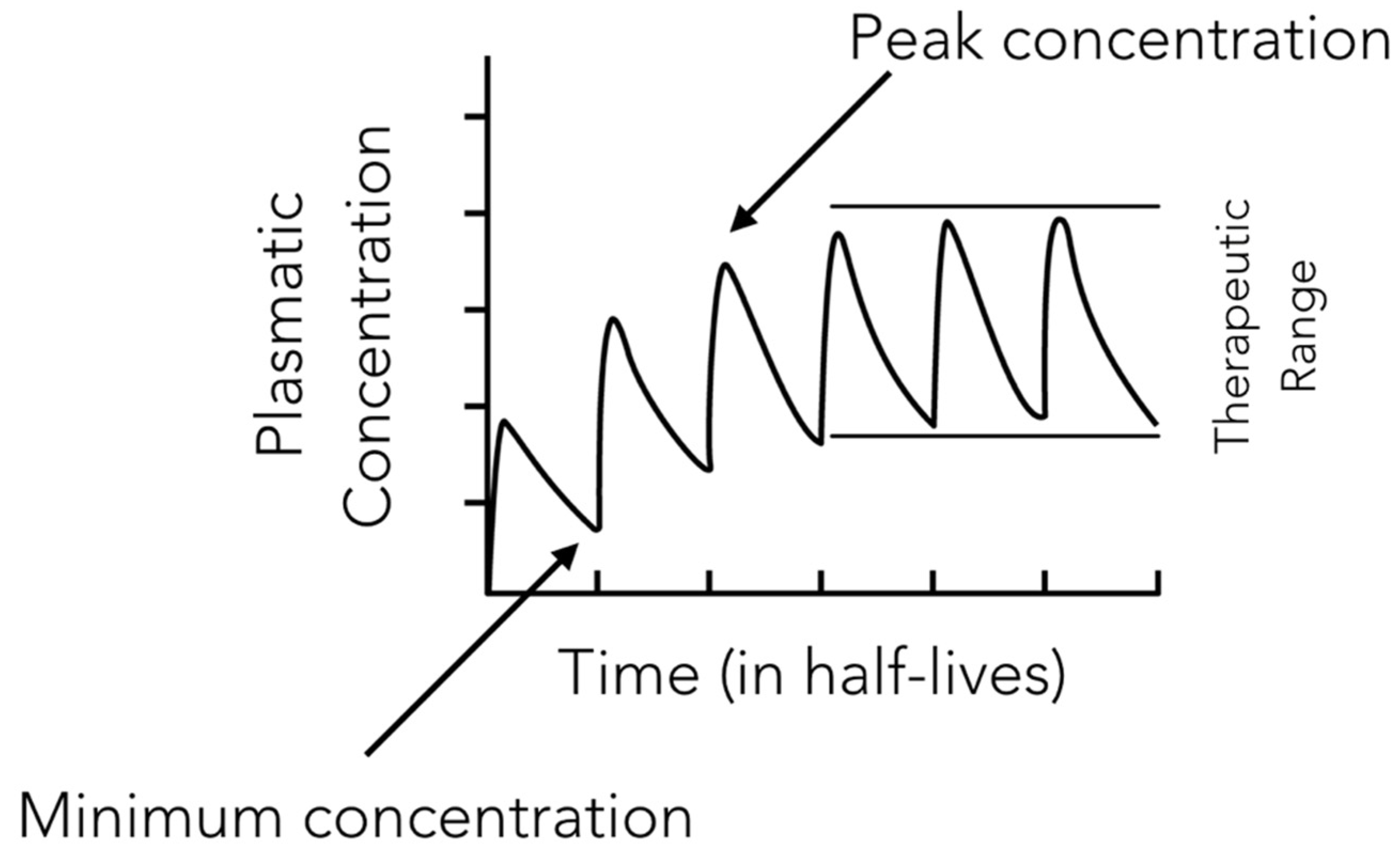
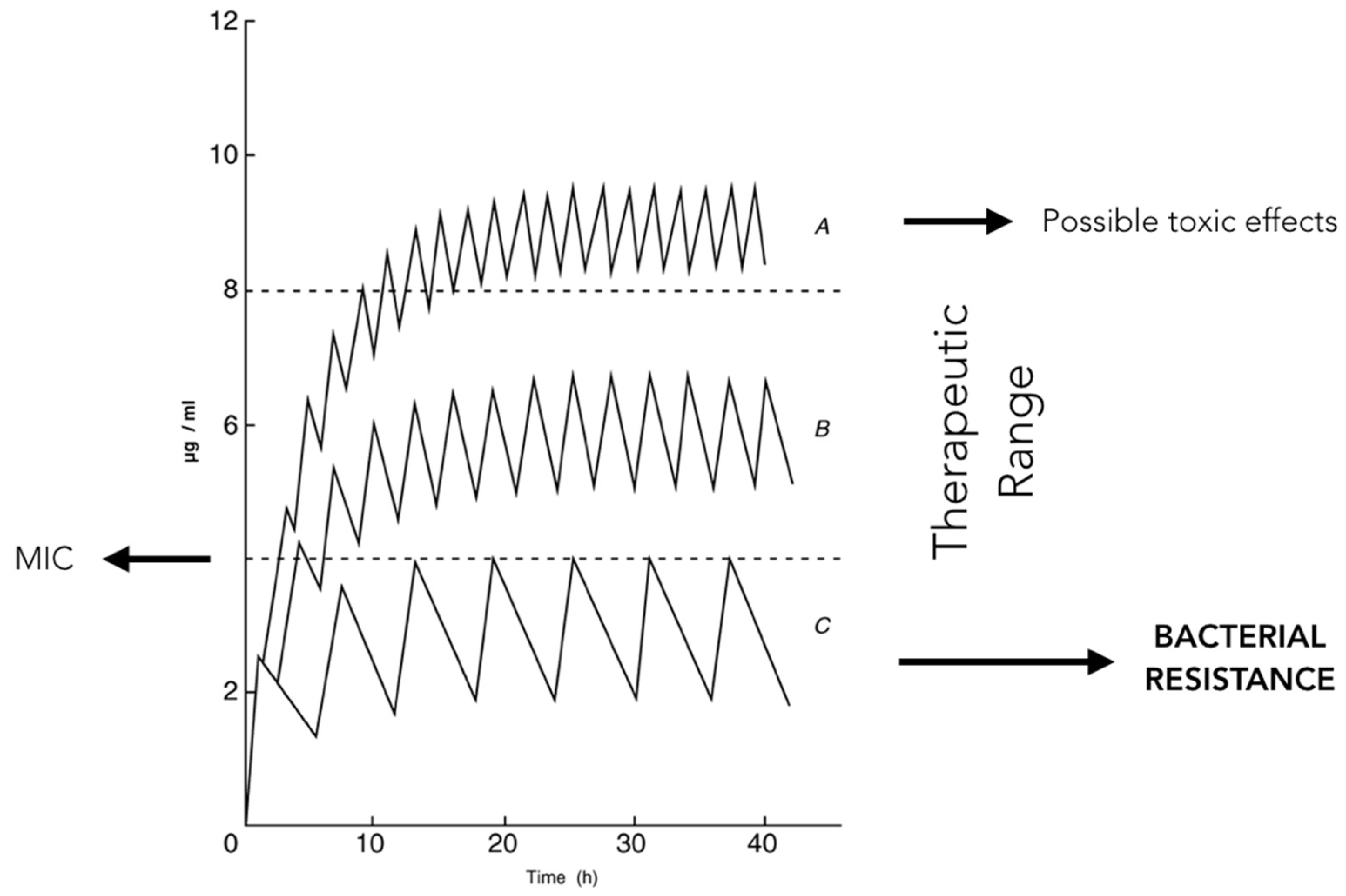
2.9. Antibiotic Working Principles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protocol and Registration
4.2. Eligibility Criteria
4.3. Information Sources and Search
4.4. Study Selection
4.5. Data Collection Process
4.6. Outcome
4.7. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies and Quality of Evidence
4.8. Data Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adopt AWaRe. Handle Antibiotics with care. Available online: https://adoptaware.org (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Katzung, B.G.; Masters, S.B.; Trevor, A.J. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 14th ed.; McGraw Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.; Pan, J.; Lu, S.; Tang, J. Patient compliance with antimicrobial drugs: A Chinese survey. Am. J. Infect. Control 2018, 46, e25–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kadota, J.; Watanabe, A.; Yamanaka, N.; Tateda, K.; Mikamo, H.; Tomono, K.; Niki, Y.; Aoki, N.; Sunakawa, K.; et al. Compliance with oral antibiotic regimens and associated factors in Japan: Compliance Survey of Multiple Oral Antibiotics (COSMOS). Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Taylor, D.M.; Cabalag, M.S.; Ugoni, A.; Yeoh, M. Factors that impact on emergency department patient compliance with antibiotic regimens. Emerg. Med. J. 2010, 27, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandrotaite, K.; Smigelskas, K.; Janusauskiene, D.; Jievaltas, M.; Maciulaitis, R.; Briedis, V. Development of a short questionnaire to identify the risk of nonadherence to antibiotic treatment. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.J.; Thottathil, S.E.; Newman, T.B. Antibiotics Overuse in Animal Agriculture: A Call to Action for Health Care Providers. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 2409–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Abu Bakar, M. Health care-associated infections-an overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patini, R.; Staderini, E.; Lajolo, C.; Lopetuso, L.; Mohammed, H.; Rimondini, L.; Rocchetti, V.; Franceschi, F.; Cordaro, M.; Gallenzi, P. Relationship between oral microbiota and periodontal disease: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5775–5788. [Google Scholar]
- Martellacci, L.; Quaranta, G.; Patini, R.; Isola, G.; Gallenzi, P.; Masucci, L. A Literature Review of Metagenomics and Culturomics of the Peri-implant Microbiome: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patini, R.; Cattani, P.; Marchetti, S.; Isola, G.; Quaranta, G.; Gallenzi, P. Evaluation of Predation Capability of Periodontopathogens Bacteria by Bdellovibrio Bacteriovorus HD100. An in Vitro Study. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemura, K.; Tanaka, K.; Yasuda, M.; Ishihara, S.; Muratani, T.; Deguchi, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Kamidono, S.; Nakano, Y.; Arakawa, S.; et al. Efficacy of 1-day prophylaxis medication with fluoroquinolone for prostate biopsy. World J. Urol. 2005, 23, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, M.; Rajeev, T.P.; Gupta, N.P. Antibiotic prophylaxis for transrectal needle biopsy of the prostate: A randomized controlled study. BJU Int. 2000, 85, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.Y.; Ding, D.C.; Chen, D.C.; Lu, M.F.; Liu, J.Y.; Chang, F.Y. Prospective randomized comparison of single-dose versus 1-day cefazolin for prophylaxis in gynecologic surgery. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2005, 84, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.T.; Myers, E.N.; Thearle, P.B.; Sigler, B.A.; Schramm, V.L., Jr. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for contaminated head and neck surgery. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khariwala, S.S.; Le, B.; Pierce, B.H.; Vogel, R.I.; Chipman, J.G. Antibiotic Use after Free Tissue Reconstruction of Head and Neck Defects: Short Course vs. Long Course. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2016, 17, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luaces-Rey, R.; Arenaz-Búa, J.; Lopez-Cedrun-Cembranos, J.L.; Martínez-Roca, C.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Sironvalle-Soliva, S. Efficacy and safety comparison of two amoxicillin administration schedules after third molar removal. A randomized, double-blind and controlled clinical trial. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2010, 15, e633–e638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feres, M.; Haffajee, A.D.; Allard, K.; Som, S.; Goodson, J.M.; Socransky, S.S. Antibiotic resistance of subgingival species during and after antibiotic therapy. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002, 29, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, C.A.; Adamsson, I.; Edlund, C.; Sjösted, S.; Seensalu, R.; Wilkström, B.; Nord, C.E. Effects of omeprazole and amoxicillin on the human oral and gastrointestinal microflora in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1996, 38, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardin, H.; Yasukawa, K.; Nouacer, N.; Plainvert, C.; Aucouturier, P.; Ergani, A.; Descroix, V.; Toledo-Arenas, R.; Azerad, J.; Bouvet, A. Reduced susceptibility to amoxicillin of oral streptococci following amoxicillin exposure. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, L.L.; Hilal-Dandan, R.; Knollmann, B.C. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th ed.; McGraw Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, R.; Sobel, J.D. Metronidazole for the treatment of vaginal infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 9.0. 2019. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Kashani, H.; Hilon, J.; Rasoul, M.H.; Friberg, B. Influence of a single preoperative dose of antibiotics on the early implant failure rate. A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, A.; Casavecchia, P.; Barone, A.; Brugnami, F. A pilot study to determine the effectiveness of different amoxicillin regimens in implant surgery. J. Oral. Implantol. 2011, 37, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Giudice, G.; Lo Giudice, R.; Matarese, G.; Isola, G.; Cicciù, M.; Terranova, A.; Palaia, G.; Romeo, U. Evaluation of magnification systems in restorative dentistry. An in-vitro study. Dental Cadmos 2015, 83, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Cannizzaro, G.; Bozzoli, P.; Consolo, U.; Felice, P.; Ferri, V.; Landriani, S.; Leone, M.; Magliano, A.; Pellitteri, G.; et al. Efficacy of prophylactic antibiotics for dental implants: A multicentre placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial. Eur. J. Oral. Implantol. 2008, 1, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, G.; Matarese, M.; Ramaglia, L.; Cicciù, M.; Matarese, G. Evaluation of the efficacy of celecoxib and ibuprofen on postoperative pain, swelling, and mouth opening after surgical removal of impacted third molars: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.C.; Ong, M.; Han, J.; Mattheos, N.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Tsai, A.Y.; Sanz, I.; Wong, M.C.; Lang, N.P.; ITI A.S. Group. Effect of systemic antibiotics on clinical and patient-reported outcomes of implant therapy—A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2014, 25, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Polizzi, A.; Muraglie, S.; Leonardi, R.; Lo Giudice, A. Assessment of Vitamin C and Antioxidant Profiles in Saliva and Serum in Patients with Periodontitis and Ischemic Heart Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Aguirre, J.J.; Gorosabel, A.; Barrio, P.; Errazquin, J.M.; Román, P.; Pla, R.; Carrete, J.; de Petro, J.; Orive, G. A multicentre placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial of antibiotic prophylaxis for placement of single dental implants. Eur. J. Oral. Implantol. 2009, 2, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, R.; Kemmoona, M.; Polyzois, I.; Claffey, N. The influence of prophylactic antibiotic administration on post-operative morbidity in dental implant surgery. A prospective double blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2014, 25, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, G.; Matarese, G.; Ramaglia, L.; Pedullà, E.; Rapisarda, E.; Iorio-Siciliano, V. Association between periodontitis and glycosylated haemoglobin before diabetes onset: a cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ta’a, M.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W.; van Steenbergh, D. Asepsis during periodontal surgery involving oral implants and the usefulness of peri-operative antibiotics: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, G.; Anastasi, G.P.; Matarese, G.; Williams, R.C.; Cutroneo, G.; Bracco, P.; Piancino, M.G. Functional and molecular outcomes of the human masticatory muscles. Oral. Dis. 2018, 24, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslemi, N.; Shahnaz, A.; Bahador, A.; Torabi, S.; Jabbari, S.; Oskouei, Z.A. Effect of Postoperative Amoxicillin on Early Bacterial Colonization of Peri-Implant Sulcus: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Dent. (Tehran) 2016, 13, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection. World Health Organization, 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/ssi-guidelines/en/ (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Staderini, E.; Patini, R.; Guglielmi, F.; Camodeca, A.; Gallenzi, P. How to manage impacted third molars: Germectomy or delayed removal? A systematic literature review. Medicina (Lith.) 2019, 55, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Varoni, E.M.; Cochis, A.; Cordaro, M.; Gallenzi, P.; Patini, R.; Staderini, E.; Lajolo, C.; Rimondini, L.; Rocchetti, V. Oral dysbiosis in pancreatic cancer and liver cirrhosis: A review of the literature. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coviello, V.; Zareh Dehkhargani, S.; Patini, R.; Cicconetti, A. Surgical ciliated cyst 12 years after Le Fort I maxillary advancement osteotomy: A case report and review of the literature. Oral Surgery 2017, 10, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzla, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Title | Author (Year) | Type of Study | Sample Size | Mean Age (SD, Range) | Antibiotic Molecule and Regimen | Bacterial Resistance Tested |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced susceptibility to amoxicillin of oral streptococci following amoxicillin exposure | Chardin et al. (2009) | Randomized clinical trial | 42 in test group; 39 in control group (no information about sex is given). | NR (NR, 19–45) for both groups. | Amoxicillin 1 g twice a day for 3 days and then placebo for test group. Amoxicillin 1 g twice a day for 7 days for control group. | Streptococci |
| Antibiotic resistance of subgingival species during and after antibiotic therapy | Feres et al. (2002) | Randomized clinical trial | 10 (1 M and 9 F) in test group; 10 (6 M and 4 F) in control group | 46 (15, NR) in test group; 42 (10, NR) in control group. | Amoxicillin 500 mg three times a day for 14 days for test group; metronidazole 250 mg three times a day for 14 days for test group. | Thirty-eight different species |
| Effects of omeprazole and amoxycillin on the human oral and gastrointestinal microflora in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection | Stark et al. (1996) | Randomized clinical trial | 14 (8 M and 6 F) in test group; 14 (7 M and 7 F) in control group. | 55.1 (NR, 22–78) in test group; 58.6 (NR, 26–81) in control group. | Amoxicillin 1 g and omeprazole 20 mg twice a day for 14 days for test group; omeprazole 20 mg twice a day for 14 days for control group | Enterobacteriaceae and Escherichia coli |
| Title | Author (Year) | Random Sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Blinding of Participants and Personnel | Blinding of Outcome Assessor | Incomplete Outcome Data | Selective Reporting | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced susceptibility to amoxicillin of oral streptococci following amoxicillin exposure | Chardin et al. (2009) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Medium |
| Antibiotic resistance of subgingival species during and after antibiotic therapy | Feres et al. (2002) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | High |
| Effects of omeprazole and amoxycillin on the human oral and gastrointestinal microflora in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection | Stark et al. (1996) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | High |
| Study | Rationale for Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Mathur et al. | No quantitative characterization of bacterial resistance |
| Kusachi et al. | No quantitative characterization of bacterial resistance |
| Avery et al. | No quantitative characterization of bacterial resistance |
| Her Young Su et al. | No quantitative characterization of bacterial resistance |
| Khariwala et al. | No quantitative characterization of bacterial resistance |
| Agarwal et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
| Johnson et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
| Liu et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
| Luaces-Rey et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
| McGowan et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
| Rizk et al. | No comparison of different antibiotic regimens |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patini, R.; Mangino, G.; Martellacci, L.; Quaranta, G.; Masucci, L.; Gallenzi, P. The Effect of Different Antibiotic Regimens on Bacterial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010022
Patini R, Mangino G, Martellacci L, Quaranta G, Masucci L, Gallenzi P. The Effect of Different Antibiotic Regimens on Bacterial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010022
Chicago/Turabian StylePatini, Romeo, Gilda Mangino, Leonardo Martellacci, Gianluca Quaranta, Luca Masucci, and Patrizia Gallenzi. 2020. "The Effect of Different Antibiotic Regimens on Bacterial Resistance: A Systematic Review" Antibiotics 9, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010022
APA StylePatini, R., Mangino, G., Martellacci, L., Quaranta, G., Masucci, L., & Gallenzi, P. (2020). The Effect of Different Antibiotic Regimens on Bacterial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics, 9(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010022








