Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2. Metal and Biocide Resistance Testing
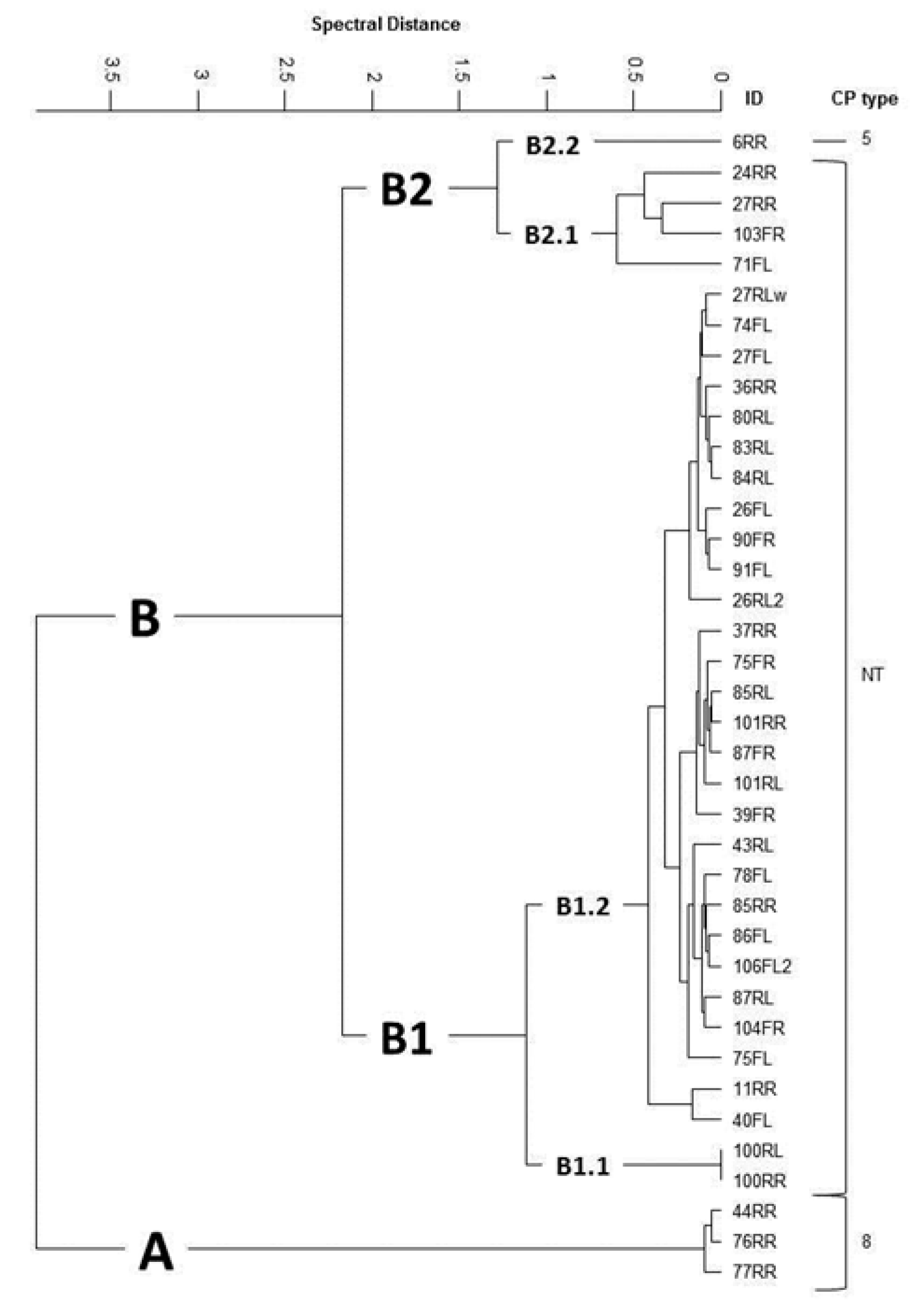
2.3. Additional Characterization of S. aureus Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococci
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Detection of Resistance Genes and SCCmec-Associated Direct Repeat Unit (dru) Typing
4.3. Additional Characterization of S. aureus Isolates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogni, C.; Odierno, L.; Raspanti, C.; Giraudo, J.; Larriestra, A.; Reinoso, E.; Lasagno, M.; Ferrari, M.; Ducrós, E.; Frigerio, C.; et al. War against mastitis: Current concepts on controlling bovine mastitis pathogens. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicafing Current Research and Technological Advances; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011; pp. 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Mazimpaka, E.; Mbuza, F.; Michael, T.; Gatari, E.N.; Bukenya, E.M.; James, O.A. Current status of cattle production system in Nyagatare District-Rwanda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laenderdaten Info. Available online: https://www.laenderdaten.info/Afrika/Ruanda/bevoelkerungswachstum.php (accessed on 11 October 2019).
- Sargeant, J.M.; Leslie, K.E.; Shirley, J.E.; Pulkrabek, B.J.; Lim, G.H. Sensitivity and specificity of somatic cell count and California Mastitis Test for identifying intramammary infection in early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 84, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpatswenumugabo, J.P.; Bebora, L.C.; Gitao, G.C.; Mobegi, V.A.; Iraguha, B.; Kamana, O.; Shumbusho, B. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis and distribution of pathogens in dairy farms of Rubavu and Nyabihu Districts, Rwanda. J. Vet. Med. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervinkova, D.; Vlkova, H.; Borodacova, I.; Makovcova, J.; Babak, V.; Lorencova, A.; Vrtkova, I.; Marosevic, D.; Jaglic, Z. Prevalence of mastitis pathogens in milk from clinically healthy cows. Vet. Med. 2013, 58, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iraguha, B.; Hamudikuwanda, H.; Mushonga, B. Bovine mastitis prevalence and associated risk factors in dairy cows in Nyagatare District, Rwanda. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2015, 86, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaarst, M.; Enevoldsen, C. Patterns of clinical mastitis manifestations in Danish organic dairy herds. J. Dairy Res. 1997, 64, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manishimwe, R.; Nishimwe, K.; Ojok, L. Assessment of antibiotic use in farm animals in Rwanda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Feßler, A.T.; Loncaric, I.; Wu, C.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Antimicrobial resistance among staphylococci of animal origin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntirenganya, C.; Manzi, O.; Muvunyi, C.M.; Ogbuagu, O. High prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among common bacterial isolates in a tertiary healthcare facility in Rwanda. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraguha, B.; Hamudikuwanda, H.; Mushonga, B.; Kandiwa, E.; Mpatswenumugabo, J.P. Comparison of cow-side diagnostic tests for subclinical mastitis of dairy cows in Musanze district, Rwanda. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2017, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndahetuye, J.B.; Persson, Y.; Nyman, A.K.; Tukei, M.; Ongol, M.P.; Båge, R. Aetiology and prevalence of subclinical mastitis in dairy herds in peri-urban areas of Kigali in Rwanda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauschild, T.; Vuković, D.; Dakić, I.; Ježek, P.; Djukić, S.; Dimitrijević, V.; Stepanović, S.; Schwarz, S. Aminoglycoside resistance in members of the Staphylococcus sciuri group. Microb. Drug Resist. 2007, 13, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahmsén, M.; Persson, Y.; Kanyima, B.M.; Båge, R. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis in dairy farms in urban and peri-urban areas of Kampala, Uganda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suleiman, T.S.; Karimuribo, E.D.; Mdegela, R.H. Prevalence of bovine subclinical mastitis and antibiotic susceptibility patterns of major mastitis pathogens isolated in Unguja island of Zanzibar, Tanzania. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Coagulase-negative staphylococci-emerging mastitis pathogens. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gitau, G.K.; Bundi, R.M.; Vanleeuwen, J.; Mulei, C.M. Mastitogenic bacteria isolated from dairy cows in Kenya and their antimicrobial sensitivity. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2014, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Piepers, S.; Leroy, F.; Van Coillie, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Identification, typing, ecology and epidemiology of coagulase negative staphylococci associated with ruminants. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorberg, B.-M.; Danielsson-Tham, M.-L.; Emanuelson, U.; Persson Waller, K. Bovine subclinical mastitis caused by different types of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4962–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasozi, K.I.; Tingiira, J.B.; Vudriko, P. High prevalence of subclinical mastitis and multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus are a threat to dairy cattle production in Kiboga District (Uganda). Open J. Vet. Med. 2014, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Issa Ibrahim, A.; Duprez, J.N.; Bada-Alambedji, R.; Moula, N.; Mainil, J.; Bardiau, M. Antibiotic resistance trend of Staphylococcus aureus isolated between 2010 and 2012 from mastitis cases in Azawak Zebu in Niger. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 3271–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Feßler, A.; Scott, C.; Kadlec, K.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Schwarz, S. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 from cases of bovine mastitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitkälä, A.; Haveri, M.; Pyörälä, S.; Myllys, V.; Honkanen-Buzalski, T. Bovine mastitis in Finland 2001—prevalence, distribution of bacteria, and antimicrobial resistance. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 87, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Martins, K.B.; Silva, V.R.D.; Mondelli, A.L.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.D. Correlation of phenotypic tests with the presence of the blaZ gene for detection of beta-lactamase. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klibi, A.; Maaroufi, A.; Torres, C.; Jouini, A. Detection and characterization of methicillin-resistant and susceptible coagulase-negative staphylococci in milk from cows with clinical mastitis in Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, M.S.; Heir, E.; Leegaard, T.; Wiger, K.; Holck, A. Frequency of disinfectant resistance genes and genetic linkage with β-lactamase transposon Tn552 among clinical staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2797–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjorland, J.; Steinum, T.; Kvitle, B.; Waage, S.; Sunde, M.; Heir, E. Widespread distribution of disinfectant resistance genes among staphylococci of bovine and caprine origin in Norway. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4363–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conceição, T.; Coelho, C.; De Lencastre, H.; Aires-De-Sousa, M. High prevalence of biocide resistance determinants in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from three African countries. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argudín, M.A.; Lauzat, B.; Kraushaar, B.; Alba, P.; Agerso, Y.; Cavaco, L.; Butaye, P.; Porrero, M.C.; Battisti, A.; Tenhagen, B.A.; et al. Heavy metal and disinfectant resistance genes among livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 191, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.A.; Butaye, P. Dissemination of metal resistance genes among animal methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 105, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidry, A.; Fattom, A.; Patel, A.; O’Brien, C. Prevalence of capsular serotypes among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cows with mastitis in the United States. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordelli, D.O.; Buzzola, F.R.; Gomez, M.I.; Steele-Moore, L.; Berg, D.; Gentilini, E.; Catalano, M.; Reitz, A.J.; Tollersrud, T.; Denamiel, G.; et al. Capsule expression by bovine isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from Argentina: Genetic and epidemiologic analyses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kümmel, J.; Stessl, B.; Gonano, M.; Walcher, G.; Bereuter, O.; Fricker, M.; Grunert, T.; Wagner, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Staphylococcus aureus entrance into the dairy chain: Tracking S. aureus from dairy cow to cheese. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grunert, T.; Stessl, B.; Wolf, F.; Sordelli, D.O.; Buzzola, F.R.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Distinct phenotypic traits of Staphylococcus aureus are associated with persistent, contagious bovine intramammary infections. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Lffler, B.; Buzzola, F.R.; Sordelli, D.O. Staphylococcus aureus adaptation to the host and persistence: Role of loss of capsular polysaccharide expression. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, R.; Cosandey, A.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Subtyping, evolution, and zoonotic transfer. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, E.; Katsuda, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Uchida, I.; Tanaka, K.; Eguchi, M. Genetic variation among Staphylococcus aureus strains from bovine milk and their relevance to methicillin-resistant isolates from humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, T.; Kock, M.M.; Ehlers, M.M. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis and close human contacts in South African dairy herds: Genetic diversity and inter-species host transmission. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkou, M.; Bouchiat, C.; Antri, K.; Bes, M.; Tristan, A.; Dauwalder, O.; Martins-Simoes, P.; Rasigade, J.P.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. New host shift from human to cows within Staphylococcus aureus involved in bovine mastitis and nasal carriage of animal’s caretakers. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiimwe, B.B.; Baldan, R.; Trovato, A.; Cirillo, D.M. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin resistant strains, isolated from bulk can milk and raw milk products in pastoral communities of South-West Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, M. Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus causing bovine mastitis between 2014 and 2015. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, S.; De Boeck, H.; Deplano, A.; Phoba, M.F.; Lunguya, O.; Falay, D.; Dauly, N.; Verhaegen, J.; Denis, O.; Jacobs, J. Characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bloodstream infections, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumburg, F.; Ngoa, U.A.; Kösters, K.; Köck, R.; Adegnika, A.A.; Kremsner, P.G.; Lell, B.; Peters, G.; Mellmann, A.; Becker, K. Virulence factors and genotypes of Staphylococcus aureus from infection and carriage in Gabon. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egyir, B.; Guardabassi, L.; Nielsen, S.S.; Larsen, J.; Addo, K.K.; Newman, M.J.; Larsen, A.R. Prevalence of nasal carriage and diversity of Staphylococcus aureus among inpatients and hospital staff at Korle Bu Teaching Hospital, Ghana. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2013, 1, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuse, G.; Zyl, K.N.; Hoek, K.; Abdulgader, S.; Kariuki, S.; Whitelaw, A.; Revathi, G. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various healthcare institutions in Nairobi, Kenya: A cross sectional study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shittu, A.O.; Oyedara, O.; Okon, K.; Raji, A.; Peters, G.; von Müller, L.; Schaumburg, F.; Herrmann, M.; Ruffing, U. An assessment on DNA microarray and sequence-based methods for the characterization of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from Nigeria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seni, J.; Bwanga, F.; Najjuka, C.F.; Makobore, P.; Okee, M.; Mshana, S.E.; Kidenya, B.R.; Joloba, M.L.; Kateete, D.P. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with surgical site infections at Mulago Hospital in Kampala, Uganda. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaumburg, F.; Alabi, A.S.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mekonnen, S.A.; Lam, T.J.G.M.; Hoekstra, J.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; Tessema, T.S.; Broens, E.M.; Riesebos, A.E.; Spaninks, M.P.; Koop, G. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk samples of dairy cows in small holder farms of North-Western Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, J.; Kamio, Y. Bacterial two-component and hetero-heptameric pore-forming cytolytic toxins: Structures, pore-forming mechanism, and organization of the genes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 981–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrieling, M.; Boerhout, E.M.; van Wigcheren, G.F.; Koymans, K.J.; Mols-Vorstermans, T.G.; de Haas, C.J.C.; Aerts, P.C.; Daemen, I.J.J.M.; van Kessel, K.P.M.; Koets, A.P.; et al. LukMF′ is the major secreted leukocidin of bovine Staphylococcus aureus and is produced in vivo during bovine mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotter, K.; Ehricht, R.; Hotzel, H.; Monecke, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Donat, K. Leukocidin genes lukF-P83 and lukM are associated with Staphylococcus aureus clonal complexes 151, 479 and 133 isolated from bovine udder infections in Thuringia, Germany. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jans, C.; Merz, A.; Johler, S.; Younan, M.; Tanner, S.A.; Kaindi, D.W.M.; Wangoh, J.; Bonfoh, B.; Meile, L.; Tasara, T. East and West African milk products are reservoirs for human and livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snel, G.G.M.; Malvisi, M.; Pilla, R.; Piccinini, R. Evaluation of biofilm formation using milk in a flow cell model and microarray characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains from bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellmann, A.; Becker, K.; Von Eiff, C.; Keckevoet, U.; Schumann, P.; Harmsen, D. Sequencing and staphylococci identification. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Künzel, F.; Licka, T.; Simhofer, H.; Spergser, J.; Rosengarten, R. Identification and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Austrian companion animals and horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Kock, M.M.; Ehlers, M.M. Diversity and antimicrobial susceptibility profiling of staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis cases and close human contacts. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6256–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, F.; Picard, F.J.; Lansac, N.; Ménard, C.; Roy, P.H.; Ouellette, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Correlation between the resistance genotype determined by multiplex PCR assays and the antibiotic susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, W.O.; Werckenthin, C.; Schwarz, S.; Roberts, M.C. Host range of the ermF rRNA methylase gene in bacteria of human and animal origin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 43, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Jia, X. Dissemination of macrolides, fusidic acid and mupirocin resistance among Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwendener, S.; Perreten, V. New MLS B resistance gene erm(43) in Staphylococcus lentus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4746–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wipf, J.R.K.; Schwendener, S.; Perreten, V. The novel macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance gene erm(44) is associated with a prophage in Staphylococcus xylosus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6133–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wendlandt, S.; Kadlec, K.; Feßler, A.T.; Schwarz, S. Identification of ABC transporter genes conferring combined pleuromutilin-lincosamide-streptogramin A resistance in bovine methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wendlandt, S.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Z.; Wei, J.; Shao, D.; Schwarz, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Detection and new genetic environment of the pleuromutilin-lincosamide-streptogramin a resistance gene lsa(e) in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus of swine origin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lina, G.; Quaglia, A.; Reverdy, M.E.; Leclercq, R.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Distribution of genes encoding resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins among staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Wendlandt, S.; Schwarz, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Ma, Z.; Shen, J. Identification of a novel vga(E) gene variant that confers resistance to pleuromutilins, lincosamides and streptogramin A antibiotics in staphylococci of porcine origin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Ojo, K.K.; Schwarz, S. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the multiresistance plasmid pSCFS1 from Staphylococcus sciuri. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Schwarz, S. Distribution of florfenicol resistance genes fexA and cfr among chloramphenicol-resistant Staphylococcus isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnellmann, C.; Gerber, V.; Rossano, A.; Jaquier, V.; Panchaud, Y.; Doherr, M.G.; Thomann, A.; Straub, R.; Perreten, V. Presence of new mecA and mph(C) variants conferring antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from the skin of horses before and after clinic admission. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4444–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argudín, M.A.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Fetsch, A.; Sachsenröder, J.; Käsbohrer, A.; Schroeter, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S.; Helmuth, R.; Bräunig, J.; et al. Virulence and resistance determinants of German Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates from nonhuman sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3052–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, S.; Roberts, M.C.; Werckenthin, C.; Pang, Y.; Lange, C. Tetracycline resistance in Staphylococcus spp. from domestic animals. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 63, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, R.V.; Morrison, D.; Al-doori, Z.; Edwards, G.F.S.; Gemmell, C.G. Usefulness of mec-associated direct repeat unit (dru) typing in the epidemiological analysis of highly clonal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Scotland. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grunert, T.; Wenning, M.; Barbagelata, M.S.; Fricker, M.; Sordelli, D.O.; Buzzola, F.R.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus capsular serotypes by means of artificial neural network-assisted Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johler, S.; Stephan, R.; Althaus, D.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Grunert, T. High-resolution subtyping of Staphylococcus aureus strains by means of Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monecke, S.; Jatzwauk, L.; Weber, S.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. DNA microarray-based genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from Eastern Saxony. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leopold, S.R.; Goering, R.V.; Witten, A.; Harmsen, D.; Mellmann, A. Bacterial whole-genome sequencing revisited: Portable, scalable, and standardized analysis for typing and detection of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lepuschitz, S.; Mach, R.; Springer, B.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W. Draft genome sequence of a community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 isolate from a river sample. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01166-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lepuschitz, S.; Huhulescu, S.; Hyden, P.; Springer, B.; Rattei, T.; Allerberger, F.; Mach, R.L.; Ruppitsch, W. Characterization of a community-acquired-MRSA USA300 isolate from a river sample in Austria and whole genome sequence based comparison to a diverse collection of USA300 isolates. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Helden, P.D.; Van Helden, L.S.; Hoal, E.G. One world, one health: Humans, animals and the environment are inextricably linked—A fact that needs to be remembered and exploited in our modern approach to health. EMBO Rep. 2013, 6, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolates | Species | Origin 1 | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile | Biocide and Metal Resistance Genes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype 2 | MIC 3 of streptomycin | Genes Detected | ||||
| 2FR | S. chromogenes | M 1 | 32 4 | str | ||
| 3RL | S. haemolyticus | M 1 | ERY, CLI | 32 | erm(C), str | |
| 4FR | S. epidermidis | M 1 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | copB, qacAB, smr |
| 4RR1 | S. hominis | M 1 | BLA, FOX, ERY, TET, CIP | ‹4 | blaZ, mecA, msr(A), tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 4RR2 | S. capitis | M 1 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 7FL | S. chromogenes | M 2 | ERY, CLI | ‹4 | erm(C), str | |
| 7RR | S. epidermidis | M 2 | PEN, ERY, CLI, TET | 32 | blaZ, erm(C), tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, arsA, smr |
| 8RL | S. haemolyticus | M 2 | ERY, CLI | 32 | erm(C), str | |
| 13FLg | S. xylosus | M 3 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD, copB |
| 13FLw | S. xylosus | M 3 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, arsA, smr |
| 13FLw wh | S. xylosus | M 3 | ERY | ‹4 | msr(A), str | |
| 13RR | S. xylosus | M 3 | ERY, CLI, CHL | ‹4 | msr(A), fexA, str | |
| 14FL1 | S. equorum | M 3 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 17RR | S. equorum | M 4 | ‹4 | str | smr | |
| 18RLw1 | S. epidermidis | M 4 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 18RLw2 | S. haemolyticus | M 4 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 18RLg | S. haemolyticus | M 4 | ‹4 | str | cadD, copB, arsA, smr | |
| 18FL | S. auricularis | M 4 | 16 | str | copB | |
| 24RLw | S. xylosus | M 5 | ‹4 | str | cadD, smr | |
| 24RLg | S. haemolyticus | M 5 | 32 | str | ||
| 25FLw | S. hominis | M 5 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 25FLg | S. xylosus | M 5 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 25FL3 | S. xylosus | M 5 | ‹4 | str | cadD | |
| 25RR | S. epidermidis | M 5 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | |
| 25RRg | S. sciuri | M 5 | CLI | ‹4 | sal(A), str | |
| 26RL1 | S. xylosus | M 6 | ‹4 | str | cadD | |
| 26RRw | S. xylosus | M 6 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 26RRg | S. xylosus | M 6 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 27RLg | S. xylosus | M 6 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 28FRg | S. xylosus | M 7 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 30FL | S. devriesei | M 8 | TET | 16 | tet(K), str | arsA |
| 30RL | S. devriesei | M 8 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | arsA |
| 30FR | S. chromogenes | M 8 | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | |
| 32FR | S. chromogenes | M 8 | 32 | str | ||
| 33RL | S. chromogenes | M 8 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | |
| 33FR | S. haemolyticus | M 8 | 32 | str | ||
| 34RLw | S. haemolyticus | M 9 | 32 | str | cadD | |
| 35FR | S. haemolyticus | M 9 | 16 | str | arsA | |
| 35RRg | S. haemolyticus | M 9 | 16 | str | arsA | |
| 36FL | S. haemolyticus | M 9 | TET | 32 | tet(K), tet(L), str | |
| 38FL | S. auricularis | M 9 | ‹4 | str | cadD | |
| 42FR | S. haemolyticus | M 11 | TET | 32 | tet(K), tet(L), str | |
| 43FRw | S. xylosus | M 11 | TET | ‹4 | tet(K), str | copB |
| 44FL | S. xylosus | M 11 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 46FR | S. epidermidis | M 11 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | cadD |
| 47RRg | S. chromogenes | M 12 | 32 | str | qacAB, smr | |
| 50RL | S. sciuri | M 12 | CLI | ‹4 | erm(44), str | |
| 50RR | S. sciuri | M 12 | CLI | ‹4 | erm(44), sal(A) str | |
| 51RR | S. xylosus | M 12 | TET | ‹4 | tet(K), str | |
| 52FL | S. haemolyticus | K | PEN, CLI, TET | 32 | blaZ, erm(C), tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, copB, qacAB, smr |
| 52FR | S. haemolyticus | K | ‹4 | str | cadD, copB, arsA | |
| 53FL | S. haemolyticus | K | PEN, CLI, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | copB |
| 53RL | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI, TET | 32 | vga(A), sal(A), Inu(A), tet(K), tet(L), str | qacAB, smr |
| 53RR | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI, TET | 32 | vga(A), sal(A), Inu(A), tet(K), tet(L), str | qacAB, smr |
| 54FR | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI | 32 | vga(A), str | |
| 54RRw | S. haemolyticus | K | PEN, CLI, SXT, TET | 32 | blaZ, dfrA, dfrD, tet(K), str | |
| 54RRg | S. xylosus | K | 32 | str | smr | |
| 55RR1 | S. epidermidis | K | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | copB, arsA, qacAB, smr |
| 55RR2 | S. capitis | K | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | copB, arsA, smr |
| 56RL | S. sciuri | K | CLI | ‹4 | vga(A), sal(A), str | |
| 57FLw | S. capitis | K | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | cadD, smr |
| 57FRw | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI, TET | 32 | tet(K), tet(L), str | copB, smr |
| 58FL | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI, TET | 32 | erm(C), sal(A), tet(K), tet(L), str | smr |
| 58FR | S. haemolyticus | K | CLI, TET | 32 | vga(A), tet(K), tet(L), str | |
| 58RR | S. xylosus | K | ‹4 | str | ||
| 61RR | S. xylosus | K | SXT, TET | ‹4 | dfrA, dfrD, dfrG, tet(K), tet(L), str | smr |
| 61RL | S. xylosus | K | TET | 32 | tet(K), str | copB, smr |
| 62FR | S. xylosus | K | ‹4 | str | copB | |
| 62RR | S. haemolyticus | K | ‹4 | str | cadD | |
| 63RL | S. sciuri | K | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 64RR | S. epidermidis | K | PEN, SXT, TET | 32 | blaZ, dfrA, dfrD, dfrG, tet(K), tet(L), tet(O), str | copB, arsA, smr |
| 65RL | S. haemolyticus | K | PEN, ERY, SXT, TET | 32 | blaZ, msr(A), dfrD, dfrG, tet(K), str | cadD, copB, arsA |
| 66RL | S. xylosus | K | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | qacAB |
| 66RR | S. epidermidis | K | PEN, TET, TEC | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | cadD, smr |
| 67RL | S. chromogenes | K | 32 | str | ||
| 68RL | S. chromogenes | K | 32 | str | ||
| 68RR | S. xylosus | K | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 70RLw | S. simulans | K | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | copB |
| 70FR | S. sciuri | K | FOX | ‹4 | mecA, str | |
| 1stCowFL | S. chromogenes | M 13 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 2ndCowRL | S. xylosus | M 13 | TET | ‹4 | tet(K), str | |
| 73RL | S. sciuri | M 14 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 73RR | S. xylosus | M 14 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 78FR | S. xylosus | M 17 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 78RL | S. sciuri | M 17 | CLI | ‹4 | vga(A), sal(A), str | |
| 81 RR | S. haemolyticus | M 18 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD |
| 82RL | S. sciuri | M 18 | CLI | ‹4 | erm(44), str | |
| 82RR | S. saprophyticus | M 18 | TET, CHL | 4 | tet(K), catpC221, str | |
| 84RR | S. saprophyticus | M 18 | TET | ‹4 | tet(K), str | copB |
| 85FR | S. xylosus | M 19 | TET | 8 | tet(K), str | |
| 85FL | S. saprophyticus | M 19 | TET | 8 | tet(K), str | copB, arsA, qacAB |
| 86FR | S. saprophyticus | M 19 | ‹4 | str | copB | |
| 87FL | S. saprophyticus | M 19 | TET | 4 | tet(K), str | copB |
| 89FR | S. sciuri | M 20 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 89RR | S. xylosus | M 20 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 94RR | S. succinus | M 21 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | copB |
| 94RL | S. sciuri | M 21 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | |
| 95FR | S. xylosus | M 21 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 95RR | S. xylosus | M 21 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 96FR | S. xylosus | M 21 | TET | ‹4 | tet(K), str | qacAB |
| 96RR | S. xylosus | M 21 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 97RL | S. sciuri | M 21 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 97RR | S. xylosus | M 21 | SXT | ‹4 | dfrD, dfrG, str | |
| 98RR | S. succinus | M 21 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD |
| 99FR | S. xylosus | M 22 | ‹4 | str | ||
| 99RL | S. xylosus | M 22 | ‹4 | str | copB | |
| 103RR | S. chromogenes | M 22 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | |
| 104RR | S. succinus | M 23 | ‹4 | str | smr | |
| 104RL | S. succinus | M 23 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | cadD, arsA, smr |
| 105RL | S. succinus | M 24 | ‹4 | str | cadD, smr | |
| 106FL1 | S. saprophyticus | M 24 | ‹4 | str | copB | |
| 107RL | S. saprophyticus | M 25 | PEN | 16 | blaZ, str | copB |
| 108FL | S. saprophyticus | M 25 | SXT | ‹4 | dfrD, dfrG, str | arsA |
| 110RL | S. xylosus | M 26 | ‹4 | str | copB, smr | |
| 110RR1 | S. saprophyticus | M 26 | ‹4 | str | copB, arsA | |
| 110RR2 | S. xylosus | M 26 | ‹4 | str | copB | |
| 111RL | S. sciuri | M 26 | PEN, CLI | ‹4 | sal(A), blaZ, str | |
| 113RL | S. sciuri | M 26 | 16 | str | ||
| Isolates | Origin 1 | CC 2 | ST 3 | spa | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile | Biocide and Metal Resistance Genes | Capsule Serotype 7 | cap gene (cap 8) | cap gene (cap 5) | Hemolysins | Leukocidin (luk) Components | Biofilm-Associated Genes | Adhesion Factors | Superantigens | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype 4 | MIC 5 of Streptomycin | Genes Detected | ||||||||||||||
| 1FR * | M 1 | ST97 | t1236 | PEN | 32 6 | blaZ, str | not tested | NEG 8 | POS 8 | hla, hlb, hld | NEG | icaC, icaD | clfA, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 6RR * | M 2 | CC152 | ST152 | t458 | ERY, CLI | 32 | erm(C), str | CP5 | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukS-PV/lukF-PV | icaA, icaD | clfA, clfB, cna, fnbA, fnbB | ||
| 11RR * | M 3 | ST97 | t1236 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | smr | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | NEG | icaC, icaD | clfA, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | ||
| 24RR * | M 5 | CC3666 | ST5477 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), tet(L), str | nt | POS | NEG | hla, hld | lukD | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | tsst-1, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu | |
| 26FR | M 6 | t1236 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 26FL | M 6 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN | 16 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 26RL2 | M 6 | nt7 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 27FL | M 6 | t1236 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | sec | |||
| 27RLw | M 6 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN | ‹4 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 27RR | M 6 | t1398 | TET | 4 | tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 36RR | M 9 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 37RR | M 9 | t9432 | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 39FR | M 10 | CC97 | t2112 | PEN | 8 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 40FL | M 10 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 43RL | M 11 | CC97 | t18835 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 44RR | M 11 | CC3591 | t458 | ‹4 | str | smr | CP8 | POS | NEG | hla, hlb, hld | lukM/lukF-PV (P83) | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, cna, fnbA | |||
| 63FL | K | CC152 | ST152 | t355 | ERY, CLI | 32 | erm(C), str | not tested | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukS-PV/lukF-PV | icaA, icaD | clfA, clfB, cna, fnbA, fnbB | ||
| 71FL | M 14 | CC3591 | ST5475 | t355 | TET | 32 | tet(K), str | nt | POS | NEG | hla, hlb, hld | NEG | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, cna, fnbA | sem, seo | |
| 74FL | M 14 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 75FR | M 15 | CC97 | t10103 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 75FL | M 15 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 76RR | M 16 | CC3591 | ST5476 | t458 | ‹4 | str | CP8 | POS | NEG | hla, hlb, hld | lukM/lukF-PV (P83) | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, cna, fnbA | |||
| 77RR | M 17 | CC3591 | t458 | 16 | str | CP8 | POS | NEG | hla, hlb, hld | lukM/lukF-PV (P83) | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, cna, fnbA | ||||
| 78FL | M 17 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 80RL | M 18 | t380 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | sec | |||
| 82FL | M 18 | t380 | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 83RL | M 18 | CC97 | t380 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 84RL | M 18 | t380 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 85RR | M 19 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 85RL | M 19 | t10103 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | qacAB | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | |||
| 86FL | M 19 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 87FR | M 19 | t10103 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 87RL | M 19 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 90FR | M 20 | t9432 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 90FL | M 20 | t9432 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 91FL | M 20 | CC97 | t9432 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 100RR | M 22 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | qacAB | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | ||
| 100RL | M 22 | CC97 | t1236 | PEN, TET | ‹4 | blaZ, tet(K), str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 101RR | M 22 | CC97 | t10103 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | NEG | POS | hla, hlb, hld | lukD, lukE | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | |||
| 101RL | M 22 | t10103 | PEN | 32 | blaZ, str | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | ||||
| 103FR | M 22 | CC3666 | t18853 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | smr | nt | POS | NEG | hla, hlb, hld | lukD | icaA, icaC, icaD | clfA, clfB, fib, fnbA, fnbB, sasG | tsst-1, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu | |
| 104FR | M 23 | t1236 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | smr | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | |||
| 106FL2 | M 24 | t18835 | PEN, TET | 32 | blaZ, tet(K), str | qacAB | nt | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | not tested | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antók, F.I.; Mayrhofer, R.; Marbach, H.; Masengesho, J.C.; Keinprecht, H.; Nyirimbuga, V.; Fischer, O.; Lepuschitz, S.; Ruppitsch, W.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; et al. Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010001
Antók FI, Mayrhofer R, Marbach H, Masengesho JC, Keinprecht H, Nyirimbuga V, Fischer O, Lepuschitz S, Ruppitsch W, Ehling-Schulz M, et al. Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntók, Fruzsina Irén, Rosa Mayrhofer, Helene Marbach, Jean Claude Masengesho, Helga Keinprecht, Vedaste Nyirimbuga, Otto Fischer, Sarah Lepuschitz, Werner Ruppitsch, Monika Ehling-Schulz, and et al. 2020. "Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda" Antibiotics 9, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010001
APA StyleAntók, F. I., Mayrhofer, R., Marbach, H., Masengesho, J. C., Keinprecht, H., Nyirimbuga, V., Fischer, O., Lepuschitz, S., Ruppitsch, W., Ehling-Schulz, M., Feßler, A. T., Schwarz, S., Monecke, S., Ehricht, R., Grunert, T., Spergser, J., & Loncaric, I. (2020). Characterization of Antibiotic and Biocide Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus Species Associated with Bovine Mastitis in Rwanda. Antibiotics, 9(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010001







