Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Antimicrobial Properties of Silver
3. The Biological Properties of Camphor
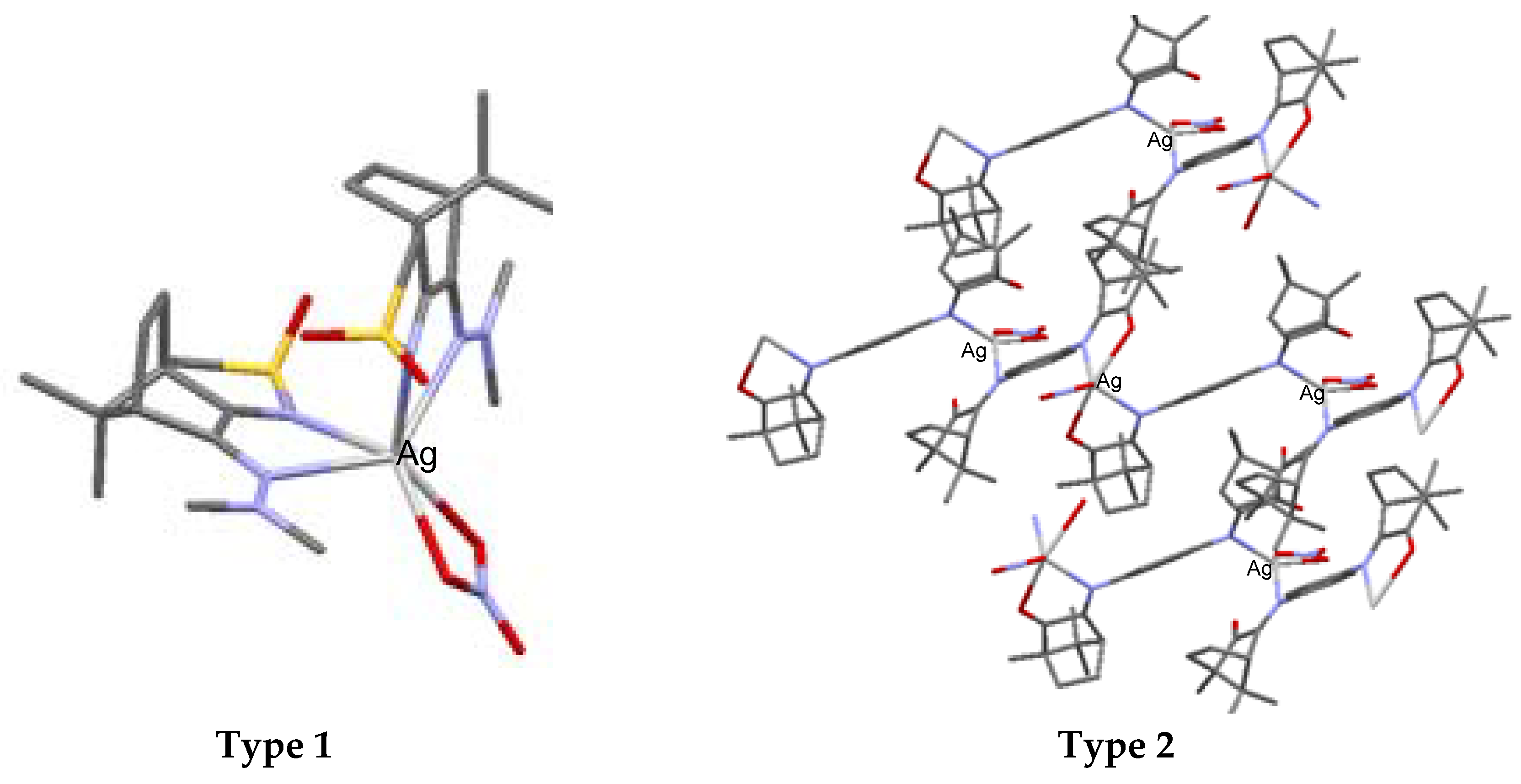
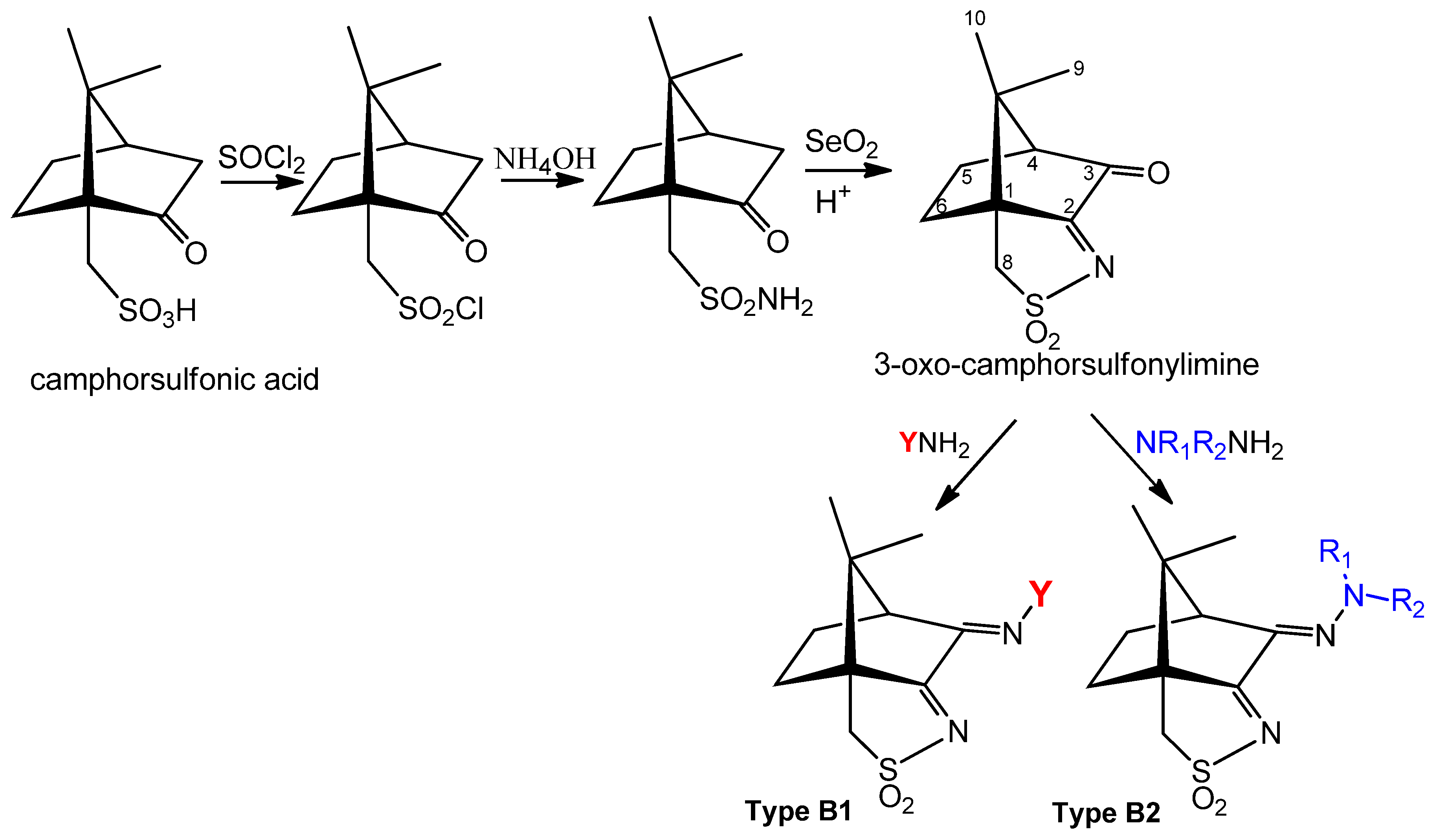
4. Silver Camphorimine Complexes
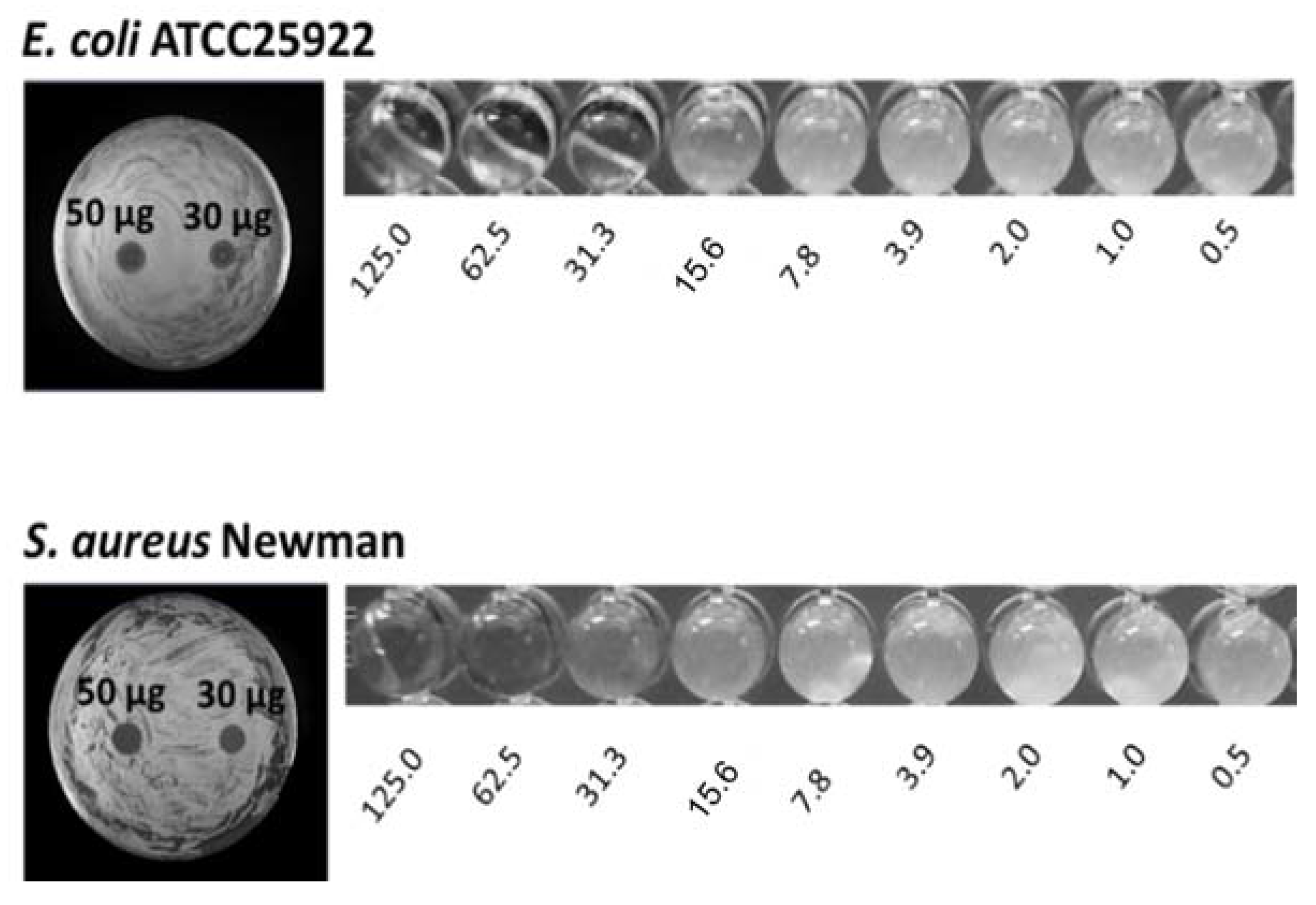
5. Antibacterial Activity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labischinski, H. New Antibiotics. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Powers, J.H.; Brass, E.P.; Miller, L.G.; Edwards, J.E. Trends in Antimicrobial Drug Development: Implications for the Future. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Microbial Threats to Health; Smolinski, M.S., Hamburg, M.A., Lederberg, J., Eds.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, B.L.; Conly, J.M. Bioterrorism in 2001: How ready are we? Can. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 12, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Clinical relevance of the ESKAPE pathogens. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuretzbacher, U. Future antibiotics scenarios: Is the tide starting to turn? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, D.J.; Gwynn, M.N.; Holmes, D.J.; Pompliano, D.L. Drugs for bad bugs: Confronting the challenges of antibacterial discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Azócar, M.I.; Gómez, G.; Levín, P.; Paez, M.; Muñoz, H.; Dinamarca, N. Review: Antibacterial behavior of carboxylate silver(I) complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 67, 3840–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasen, H.J. Historical review of the use of silver in the treatment of burns. I. Early uses. Burns 2000, 26, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, C.A.; Brentano, L.; Gravens, D.L.; Margraf, H.W.; Monafo, W.W. Treatment of large human burns with 0.5% silver nitrate solution. Arch. Surg. 1965, 90, 812–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, E.; Facchin, G.; Estévez, E.; Alborés, P.; Baran, E.J.; Ellena, J.; Torre, M.H. Copper complexes with heterocyclic sulfonamides: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, microbiological and SOD-like activities: Crystal structure of [Cu(sulfisoxazole)2(H2O)4]·2H2O. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetto, P.S.; Slenters, T.V.; Fromm, K.M. In vitro biocompatibility of new silver(I) coordination compound coated-surfaces for dental implant applications. Materials (Basel) 2011, 4, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, J.-Y.; Hartemann, P. Silver as an antimicrobial: Facts and gaps in knowledge. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 39, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormio Nunes, J.H.; de Paiva, R.E.F.; Cuin, A.; Lustri, W.R.; Corbi, P.P. Silver complexes with sulfathiazole and sulfamethoxazole: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, crystal structure and antibacterial assays. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.; Curran, R.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; McKee, V.; Devereux, M.; Kavanagh, K.; Kellett, A. Synthesis, structure and biological activity of silver(I) complexes of substituted imidazoles. Polyhedron 2013, 56, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: Review of the literature. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W. History of the medical use of silver. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2009, 10, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Tang, S.; Li, S.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Peng, L. Toxicological evaluation of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate in rats following 28 days of repeated oral exposure. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeykina, A.L.; Skulachev, V.P. Submicromolar Ag+ increases passive Na+ permeability and inhibits the respiration-supported formation of Na+ gradient in Bacillus FTU vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1990, 269, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, W.J.; Rosenberg, H. Effect of silver ions on transport and retention of phosphate by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 152, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Pal, R.; Cameotra, S.S. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with Escherichia coli and their cell envelope biomolecules. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Häse, C.C. Chemiosmotic mechanism of antimicrobial activity of Ag(+) in Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachicho, N.; Hoffmann, P.; Ahlert, K.; Heipieper, H.J. Effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on growth and adaptive response mechanisms of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 355, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-R.; Xie, X.-B.; Shi, Q.-S.; Zeng, H.-Y.; OU-Yang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; He, B.; Liu, L.; Qu, G.; Shi, J.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. Antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Proteomics approach. Metallomics 2018, 10, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Catechol-functional chitosan/silver nanoparticle composite as a highly effective antibacterial agent with species-specific mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Vermaak, I.; Viljoen, A. Camphor—A fumigant during the black death and a coveted fragrant wood in ancient Egypt and Babylon—A review. Molecules 2013, 18, 5434–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Blair, N.T.; Clapham, D.E. Camphor activates and strongly desensitizes the transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 channel in a vanilloid-independent mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8924–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, A.S.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Korchagina, D.V.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Tretiak, T.S.; Anfimov, P.M.; Kiselev, O.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Camphor-based symmetric diimines as inhibitors of influenza virus reproduction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justino, G.C.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Roseiro, A.P.S.; Knittel, A.S.O.; Gonçalves, J.; Justino, M.C.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Camphor-based CCR5 blocker lead compounds—A computational and experimental approach. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56249–56259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, A.S.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Shernyukov, A.V.; Gatilov, Y.V.; Razumova, Y.V.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Tretiak, T.S.; Pokrovsky, A.G.; Kiselev, O.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Discovery of a new class of antiviral compounds: Camphor imine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 105, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itani, W.S.; El-Banna, S.H.; Hassan, S.B.; Larsson, R.L.; Bazarbachi, A.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.U. Anti colon cancer components from Lebanese sage (Salvia libanotica) essential oil: Mechanistic basis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Winkel, A.; Eisenburger, M.; Menzel, H. Carboxylated camphorquinone as visible-light photoinitiator for biomedical application: Synthesis, characterization, and application. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, A.S.; Morozova, E.A.; Vasilev, V.G.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Curare-like camphor derivatives and their biological activity. Russ. J. Bioorgan. Chem. 2015, 41, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Busch-Petersen, J.; Wang, F.; Kiesow, T.J.; Graybill, T.L.; Jin, J.; Yang, Z.; Foley, J.J.; Hunsberger, G.E.; Schmidt, D.B.; et al. Camphor sulfonamide derivatives as novel, potent and selective CXCR3 antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, A.S.; Yarovaya, О.I.; Baev, D.S.; Shernyukov, O.V.; Shtro, A.A.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Aliphatic and alicyclic camphor imines as effective inhibitors of influenza virus H1N1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, V.K.-Y.; Chan, A.O.-Y.; Che, C.-M. Gold and silver catalysis: From organic transformation to bioconjugation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 6667–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Lourenço, A.; Alves, M.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Mira, N.P.; Leitão, J.H.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Ag(I) camphorimine complexes with antimicrobial activity towards clinically important bacteria and species of the Candida genus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Correia, I.; Galvão, A.M.; Marques, F.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Synthesis of Ag(I) camphor sulphonylimine complexes and assessment of their cytotoxic properties against cisplatin -resistant A2780cisR and A2780 cell lines. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 166, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Galvão, A.M.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Leitão, J.H.; Suarez, A.C.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Antibacterial activity of silver camphorimine coordination polymers. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7114–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline; NCCLS Document M26-A; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, S.A.; Feliciano, J.R.; Pita, T.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Leitão, J.H. Burkholderia cepacia complex regulation of virulence gene expression: A review. Genes 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, C.P.; Barreto, C.; Pereira, L.; Lito, L.; Cristino, J.M.; Sá-Correia, I. Incidence of Burkholderia contaminans at a cystic fibrosis centre with an unusually high representation of Burkholderia cepacia during 15 years of epidemiological surveillance. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.D.; Wardrop, D.J.; Sundermann, K.F. Camphorquinone and camphorquinone monoxime. Org. Synth. 2002, 79, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, M.O.; Zimmerli, A. CCXXV.—Studies in the camphane series. Part XXVIII. Stereoisomeric hydrazones and semicarbazones of camphorquinone. J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 1910, 97, 2156–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.N.; Costa, L.M.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Schier, A.; Scherer, W.; Harbi, S.K.; Verfuerth, U.; Herrmann, R. Synthesis, structure, and electrochemistry of palladium complexes with camphor-derived chiral ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 6270–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.A.; Mendes, F.; Roseiro, A.P.S.; Santos, I.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Insight into the cytotoxicity of polynuclear Cu(I) camphor complexes. Polyhedron 2015, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitchett, C.M.; Steel, P.J. Chiral heterocyclic ligands. XII. Metal complexes of a pyrazine ligand derived from camphor. Arkivoc 2005, 2006, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, S.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Leitão, J.H. Burkholderia cepacia complex: Emerging multihost pathogens equipped with a wide range of virulence factors and determinants. Int. J. Microbiol. 2011, 2011, 607575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, J.H.; Sousa, S.A.; Ferreira, A.S.; Ramos, C.G.; Silva, I.N.; Moreira, L.M. Pathogenicity, virulence factors, and strategies to fight against Burkholderia cepacia complex pathogens and related species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, J.H.; Sousa, S.A.; Cunha, M.V.; Salgado, M.J.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Barreto, M.C.; Sá-Correia, I. Variation of the antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Burkholderia cepacia complex clonal isolates obtained from chronically infected cystic fibrosis patients: A five-year survey in the major Portuguese treatment center. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

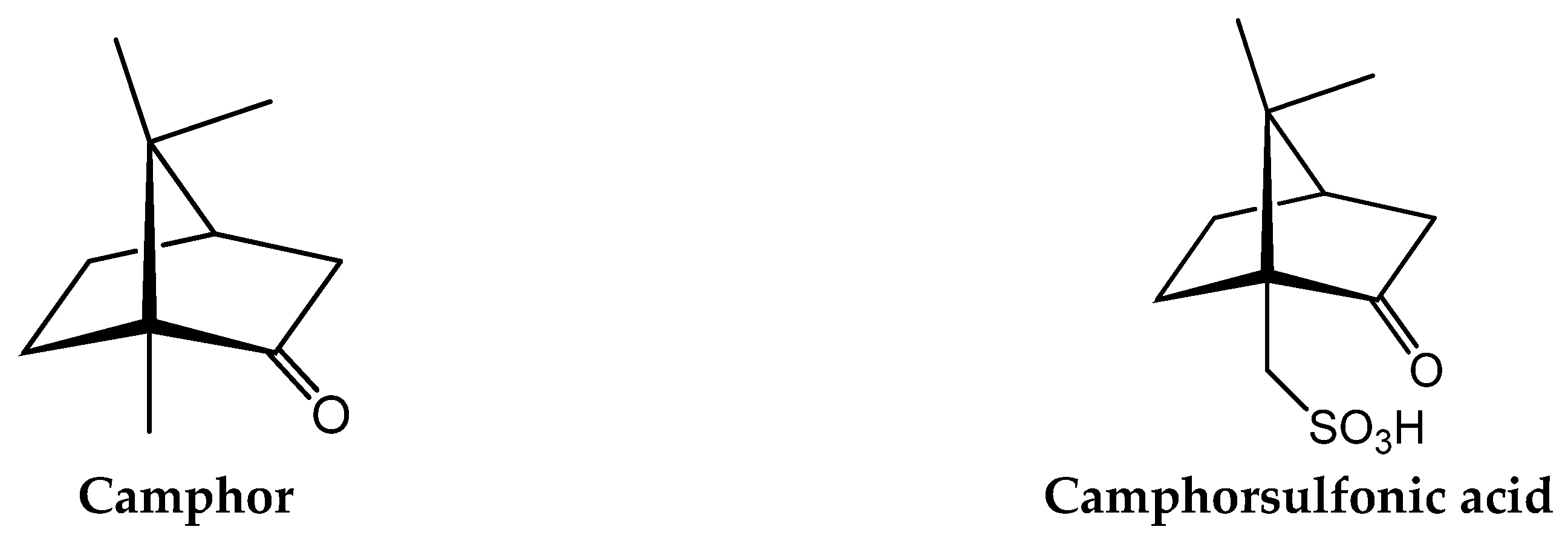

| Ligand (L) | Complex | S. aureus | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | B. contaminans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
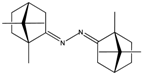 | 1 | 66 ± 5 | 50 ± 1 | 56 ± 4 | 79 ± 4 |
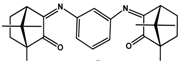 | 2 | 183 ± 3 | 65 ± 2 | 121 ± 2 | 144 ± 1 |
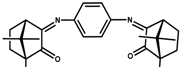 | 3 | 73 ± 2 | 20 ± 1 | 19 ± 4 | 36 ± 3 |
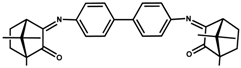 | 4 | ˃100 | ˃100 | 86 ± 7 | ˃100 |
| AgNO3 (Control) | - | 73 | 47 | 39 | 74 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leitão, J.H.; Sousa, S.A.; Leite, S.A.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030065
Leitão JH, Sousa SA, Leite SA, Carvalho MFNN. Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines. Antibiotics. 2018; 7(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeitão, Jorge H., Silvia A. Sousa, Silvestre A. Leite, and Maria Fernanda N. N. Carvalho. 2018. "Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines" Antibiotics 7, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030065
APA StyleLeitão, J. H., Sousa, S. A., Leite, S. A., & Carvalho, M. F. N. N. (2018). Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines. Antibiotics, 7(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030065








