The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Improved nanomaterials (the presence of nanoparticles in the polymeric matrix improves the mechanical and/or chemical properties of the packaging, but they are not in direct interaction with food);
- (2)
- Active nanomaterials (dispersed nanoparticles into polymeric bulk enable the packaging to interact actively with environment and regulate the preservation of food);
- (3)
2. Silver Nanoparticles
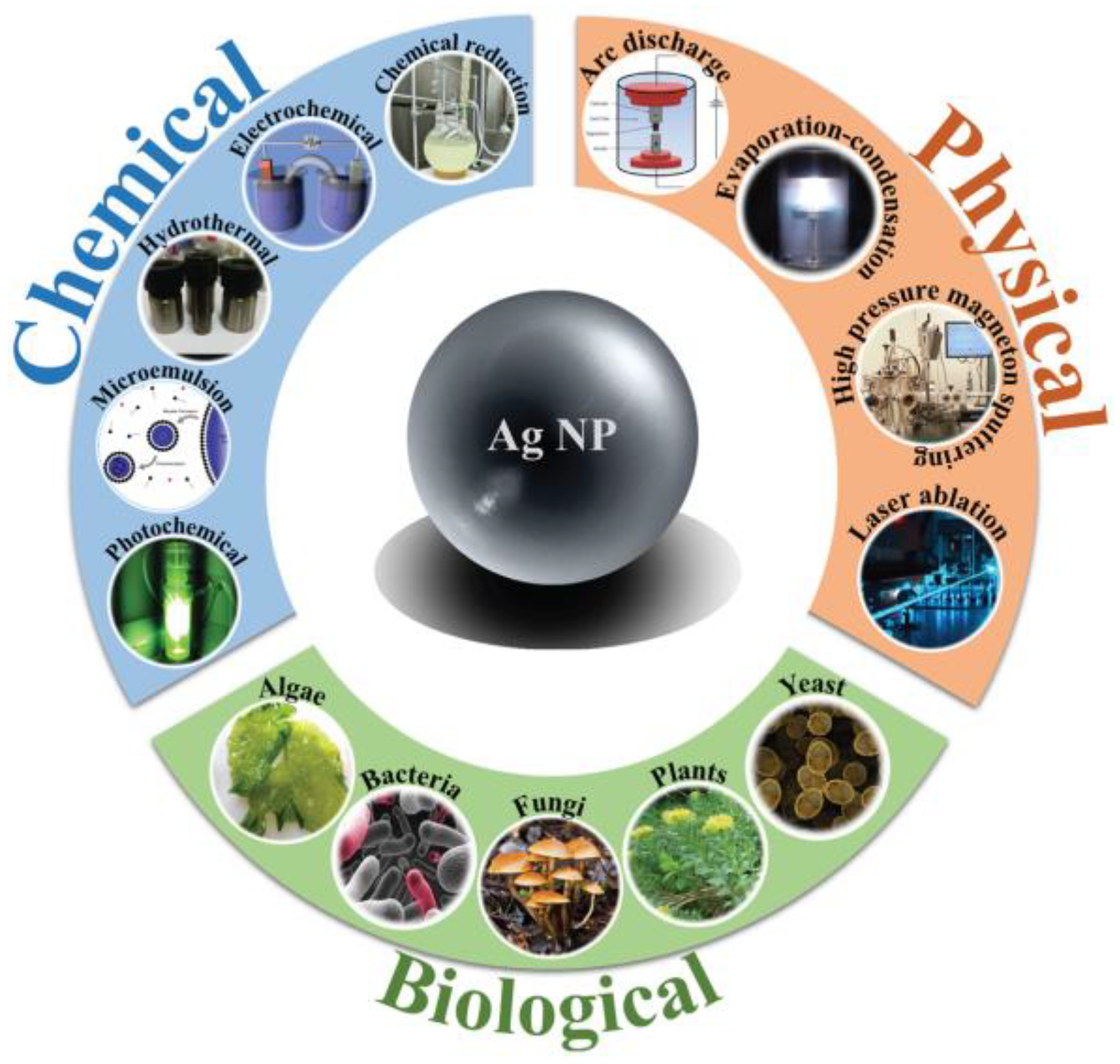
2.1. Synthesis Methods
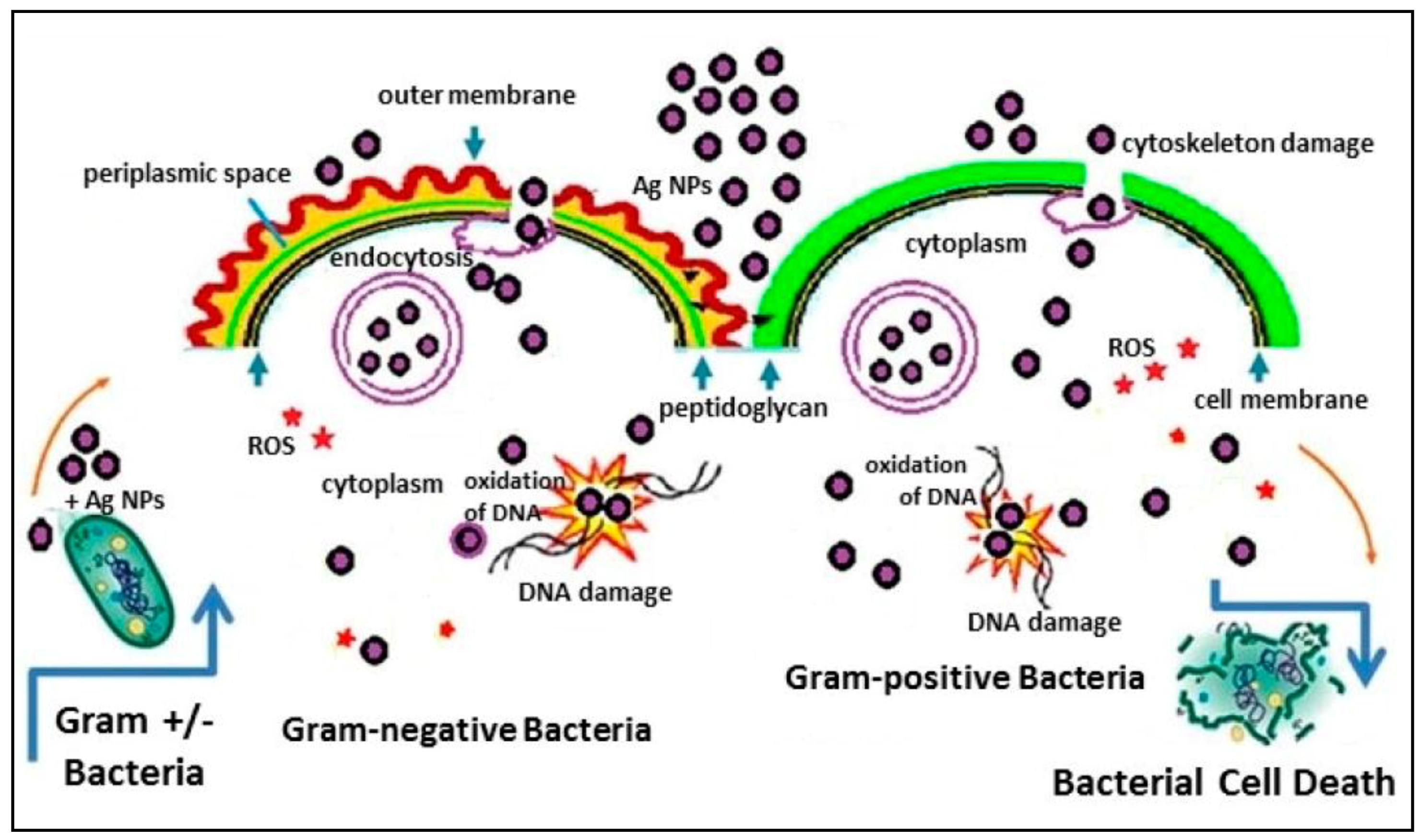
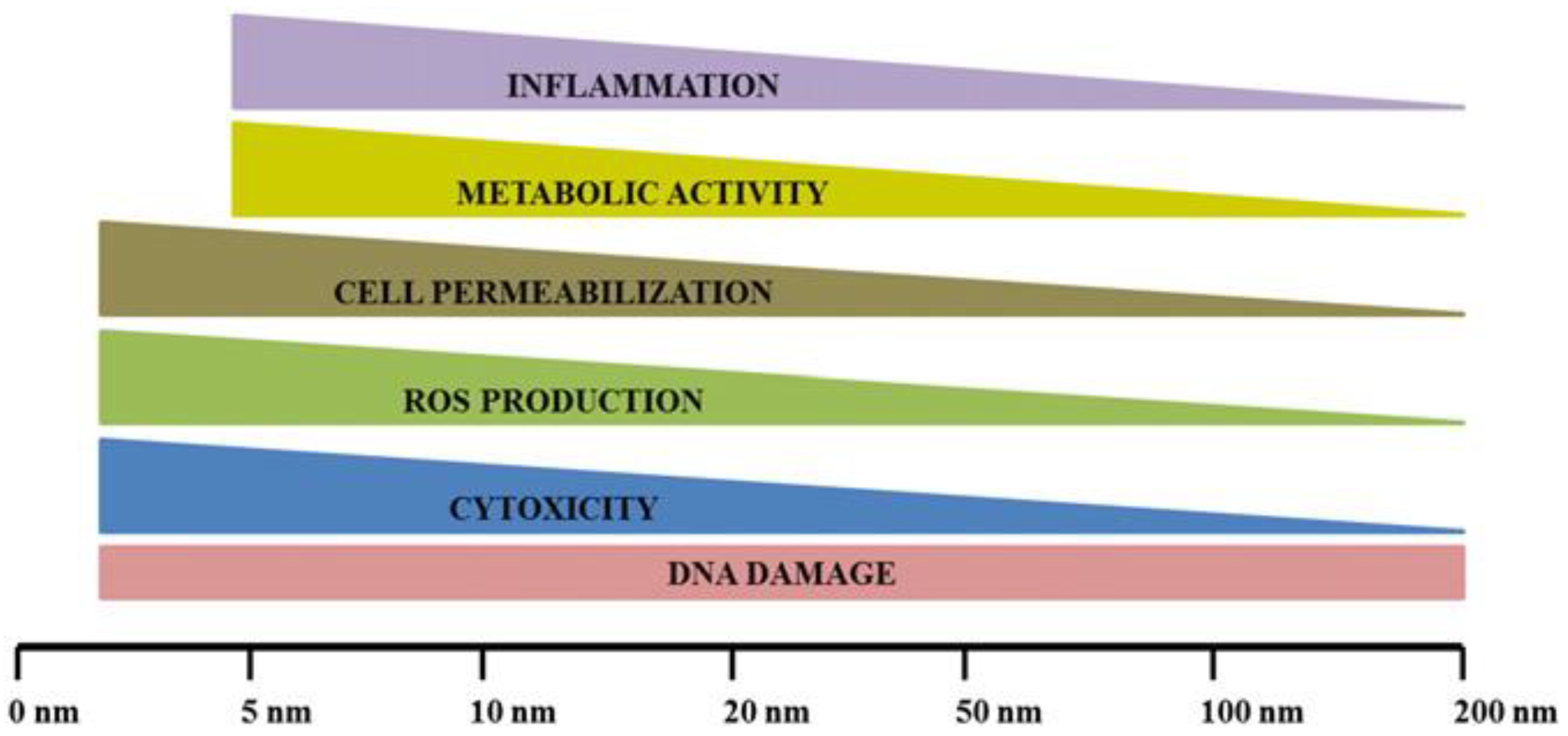
2.2. Bioactivity of AgNPs
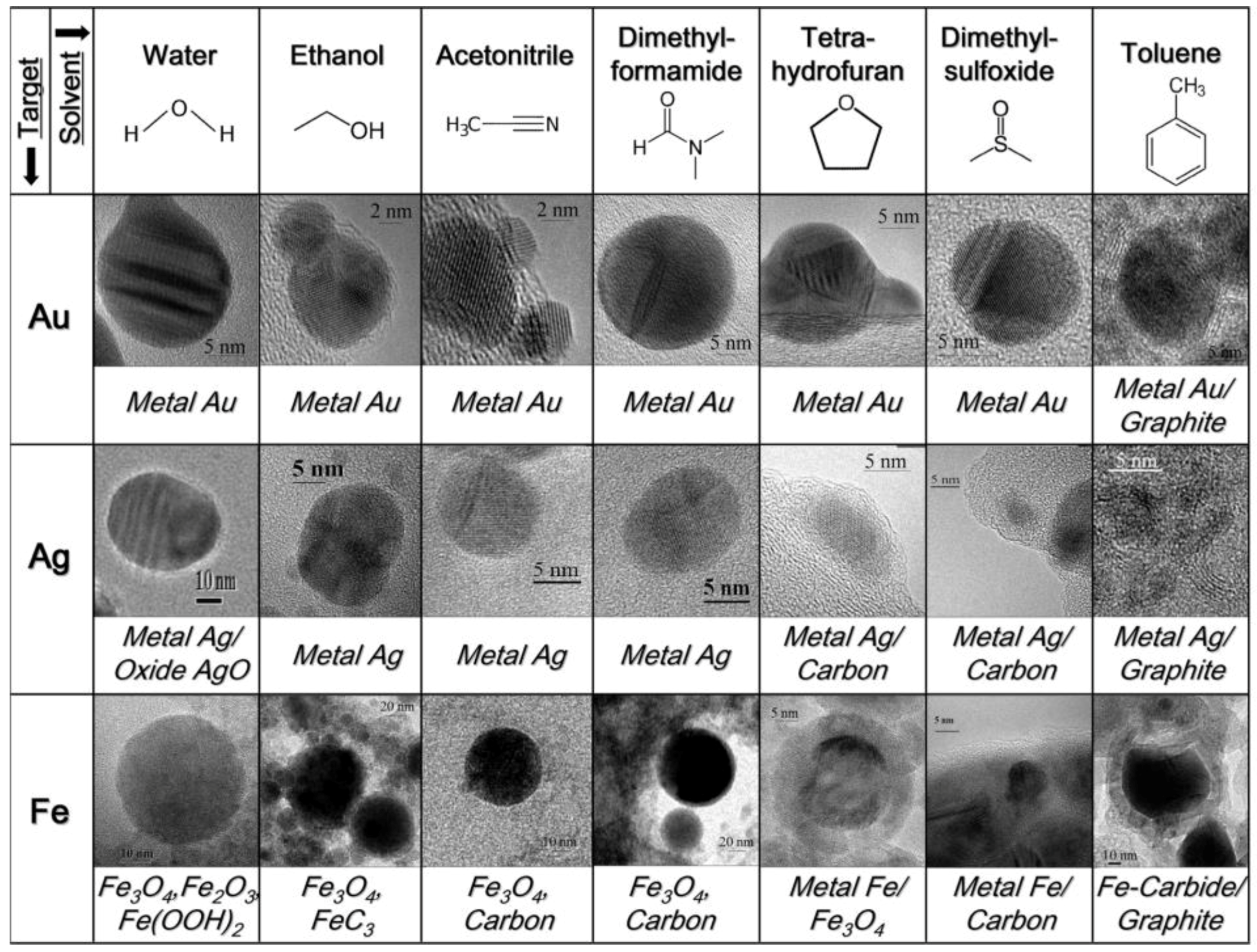
3. Laser Ablation Synthesis in Solution
3.1. Ablation Medium
3.2. Pulse Duration
3.3. Laser Wavelength
3.4. Laser Fluence and Energy Pulse
3.5. Repetition Rate
4. AgNPs in Food Packaging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lue, J.T. Physical Properties of Nanomaterials. In Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Nalwa, H.S., Ed.; American Scientific Publishers: Valencia, CA, USA, 2007; Volume 10, pp. 1–46. ISBN 1-58883-058-6. [Google Scholar]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Jia, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhai, S. Gold Nanoparticle-Induced Cell Death and Potential Applications in Nanomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoot, S.M.; Salem, N.F. A Sonochemical-assisted Simple and Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and its Use in Cosmetics. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 12, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pérez, Z.E.; Singh, P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, M.H.; Yang, D.C. Applications of Panax ginseng leaves-mediated gold nanoparticles in cosmetics relation to antioxidant, moisture retention, and whitening effect on B16BL6 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, B.; Tatiana, V.; Prudnikova, S.V.; Satish, S.; Prasad, N. Nanoagroparticles emerging trends and future prospect in modern agriculture system. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 53, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphle, A.; Navya, P.N.; Umapathi, A.; Daima, H.K. Nanomaterials for agriculture, food and environment: Applications, toxicity and regulation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Dhiman, R.; Rokana, N.; Panwar, H. Nanotechnology: An Untapped Resource for Food Packaging. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Dev, A.; Karmakar, S. Nanosensors and nanobiosensors in food and agriculture. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H. Low temperature thermal engineering of nanoparticle ink for flexible electronics applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 073003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Iocozzia, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z. Noble metal-metal oxide nanohybrids with tailored nanostructures for efficient solar energy conversion, photocatalysis and environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 402–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Amini, M.; Tarassoli, A.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Ghasemian, N.; Jabbari, E. Transition metal oxide nanoparticles as efficient catalysts in oxidation reactions. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 14, 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Volova, T.; Prudnikova, S.V.; Satish, S.; Prasad, N. Nanoagroparticles emerging trends and future prospect in modern agriculture system. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 53, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhan, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, P.; Nehra, K.; Duhan, S. Nanotechnology: The new perspective in precision agriculture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.S. Nanotechnologies associated to floral resources in agri-food sector. Acta Agron. 2018, 67, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, Y.; Gangadhara, K.; Rabinal, C.; Chaudhari, G.; Ugale, P. Nanotechnology in agriculture: A review. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 737–747. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, T.V. Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: Barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, R.A.; Di Maria, A.; Riháková, L.; Volpe, A.; Sportelli, M.C.; Lugarà, P.M.; Ancona, A.; Cioffi, N. Laser ablation synthesis of hybrid copper/silver Nanocolloids for prospective application as Nanoantimicrobial agents for food packaging. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Volpe, A.; Picca, R.A.; Trapani, A.; Palazzo, C.; Ancona, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Trapani, G.; Cioffi, N. Spectroscopic characterization of copper-chitosan Nanoantimicrobials prepared by laser ablation synthesis in aqueous solutions. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azeredo, H.M. Nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Bhatnagar, S.; Dubey, S.D.; Saxena, R.; Sharma, S.; Dutta, R. Nanopackaging in Food and Electronics. In Nanoscience in Food and Agriculture 4; Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 45–97. ISBN 978-3-319-53111-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Cioffi, N. Nano-antimicrobials based on metals. In Novel Antimicrobial Agents and Strategies; Phoenix, D.A., Harris, F., Dennison, S.R., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 181–218. ISBN 978-3-527-67613-2. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, M.; Donia, D.T.; Sabbatella, G.; Antiochia, R. Silver nanoparticles in polymeric matrices for fresh food packaging. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2016, 28, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoodi, M. Nanocomposite materials for food packaging applications: Characterization and safety evaluation. Food Eng. Rev. 2016, 8, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, J.C.; Kerry, J.; Cruz-Romero, M.; Morris, M.; Cummins, E. Advances and challenges for the use of engineered nanoparticles in food contact materials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinnejad, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Katouzian, I. Inorganic and metal nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity in food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuswandi, B. Environmental friendly food nano-packaging. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, A.; Lloret, E.; Picouet, P.A.; Trbojevich, R.; Fernandez, A. Metallic-based micro and nanocomposites in food contact materials and active food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.J.; Adiga, S.P.; Pellin, M.J.; Curtiss, L.A.; Stafslien, S.; Chisholm, B.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Brigmon, R.L.; Elam, J.W. Atomic layer deposition of nanoporous biomaterials. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Karamanou, K.; Engin, A.B.; Gialeli, C.; Docea, A.O.; Vynios, D.H.; Pavão, M.S.G.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Shtilman, M.I.; Argiris, A.; et al. Emerging aspects of nanotoxicology in health and disease: From agriculture and food sector to cancer therapeutics. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azeredo, H.M. Antimicrobial nanostructures in food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Hong, S.-I.; Park, H.-M.; Ng, P.K.W. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-based nanocomposite films with antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5814–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, S.M.; Popok, V.N.; Evlyukhin, A.B.; Hanif, M.; Morgen, P.; Fiutowski, J.; Beermann, J.; Rubahn, H.-G.; Bozhevolnyi, S.I. Highly stable monocrystalline silver clusters for plasmonic applications. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6062–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugazhendhi, S.; Palanisamy, P.K.; Jayavel, R. Synthesis of highly stable silver nanoparticles through a novel green method using Mirabillis jalapa for antibacterial, nonlinear optical applications. Opt. Mater. 2018, 79, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nanoparticles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, T.; Arai, Y.; Hirano, S. Health Effects of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions. In Biological Effects of Fibrous and Particulate Substances; Current Topics in Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 137–147. ISBN 978-4-431-55731-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.F.; Baun, A. European regulation affecting nanomaterials—Review of limitations and future recommendations. Dose-Response 2011, 10, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, W.; Long, Y.; Sun, C.; Jiang, G. Toxicological effects and mechanisms of silver nanoparticles. In Silver Nanoparticles in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 109–138. ISBN 978-3-662-46069-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Cioffi, N. Silver Nanoparticles as Nano-antimicrobials: Bioactivity, benefits and bottlenecks. In Nano-Antimicrobials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 211–224. ISBN 978-3-642-24427-8. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ansary, A.; Al-Daihan, S. On the Toxicity of Therapeutically Used Nanoparticles: An Overview. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jt/2009/754810/ (accessed on 23 June 2018).
- Gaillet, S.; Rouanet, J.-M. Silver nanoparticles: Their potential toxic effects after oral exposure and underlying mechanisms—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 77, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, I.; Duran, N.; Rai, M. Nano-silver toxicity: Emerging concerns and consequences in human health. In Nano-Antimicrobials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 525–548. ISBN 978-3-642-24427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jamuna, B.A.; Ravishankar, R.V. Environmental risk, human health, and toxic effects of nanoparticles. In Nanomaterials for Environmental Protection; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 523–535. ISBN 978-1-118-84553-0. [Google Scholar]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.A.D.; Seckler, M.M.; Ingle, A.P.; Gupta, I.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Silver Nanoparticles: Therapeutical Uses, Toxicity, and Safety Issues. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.; Rosas-Hernandez, H.; Ramirez-Lee, M.A.; Salazar-García, S.; Ali, S.F. Role of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on the cardiovascular system. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, E.; Milani, M.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Nasrabadi, H.T.; Nikasa, P.; Joo, S.W.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; et al. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Al-Rajhi, A.M.H.; Abboud, M.A.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Magdah, A.G.; Helmy, E.A.M.; Mabrouk, A.S. Recent advances in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications: About future directions. A review. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, H.D.; Werkneh, A.A.; Bezabh, H.K.; Ambaye, T.G. Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2017, 13, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Jiménez, B.; Johnson, M.E.; Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Murphy, K.E.; Winchester, M.R.; Vega Baudrit, J.R. Silver Nanoparticles: Technological advances, societal impacts, and metrological challenges. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matteis, V.; Cascione, M.; Toma, C.C.; Leporatti, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthetic Routes, In vitro toxicity and theranostic applications for cancer disease. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, A.; Oloketuyi, S.F.; Khan, M.M.; Khan, F. Diversity of Bacterial Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Malik, N.; Khan, M.; Cho, M.H.; Khan, M.M. Fungi-assisted silver nanoparticle synthesis and their applications. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, U.T.; Rao, G.V.S.N.; Mantravadi, K.M.; Oztekin, Y. Strategies to synthesize various nanostructures of silver and their applications—A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19739–19753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, B.; Pirzadah, T.B.; Kumar, M.; Rehman, R.U. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles and their application in pharmaceutical industry. In Nanotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 235–252. ISBN 978-981-10-4677-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pandiarajan, J.; Krishnan, M. Properties, synthesis and toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.J.B.; Nasirpour, M.; Carrola, J.; Oliveira, H.; Freire, C.S.R.; Duarte, I.F. Antimicrobial properties and therapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles and nanocomposites. In Antimicrobial Nanoarchitectonics; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 9; pp. 223–259. ISBN 978-0-323-52733-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, M.S.; Tahir, M.B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Gopinath, S.C.B. Potentials in synthesizing nanostructured silver particles. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 4345–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Salmiati; Salim, M.R.; Kueh, A.B.H.; Hadibarata, T.; Nur, H. A Review of silver nanoparticles: Research trends, global consumption, synthesis, properties, and future challenges. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 732–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Saleh, T.A.; Wahab, A.; Khan, M.H.U.; Khan, D.; Khan, W.U.; Rahim, A.; Kamal, S.; Khan, F.U.; Fahad, S. Nanosilver: New Ageless and Versatile Biomedical Therapeutic Scaffold. Available online: https://www.dovepress.com/nanosilver-new-ageless-and-versatile-biomedical-therapeutic-scaffold-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-IJN (accessed on 23 June 2018).
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q. Significant parameters in the optimization of synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Divya, A.; Kumar, K.S.; Reddy, P.S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by soft chemical method: Effect of reducing agent concentration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Nanomaterials Emerging Engineering Technologies, Chennai, India, 24–26 July 2013; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Qiao, X.; Qiu, X.; Chen, J. Preparation and characterization of stable monodisperse silver nanoparticles via photoreduction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 320, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, T.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Ali, Z.I. Structural and morphological study of gamma-irradiation synthesized silver nanoparticles. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2687–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.; Araby, E. Bactericidal effect of poly(acrylamide/itaconic acid)–silver nanoparticles synthesized by gamma irradiation against pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatema, U.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Mollah, M.Y.A.; Susan, M.A.B.H. Silver/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite film prepared using water in oil microemulsion for antibacterial applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 514, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Yin, R. A facile synthesis of high antibacterial polymer nanocomposite containing uniformly dispersed silver nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuc, D.T.; Huy, T.Q.; Hoang, L.H.; Tien, B.C.; Van Chung, P.; Thuy, N.T.; Le, A.-T. Green synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles through electrochemical method and their antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2016, 181, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Electrochemical Synthesis of silver nanoparticles under protection of poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8898–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, N.; Colaianni, L.; Pilolli, R.; Calvano, C.; Palmisano, F.; Zambonin, P. Silver nanofractals: Electrochemical synthesis, XPS characterization and application in LDI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D.J.; Shah, S.I. Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, P.; Iydroose, M.; Mohideen, M.H.A.K.; Mohan, T.S.; Cho, M.; Oh, B.-T. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Bacillus subtilis EWP-46 cell-free extract and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L.V. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles—A review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terenteva, E.A.; Apyari, V.V.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Formation of plasmonic silver nanoparticles by flavonoid reduction: A comparative study and application for determination of these substances. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 151, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou El-Nour, K.M.M.; Eftaiha, A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jokar, M.; Rahman, R.A. Study of silver ion migration from melt-blended and layered-deposited silver polyethylene nanocomposite into food simulants and apple juice. Food Addit. Contamin. Part A 2014, 31, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.L.; Cheng, C.; Ma, Y.L.; Zhao, C.S. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activities and the researches of their biocompatibilities. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 21, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Mashaly, H.M.; Wilken, R. Nanocomposites based on chitosan/silver/clay for durable multi-functional properties of cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regiel-Futyra, A.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M.; Sebastian, V.; Irusta, S.; Arruebo, M.; Kyzioł, A.; Stochel, G. Development of noncytotoxic silver-chitosan nanocomposites for efficient control of biofilm forming microbes. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52398–52413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Shaheen, T.I.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Hebeish, A.A. Eco-friendly microwave-assisted green and rapid synthesis of well-stabilized gold and core-shell silver-gold nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Sannino, A.; Picca, R.A.; Sportelli, M.C.; Cioffi, N.; Nitti, M.A.; Valentini, M.; Valentini, A. Nonconventional routes to silver nanoantimicrobials: Technological issues, bioactivity, and applications. In Nanotechnology in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prophylaxis of Infectious Diseases; Kon, M.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, FL, USA, 2015; Chapter 6; pp. 87–105. ISBN 978-0-12-801317-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoir, S.A.; Chawla, S.P. Silver nanoparticles synthesized using mint extract and their application in chitosan/gelatin composite packaging film. Int. J. Nanosci. 2016, 16, 1650022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. Laser ablation synthesis in solution and size manipulation of noble metal nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 3805–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegedi, Á.; Popova, M.; Valyon, J.; Guarnaccio, A.; Stefanis, A.D.; Bonis, A.D.; Orlando, S.; Sansone, M.; Teghil, R.; Santagata, A. Comparison of silver nanoparticles confined in nanoporous silica prepared by chemical synthesis and by ultra-short pulsed laser ablation in liquid. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chaker, M.; Ma, D. Pulsed laser ablation based synthesis of colloidal metal nanoparticles for catalytic applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 489, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.G.; Petersen, S.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T.; Barcikowski, S. Laser ablation-based one-step generation and bio-functionalization of gold nanoparticles conjugated with aptamers. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendrzej, S.; Gökce, B.; Epple, M.; Barcikowski, S. How size determines the value of gold: Economic aspects of wet chemical and laser-based metal colloid synthesis. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcikowski, S.; Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Chichkov, B.; Brikas, M.; Račiukaitis, G. Generation of nanoparticle colloids by picosecond and femtosecond laser ablations in liquid flow. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 083113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajti, C.L.; Sattari, R.; Chichkov, B.N.; Barcikowski, S. Gram scale synthesis of pure ceramic nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2421–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streubel, R.; Barcikowski, S.; Gökce, B. Continuous multigram nanoparticle synthesis by high-power, high-repetition-rate ultrafast laser ablation in liquids. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Proteomics analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of nanoparticles and their interactions with proteins. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, V.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Imran, A.; Abaza, U.M. Bacilli as biological nano-factories intended for synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its application in human welfare. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1775–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Ahmed, K.B.; Nagy, A.M.; Brown, R.P.; Zhang, Q.; Malghan, S.G.; Goering, P.L. Silver nanoparticles: Significance of physicochemical properties and assay interference on the interpretation of in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Toxicology In Vitro 2017, 38, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; de Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbus, A.F.; Horozov, T.S.; Paunov, V.N. Colloid particle formulations for antimicrobial applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kędziora, A.; Speruda, M.; Krzyżewska, E.; Rybka, J.; Łukowiak, A.; Bugla-Płoskońska, G. Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalandi, B.; Asadi, N.; Milani, M.; Davaran, S.; Abadi, A.J.N.; Abasi, E.; Akbarzadeh, A. A review on potential role of silver nanoparticles and possible mechanisms of their actions on bacteria. Drug Res. 2017, 11, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review on SERS of bacteria. Biosensors 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Krishna, S.; Govender, P.; Adam, J.K. Nano silver particles in biomedical and clinical applications: Review. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Natan, M.; Banin, E. From Nano to Micro: Using nanotechnology to combat microorganisms and their multidrug resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, V.; Gupta, R.; Panwar, J. Do physico-chemical properties of silver nanoparticles decide their interaction with biological media and bactericidal action? A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Pandit, R.; Paralikar, P.; Gupta, I.; Chaud, M.V.; dos Santos, C.A. Broadening the spectrum of small-molecule antibacterials by metallic nanoparticles to overcome microbial resistance. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gupta, I.R.; Galdiero, M.; Galdiero, S. Metal nanoparticles: The protective nanoshield against virus infection. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudramurthy, G.R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sinniah, U.R.; Ghasemzadeh, A. Nanoparticles: Alternatives against drug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Molecules 2016, 21, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashi, T.; Gupta, N.V.; Mbuya, V.B. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, mechanism of antimicrobial action, characterization, medical applications, and toxicity effects. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in various cell lines: An in vitro model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Sen, A. Silver nanoparticle antimicrobials and related materials. In Nano-Antimicrobials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–45. ISBN 978-3-642-24427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nomiya, K.; Takahashi, S.; Noguchi, R.; Nemoto, S.; Takayama, T.; Oda, M. Synthesis and characterization of water-soluble silver(I) complexes with l-Histidine (H2his) and (S)-(−)-2-Pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic Acid (H2pyrrld) showing a wide spectrum of effective antibacterial and antifungal activities. Crystal structures of chiral helical polymers [Ag(Hhis)]n and {[Ag(Hpyrrld)]2}n in the solid state. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 3301–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Fromm, K.M.; Akbar Ashkarran, A.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; De Larramendi, I.R.; Rojo, T.; Serpooshan, V.; Parak, W.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShan, D.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-R.; Sun, T.-L.; Zhou, S.-L.; Ma, Y.-K.; Shi, Q.-S.; Xie, X.-B.; Huang, X.-M. A comparative analysis of antibacterial activity, dynamics, and effects of silver ions and silver nanoparticles against four bacterial strains. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: A case study on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli as models for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, J.K.; Swarnkar, R.K.; Soumya, K.K.; Dwivedi, P.; Singh, M.K.; Sundaram, S.; Gopal, R. Silver nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation: As a potent antibacterial agent for human enteropathogenic gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos-Ortiz, E.; Roque-Ruiz, J.H.; Hinojos-Márquez, E.A.; López-Esparza, J.; Donohué-Cornejo, A.; Cuevas-González, J.C.; Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Reyes-López, S.Y. Dose-dependent antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles on polycaprolactone fibers against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 4752314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? a study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butkus, M.A.; Labare, M.P.; Starke, J.A.; Moon, K.; Talbot, M. Use of aqueous silver to enhance inactivation of coliphage MS-2 by UV disinfection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2848–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, M.; Hara, K.; Kudo, J. Bactericidal actions of a silver ion solution on Escherichia coli, studied by energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy and proteomic analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7589–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Pierrat, S.; Sonnichsen, C.; Rai, M. Mycosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Fungus Fusarium acuminatum and Its Activity Against Some Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com/66921/article (accessed on 22 June 2018).
- Gajbhiye, M.; Kesharwani, J.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic fungi in combination with fluconazole. Nanomedicine 2009, 5, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birla, S.S.; Tiwari, V.V.; Gade, A.K.; Ingle, A.P.; Yadav, A.P.; Rai, M.K. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata and its combined effect against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Letters Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, K.; Tamilselvan, S.; Kiruthiga, V.; Singaravelu, G. Biogenic silver nanoparticles by Solanum torvum and their promising antimicrobial activity. J. Biopestic. 2010, 3, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Namasivayam, S.K.R. Evaluation of anti bacterial activity of biocompatible polymer chitosan coated biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized from Klebsiella ornithinolytica. BioMedRx 2013, 1, 459–563. [Google Scholar]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Silva, R.G.; Morris, B.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Surface charge-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Lim, D.W.; Choi, J. Assessment of size-dependent antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 763807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Pandey, S.; Giri, V.P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Shukla, R.; Mishra, A.; Nautiyal, C.S. Tailoring shape and size of biogenic silver nanoparticles to enhance antimicrobial efficacy against MDR bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zook, J.M.; Halter, M.D.; Cleveland, D.; Long, S.E. Disentangling the effects of polymer coatings on silver nanoparticle agglomeration, dissolution, and toxicity to determine mechanisms of nanotoxicity. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Störmer, A.; Bott, J.; Kemmer, D.; Franz, R. Critical review of the migration potential of nanoparticles in food contact plastics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aueviriyavit, S.; Phummiratch, D.; Maniratanachote, R. Mechanistic study on the biological effects of silver and gold nanoparticles in Caco-2 cells—Induction of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway by high concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Bala, N. Comparative studies of cold and thermal sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for biomedical applications—A review. In Biomaterials Science: Processing, Properties and Applications II; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 249–259. ISBN 978-1-118-51146-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Rahman, M.F.; Duhart, H.M.; Newport, G.D.; Patterson, T.A.; Murdock, R.C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Ali, S.F. Expression changes of dopaminergic system-related genes in PC12 cells induced by manganese, silver, or copper nanoparticles. NeuroToxicology 2009, 30, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.V.D.Z.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perito, B.; Giorgetti, E.; Marsili, P.; Muniz-Miranda, M. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation in pure water and in chloride solution. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Rong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Size-dependent antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against oral anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Niño-Martínez, N.; Martínez-Gutierrez, F.; Martínez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kőrösi, L.; Rodio, M.; Dömötör, D.; Kovács, T.; Papp, S.; Diaspro, A.; Intartaglia, R.; Beke, S. Ultrasmall, ligand-free Ag nanoparticles with high antibacterial activity prepared by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4143560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshed, P.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T. The molecular mechanisms of the antibacterial effect of picosecond laser generated silver nanoparticles and their toxicity to human cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, N.; Shamaila, S.; Nazir, J.; Sharif, R.; Shahid Rafique, M.; Ul-Hasan, J.; Ammara, S.; Khalid, H. Antibacterial action of chemically synthesized and laser generated silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Roy, N.; Mandal, D.; Begum, N.A. Green chemistry for nanochemistry: Exploring medicinal plants for the biogenic synthesis of metal NPs with fine-tuned properties. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 11935–11956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Cioffi, N. Recent advances in the synthesis and characterization of nano-antimicrobials. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-Y.; Streubel, R.; Heberle, J.; Letzel, A.; Shugaev, M.V.; Wu, C.; Schmidt, M.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Two mechanisms of nanoparticle generation in picosecond laser ablation in liquids: The origin of the bimodal size distribution. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6900–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simakin, A.V.; Voronov, V.V.; Shafeev, G.A.; Brayner, R.; Bozon-Verduraz, F. Nanodisks of Au and Ag produced by laser ablation in liquid environment. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 348, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, G.; Valenza, G.; Dell’Aglio, M.; De Giacomo, A. On the stability of gold nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 489, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafuné, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. Structure and stability of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution produced by laser ablation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 8333–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuné, F.; Kondow, T. Selective laser fabrication of small nanoparticles and nano-networks in solution by irradiation of UV pulsed laser onto platinum nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 383, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuné, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 9111–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruusing, A. Underwater and water-assisted laser processing: Part 1—General features, steam cleaning and shock processing. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2004, 41, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseguera-Galindo, D.O.; Martínez-Benítez, A.; Chávez-Chávez, A.; Gómez-Rosas, G.; Pérez-Centeno, A.; Santana-Aranda, M.A. Effects of the confining solvent on the size distribution of silver NPs by laser ablation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.; Hashimoto, S.; Tomita, T.; Matsuo, S.; Makita, Y. Examination of silver nanoparticle fabrication by pulsed-laser ablation of flakes in primary alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.G.; Pereira, R.S.F.; Andritschky, M.; Lopes, A.L.B.; de Freitas Grilo, J.P.; do Nascimento, R.M.; Silva, F.S. Effects of laser fluence and liquid media on preparation of small Ag nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 97, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3027–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalus, M.-R.; Bärsch, N.; Streubel, R.; Gökce, E.; Barcikowski, S.; Gökce, B. How persistent microbubbles shield nanoparticle productivity in laser synthesis of colloids—Quantification of their volume, dwell dynamics, and gas composition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 7112–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajdidzadeh, M.; Azmi, B.Z.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Talib, Z.A.; Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Karimzadeh, K.; Gene, S.A.; Dorraj, M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles dispersed in various aqueous media using laser ablation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 324921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, E.; Schatz, G.C. Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 120, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Azawi, M.A.; Bidin, N.; Bououdina, M.; Abbas, K.N.; Al-Asedy, H.J.; Ahmed, O.H.; Thahe, A.A. The effects of the ambient liquid medium on the ablation efficiency, size and stability of silver nanoparticles prepared by pulse laser ablation in liquid technique. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeev, R.A.; Baba, M.; Ryasnyanskii, A.I.; Suzuki, M.; Kuroda, H. Laser ablation of silver in different liquids: Optical and nonlinear optical properties of silver nanoparticles. Opt. Spectrosc. 2005, 99, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. A comparison of the characteristics of nanosecond, picosecond and femtosecond lasers generated Ag, TiO2 and Au nanoparticles in deionised water. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 120, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Kakita, T.; Tsuji, M. Preparation of nano-size particles of silver with femtosecond laser ablation in water. Appl. Surface Sci. 2003, 206, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. Comparison of characteristics of selected metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles produced by picosecond laser ablation at 532 and 1064 nm wavelengths. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solati, E.; Mashayekh, M.; Dorranian, D. Effects of laser pulse wavelength and laser fluence on the characteristics of silver nanoparticle generated by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 112, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Iryo, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Tsuji, M. Preparation of metal colloids by a laser ablation technique in solution: Influence of laser wavelength on the ablation efficiency (II). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2001, 145, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Iryo, K.; Watanabe, N.; Tsuji, M. Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in solution: Influence of laser wavelength on particle size. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 202, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Schönfeld, P.; Letzel, A.; Kohsakowski, S.; Olbinado, M.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S.; Plech, A. Fluence threshold behaviour on ablation and bubble formation in pulsed laser ablation in liquids. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorranian, D.; Tajmir, S.; Khazanehfar, F. Effect of laser fluence on the characteristics of Ag nanoparticles produced by laser ablation. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 2013, 3, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdieh, M.H.; Fattahi, B. Size properties of colloidal nanoparticles produced by nanosecond pulsed laser ablation and studying the effects of liquid medium and laser fluence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.S.; Nedyalkov, N.N.; Nikov, R.G.; Atanasov, P.A.; Alexandrov, M.T.; Karashanova, D.B. Investigation of Ag nanoparticles produced by nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in water. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 109, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.S.; Nedyalkov, N.N.; Nikov, R.G.; Atanasov, P.A.; Alexandrov, M.T. Characterization of Ag and Au nanoparticles created by nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in double distilled water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5278–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Alva, M.A.; García-Fernández, T.; Villagrán-Muniz, M.; Sánchez-Aké, C.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Esparza-Alegría, E.; Sánchez-Valdés, C.F.; Llamazares, J.L.S.; Herrera, C.E.M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in ethanol: A pulsed photoacoustic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamiri, R.; Zakaria, A.; Ahangar, H.A.; Darroudi, M.; Zamiri, G.; Rizwan, Z.; Drummen, G.P.C. The effect of laser repetition rate on the LASiS synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles in aqueous starch solution. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Barcikowski, S. Hydrodynamic size distribution of gold nanoparticles controlled by repetition rate during pulsed laser ablation in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mirmoghtadaie, L. Nanoantimicrobials in Food Industry. In Nanotechnology Applications in Food; Oprea, A.E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 11; pp. 223–243. ISBN 978-0-12-811942-6. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Conte, A.; Alessandro, M.; Nobile, D. Use of Metal Nanoparticles for Active Packaging Applications. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Barros-Velázquez, J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Chapter 31; pp. 399–406. ISBN 978-0-12-800723-5. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Conte, A.; Buonocore, G.G.; Del Nobile, M.A. Antimicrobial silver-montmorillonite nanoparticles to prolong the shelf life of fresh fruit salad. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 148, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, P.; Sivakumar, P.; Anbarasu, K.; Pandian, K.; Renganathan, S. Synthesis of silver nanorods from food industrial waste and their application in improving the keeping quality of milk. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17676–17681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, A. The Nanotechnology Consumer Products Inventory; Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Dekkers, S.; Noordam, M.; Hagens, W.; Bulder, A.; De Heer, C.; ten Voorde, S.E.C.G.; Wijnhoven, S.; Sips, A. Health Impact of Nanotechnologies in Food Production; Netherlands National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2007.
- Von Goetz, N.; Fabricius, L.; Glaus, R.; Weitbrecht, V.; Günther, D.; Hungerbühler, K. Migration of silver from commercial plastic food containers and implications for consumer exposure assessment. Food Addit. Contamin. Part A 2013, 30, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echegoyen, Y.; Nerín, C. Nanoparticle release from nano-silver antimicrobial food containers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerin, C.; Silva, F.; Manso, S.; Becerril, R. The downside of antimicrobial packaging: Migration of packaging elements into food. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Barros-Velázquez, J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Chapter 6; pp. 81–93. ISBN 978-0-12-800723-5. [Google Scholar]
- Biji, K.B.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Mohan, C.O.; Gopal, T.K.S. Smart packaging systems for food applications: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6125–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Fabra, M.F.; Lagarón, J.M.; Ocio, M.J.; Sánchez, G. Silver-Based Antibacterial and Virucide Biopolymers: Usage and potential in antimicrobial packaging. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Barros-Velázquez, J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Chapter 32; pp. 407–416. ISBN 978-0-12-800723-5. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request related to a 17th list of substances for food contact materials: Opinion of the scientific panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) on a request related to a 17t. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Prasanna, P.H.P.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; McConchie, R.; Naumovski, N.; Mellor, D. Nanotechnology in Microbial Food Safety. In Nanotechnology Applications in Food; Oprea, A.E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Chapter 12; pp. 245–265. ISBN 978-0-12-811942-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M.; Cubadda, F.; Dini, L.; Terranova, M.L.; Aureli, F.; Sorbo, A.; Passeri, D. Scientific basis of nanotechnology, implications for the food sector and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 40, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


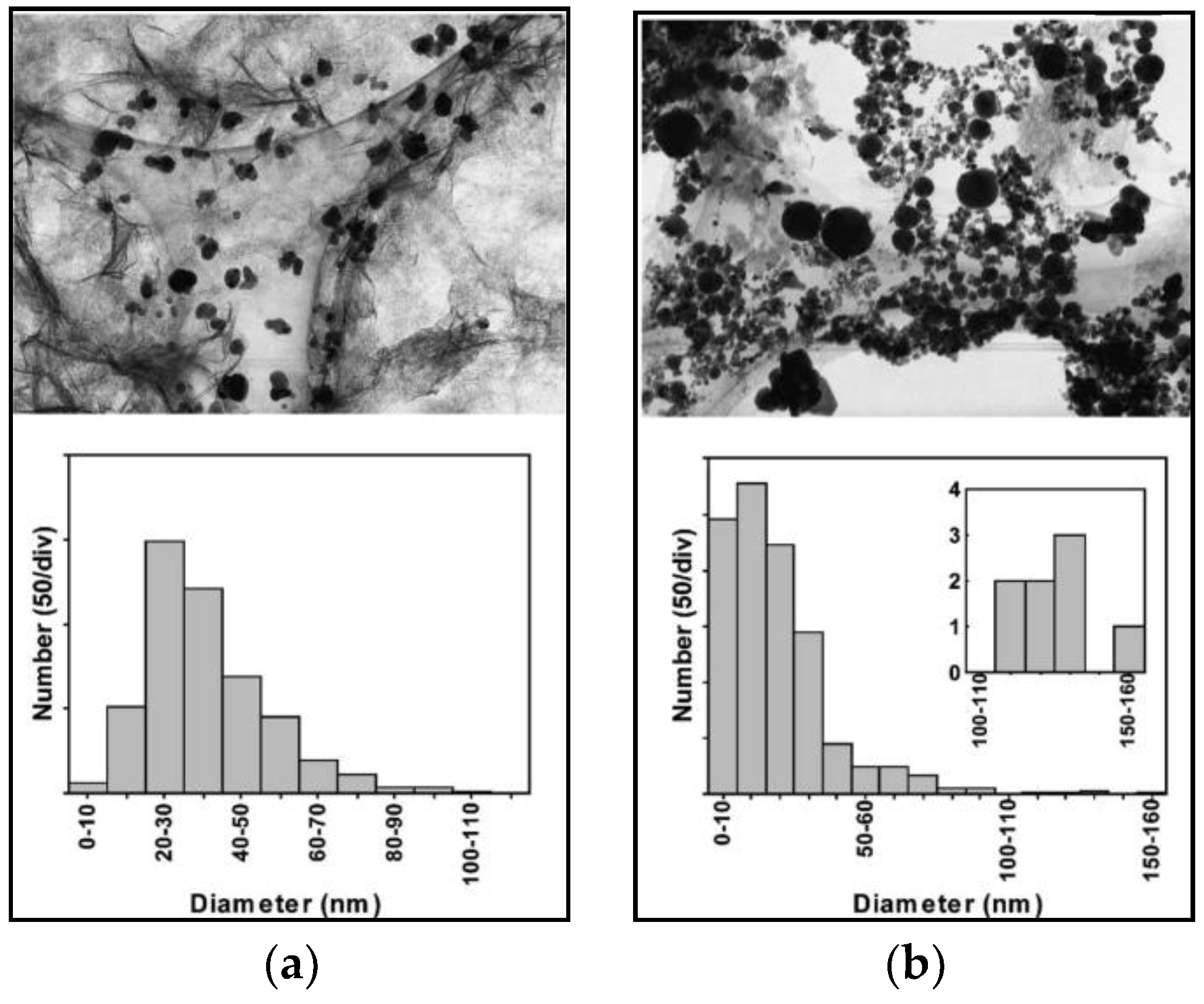
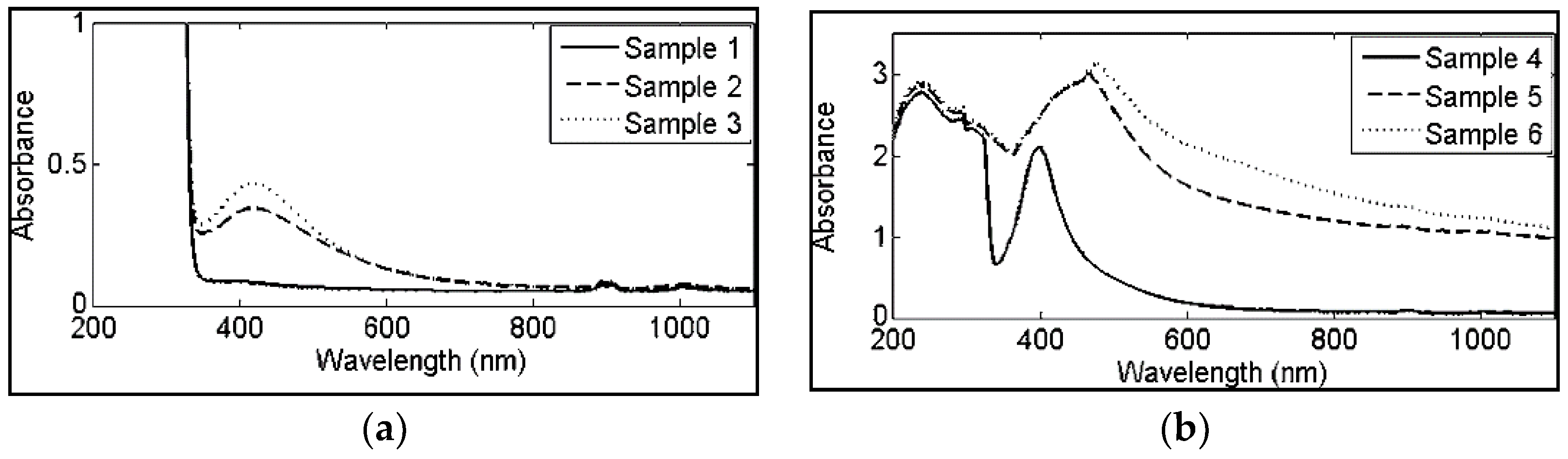
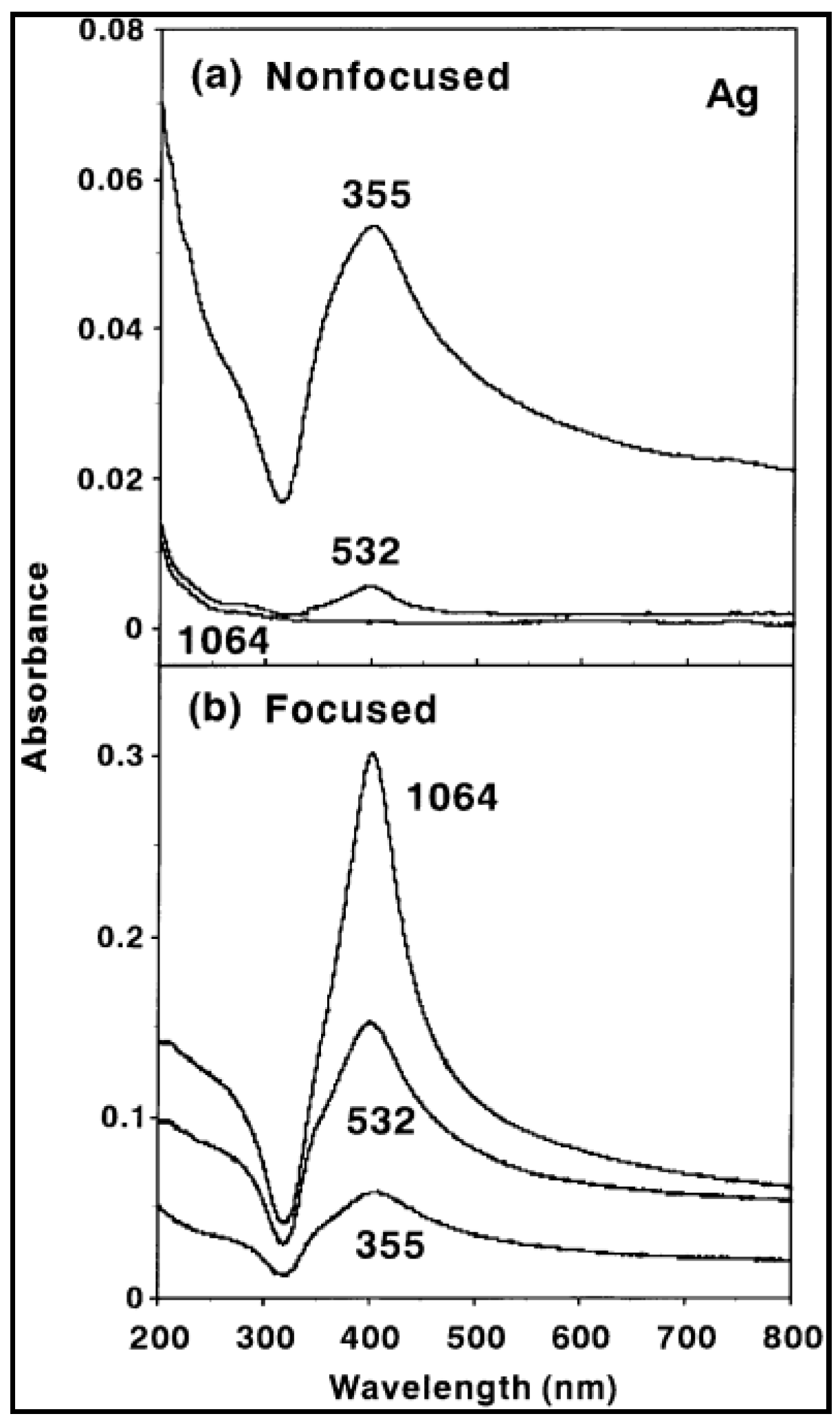
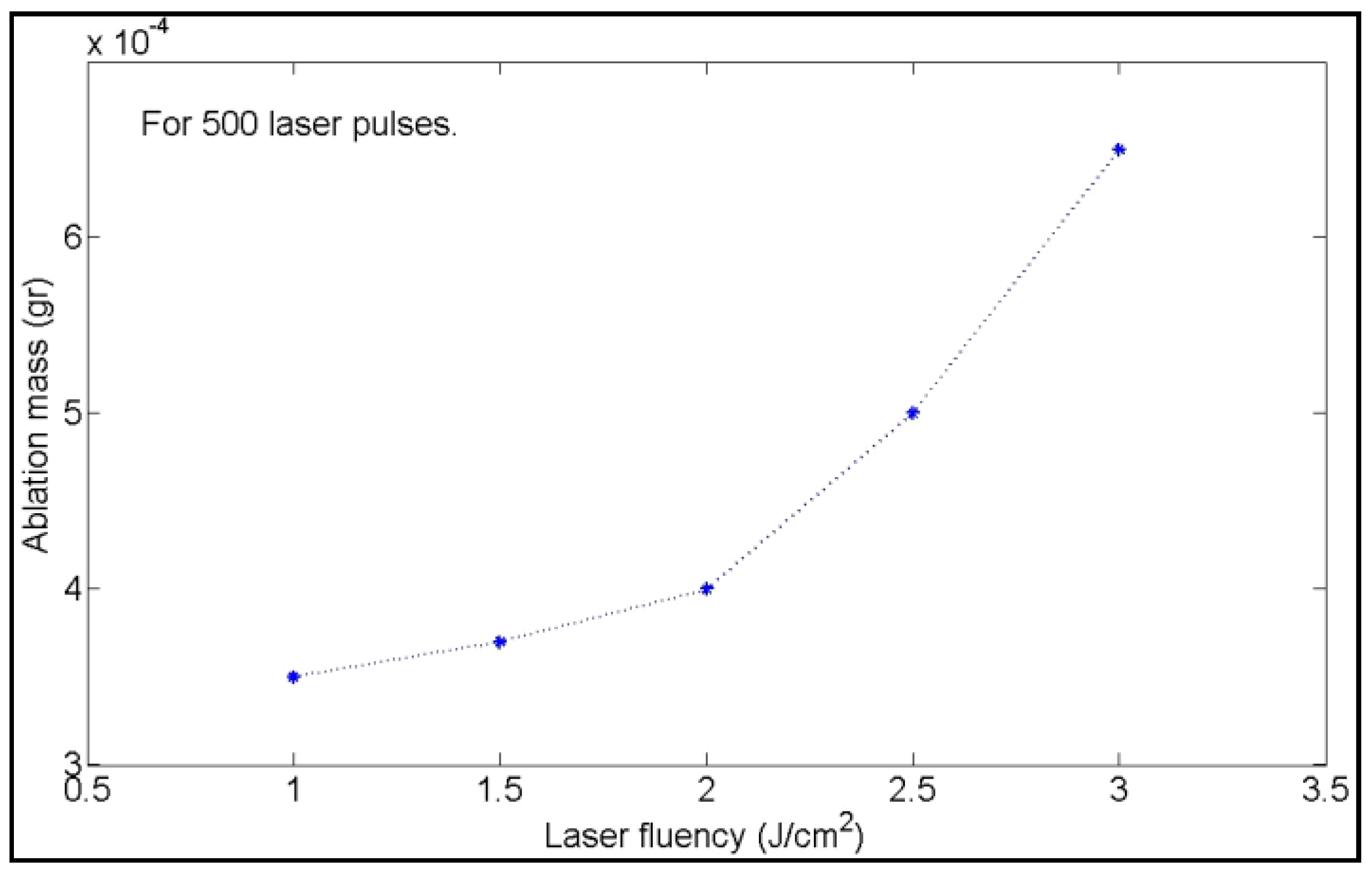
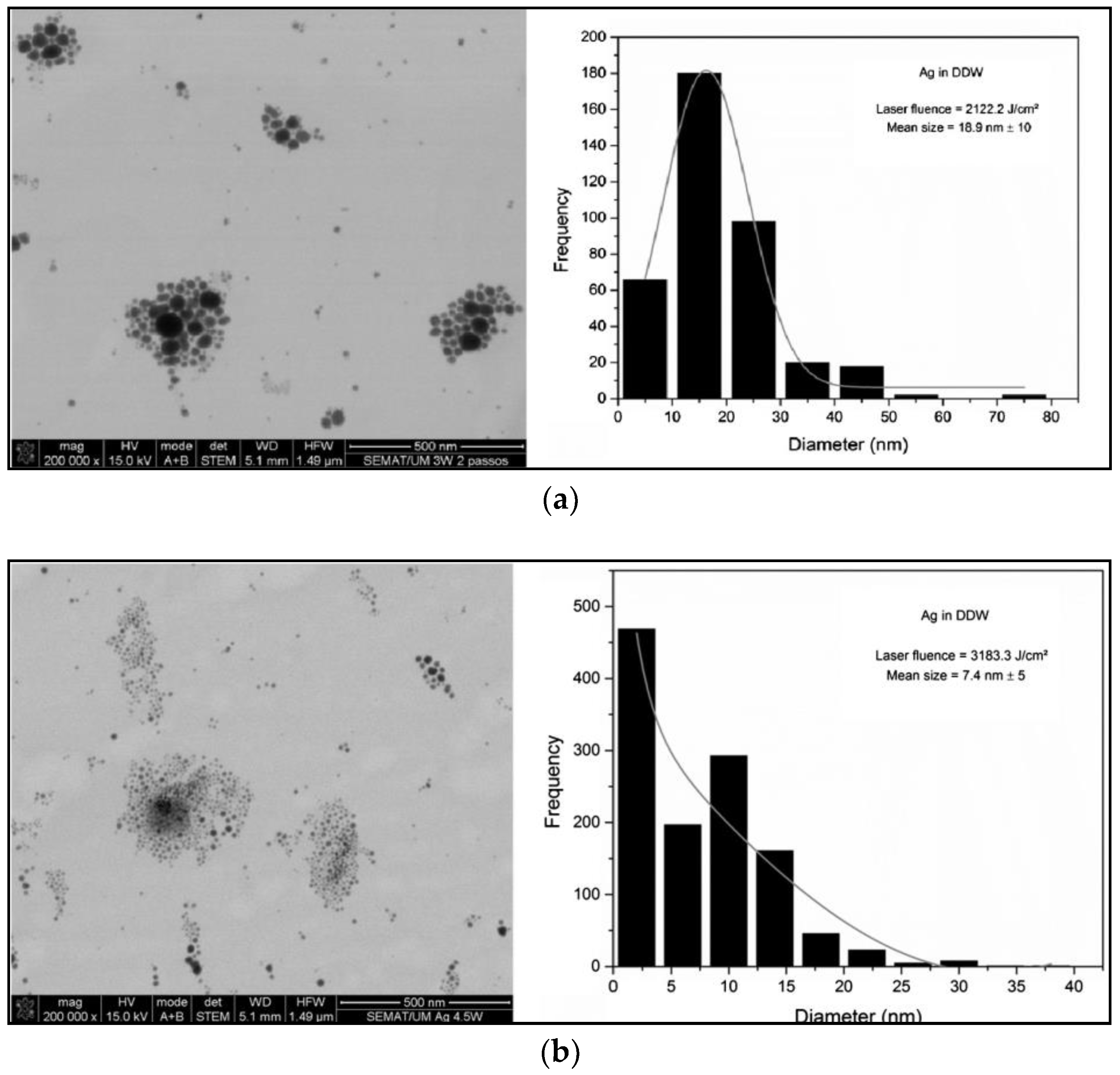
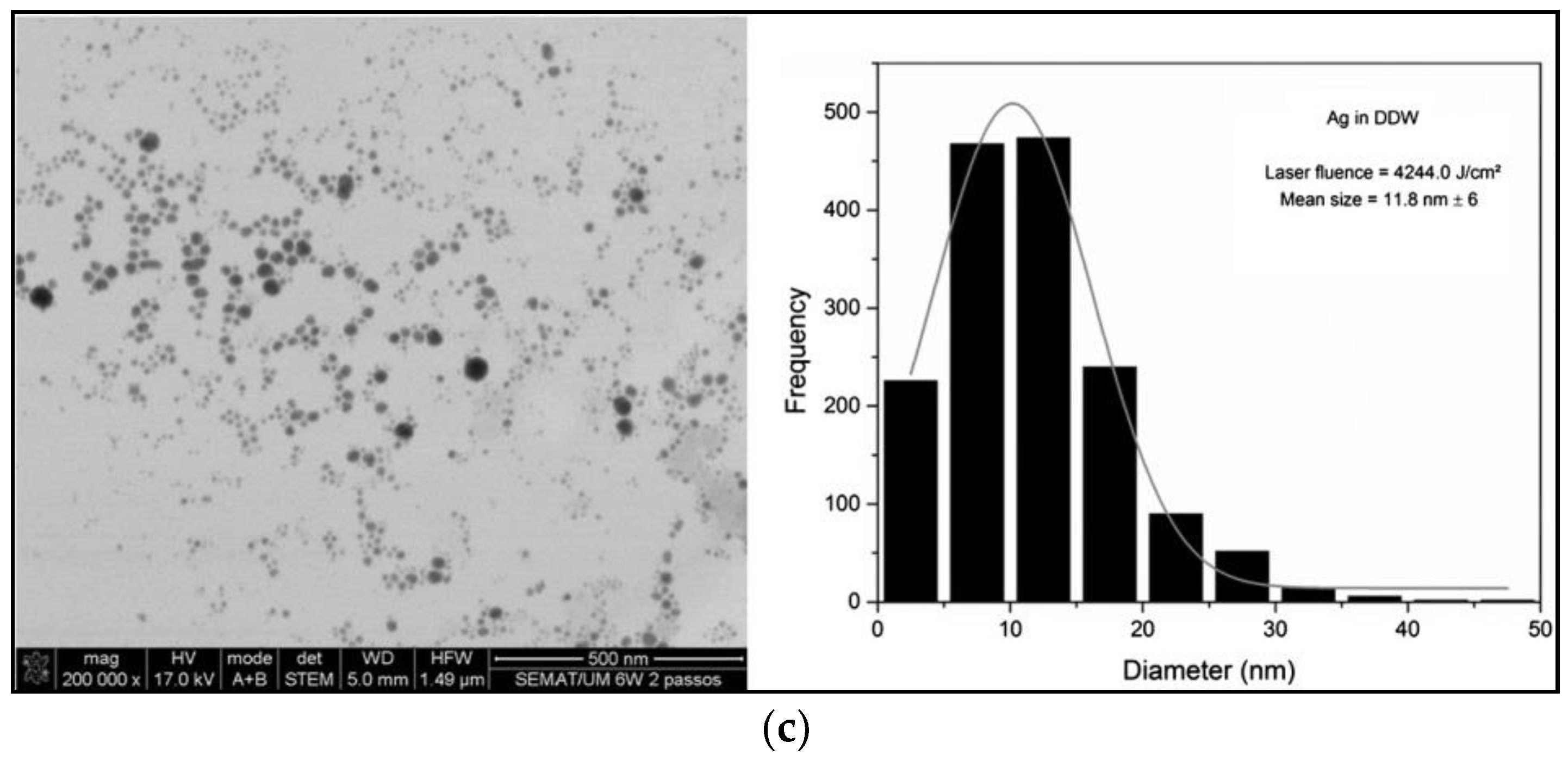
| Target Organism | Different Form of Silver | References |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli | Silver ions | [125] |
| Escherichiacoli | Silver nanoparticles | [126,127] |
| RNA viruses | Silver ions | [128] |
| Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella typhus | Silver nanoparticles | [129] |
| Escherichia coli | Silver ions | [130] |
| Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Staphylococcus epidermidis, StreptococcusAureus | Silver nanoparticles | [131] |
| Phoma glomerata, Phoma herbarum, Fusarium semitectum, Trichoderma specie and Candida albicans | Silver nanoparticles | [132] |
| Escherichia coli, Streptococcusaureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Silver nanoparticles | [133] |
| P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, pathogenic fungi Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus niger | Silver nanoparticles | [134] |
| S. aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Bacillussubtilis, Enterococcus faecalis, P. aeruginosa | Silver nanoparticles | [135] |
| Concentration Range | Effects of AgNPs | References |
|---|---|---|
| 25–75 μg/mL | In rat alveolar macrophage cell line, cytotoxicity increases in a concentration-dependent manner | [141] |
| 5, 15, 40, 125 μg/mL | Cytotoxicity occurred through mitochondrial depolarization | [142] |
| 20–250 μg/mL | Apoptosis and necrosis induced in an Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) cell line | [143] |
| 1, 2, 4 μg/mL | Cell viability decreased in a concentration-dependent manner | [144] |
| 0.4 and 0.8 μg/mL | Arrest G1 phase in cell cycle in a Murine Macrophages cell line (#RAW 264.7) | [145] |
| Nanomaterial Product | Packaging Manufacturer | Country | NP Size | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-silver salad bowl | Changmin Chemicals | Korea | not reported | [190] |
| Nano silver baby mug cup and nurser | Baby Dream® Co., Ltd. | Korea | not reported | [191] |
| Fresh Box® food storage containers | BlueMoonGoods™ | USA | not reported | [190] |
| FresherLonger™ containers and bags | SharperImage® | USA | 25 nm and 1–100 nm | [192] |
| Nano-silver storage box | Quan Zhou Hu Zeng Nano Technology® Co., Ltd. | China | not reported | [190] |
| Plastic food containers and water bottle | A-Do Global | Korea | not reported | [191] |
| Fresh food containers | Oso Fresh | USA | 40–60 nm | [193] |
| Smartwist food storage with nano-silver | Kinetic Go Green | USA | 10–20 nm | [193] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sportelli, M.C.; Izzi, M.; Volpe, A.; Clemente, M.; Picca, R.A.; Ancona, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Palazzo, G.; Cioffi, N. The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030067
Sportelli MC, Izzi M, Volpe A, Clemente M, Picca RA, Ancona A, Lugarà PM, Palazzo G, Cioffi N. The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials. Antibiotics. 2018; 7(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleSportelli, Maria Chiara, Margherita Izzi, Annalisa Volpe, Maurizio Clemente, Rosaria Anna Picca, Antonio Ancona, Pietro Mario Lugarà, Gerardo Palazzo, and Nicola Cioffi. 2018. "The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials" Antibiotics 7, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030067
APA StyleSportelli, M. C., Izzi, M., Volpe, A., Clemente, M., Picca, R. A., Ancona, A., Lugarà, P. M., Palazzo, G., & Cioffi, N. (2018). The Pros and Cons of the Use of Laser Ablation Synthesis for the Production of Silver Nano-Antimicrobials. Antibiotics, 7(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030067











