Temperature Adaptive Biofilm Formation in Yersinia enterocolitica in Response to pYV Plasmid and Calcium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
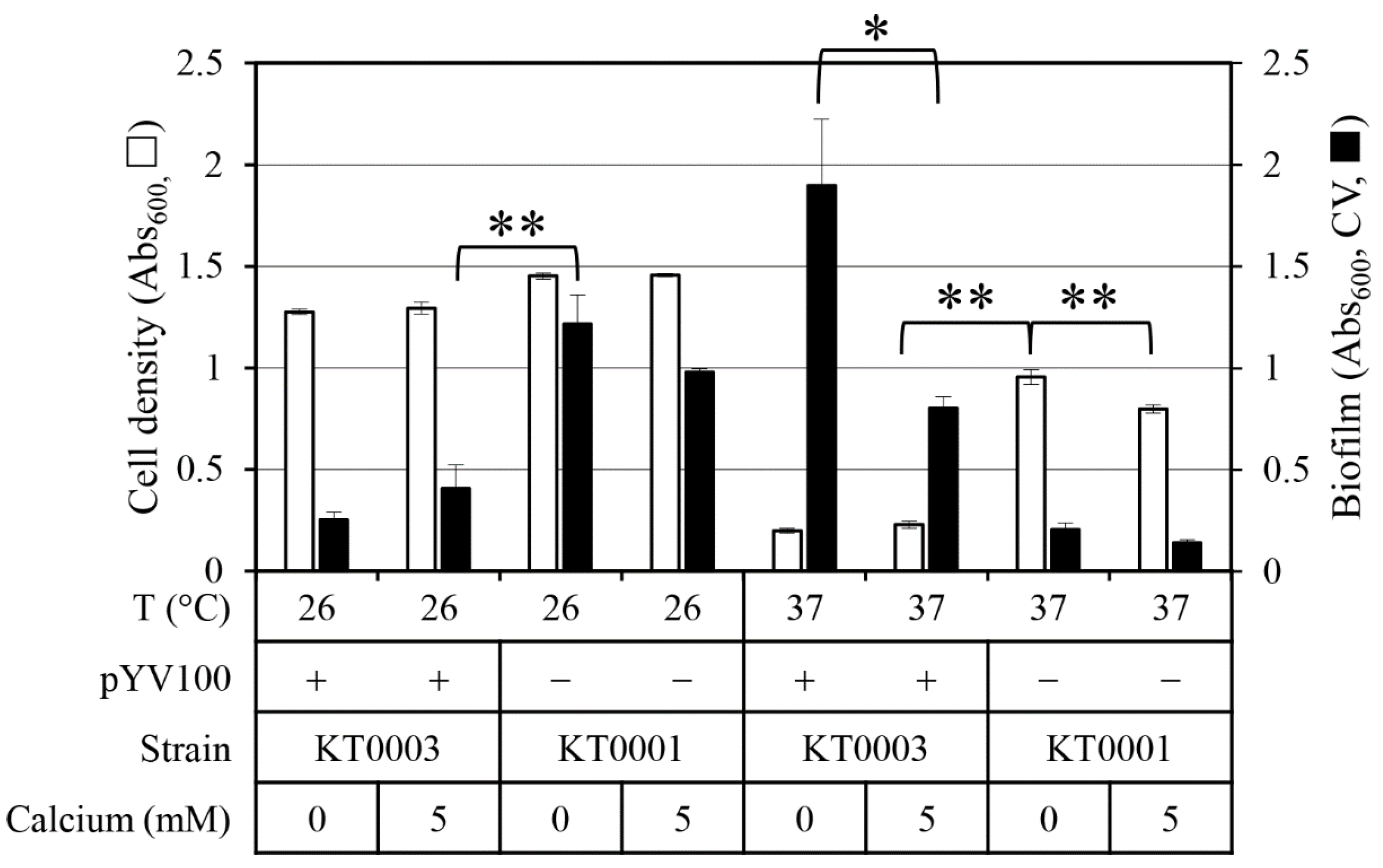
2.1. Effects of Temperature, the Virulence Plasmid (pYV100), and Calcium on Cell Growth and Biofilm Formation
2.2. Effects of Temperature, the Virulence Plasmid, and Calcium on Motility and Flagellar Expression
2.3. Effect of Temperature, the pYV Plasmid, and Calcium on Extracellular Polymeric Substance Production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Cell Density and Biofilm Quantification
4.3. Cell Motility Measurement
4.4. Flagellar Staining
4.5. Measuring flhDC Expression Level Using Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.6. Extracellular Polymeric Substance Quantification
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substance |
| T3SS | Type III secretion system |
| Yops | Yersinia outer proteins |
| TYE | Tryptone-yeast extract |
| eDNA | Extracellular DNA |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
References
- Abdel-Haq, N.M.; Asmar, B.I.; Abuhammour, W.M.; Brown, W.J. Yersinia enterocolitica infection in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Zheng, J.; Sheng, M.; Liu, X.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, Z.; Hou, X.; Jing, H.; et al. Public health implications of Yersinia enterocolitica investigation: An ecological modeling and molecular epidemiology study. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Grönthal, T.; Heljanko, V.; Johansson, V.; Rantala, M.; Heikinheimo, A.; Laukkanen-Ninios, R. Enteropathogenic Yersinia with public health relevance found in dogs and cats in Finland. Pathogens 2024, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tay, M.; Palmer, J.; Flint, S. Biofilm formation of Yersinia enterocolitica and its persistence following treatment with different sanitation agents. Food Control 2017, 73, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.; Kim, T.-J. Inhibition of biofilm formation in Yersinia enterocolitica by edible plant extracts including Polygoni Multiflori Radix. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoechea, J.A.; Najdenski, H.; Skurnik, M. Lipopolysaccharide O antigen status of Yersinia enterocolitica O:8 is essential for virulence and absence of O antigen affects the expression of other Yersinia virulence factors. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-J.; Young, B.M.; Young, G.M. Effect of flagellar mutations on Yersinia enterocolitica biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5466–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiesow, L.; Lam, H.; Dersch, P.; Auerbuch, V. Yersinia type III secretion system master regulator LcrF. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Yang, H.; Fang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yang, R. RcsAB is a major repressor of Yersinia biofilm development through directly acting on hmsCDE, hmsT and hmsHFRS. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, B.; Yang, L.; Gu, J.-D. Biofilm control by interfering with c-di-GMP metabolism and signaling. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 56, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.M.; Smith, M.J.; Minnich, S.A.; Miller, V.L. The Yersinia enterocolitica motility master regulatory operon, flhDC, is required for flagellin production, swimming motility, and swarming motility. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2823–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Palmer, J.; Flint, S. Function of pYV plasmid on biofilm formation of Yersinia enterocolitica ERL032123 in the presence of Ca2+. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Bai, J.; Chen, J. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of RcsB in suppressing bacterial chemotaxis, flagellar assembly and infection in Yersinia enterocolitica. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottone, E.J. Yersinia enterocolitica: The charisma continues. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, G.; Vanootegem, J.C.; Sluiters, C. Transcription of the yop regulon from Y. enterocolitica requires trans acting pYV and chromosomal genes. Microb. Pathog. 1987, 2, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBord, K.L.; Galanopoulos, N.S.; Schneewind, O. The ttsA gene is required for low-calcium-induced yype III secretion of Yop proteins and virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica W22703. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goverde, R.L.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Huis in‘t Veld, J.H.J. Growth rate and physiology of Yersinia enterocolitica; influence of temperature and presence of the virulence plasmid. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 77, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemski, P.; Lazere, J.R.; Casey, T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect. Immun. 1980, 27, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapatral, V.; Olson, J.W.; Pepe, J.C.; Miller, V.L.; Minnich, S.A. Temperature-dependent regulation of Yersinia enterocolitica Class III flagellar genes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, J. Rcs phosphorelay responses to truncated lipopolysaccharide-induced cell envelope stress in Yersinia enterocolitica. Molecules 2020, 25, 5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprokostopoulou, A.; Römling, U. Yin and Yang of biofilm formation and cyclic di-GMP signaling of the gastrointestinal pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Innate Immun. 2021, 14, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Little, B.J.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in the environment, technology and medicine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.M.; Young, G.M. An amino-terminal secretion signal Is required for YplA export by the Ysa, Ysc, and flagellar type III secretion systems of Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1B. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6075–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, Y.; Xu, D.; Kim, T.-J. Effect of licorice extract on biofilm formation in two pathogenic bacteria: Aeromonas hydrophila and Yersinia enterocolitica. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2025, 53, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidese, R.; Nishikawa, R.; Gao, L.; Katano, M.; Imai, T.; Kato, S.; Kanai, T.; Atomi, H.; Imanaka, T.; Fujiwara, S. Different roles of two transcription factor B proteins in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.-J. Inhibitory effect of Moringa oleifera seed extract and its behenic acid component on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Description | Source/ Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Yersinia enterocolitica | ||
| KT0001 | biotype 1B, serotype O:8, Sal/Esc-Ptz-CRMOX- | KCCM 41657 |
| KT0002 | KCCM 41657, NalR | In this study |
| KT0003 | KT0002 with pYV100, NalR | In this study |
| Plasmid | ||
| pYV100 | mob+, mobilizable derivative of pYV8081, Str/SpcR | [23] |
| Primers | ||
| flhDC-F | CCTCAGCGATGTTTCGTCTC | [20] |
| flhDC-R | CTGCAAGTCATCCACACGAG | [20] |
| 16S rRNA-F | GCACGTAATGGTGGGAACTC | [20] |
| 16S rRNA-R | CTCCAATCCGGACTACGACA | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.; Kim, T.-J. Temperature Adaptive Biofilm Formation in Yersinia enterocolitica in Response to pYV Plasmid and Calcium. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090857
Oh Y, Kim T-J. Temperature Adaptive Biofilm Formation in Yersinia enterocolitica in Response to pYV Plasmid and Calcium. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090857
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yunah, and Tae-Jong Kim. 2025. "Temperature Adaptive Biofilm Formation in Yersinia enterocolitica in Response to pYV Plasmid and Calcium" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090857
APA StyleOh, Y., & Kim, T.-J. (2025). Temperature Adaptive Biofilm Formation in Yersinia enterocolitica in Response to pYV Plasmid and Calcium. Antibiotics, 14(9), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090857







