Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Traits of Salmonella enterica Isolated from Cattle: Genotypic and Phenotypic Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Bacterial Isolation, and Characterization
2.2. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.3. Motility Assay
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.5. Detection of Virulence Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence and Serotype Distribution of Salmonella
3.2. Biofilm Formation Within the Salmonella Isolates
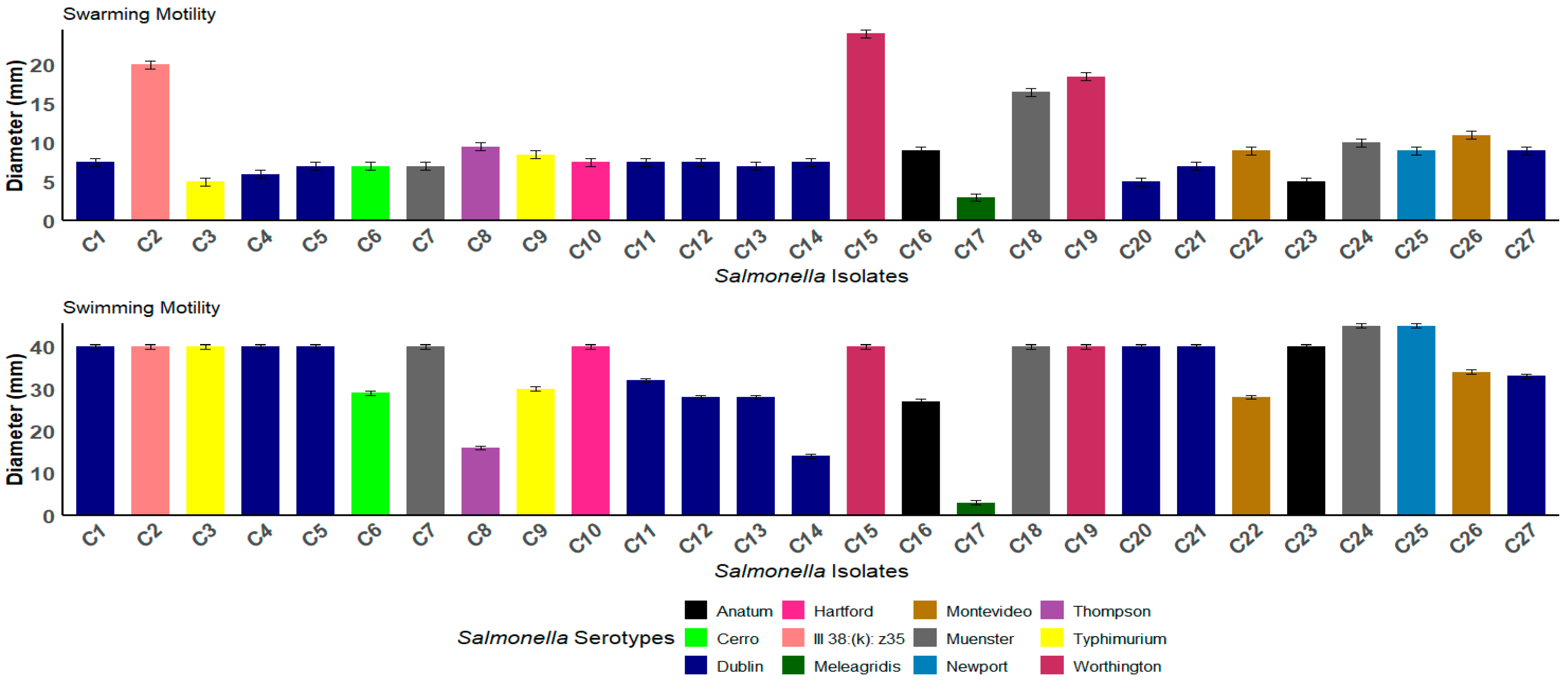
3.3. Swimming and Swarming Motility
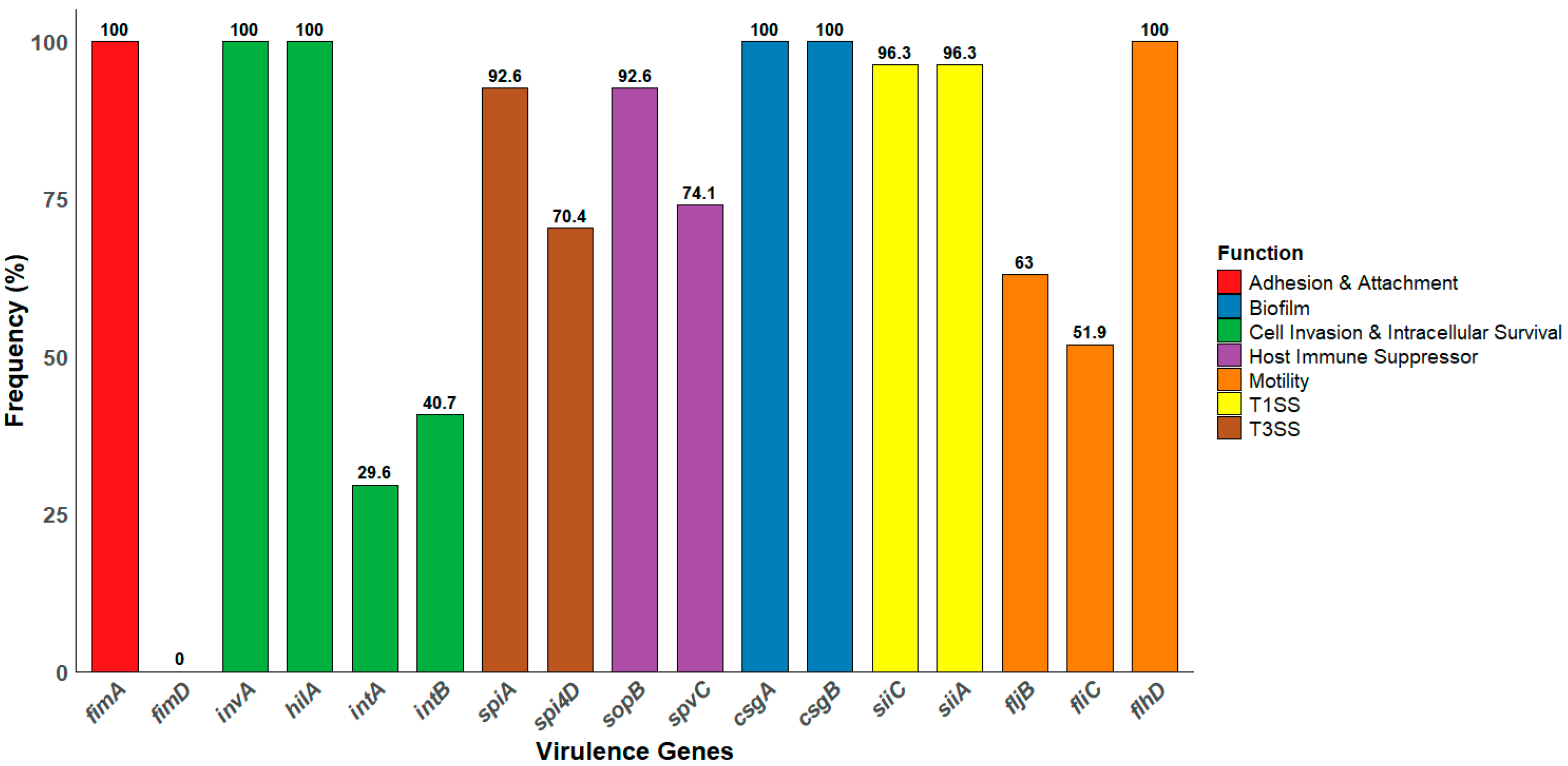
3.4. Distribution of Virulence Genes Among Salmonella Isolates
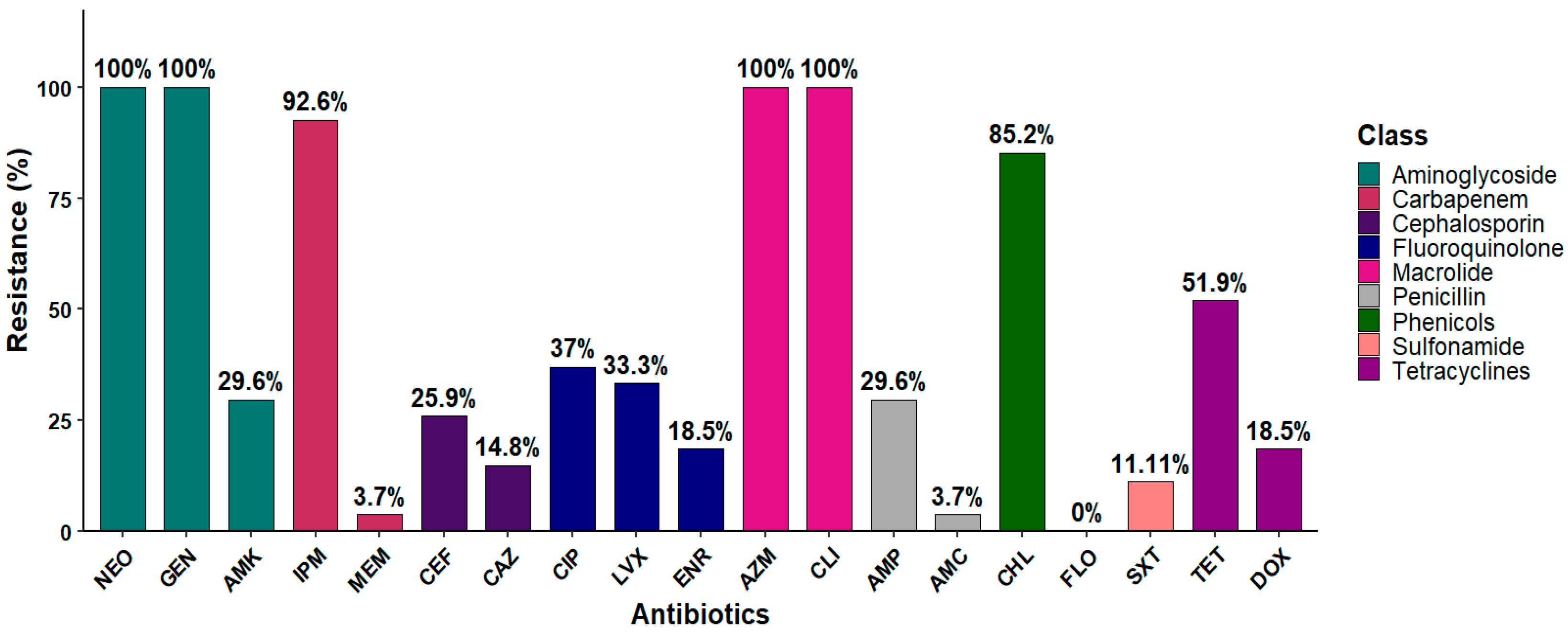
3.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile
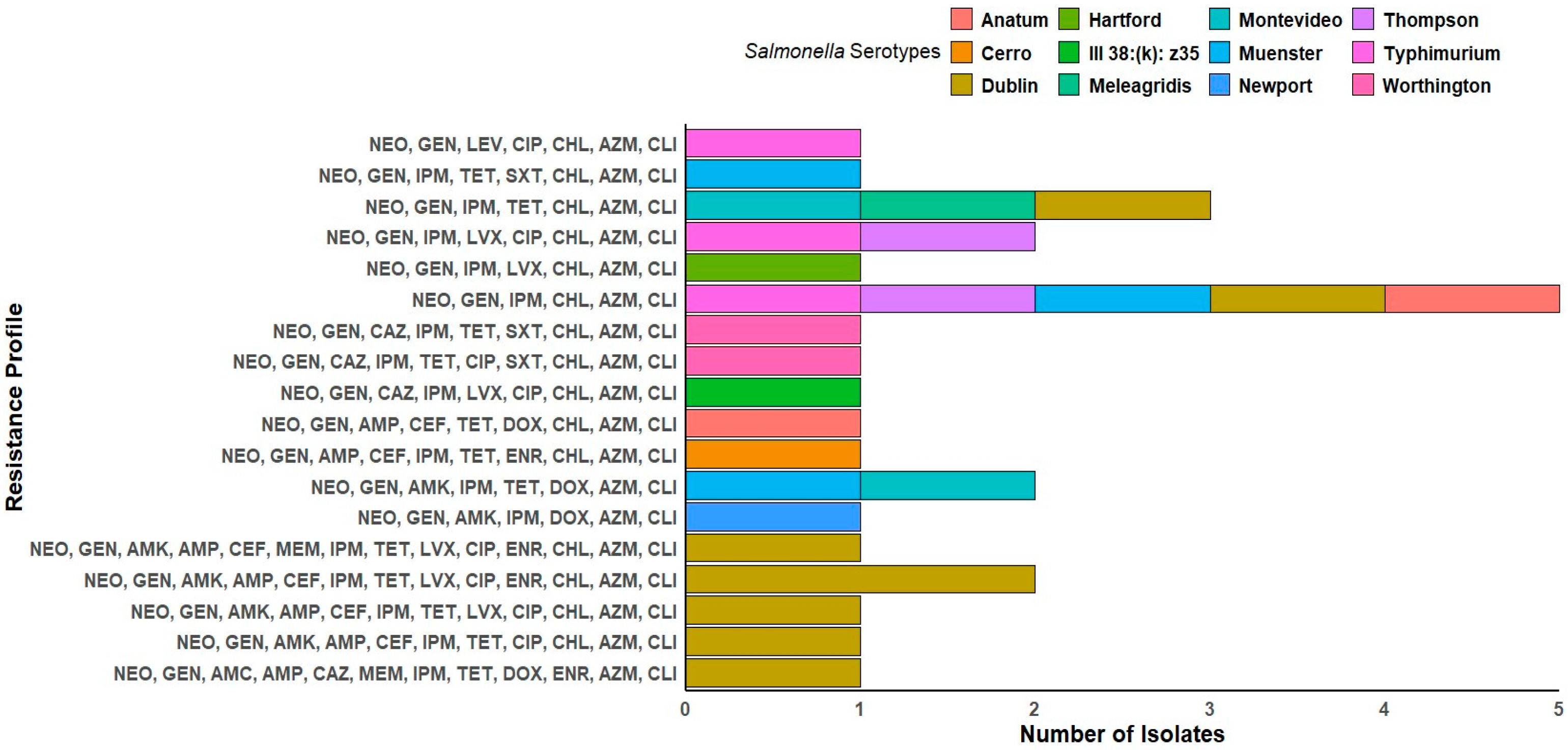
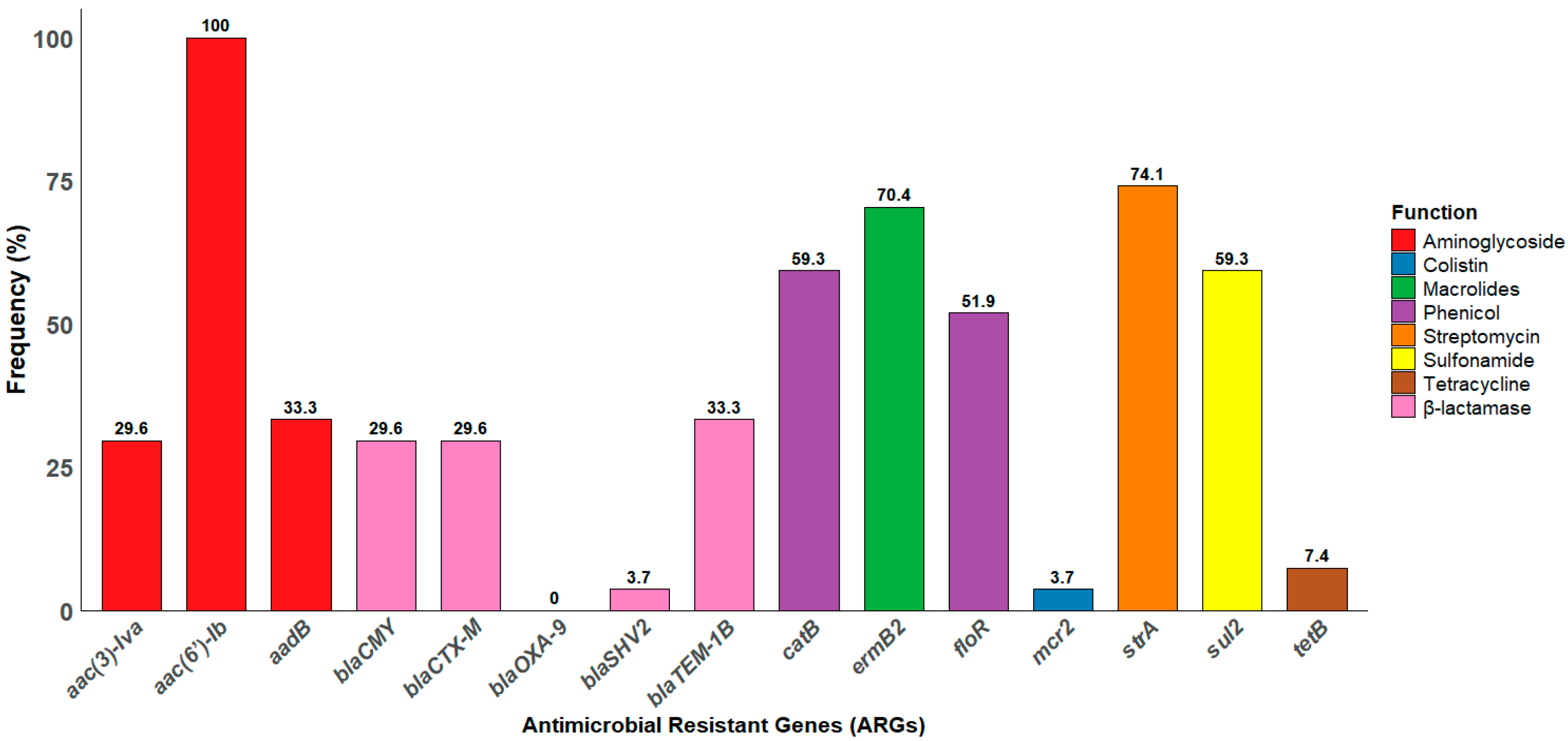
3.6. Distribution of ARGs Among Salmonella Isolates
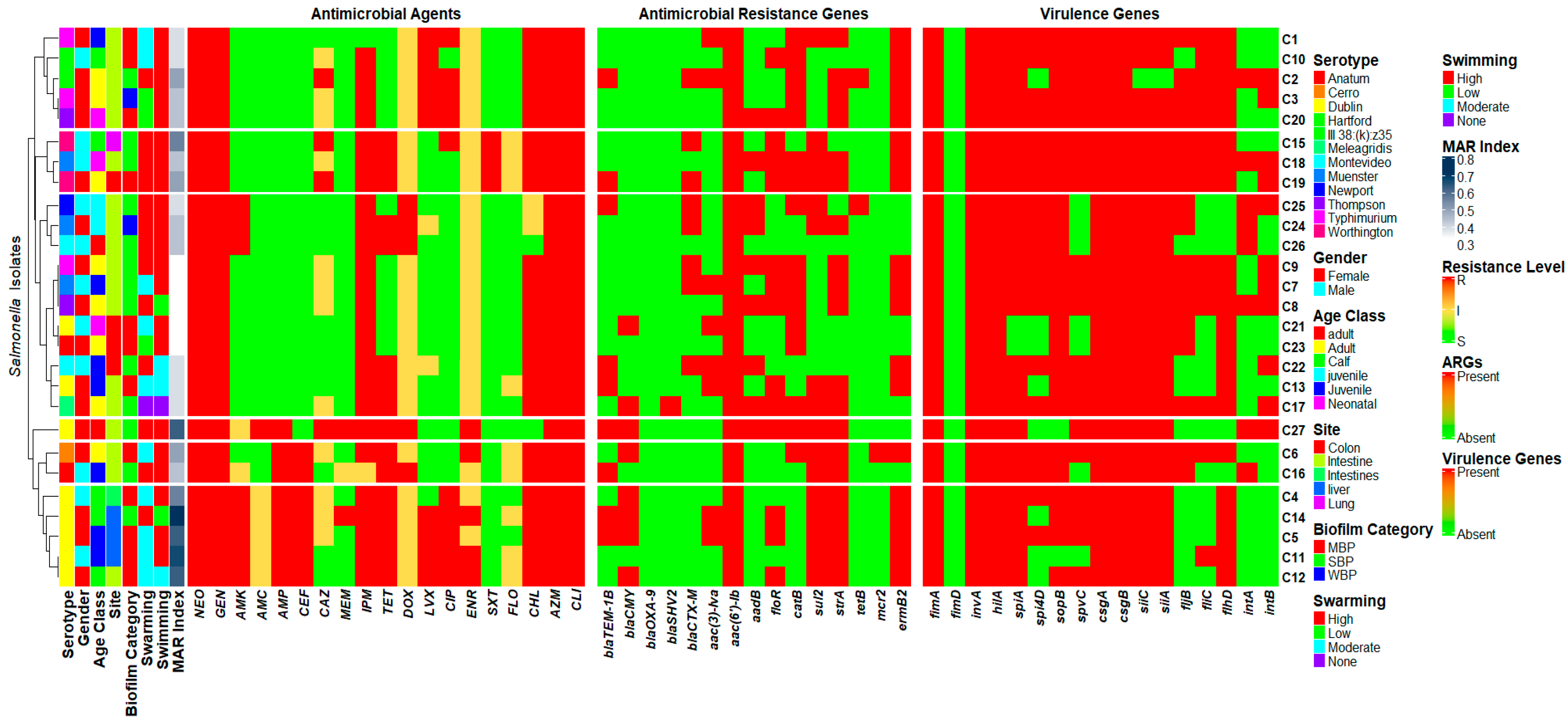
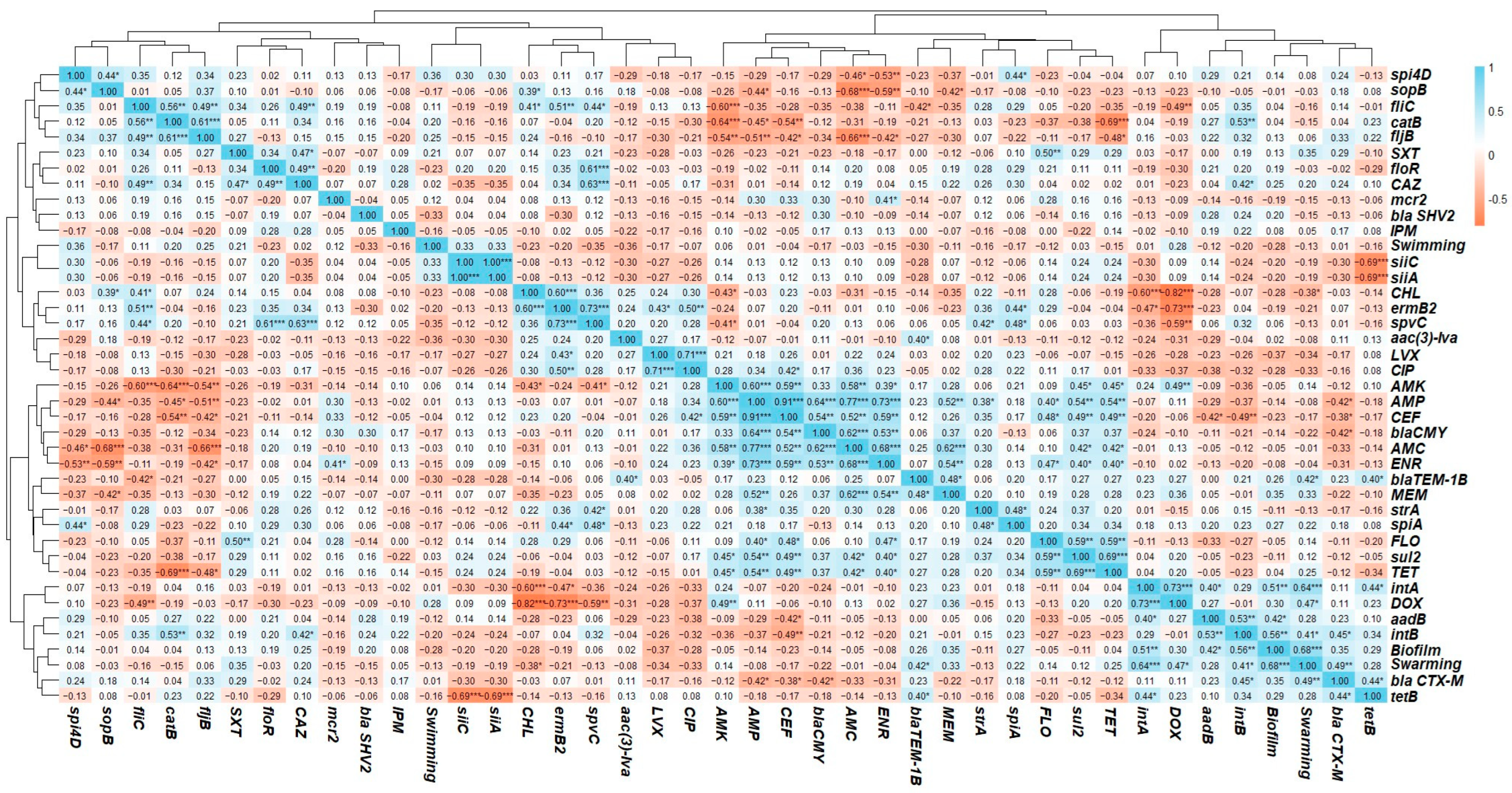
3.7. Phenotypic and Genotyping Correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nhung, N.T.; Phu, D.H.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Padungtod, P. A review and meta-analysis of non-typhoidal Salmonella in Vietnam: Challenges to the control and antimicrobial resistance traits of a neglected zoonotic pathogen. One Health 2024, 18, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, E.O.; Carvalho, T.; Silva, E.M.; Ricke, S.C.; Hite, J.L. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance on organic and conventional farms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickodem, C.; Arnold, A.N.; Gehring, K.B.; Gill, J.J.; Richeson, J.T.; Samuelson, K.L.; Scott, H.M.; Smith, J.K.; Taylor, T.M.; Vinasco, J. A longitudinal study on the dynamics of Salmonella enterica prevalence and serovar composition in beef cattle feces and lymph nodes and potential contributing sources from the feedlot environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00033-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, S.; Batz, M.B.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Annual cost of illness and quality-adjusted life year losses in the United States due to 14 foodborne pathogens. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Naushad, S. Salmonella: Perspectives for Low-Cost Prevention, Control and Treatment; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ballash, G.A.; Parker, E.M.; Mollenkopf, D.F.; Wittum, T.E. The One Health dissemination of antimicrobial resistance occurs in both natural and clinical environments. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2024, 1, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, S.A.; Deng, L.; Adam, E.A.; Benedict, K.M.; Beshearse, E.M.; Blackstock, A.J.; Bruce, B.B.; Derado, G.; Edens, C.; Fullerton, K.E. Estimate of burden and direct healthcare cost of infectious waterborne disease in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Rahman, M.S. Salmonella in the environment: A review on ecology, antimicrobial resistance, seafood contaminations, and human health implications. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- About Salmonella Infection. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/about/index.html (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Chenu, J.; Cox, J.; Pavic, A. Classification of Salmonella enterica serotypes from Australian poultry using repetitive sequence-based PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.A.; Eade, C.R.; Wiedmann, M. Embracing diversity: Differences in virulence mechanisms, disease severity, and host adaptations contribute to the success of nontyphoidal Salmonella as a foodborne pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, C.; Macklin, K.; Kumar, S.; Bailey, M.; Ebner, P.; Oliver, H.; Martin-Gonzalez, F.; Singh, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella isolated from poultry farms in southeastern United States. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, C.L.; Peek, S.F. Salmonella in dairy cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2017, 34, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, Y.; Orsi, R.H.; Rodriguez-Rivera, L.D.; Sun, Q.; Wiedmann, M. Genome wide evolutionary analyses reveal serotype specific patterns of positive selection in selected Salmonella serotypes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, H.; Chowdhury, M.S.R.; Hossain, M.M.; Saleh, A.; Binsuwaidan, R.; Noreddin, A.; Helmy, Y.A.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamases-producing Salmonella enterica serovars enteritidis and typhimurium isolated from raw meat in retail markets. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, B.; Mawad, A.M.; Saleh, M.; Kelley, W.G.; Harrington, P.J.; Lovestad, C.W.; Amezcua, J.; Sarhan, M.M.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Ramadan, H. Salmonellosis: An overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and innovative approaches to mitigate the antimicrobial resistant infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, A.; Wu, C.-J.; Dulanto Chiang, A.; Youn, J.-H.; Khil, P.; Dekker, J. In vivo evolution of an emerging zoonotic bacterial pathogen in an immunocompromised human host. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowright, R.K.; Parrish, C.R.; McCallum, H.; Hudson, P.J.; Ko, A.I.; Graham, A.L.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Pathways to zoonotic spillover. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentum, K.E.; Kuufire, E.; Nyarku, R.; Osei, V.; Price, S.; Bourassa, D.; Samuel, T.; Jackson, C.R.; Abebe, W. Salmonellosis in Cattle: Sources and Risk of Infection, Control, and Prevention. Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, V.; Heithoff, D.; Mahan, M.; Walker, K.; Hornitzky, M.; Shum, L.; Makin, K.; House, J. Cross-protective immunity conferred by a DNA adenine methylase deficient Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine in calves challenged with Salmonella serovar Newport. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.P. Large Animal Internal Medicine-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Divers, T.J.; Peek, S.F. Rebhun’s Diseases of Dairy Cattle; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Alenazy, R. Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella: Targeting multidrug resistance by understanding efflux pumps, regulators and the inhibitors. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Grass, J.; Richardson, L.; Nisler, A.; Bicknese, A.; Gould, L. Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella that caused foodborne disease outbreaks: United States, 2003–2012. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, T.; Yin, L.; Latif, M.B.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Geng, Y.; Huang, X.; Abaidullah, M.; Guo, H.; Ouyang, P. Adhesive mechanism of different Salmonella fimbrial adhesins. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, S.; Huang, K.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, R. Salmonella pSLT-encoded effector SpvB promotes RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, C.M.; Pearson, J.S.; Howden, B.P.; Williamson, D.A.; Ingle, D.J. Salmonella pathogenicity islands in the genomic era. Trends Microbiol. 2025, 33, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulig, P.A. Virulence plasmids of Salmonella typhimurium and other salmonellae. Microb. Pathog. 1990, 8, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campioni, F.; Vilela, F.P.; Cao, G.; Kastanis, G.; dos Prazeres Rodrigues, D.; Costa, R.G.; Tiba-Casas, M.R.; Yin, L.; Allard, M.; Falcão, J.P. Whole genome sequencing analyses revealed that Salmonella enterica serovar Dublin strains from Brazil belonged to two predominant clades. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, J.; Szabo, I.; Tausch, S.H.; Deneke, C.; Methner, U. Clonal relation between Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Dublin strains of bovine and food origin in Germany. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1081611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Mylona, E.; Frankel, G. Typhoidal Salmonella: Distinctive virulence factors and pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, E.A.; Ochman, H. How Salmonella became a pathogen. Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, L.; Betancor, L.; Martínez, A.; Bryant, C.; Maskell, D.; Chabalgoity, J.A. Naturally occurring motility-defective mutants of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolated preferentially from nonhuman rather than human sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7740–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, S.L.; Brumell, J.H.; Pfeifer, C.G.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella pathogenicity islands: Big virulence in small packages. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamamura, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Uchida, I. Characterization of pertussis-like toxin from Salmonella spp. that catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of G proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampari, E.; Holden, E.; Wickham, G.; Ravi, A.; Martins, L.d.O.; Savva, G.; Webber, M. Exposure of Salmonella biofilms to antibiotic concentrations rapidly selects resistance with collateral tradeoffs. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The biofilm life cycle: Expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Paulsen, I.T.; Kjelleberg, S.; Gillings, M.R. Three faces of biofilms: A microbial lifestyle, a nascent multicellular organism, and an incubator for diversity. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robi, D.T.; Mossie, T.; Temteme, S. A comprehensive review of the common bacterial infections in dairy calves and advanced strategies for health management. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2024, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Hawwas, H.A.E.-H.; Ghosh, S.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Moawad, M.M.; Saied, E.M.; Kassem, I.I.; Mawad, A.M. Antimicrobial resistance and recent alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial pathogens with an emphasis on foodborne pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentucky Agriculture Expects Highs and Lows in 2025. Available online: https://news.ca.uky.edu/article/kentucky-agriculture-expects-highs-and-lows-2025 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- das Mercês Santos, A.F.; Amparo, L.F.V.; Machado, S.C.A.; Dias, T.S.; Berto, L.H.; da Costa Abreu, D.L.; de Aquino, M.H.C.; dos Prazeres Rodrigues, D.; de Almeida Pereira, V.L. Salmonella serovars associated with human salmonellosis in Brazil (2011–2020). Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e28011830533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Kelley, W.G.; Glover, C.; Erol, E.; Helmy, Y.A. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of antimicrobial resistance and virulence profiles of Salmonella enterica serotypes isolated from necropsied horses in Kentucky. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e02501–e02524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obe, T.; Nannapaneni, R.; Sharma, C.S.; Kiess, A. Homologous stress adaptation, antibiotic resistance, and biofilm forming ability of Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg ATCC8326 on different food-contact surfaces following exposure to sublethal chlorine concentrations. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, D.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Deng, Y. Crystal violet and XTT assays on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm quantification. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Prakash, P.; Achra, A.; Singh, G.P.; Das, A.; Singh, R.K. Standardization and classification of in vitro biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Partridge, J.D.; Harshey, R.M. Swarming motility assays in Salmonella. In Bacterial and Archaeal Motility; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle, B.W.; Bearson, B.L.; Bearson, S.M.; Casey, T.A. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium isolates are resistant to antibiotics that influence their swimming and swarming motility. MSphere 2017, 2, e00306–e00317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, D.B. A field guide to bacterial swarming motility. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittsler, R.P.; Sandholzer, L.A. The use of semi-solid agar for the detection of bacterial motility. J. Bacteriol. 1936, 31, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shryock, T.R. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals: Approved Standard; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, J.A.; Irfan, A.; Soni, S.; Maherchandani, S.; Soni, S.; Maherchandani, S. Antibiogram and multiple antibiotic resistance index of Salmonella enterica isolates from poultry. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Mthembu, T.P.; Zishiri, O.T.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Molecular detection of multidrug-resistant Salmonella isolated from livestock production systems in South Africa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3537–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.; Brown, P.D. Multiple antibiotic resistance index, fitness and virulence potential in respiratory Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Jamaica. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.; Giske, C.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashoma, I.P.; Kassem, I.I.; John, J.; Kessy, B.M.; Gebreyes, W.; Kazwala, R.R.; Rajashekara, G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter isolated from dressed beef carcasses and raw milk in Tanzania. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailu, W.; Helmy, Y.A.; Carney-Knisely, G.; Kauffman, M.; Fraga, D.; Rajashekara, G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of foodborne pathogens isolated from dairy cattle and poultry manure amended farms in northeastern Ohio, the United States. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, H.; Hossain, A. R package to estimate intracluster correlation coefficient with confidence interval for binary data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 155, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Hübschmann, D. Make interactive complex heatmaps in R. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V.; Levy, M.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zemla, J. Package ‘corrplot’. Statistician 2017, 56, e24. [Google Scholar]
- Eng, S.-K.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Ser, H.-L.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.A.; Maculloch, B.; Batz, M. Economic Burden of Major Foodborne Illnesses Acquired in the United States; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.J.; Kelly, E.J.; Gucwa, S. Causes of mortality of dairy cattle diagnosed by complete necropsy. Animals 2022, 12, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutema, F.D.; Agga, G.E.; Abdi, R.D.; De Zutter, L.; Duchateau, L.; Gabriël, S. Prevalence and serotype diversity of Salmonella in apparently healthy cattle: Systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies, 2000–2017. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, K.J.; Siler, J.D.; Abou-Madi, N.; Goodman, L.B.; Mitchell, P.K.; Palena, L.; Childs-Sanford, S.E. Salmonella isolated from Central New York wildlife admitted to a veterinary medical teaching hospital. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimschuessel, R.; Grabenstein, M.; Guag, J.; Nemser, S.M.; Song, K.; Qiu, J.; Clothier, K.A.; Byrne, B.A.; Marks, S.L.; Cadmus, K. Multilaboratory survey to evaluate Salmonella prevalence in diarrheic and nondiarrheic dogs and cats in the United States between 2012 and 2014. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, F.; Ventura, G.; Rosignoli, C.; Rota Nodari, S.; D’incau, M.; Marocchi, L.; Santucci, G.; Boldini, M.; Gradassi, M. Detection and phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serotypes in dairy cattle farms in the Po valley, Northern Italy. Animals 2024, 14, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, D.; Loneragan, G.; Brown, T.; Nisbet, D.; Hume, M.; Edrington, T. Evidence supporting vertical transmission of Salmonella in dairy cattle. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same species, different diseases: How and why typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauxe, R.V.; Doyle, M.P.; Kuchenmüller, T.; Schlundt, J.; Stein, C. Evolving public health approaches to the global challenge of foodborne infections. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S16–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, K.; Warnick, L.; Alexander, K.; Cripps, C.; Gröhn, Y.; McDonough, P.; Nydam, D.; Reed, K. The incidence of salmonellosis among dairy herds in the northeastern United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3766–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossler, C.; Wells, S.; Kaneene, J.; Ruegg, P.; Warnick, L.; Eberly, L.; Godden, S.; Halbert, L.; Campbell, A.; Bolin, C. Cattle and environmental sample-level factors associated with the presence of Salmonella in a multi-state study of conventional and organic dairy farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 67, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, A.; Robertsson, J. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: Cell-mediated and humoral immune reactions before and after challenge with live virulent bacteria in calves given live or inactivated vaccines. Infect. Immun. 1983, 41, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhou, D. Organoid and enteroid modeling of Salmonella infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.W.; Keestra, A.M.; Winter, S.E.; Xavier, M.N.; Tsolis, R.M.; Tolstikov, V.; Bäumler, A.J. Very long O-antigen chains enhance fitness during Salmonella-induced colitis by increasing bile resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.M.; Pereira, R.V.; Toohey-Kurth, K.; Marshall, E.; Tucker, J.; Clothier, K.A. Salmonella enterica serovar Dublin from cattle in California from 1993–2019: Antimicrobial resistance trends of clinical relevance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, J.; Huisman, J.S.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Multidrug resistance dynamics in Salmonella in food animals in the United States: An analysis of genomes from public databases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Doblies, D.; Speed, K.; Kidd, S.; Davies, R. Salmonella Typhimurium in livestock in Great Britain–trends observed over a 32-year period. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burson, W.C. Confined Versus Conventional Cow-Calf Management Systems: Implications for Calf Health. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rabsch, W.; Andrews, H.L.; Kingsley, R.A.; Prager, R.; Tschäpe, H.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and its host-adapted variants. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Kabir, A.; Saleh, M.; Kennedy, L.A.; Burns, L.; Johnson, B. Draft genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Mbandaka harboring colistin resistance gene mcr-9.1 isolated from foals in Kentucky, USA. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024, 13, e00724–e00737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perov, S.; Lidor, O.; Salinas, N.; Golan, N.; Tayeb-Fligelman, E.; Deshmukh, M.; Willbold, D.; Landau, M. Structural insights into curli CsgA cross-β fibril architecture inspire repurposing of anti-amyloid compounds as anti-biofilm agents. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hag, M.; Feng, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yassin, A.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Contribution of the csgA and bcsA genes to Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum biofilm formation and virulence. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yin, M.; Chen, J.; Li, X. Assembly and substrate recognition of curli biogenesis system. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.; Azim, S.; Ali, A.; Andleeb, S.; Ahsan, A.; Imran, M.; Rahman, A. Antimicrobial resistance profiling of biofilm forming non typhoidal Salmonella enterica isolates from poultry and its associated food products from Pakistan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.d.O.; Freitas, O.C.d.; Batista, D.F.A.; Almeida, A.M.d.; Rubio, M.d.S.; Alves, L.B.R.; Vasconcelos, R.d.O.; Barrow, P.A.; Berchieri, A. Contribution of flagella and motility to gut colonisation and pathogenicity of Salmonella Enteritidis in the chicken. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, J.D.; Harshey, R.M. Swarming: Flexible roaming plans. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernday, A.; Krabbe, M.; Braaten, B.; Low, D. Self-perpetuating epigenetic pili switches in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16470–16476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Neoh, H.-M.; Iwamoto, A.; Hiramatsu, K. Coordinated phenotype switching with large-scale chromosome flip-flop inversion observed in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1647–E1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdouri, N.; Ginet, N.; Denis, Y.; Ansaldi, M.; Battesti, A. The prophage-encoded transcriptional regulator AppY has pleiotropic effects on E. coli physiology. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.R.; Kingsley, R.A. Evolution of Salmonella within hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-S.; Lo, T.-H.; Tu, T.-J.; Chueh, D.-Y.; Yao, C.-I.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, P.; Liu, F.-T. Cytosolic galectin-4 enchains bacteria, restricts their motility, and promotes inflammasome activation in intestinal epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2207091120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazza, N.C.; Merritt, J.H.; Brothers, K.M.; O’Toole, G.A. Inverse regulation of biofilm formation and swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3603–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, J.D.; Chopp, D.L.; Just, C.L.; Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M.; Parsek, M.R. The impact of quorum sensing and swarming motility on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation is nutritionally conditional. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalai Chelvam, K.; Chai, L.C.; Thong, K.L. Variations in motility and biofilm formation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Gut Pathog. 2014, 6, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, T.; Zamirnasta, M.; Sani, M.A.; Soltan Dallal, M.M.; Nasser, A. Molecular mechanisms of Salmonella effector proteins: A comprehensive review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, M.A.; Jones, B.D. The fimYZ genes regulate Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invasion in addition to type 1 fimbrial expression and bacterial motility. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ren, Q.; Ni, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, Z.; Luo, R.; Li, Z.; Li, S. Strategies adopted by Salmonella to survive in host: A review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänisch, J.; Ehinger, J.; Ladwein, M.; Rohde, M.; Derivery, E.; Bosse, T.; Steffen, A.; Bumann, D.; Misselwitz, B.; Hardt, W.D. Molecular dissection of Salmonella-induced membrane ruffling versus invasion. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorvel, J.-P.; Méresse, S. Maturation steps of the Salmonella-containing vacuole. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olekhnovich, I.N.; Kadner, R.J. Crucial roles of both flanking sequences in silencing of the hilA promoter in Salmonella enterica. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, P.; Thomas, J.; Thompson, J.A.; Liu, M.; Arbibe, L.; Sansonetti, P.; Holden, D.W. SpvC is a Salmonella effector with phosphothreonine lyase activity on host mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Angel, C.; Craig, M.; Osman, M.; Cummings, K.J.; Cazer, C.L. Antimicrobial use regulations are associated with increased susceptibility among bovine Salmonella isolates from a US surveillance system. One Health 2025, 20, 100983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.; Carranza, A.; Alvarez, J.; Pichel, M.; Tamiozzo, P.; Busso, J.; Ambrogi, A. Spatial distribution and risk factors associated with Salmonella enterica in pigs. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez-Munoz, A.; Castro-Vargas, R.; Cullens-Nobis, F.M.; Mani, R.; Abuelo, A. Salmonella Dublin in dairy cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 10, 1331767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srednik, M.E.; Lantz, K.; Hicks, J.A.; Morningstar-Shaw, B.R.; Mackie, T.A.; Schlater, L.K. Antimicrobial resistance and genomic characterization of Salmonella Dublin isolates in cattle from the United States. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.K.; Roy, A.K. High Prevalence of metal resistant genes in Salmonella enterica MDR Plasmids correlates severe toxicities of water with higher Typhoid AMR. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rather, P.; Munayyer, H.; Mann, P.; Hare, R.; Miller, G.; Shaw, K. Genetic analysis of bacterial acetyltransferases: Identification of amino acids determining the specificities of the aminoglycoside 6’-N-acetyltransferase Ib and IIa proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mansour, M.N.; Yaghi, J.; El Khoury, A.; Felten, A.; Mistou, M.-Y.; Atoui, A.; Radomski, N. Prediction of Salmonella serovars isolated from clinical and food matrices in Lebanon and genomic-based investigation focusing on Enteritidis serovar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, K.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Du, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Song, H. Genetic characterization of a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium isolated from an infant with concurrent resistance to ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin and azithromycin. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 35, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.; Poelstra, J.W.; Kauffman, M.; Varghese, B.; Helmy, Y.A.; Scaria, J.; Rajashekara, G. Genomic diversity, antimicrobial resistance, plasmidome, and virulence profiles of Salmonella isolated from small specialty crop farms revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingault, J.-B.; Richmond, R.; Smith, G.D. Causal inference with genetic data: Past, present, and future. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2022, 12, a041271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? J. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closs Jr, G.; Bhandari, M.; Helmy, Y.A.; Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Jung, K.; Suazo, I.D.; Srivastava, V.; Deblais, L.; Rajashekara, G. The probiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation reduces Salmonella load and modulates growth, intestinal morphology, gut microbiota, and immune responses in chickens. Infect. Immun. 2025, 93, e00420–e00424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblais, L.; Helmy, Y.A.; Kathayat, D.; Huang, H.-c.; Miller, S.A.; Rajashekara, G. Novel imidazole and methoxybenzylamine growth inhibitors affecting Salmonella cell envelope integrity and its persistence in chickens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazl, A.A.; Salehi, T.Z.; Jamshidian, M.; Amini, K.; Jangjou, A.H. Molecular detection of invA, ssaP, sseC and pipB genes in Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from human and poultry in Iran. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yan, C.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lv, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Elkins, C.A. Punicalagin Inhibits Salmonella Virulence Factors and Has Anti-Quorum-Sensing Potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6204–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, L.; Liebert, C.A.; Lee, M.D.; Summers, A.O.; White, D.G.; Thayer, S.G.; Maurer, J.J. Incidence and Characterization of Integrons, Genetic Elements Mediating Multiple-Drug Resistance, in Avian Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, C.; Lee, M.D.; Sanchez, S.; Hudson, C.; Phillips, B.; Register, B.; Grady, M.; Liebert, C.; Summers, A.O.; White, D.G.; et al. Incidence of Class 1 and 2 Integrases in Clinical and Commensal Bacteria from Livestock, Companion Animals, and Exotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, N.K.; Akan, M. Molecular analysis of virulence genes of Salmonella Infantis isolated from chickens and turkeys. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, Y.; Mehr, I.; Ouzari, H.; Khessairi, A.; Hassen, A. Molecular typing, antibiotic resistance, virulence gene and biofilm formation of different Salmonella enterica serotypes. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.E.; Boerlin, P.; Janecko, N.; Lumsden, J.S.; Barker, I.K.; Pearl, D.L.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Jardine, C. Antimicrobial resistance in generic Escherichia coli isolates from wild small mammals living in swine farm, residential, landfill, and natural environments in southern Ontario, Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Cui, H. Inhibitory effect of cold nitrogen plasma on Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm and its application on poultry egg preservation. LWT 2020, 126, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Abdelhamid, A.G.; Sabag-Daigle, A.; Sovic, M.G.; Ahmer, B.M.; Yousef, A.E. The Role of Egg Yolk in Modulating the Virulence of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 903979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassena, A.B.; Barkallah, M.; Fendri, I.; Grosset, N.; Neila, I.B.; Gautier, M.; Gdoura, R. Real time PCR gene profiling and detection of Salmonella using a novel target: The siiA gene. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 109, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearson, B.L.; Bearson, S.M. The role of the QseC quorum-sensing sensor kinase in colonization and norepinephrine-enhanced motility of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 44, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, V. Detection of Salmonella in Blood by PCR using iroB gene. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, DC01-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, T.; Zhu, C.; Shah, C.; Upadhyaya, I.; Upadhyay, A. Trans-cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion reduces Salmonella Enteritidis biofilm on steel and plastic surfaces and downregulates expression of biofilm associated genes. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wen, J.; Gao, Y.; Liao, M.; et al. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, virulence genes and genetic diversity of Salmonella isolated from retail duck meat in southern China. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Xu, J.W.; Gao, M.; Li, X.S.; Zhai, Y.J.; Yu, K.; Wan, M.; Luan, X.H. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolates from goose farms in Northeast China. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 21, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Asgharpour, F.; Mahmoud, S.; Marashi, A.; Moulana, Z. Molecular detection of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons and some antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella Infantis isolates. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2018, 10, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Chuanchuen, R.; Padungtod, P. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica Isolates from Poultry and Swine in Thailand. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, A.R.; Bortolaia, V.; Kjeldgaard, J.S.; Pedersen, S.K.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hansen, I.M.; Guerra, B.; Malorny, B.; Borowiak, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; et al. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance determinants, mcr-1, mcr-2, mcr-3, mcr-4 and mcr-5 for surveillance purposes. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00672-39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiak, M.; Fischer, J.; A Hammerl, J.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Szabo, I.; Malorny, B. Identification of a novel transposon-associated phosphoethanolamine transferase gene, mcr-5, conferring colistin resistance in d-tartrate fermenting Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Paratyphi B. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiak, M.; Baumann, B.; Fischer, J.; Thomas, K.; Deneke, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Szabo, I.; Malorny, B. Development of a Novel mcr-6 to mcr-9 Multiplex PCR and Assessment of mcr-1 to mcr-9 Occurrence in Colistin-Resistant Salmonella enterica Isolates From Environment, Feed, Animals and Food (2011–2018) in Germany. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Shu, G.; Fu, H.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Yin, L.; Zhao, L.; Lin, J. Antimicrobial resistance and genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus obtained from food animals in Sichuan Province, China. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Variable | Count (n) | Percentage (%) | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 16 | 59.3 | 40.7–77.8 | 0.4421 |
| Male | 11 | 40.7 | 22.2–59.3 | 0.4421 | |
| Age Group | Neonatal | 3 | 11.1 | 0.0–23.0 | <0.05 |
| Calf | 5 | 18.5 | 3.9–33.2 | <0.05 | |
| Juvenile | 9 | 33.3 | 15.6–51.1 | <0.05 | |
| Adult | 10 | 37 | 18.8–55.3 | <0.05 | |
| Organ | Intestine | 21 | 77.8 | 62.1–93.5 | <0.0001 |
| Liver | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Colon | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Lung | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| Kidney | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| Serotypes | Dublin | 8 | 29.6 | 12.4–46.9 | <0.05 |
| Typhimurium | 3 | 11.1 | 0.0–23.0 | <0.05 | |
| Muenster | 3 | 11.1 | 0.0–23.0 | <0.05 | |
| Montevideo | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Thompson | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Worthington | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Anatum | 2 | 7.4 | 0.0–17.3 | <0.05 | |
| Cerro | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| Hartford | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| Meleagridis | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| Newport | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 | |
| III 38:(k): z35 | 1 | 3.7 | 0.0–10.8 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahmy, N.A.; Karna, S.; Bhusal, A.; Kabir, A.; Erol, E.; Helmy, Y.A. Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Traits of Salmonella enterica Isolated from Cattle: Genotypic and Phenotypic Insights. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070689
Fahmy NA, Karna S, Bhusal A, Kabir A, Erol E, Helmy YA. Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Traits of Salmonella enterica Isolated from Cattle: Genotypic and Phenotypic Insights. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070689
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahmy, Nada A., Sumin Karna, Angel Bhusal, Ajran Kabir, Erdal Erol, and Yosra A. Helmy. 2025. "Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Traits of Salmonella enterica Isolated from Cattle: Genotypic and Phenotypic Insights" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070689
APA StyleFahmy, N. A., Karna, S., Bhusal, A., Kabir, A., Erol, E., & Helmy, Y. A. (2025). Multidrug Resistance and Virulence Traits of Salmonella enterica Isolated from Cattle: Genotypic and Phenotypic Insights. Antibiotics, 14(7), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070689








