Antimicrobial Performance of a Novel Drug-Eluting Bioenvelope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
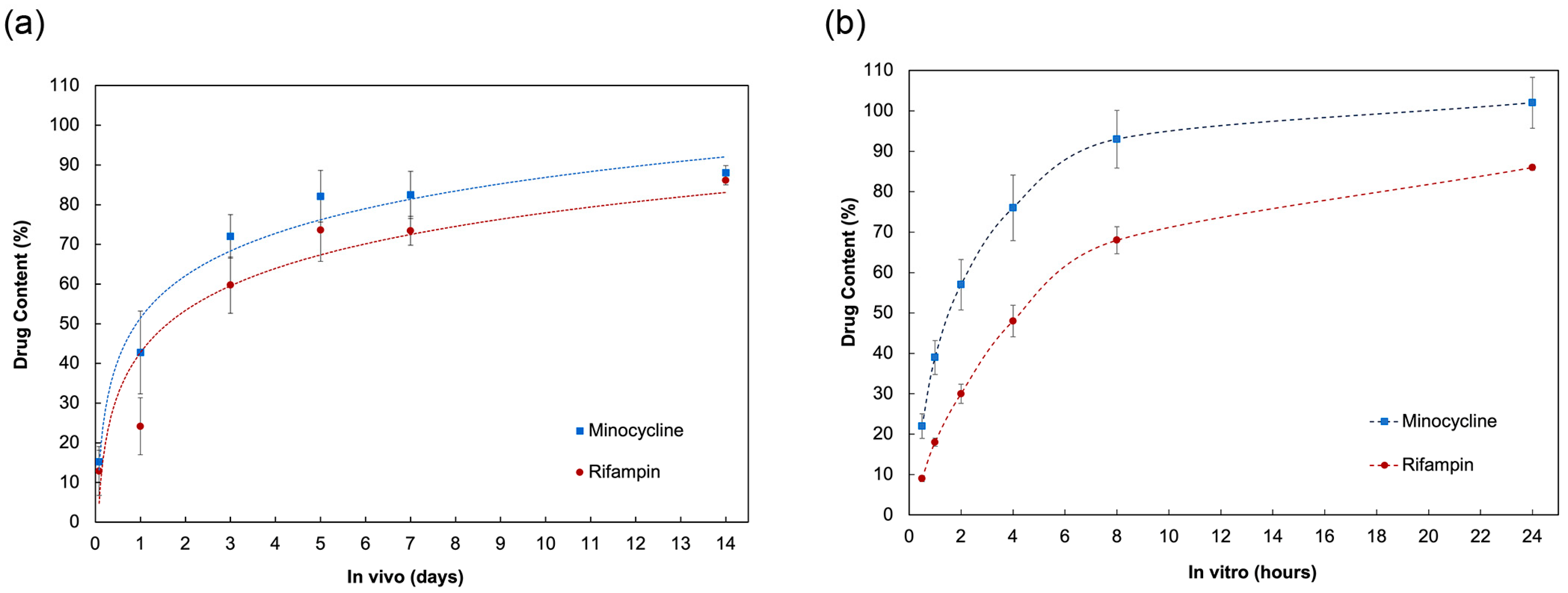
2.1. In Vivo Animal Pharmacokinetics Study
2.2. In Vitro Elution of Antibiotics
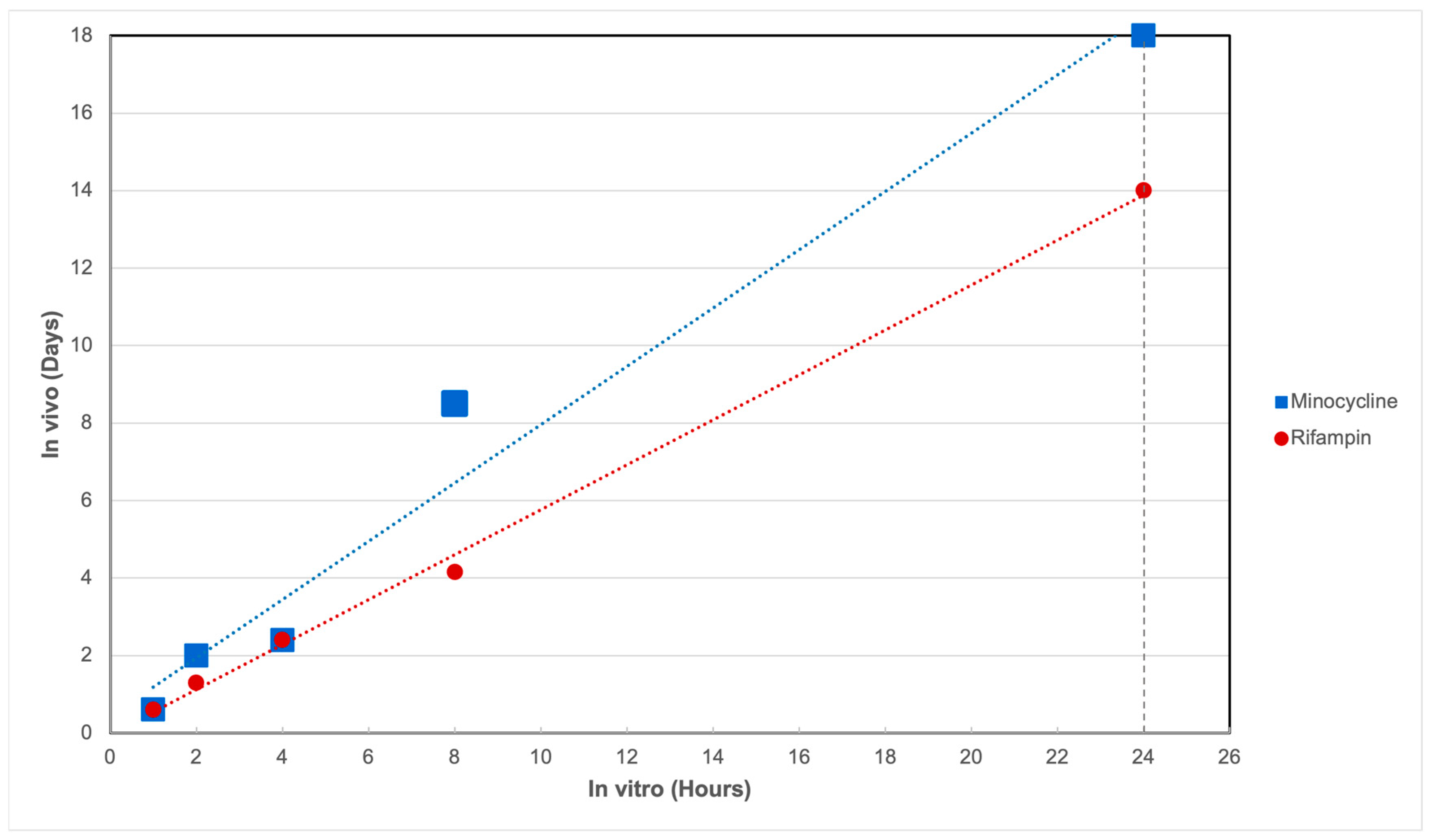
2.3. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation
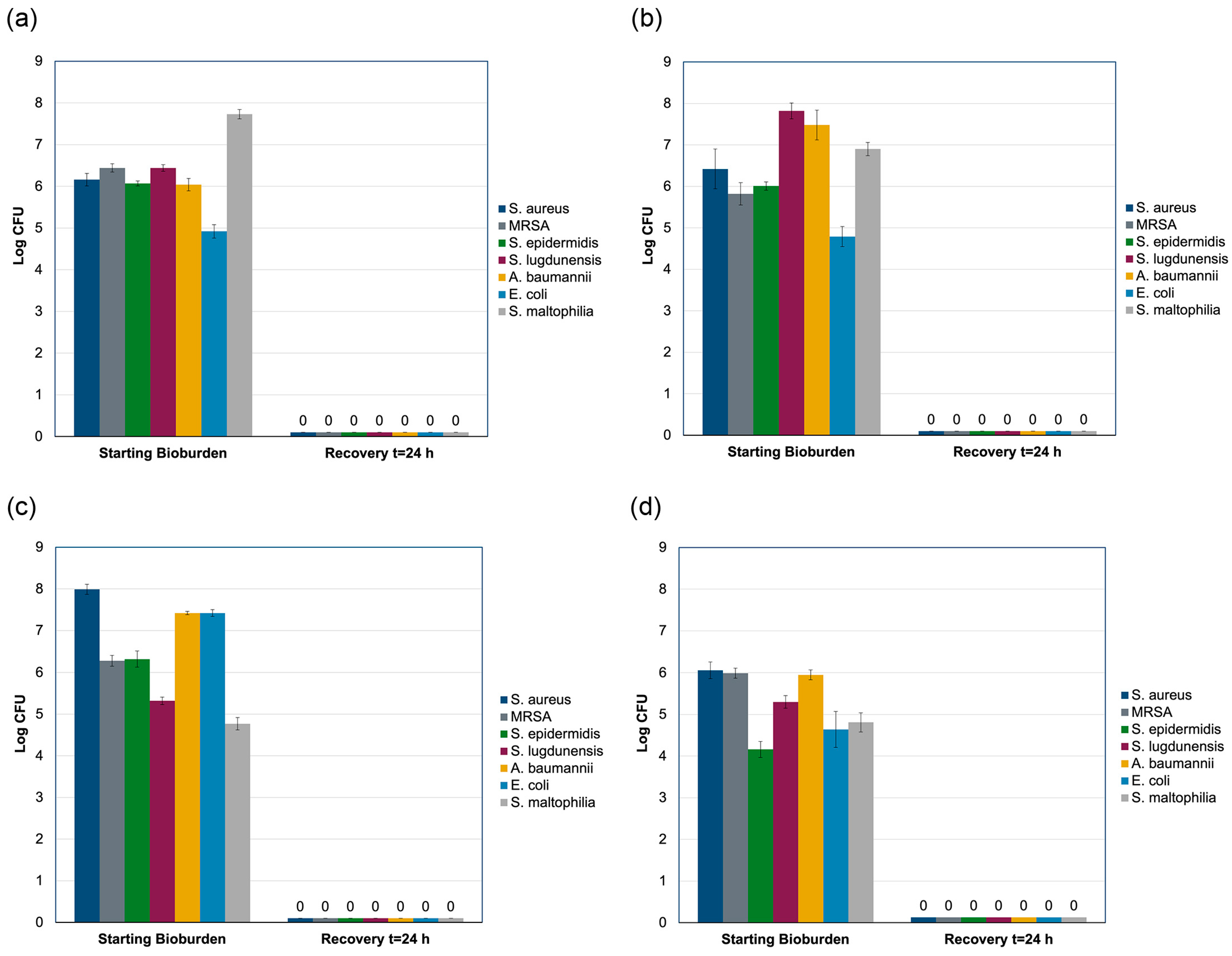
2.4. Modified AATCC Test Method 100 Study
3. Discussion
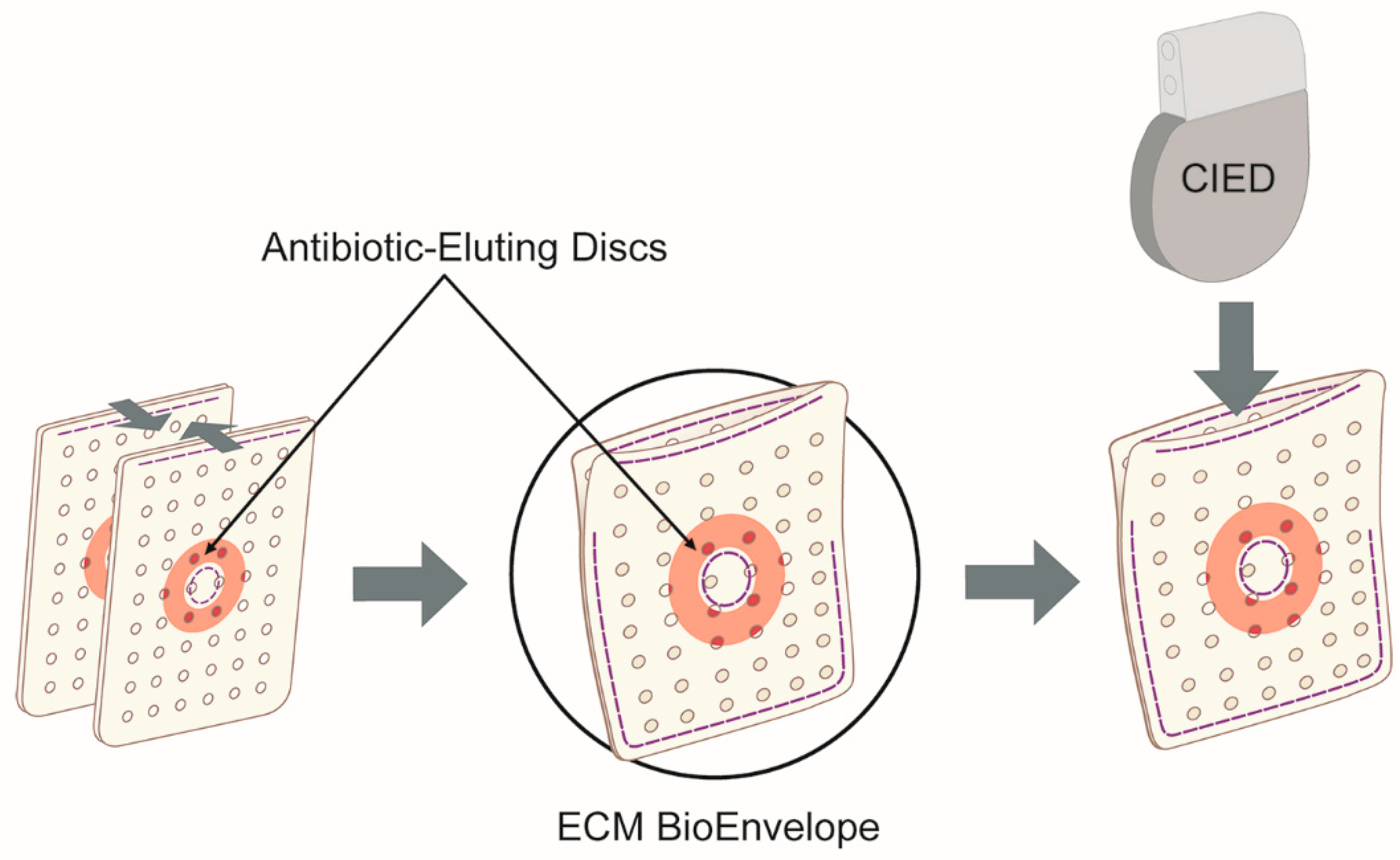
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics Study
4.2. In Vitro Elution of Antibiotics
4.3. HPLC-UV Quantification
4.4. Determination of In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation
4.5. Preconditioning
4.6. Modified AATCC Test Method 100 Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poole, J.E.; Gleva, M.J.; Mela, T.; Chung, M.K.; Uslan, D.Z.; Borge, R.; Gottipaty, V.; Shinn, T.; Dan, D.; Feldman, L.A.; et al. Complication rates associated with pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator generator replacements and upgrade procedures: Results from the REPLACE registry. Circulation 2010, 122, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.C.; Hawkins, N.M.; Pearman, C.M.; Birnie, D.H.; Krahn, A.D. Epidemiology of cardiac implantable electronic device infections: Incidence and risk factors. Europace 2021, 23 (Suppl. 4), iv3–iv10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.R.; Eby, E.L.; Ryan, M.P.; Gunnarsson, C.; Wright, L.A.; Greenspon, A.J. Incidence, Treatment Intensity, and Incremental Annual Expenditures for Patients Experiencing a Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infection: Evidence From a Large US Payer Database 1-Year Post Implantation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e003929. [Google Scholar]
- Deering, T.F.; Chang, C.; Snyder, C.; Natarajan, S.K.; Matheny, R. Enhanced Antimicrobial Effects of Decellularized Extracellular Matrix (CorMatrix) with Added Vancomycin and Gentamicin for Device Implant Protection. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 40, 615–623. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, M.R.; Esquer Garrigos, Z.; Elayi, C.S.; Xiang, K.; Catanzaro, J.N. Preclinical evaluation of efficacy and pharmacokinetics of gentamicin containing extracellular-matrix envelope. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 43, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, S.M.; Tennent, D.J.; Lofgren, A.L.; Wenke, J.C. Topical rifampin powder for orthopaedic trauma part II: Topical rifampin allows for spontaneous bone healing in sterile and contaminated wounds. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarakji, K.G.; Mittal, S.; Kennergren, C.; Corey, R.; Poole, J.E.; Schloss, E.; Gallastegui, J.; Pickett, R.A.; Evonich, R.; Philippon, F.; et al. Antibacterial Envelope to Prevent Cardiac Implantable Device Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.; Teixeira, P.; Ceri, H.; Oliveira, R. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of certain combinations of antibiotics against in vitro Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 542–547. [Google Scholar]
- Bowker, K.E.; Noel, A.R.; Macgowan, A.P. Pharmacodynamics of minocycline against Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4370–4373. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, K.; Catanzaro, J.N.; Elayi, C.; Esquer Garrigos, Z.; Sohail, M.R. Antibiotic-Eluting Envelopes to Prevent Cardiac-Implantable Electronic Device Infection: Past, Present, and Future. Cureus 2021, 13, e13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badylak, S.F.; Freytes, D.O.; Gilbert, T.W. Reprint of: Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23 (Suppl. 1), S17–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.N.; Badylak, S.F. Extracellular matrix as an inductive scaffold for functional tissue reconstruction. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists. TM 100 Test Method for Antibacterial Finishes on Textile Materials: Assessment 2019. Available online: https://members.aatcc.org/store/tm100/513/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Lee, S.H.; Glover, T.; Lavey, N.; Fu, X.; Donohue, M.; Karunasena, E. Modified in-vitro AATCC-100 procedure to measure viable bacteria from wound dressings. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellinghoff, S.C.; Bruns, C.; Albertsmeier, M.; Ankert, J.; Bernard, L.; Budin, S.; Bataille, C.; Classen, A.Y.; Cornely, F.B.; Couvé-Deacon, E.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus surgical site infection rates in 5 European countries. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalot, M.A.; Bahuva, R.; Pandey, R.; Farooq, W.; Mir, A.; Khan, A.; Kerling, D.; Aftab, H.; Kovacs, A.; Gupta, S.; et al. Risk factors associated with higher mortality in patients with cardiac implantable electronic device infection. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, S.M.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Edmond, M.B. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Epstein, A.E.; Erickson, C.C.; Knight, B.P.; Levison, M.E.; Lockhart, P.B.; Masoudi, F.A.; Okum, E.J.; Wilson, W.R.; Beerman, L.B.; et al. Update on cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections and their management: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Doshi, R.; Shariff, M. Role of antibiotic envelopes in preventing cardiac implantable electronic device infection: A meta-analysis of 14 859 procedures. J. Arrhythm. 2020, 36, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Nadeem, N.; Haq, S.; Thelmo, F.L., Jr.; Abdullah, H.M.; Haas, D.C. Efficacy of antibacterial envelope in prevention of cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections in high-risk patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 315, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerber, S.M.; Turagam, M.K.; Winterfield, J.; Gautam, S.; Gold, M.R. Use of antibiotic envelopes to prevent cardiac implantable electronic device infections: A meta-analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, A.D.; Longtin, Y.; Philippon, F.; Birnie, D.H.; Manlucu, J.; Angaran, P.; Rinne, C.; Coutu, B.; Low, R.A.; Essebag, V.; et al. Prevention of Arrhythmia Device Infection Trial: The PADIT Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3098–3109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, J.; Vargas-Cruz, N.; Reitzel, R.A.; Raad, I.I. Assessment of the Potential for Inducing Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Organisms from Exposure to Minocycline, Rifampin, and Chlorhexidine Used To Treat Intravascular Devices. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00040-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, N.; Skovdal, S.; Meyer, R.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Fuursted, K.; Petersen, E. Rifampicin-containing combinations are superior to combinations of vancomycin, linezolid and daptomycin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection in vivo and in vitro. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw019. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo, J.A.; Greco, S.C.; Liu, J.; Frisella, M.M.; Deeken, C.R.; Matthews, B.D. Remodeling characteristics and biomechanical properties of a crosslinked versus a non-crosslinked porcine dermis scaffolds in a porcine model of ventral hernia repair. Hernia 2015, 19, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Reing, J.E.; Zhang, L.; Myers-Irvin, J.; Cordero, K.E.; Freytes, D.O.; Heber-Katz, E.; Bedelbaeva, K.; McIntosh, D.; Dewilde, A.; Braunhut, S.J.; et al. Degradation products of extracellular matrix affect cell migration and proliferation. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2009, 15, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Medberry, C.J.; Tottey, S.; Jiang, H.; Johnson, S.A.; Badylak, S.F. Resistance to infection of five different materials in a rat body wall model. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 173, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Milburn, M.L.; Holton, L.H.; Chung, T.L.; Li, E.N.; Bochicchio, G.V.; Goldberg, N.H.; Silverman, R.P. Acellular dermal matrix compared with synthetic implant material for repair of ventral hernia in the setting of peri-operative Staphylococcus aureus implant contamination: A rabbit model. Surg. Infect. 2008, 9, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, E.P.; Reing, J.; Chew, D.; Myers-Irvin, J.M.; Young, E.J.; Badylak, S.F. Antibacterial activity within degradation products of biological scaffolds composed of extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Deegan, D.; Piasecki, S.K.; Riebman, J. An Acellular Biologic Extracellular Matrix Envelope for Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Devices: Preclinical Evaluation. J. Regen. Med. 2022, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.T.; Carruthers, C.A.; Dearth, C.L.; Crapo, P.M.; Huber, A.; Burnsed, O.A.; Londono, R.; Johnson, S.A.; Daly, K.A.; Stahl, E.C.; et al. Polypropylene surgical mesh coated with extracellular matrix mitigates the host foreign body response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, H.; Beaser, A.D.; Aziz, Z.A. Patient Profiles in the Utilization of the CanGaroo(R) Envelope. Cureus 2021, 13, e12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, L.H., 3rd; Chung, T.; Silverman, R.P.; Haerian, H.; Goldberg, N.H.; Burrows, W.M.; Gobin, A.; Butler, C.E. Comparison of acellular dermal matrix and synthetic mesh for lateral chest wall reconstruction in a rabbit model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschke, M.W.; Haufel, J.M.; Scheuer, C.; Menger, M.D. Angiogenic and inflammatory host response to surgical meshes of different mesh architecture and polymer composition. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scislowska-Czarnecka, A.; Pamula, E.; Tlalka, A.; Kolaczkowska, E. Effects of aliphatic polyesters on activation of the immune system: Studies on macrophages. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 715–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, A.M.; Gao, R.; Naot, D.; Coleman, B.; Cornish, J.; Musson, D.S. Induction of immune gene expression and inflammatory mediator release by commonly used surgical suture materials: An experimental in vitro study. Patient Saf. Surg. 2017, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-6:2016; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 6: Tests for Local Effects After Implantation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Hines, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid-controlled-release systems: Experimental and modeling insights. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.K.; Brown, M.; Johnson, D.; Palme Ii, D.F.; Love, C.; Darouiche, R. In vivo model of human pathogen infection and demonstration of efficacy by an antimicrobial pouch for pacing devices. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.R.; Uslan, D.Z.; Khan, A.H.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Stoner, S.; Baddour, L.M. Management and outcome of permanent pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator infections. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Baghdy, Y.; Wazni, O.M.; Brunner, M.P.; Kabbach, G.; Shao, M.; Gordon, S.; Saliba, W.I.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Tarakji, K.G. Microbiology of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakji, K.G.; Chan, E.J.; Cantillon, D.J.; Doonan, A.L.; Hu, T.; Schmitt, S.; Fraser, T.G.; Kim, A.; Gordon, S.M.; Wilkoff, B.L. Cardiac implantable electronic device infections: Presentation, management, and patient outcomes. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichlmaier, M.; Knigina, L.; Kutschka, I.; Bara, C.; Oswald, H.; Klein, G.; Bisdas, T.; Haverich, A. Complete removal as a routine treatment for any cardiovascular implantable electronic device-associated infection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrigos, Z.E.; George, M.P.; Farid, S.; Abu Saleh, O.M.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Mahmood, M.; Friedman, P.A.; Steckelberg, J.M.; DeSimone, D.C.; Wilson, W.R.; et al. Diagnostic evaluation and management of culture-negative cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 933–942. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, L.C.; Visca, P.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of a global pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 71, 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Looney, W.J.; Narita, M.; Muhlemann, K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging opportunist human pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesdachai, S.; Baddour, L.M.; Sohail, M.R.; Palraj, B.R.; Madhavan, M.; Tabaja, H.; Fida, M.; Lahr, B.D.; DeSimone, D.C. Risk of cardiovascular implantable electronic device infection in patients presenting with gram-negative bacteremia. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disc | Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minocycline | Rifampin | Minocycline | Rifampin | |
| Device 1 | 7.0% | 14.7% | 9.6% | 13.4% |
| Device 2 | 6.1% | 12.7% | 9.8% | 11.3% |
| Device 3 | 6.3% | 13.9% | 9.4% | 10.8% |
| Mean | 6.5% | 13.8% | 9.6% | 11.8% |
| Type | Organism | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | Common cause of surgical site infections, including CIED implants in 30–35% of cases | Sohail 2007 [41] Hussein 2016 [42] Tarakji 2010 [43] Pichlmaier 2011 [44] |
| Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) ATCC 335912 | Resistant variant of S. aureus, a significant concern in healthcare settings due to antibiotic resistance | Sohail 2007 [41] | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 35984 | Causative agent in approximately one-third of CIED infections | Sohail 2007 [41] Hussein 2016 [42] Tarakji 2010 [43] | |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis ATCC 49576 | Coagulase-negative staphylococcus associated with skin and soft tissue infections | Sohail 2007 [41] Tarakji 2010 [43] Pichlmaier 2011 [44] | |
| Gram-negative | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | Opportunistic pathogen known for its ability to cause healthcare-associated infections; notable for its resilience and multidrug-resistant nature | Sohail 2007 [41] Antunes 2014 [46] |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia ATCC 17666 | Environmental bacterium with ability to adhere to and colonize medical device surfaces; associated with bloodstream infections and pneumonia | Sohail 2007 [41] Looney 2009 [47] | |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | Pathogen capable of causing infections in various body sites, including the bloodstream and subcutaneous tissues | Chesdachai 2022 [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrigos, Z.E.; Kapur, S.; Williams, M.L.; Sohail, M.R. Antimicrobial Performance of a Novel Drug-Eluting Bioenvelope. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040330
Garrigos ZE, Kapur S, Williams ML, Sohail MR. Antimicrobial Performance of a Novel Drug-Eluting Bioenvelope. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040330
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrigos, Zerelda Esquer, Sunil Kapur, Michelle LeRoux Williams, and M. Rizwan Sohail. 2025. "Antimicrobial Performance of a Novel Drug-Eluting Bioenvelope" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040330
APA StyleGarrigos, Z. E., Kapur, S., Williams, M. L., & Sohail, M. R. (2025). Antimicrobial Performance of a Novel Drug-Eluting Bioenvelope. Antibiotics, 14(4), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040330






