Role of Rifaximin in the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Prevention Cohort
Rifaximin and Risk of ICU Admission
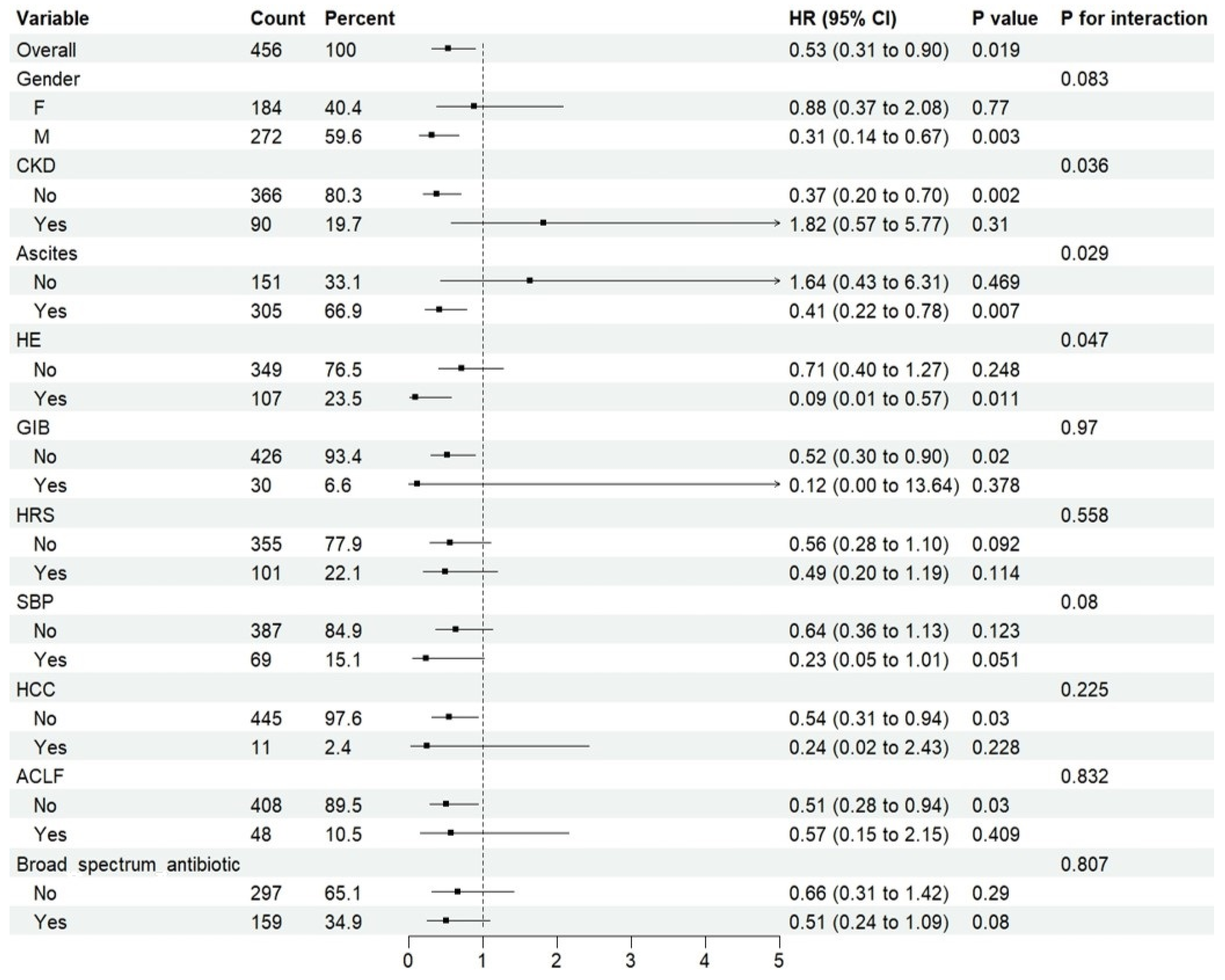
2.3. Treatment Cohort—ICU Sub-Cohort
Rifaximin and Risk of ICU Death
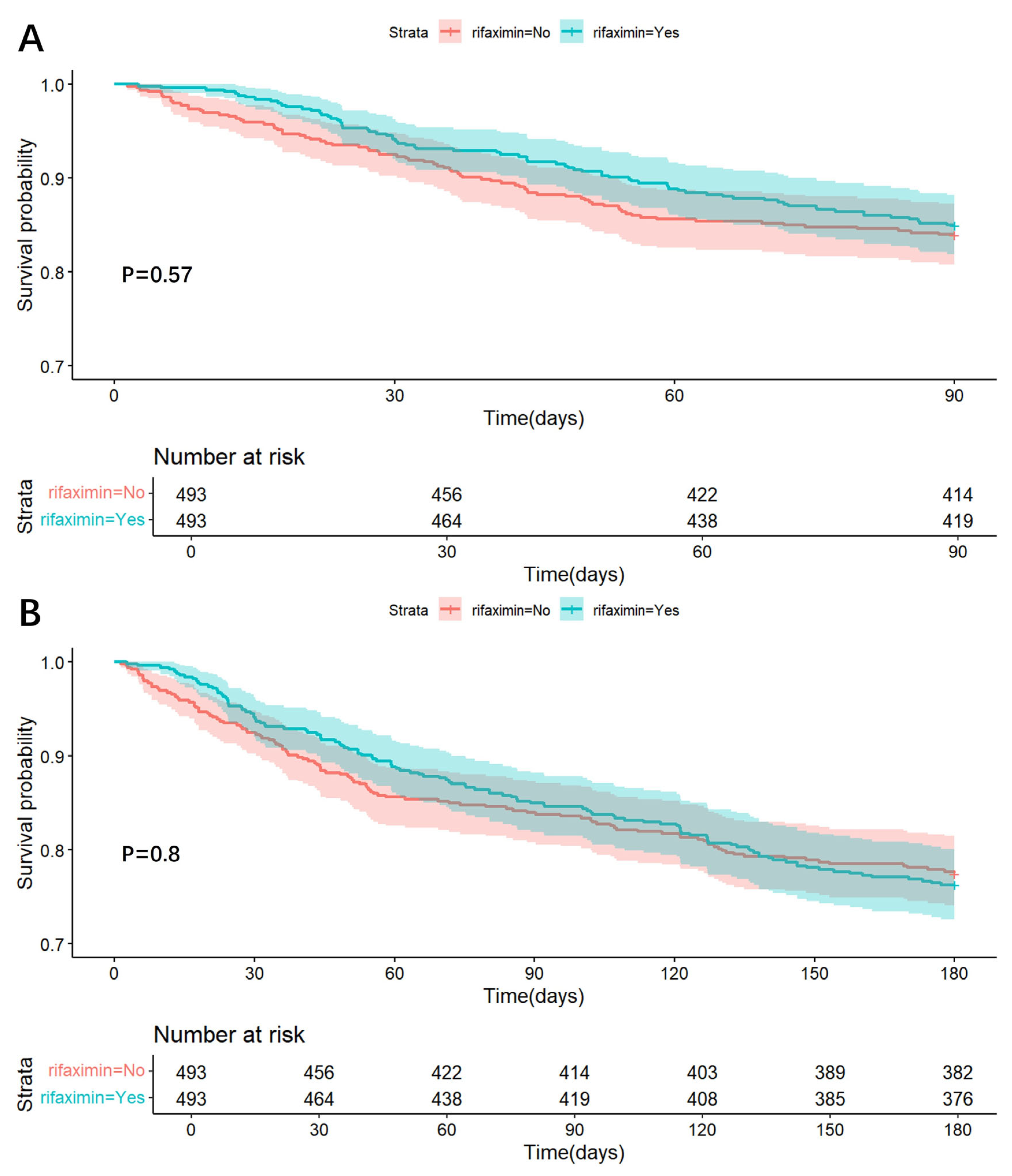
2.4. Treatment Cohort—Non-ICU Sub-Cohort
Rifaximin and Risk of In-Hospital, 90-Day, and 180-Day Death
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source and Study Design
4.2. Variable Extraction and Data Collection
4.3. Definitions and Outcomes
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACLF | Acute-on-chronic liver failure |
| ALB | serum albumin |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| GGT | glutamyl transpeptidase |
| GIB | gastrointestinal bleeding |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HE | hepatic encephalopathy |
| HR | hazard ratios |
| HRS | hepatorenal syndrome |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| INR | international normalized ratio |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| K | potassium |
| MELD | model for end-stage liver disease |
| MICE | multivariate imputation by chained equations |
| MIMIC | medical information mart for intensive care |
| MDR | multi-drug resistant |
| Na | sodium |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| PLT | platelet |
| PSM | propensity score matching |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| RCS | Restricted cubic spline |
| RR | respiratory rate |
| Scr | serum creatinine |
| SBP | spontaneous bacterial peritonitis |
| SOFA | sequential organ failure assessment |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| WBC | white blood cell |
References
- GBD Cirrhosis Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Hao, M.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Jia, X.; Zhang, X.; Dang, S. Global burden of liver cirrhosis 1990–2019 and 20 years forecast: Results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2328521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvellas, C.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Kamath, P.S.; Napolitano, L.; O’Leary, J.G.; Solà, E.; Subramanian, R.; Wong, F.; Asrani, S.K. AASLD Practice Guidance on Acute-on-chronic liver failure and the management of critically ill patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1463–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadim, M.K.; Durand, F.; Kellum, J.A.; Levitsky, J.; O’Leary, J.G.; Karvellas, C.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Davenport, A.; Jalan, R.; Angeli, P.; et al. Management of the critically ill patient with cirrhosis: A multidisciplinary perspective. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Kim, W.R.; Moriarty, J.P.; Shah, N.D.; Larson, J.J.; Kamath, P.S. Time trends in the health care burden and mortality of acute on chronic liver failure in the United States. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.C.; Wendon, J.A.; Kramer, D.J.; Arroyo, V.; Jalan, R.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Kamath, P.S. Intensive care of the patient with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; O’Leary, J.G.; Reddy, K.R.; Wong, F.; Olson, J.C.; Subramanian, R.M.; Brown, G.; Noble, N.A.; Thacker, L.R.; Kamath, P.S.; et al. Second infections independently increase mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis: The North American consortium for the study of end-stage liver disease (NACSELD) experience. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kamath, P.S.; Reddy, K.R. The Evolving Challenge of Infections in Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Bunchorntavakul, C.; Marciano, S.; Rajender Reddy, K. Infections in cirrhosis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, R.; Fernandez, J.; Wiest, R.; Schnabl, B.; Moreau, R.; Angeli, P.; Stadlbauer, V.; Gustot, T.; Bernardi, M.; Canton, R.; et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: A position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, M.; Maraolo, A.E.; Gentile, I.; Borgia, G.; Leone, S.; Sansone, P.; Passavanti, M.B.; Aurilio, C.; Pace, M.C. Current concepts and future strategies in the antimicrobial therapy of emerging Gram-positive spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Prado, V.; Trebicka, J.; Amoros, A.; Gustot, T.; Wiest, R.; Deulofeu, C.; Garcia, E.; Acevedo, J.; Fuhrmann, V.; et al. Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and with acute-on-chronic liver failure in Europe. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, S.; Singh, V.; Caraceni, P.; Maiwall, R.; Alessandria, C.; Fernandez, J.; Soares, E.C.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.E.; Marino, M.; et al. Epidemiology and Effects of Bacterial Infections in Patients With Cirrhosis Worldwide. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1368–1380.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C.; Pelosini, I. Rifaximin, a poorly absorbed antibiotic: Pharmacology and clinical potential. Chemotherapy 2005, 51 (Suppl. 1), 36–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=021361 (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Solà, E.; Alessandria, C.; de Wit, K.; Trebicka, J.; Angeli, P.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Durand, F.; Pose, E.; et al. The Use of Rifaximin in Patients With Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Abraldes, J.G.; Ginès, P.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K. The search for disease-modifying agents in decompensated cirrhosis: From drug repurposing to drug discovery. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. 1), S118–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanchal, R.; Subramanian, R.; Alhazzani, W.; Dionne, J.C.; Peppard, W.J.; Singbartl, K.; Truwit, J.; Al-Khafaji, A.H.; Killian, A.J.; Alquraini, M.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Adult Acute and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in the ICU: Neurology, Peri-Transplant Medicine, Infectious Disease, and Gastroenterology Considerations. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 51, 657–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.A.; Yerke, J.; Lumpkin, M.; Kapoor, A.; Lindenmeyer, C.C.; Bass, S. Evaluation of a protocol for rifaximin discontinuation in critically ill patients with liver disease receiving broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Avadhanam, M.; Karandikar, P.; Rakam, K.; Gupta, A.; Simhadri, V.; Premkumar, M.; Zuberi, A.A.; Gujjarlapudi, D.; Narendran, R.; et al. Antibiotics With or Without Rifaximin for Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy in Critically Ill Patients with Cirrhosis: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled (ARiE) Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücke, M.M.; Mücke, V.T.; Graf, C.; Schwarzkopf, K.M.; Ferstl, P.G.; Fernandez, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Trebicka, J.; Lange, C.M.; Herrmann, E. Efficacy of Norfloxacin Prophylaxis to Prevent Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanvoine, A.; Bouxom, H.; Leroy, J.; Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; Bertrand, X.; Slekovec, C. Resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in Escherichia coli in the French community: The times they are a-changin’? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, Z.H.; Xiao, M.X.; Li, J.K.; Liu, H.Y.; Cai, H.L.; Cao, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.-K.; Yan, M. Analyzing the correlation between quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli resistance rates and climate factors: A comprehensive analysis across 31 Chinese provinces. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Clària, J.; Szabo, G.; Bosch, J.; Bernardi, M. Pathophysiology of decompensated cirrhosis: Portal hypertension, circulatory dysfunction, inflammation, metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. 1), S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.M.; Li, L.; Monk, I.R.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Ingle, D.J.; Portelli, S.; Sherry, N.L.; Isles, N.; Seemann, T.; Sharkey, L.K.; et al. Rifaximin prophylaxis causes resistance to the last-resort antibiotic daptomycin. Nature 2024, 635, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C. Rifaximin in cirrhosis: Is its microbiological spotless record under threat? J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Bulgarelli, L.; Shen, L.; Gayles, A.; Shammout, A.; Horng, S.; Pollard, T.J.; Hao, S.; Moody, B.; Gow, B.; et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.; Obeid, J.S.; Gregoski, M.J.; Rockey, D.C. Accurate Identification of Patients with Cirrhosis and Its Complications in the Electronic Health Record. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, H.; Ma, C.; Sun, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Peng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; et al. Identification of indications for albumin administration in septic patients with liver cirrhosis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Overall (n = 5381) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) (median [IQR]) | 59.67 [52.28, 68.10] |
| Gender (female) (%) | 1894 (35.2) |
| Race (%) | |
| Asian | 173 (3.2) |
| Black | 453 (8.4) |
| White | 3730 (69.3) |
| Other | 1025 (19.0) |
| Admission type (%) | |
| Elective | 78 (1.4) |
| Observation | 916 (17.0) |
| Surgical | 307 (5.7) |
| Urgent | 4080 (75.8) |
| MELD score (median [IQR]) | 14.74 [10.28, 21.08] |
| Hypertension (%) | 1945 (36.1) |
| Diabetes (%) | 1665 (30.9) |
| CKD (%) | 879 (16.3) |
| Infection (%) | 3665 (68.1) |
| Etiology of liver cirrhosis | |
| Viral hepatitis (%) | 1767 (32.8) |
| Alcohol hepatitis (%) | 1336 (24.8) |
| Autoimmune hepatitis (%) | 106 (2.0) |
| NAFLD (%) | 284 (5.3) |
| Ascites (%) | 1891 (35.1) |
| HE (%) | 378 (7.0) |
| GIB (%) | 139 (2.6) |
| HRS (%) | 302 (5.6) |
| HCC (%) | 130 (2.4) |
| ACLF (%) | 146 (2.7) |
| SBP (%) | 267 (5.0) |
| Other liver failure (%) | 578 (10.7) |
| Hb (g/dL) (median [IQR]) | 10.70 [9.10, 12.20] |
| WBC (109/L) (median [IQR]) | 7.10 [4.70, 10.40] |
| PLT (109/L) (median [IQR]) | 118.00 [75.00, 181.00] |
| TBIL (mg/dL) (median [IQR]) | 1.60 [0.80, 4.10] |
| ALT (U/L) (median [IQR]) | 34.00 [21.00, 61.00] |
| AST (U/L) (median [IQR]) | 61.00 [36.00, 114.00] |
| ALB (g/dL) (median [IQR]) | 3.10 [2.60, 3.50] |
| ALP (U/L) (median [IQR]) | 111.00 [78.00, 167.00] |
| Scr (mg/dL) (median [IQR]) | 0.90 [0.70, 1.40] |
| PT (s) (median [IQR]) | 15.60 [13.40, 19.30] |
| INR (median [IQR]) | 1.40 [1.20, 1.80] |
| Na (mmol/L) (median [IQR]) | 137.00 [134.00, 140.00] |
| K (mmol/L) (median [IQR]) | 4.00 [3.60, 4.40] |
| Ventilation (%) | 470 (8.7) |
| Liver transplantation (%) | 26 (0.5) |
| Hemodialysis (%) | 194 (3.6) |
| Rifaximin (%) | 806 (15.0) |
| Monotherapy (%) | 696 (12.9) |
| Broad-spectrum antibiotic (%) | 711 (13.2) |
| Human albumin (%) | 1114 (20.7) |
| Vasoactive agent (%) | 29 (0.5) |
| ICU admission (%) | 1910 (35.5) |
| In-hospital death (%) | 502 (9.3) |
| Outcomes | Crude | Adjusted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| ICU admission | 0.421 | 0.334–0.531 | <0.001 | 0.427 | 0.338–0.539 | <0.001 |
| ICU death | 0.516 | 0.304–0.876 | 0.014 | 0.530 | 0.311–0.902 | 0.019 |
| In-hospital death | 0.141 | 0.040–0.494 | 0.002 | 0.119 | 0.033–0.429 | 0.001 |
| 90-day death | 0.912 | 0.664–1.253 | 0.571 | 0.905 | 0.658–1.245 | 0.541 |
| 180-day death | 1.035 | 0.798–1.342 | 0.796 | 1.043 | 0.804–1.353 | 0.751 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Z.; Li, C.; Lai, Y.; Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Guan, X.; Xu, Y. Role of Rifaximin in the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030287
Bai Z, Li C, Lai Y, Hu X, Shi L, Guan X, Xu Y. Role of Rifaximin in the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(3):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030287
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Zhaohui, Congcong Li, Yongjie Lai, Xiaojuan Hu, Luwen Shi, Xiaodong Guan, and Yang Xu. 2025. "Role of Rifaximin in the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis" Antibiotics 14, no. 3: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030287
APA StyleBai, Z., Li, C., Lai, Y., Hu, X., Shi, L., Guan, X., & Xu, Y. (2025). Role of Rifaximin in the Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Antibiotics, 14(3), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030287










