Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination of Less Frequently Isolated Legionella Species by Broth and Agar Dilution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Legionella Species Growth by Method of MIC Determination
2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.2.1. LASARUS Agar Dilution
2.2.2. Broth Microdilution
2.2.3. BCYE Agar Dilution
2.3. Differences Between Legionella Species
2.4. Agreement of Legionella Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing Methods
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Microbial Culturing
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Ethical Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AST | Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| BCYE | Buffered Charcoal Yeast Extract |
| BMD | Broth Microdilution |
| BYE | Buffered Yeast Extract |
| DWD | Drinking Water Directive |
| ECOFF | Epidemiological Cut-Off Value |
| EUCAST | The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| LASARUS | Legionella Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance Universal Screening Medium |
| LD | Legionnaire’s Disease |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| NCTC | National Collection of Type Cultures |
| UAT | Urine Antigen Test |
| UKHSA | Uk Health Security Agency |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Legionella Species | Sample Origin | Isolates (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type Strain | Clinical | Environmental | ||
| L. anisa | - | - | 14 | 14 |
| L. beliardensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. birminghamensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. bozemanae | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| L. brunensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. busanensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. cherrii | 1 | - | 2 | 3 |
| L. cincinnatiensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. donaldsonii | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. dresdenensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. dumoffii | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| L. erythra | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| L. fairfieldensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. fallonii | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| L. feeleii | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| L. gormanii | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| L. hackeliae | 2 | - | - | 2 |
| L. israelensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. jamestowniensis | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| L. jordanis | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| L. londiniensis | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| L. longbeachae | - | 10 | - | 10 |
| L. maceachernii | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. micdadei | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| L. nautarum | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. oakridgensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. parisiensis | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. pneumophila | 13 | - | - | 13 |
| L. quinlivanii | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| L. rubrilucens | 1 | - | 6 | 7 |
| L. sainthelensi | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| L. shakespearei | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| L. spiritensis | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| L. wadsworthii | - | 1 | - | 1 |
Appendix A.2
| Legionella Species | Serogroup | NCTC | ATCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. beliardensis | - | 13315 | 700512 |
| L. birminghamensis | - | 12437 | 43702 |
| L. brunensis | - | 12240 | 43878 |
| L. busanensis | - | 13316 | BAA-518 |
| L. cherrii | - | 11976 | 35252 |
| L. cincinnatiensis | - | 12438 | 43753 |
| L. donaldsonii | - | - | - |
| L. dresdenensis | - | 13409 | - |
| L. erythra | - | 11977 | 35303 |
| L. fairfieldensis | - | 12488 | 49588 |
| L. feeleii | 1 | 12022 | 35072 |
| L. feeleii | 2 | 11978 | 35849 |
| L. hackeliae | 1 | 11979 | 35250 |
| L. hackeliae | 2 | 11980 | 35999 |
| L. israelensis | - | 12010 | 43119 |
| L. londiniensis | - | 12931 | 49505 |
| L. maceachernii | - | 11982 | 35300 |
| L. nautarum | - | 12932 | 49506 |
| L. oakridgensis | - | 11531 | 33761 |
| L. parisiensis | - | 11983 | 35299 |
| L. pneumophila (Philadelphia 1) | 1 | 11192 | 33152 |
| L. pneumophila (Knoxville-1) | 1 | 11286 | 33153 |
| L. pneumophila (OLDA) | 1 | 12008 | 43109 |
| L. pneumophila (Allentown 1) | 1 | 12024 | 43106 |
| L. pneumophila (Togus 1) | 2 | 11230 | 33154 |
| L. pneumophila (Bloomington-2) | 3 | 11232 | 33155 |
| L. pneumophila (Los Angeles-1) | 4 | 11233 | 33156 |
| L. pneumophila (Chicago-2) | 6 | 11406 | 33215 |
| L. pneumophila (Chicago 8) | 7 | 11984 | 33823 |
| L. pneumophila (Concorde 3) | 8 | 11985 | 35096 |
| L. pneumophila (570-CO-H) | 12 | 12180 | 43290 |
| L. pneumophila (82A3105) | 13 | 12181 | 43736 |
| L. pneumophila (1169-MN-H) | 14 | 12174 | 43703 |
| L. quinlivanii | - | 12433 | 43830 |
| L. rubrilucens | - | 11987 | 35304 |
| L. shakespearei | - | 12829 | 49655 |
References
- Mondino, S.; Schmidt, S.; Rolando, M.; Escoll, P.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Buchrieser, C. Legionnaires’ Disease: State of the Art Knowledge of Pathogenesis Mechanisms of Legionella. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2020, 15, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legionella—LPSN (List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature). Available online: https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/legionella (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Cunha, B.A.; Burillo, A.; Bouza, E. Legionnaires’ Disease. Lancet 2016, 387, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legionellosis in Residents of England and Wales: 2017 to 2023 Report. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/legionellosis-in-residents-of-england-and-wales-2017-to-2023/legionellosis-in-residents-of-england-and-wales-2017-to-2023-report (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- CDC Surveillance Report 2018–2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/legionella/php/surveillance/surveillance-report-2018-2019.html (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Chambers, S.T.; Slow, S.; Scott-Thomas, A.; Murdoch, D.R. Legionellosis Caused by Non-Legionella pneumophila Species, with a Focus on Legionella longbeachae. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussotte, M.; Massy, E. Case Report of Arthritis Caused by Legionella Anisa and Review of the Literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, G.; Rizzo, R.; Lavoro, A.; Spoto, V.; Porciello, G.; Montagnese, C.; Cinà, D.; Cosentino, A.; Lombardo, C.; Mezzatesta, M.L.; et al. Overview of the Clinical and Molecular Features of Legionella pneumophila: Focus on Novel Surveillance and Diagnostic Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viasus, D.; Gaia, V.; Manzur-Barbur, C.; Carratalà, J. Legionnaires’ Disease: Update on Diagnosis and Treatment. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Shames, S.R. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Legionella: Intracellular Replication and Host Response. Virulence 2021, 12, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, H.J.; Ang, D.K.; van Driel, I.R.; Hartland, E.L. Molecular Pathogenesis of Infections Caused by Legionella pneumophila. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S.; Arcari, T.; O’Connor, O. Legionella Water Testing and the EU Drinking Water Directive: Could Potentially Harmful Legionella Bacteria Slip through the Gaps? BioTechniques 2022, 72, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodr, A.; Kay, E.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Ginevra, C.; Doublet, P.; Buchrieser, C.; Jarraud, S. Molecular Epidemiology, Phylogeny and Evolution of Legionella. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the quality of water intended for human consumption (recast) (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, L 435, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, R.; Heilmann, A.; Lother, S.A.; Turenne, C.; Alexander, D.; Keynan, Y.; Rueda, Z.V. The Adequacy of Current Legionnaires’ Disease Diagnostic Practices in Capturing the Epidemiology of Clinically Relevant Legionella: A Scoping Review. Pathogens 2024, 13, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portal, E.; Sands, K.; Portnojs, A.; Chalker, V.J.; Spiller, O.B. Legionella Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing: Comparison of Microbroth Dilution with BCYE and LASARUS Solid Media. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaby, Y.; Nitzan, O.; Brettar, I.; Höfle, M.G.; Peretz, A.; Halpern, M. Antimicrobial Agent Susceptibilities of Legionella pneumophila MLVA-8 Genotypes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocuzza, C.E.; Martinelli, M.; Perdoni, F.; Giubbi, C.; Vinetti, M.E.A.; Calaresu, E.; Frugoni, S.; Scaturro, M.; Ricci, M.L.; Musumeci, R. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Environmental Legionella pneumophila Strains Isolated in Northern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendland, S.L.; Martin, S.J.; Chen, C.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; Danziger, L.H. Comparison of Charcoal- and Starch-Based Media for Testing Susceptibilities of Legionella Species to Macrolides, Azalides, and Fluoroquinolones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3004–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Paul, M.L.; Gilbert, G.L. Susceptibility of Legionella Species to Antimicrobial Agents. Pathology 1993, 25, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, M.; Farley, C.; Portal, E.A.R.; Lindsay, D.; Ricci, M.L.; Jarraud, S.; Scaturro, M.; Descours, G.; Krøvel, A.V.; Barton, R.; et al. Broth Microdilution Protocol for Determining Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to Clinically Relevant Antimicrobials. J. Microbiol. Methods 2025, 228, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portal, E.; Descours, G.; Ginevra, C.; Mentasti, M.; Afshar, B.; Chand, M.; Day, J.; Echahidi, F.; Franzin, L.; Gaia, V.; et al. Legionella Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing: Is It Time for International Standardization and Evidence-Based Guidance? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, S.; Hellebrekers, P.; Leenen, L.P.H.; Koenderman, L.; Hietbrink, F. Intracellular Penetration and Effects of Antibiotics on Staphylococcus Aureus Inside Human Neutrophils: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle-Capo, M.; Massip, C.; Descours, G.; Charavit, J.; Chastang, J.; Billy, P.A.; Boisset, S.; Lina, G.; Gilbert, C.; Maurin, M.; et al. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Distribution among Wild-Type Strains of Legionella pneumophila Identifies a Subpopulation with Reduced Susceptibility to Macrolides Owing to Efflux Pump Genes. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginevra, C.; Beraud, L.; Pionnier, I.; Sallabery, K.; Bentayeb, H.; Simon, B.; Allam, C.; Chastang, J.; Ibranosyan, M.; Decroix, V.; et al. Detection of Highly Macrolide-Resistant Legionella pneumophila Strains from a Hotel Water Network Using Systematic Whole-Genome Sequencing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2167–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Guidance Document on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Legionella pneumophila; European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST): Växjö, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K.; Bangsborg, J.M.; Høiby, N. Susceptibility of Legionella Species to Five Antibiotics and Development of Resistance by Exposure to Erythromycin, Ciprofloxacin, and Rifampicin. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 36, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, A.; Gładysz, I.; Kozioł-Montewka, M.; Wójtowicz-Bobin, M.; Stańczak, T.; Matuszewska, R.; Krogulska, B. Assessment of Antibiotic Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila Isolated from Water Systems in Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schülin, T.; Wennersten, C.B.; Ferraro, M.J.; Moellering, R.C.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Susceptibilities of Legionella Spp. to Newer Antimicrobials In Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.T.; Pelaz, C.; Giménez, M.J.; Aguilar, L. In Vitro Activities of Gemifloxacin versus Five Quinolones and Two Macrolides against 271 Spanish Isolates of Legionella pneumophila: Influence of Charcoal on Susceptibility Test Results. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2176–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendland, S.L.; Losnedahl, K.J.; Schriever, C.A. In-Vitro Activity of Gatifloxacin, a Novel Fluoroquinolone, Compared with That of Ciprofloxacin against Legionella spp. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 44, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, J.W.; Winchell, J.M. Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics for Laboratory and Outbreak Investigations. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 95–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenman, H.; Anderson, T.; Chambers, S.T.; Podmore, R.G.; Murdoch, D.R. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Clinical Legionella longbeachae Isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lus, R.; Adrián, F.; del Campo, R.; Gómez-Lus, P.; Sánchez, S.; García, C.; Rubio, M.C. Comparative in Vitro Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Activity of Trovafloxacin, Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin against Clinical and Environmental Isolates of Legionella spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, G.R.; Bull, J.Z. Comparative Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila and Legionella longbeachae to 12 Antimicrobial Agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1995, 36, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E.; Arnold, B.; Yu, V.L. Comparative Activity of Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin, and Erythromycin Against Legionella Species by Broth Microdilution and Intracellular Susceptibility Testing in HL-60 Cells. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopp, L.H.; Baltch, A.L.; Ritz, W.J.; Michelsen, P.B.; Smith, R.P. Activities of Tigecycline and Comparators against Legionella pneumophila and Legionella Micdadei Extracellularly and in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 69, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Fernandes, F.; Santos, R.; Paixão, P.; Chasqueira, M.J. Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Portuguese Environmental Legionella Isolates. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1141115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, J.E.; Sens, K.; Mietzner, S.; Obman, A.; Yu, V.L. Comparative Activity of Quinolones, Macrolides and Ketolides against Legionella Species Using in Vitro Broth Dilution and Intracellular Susceptibility Testing. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.E.; Hill, R.L.R.; Chalker, V.J.; Mentasti, M.; Ready, D. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila Strains Isolated in England and Wales 2007–17. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2757–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, T.; Bieber, A.; Green, H.; Steinmetz, T.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of PCR Alone and Compared to Urinary Antigen Testing for Detection of Legionella spp.: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Laboratory Testing for Legionella. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/legionella/php/laboratories/index.html (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Pascale, M.R.; Salaris, S.; Mazzotta, M.; Girolamini, L.; Fregni Serpini, G.; Manni, L.; Grottola, A.; Cristino, S. New Insight Regarding Legionella Non-Pneumophila Species Identification: Comparison between the Traditional Mip Gene Classification Scheme and a Newly Proposed Scheme Targeting the rpoB Gene. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01161-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, J.P.; Koshkolda, T.; IJzerman, E.P.F.; Lück, C.; Diederen, B.M.W.; Den Boer, J.W.; Mouton, J.W. Isolation of Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Legionella pneumophila in a Patient with Severe Pneumonia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2869–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadoud, L.; Almahmoud, I.; Jarraud, S.; Etienne, J.; Larrat, S.; Schwebel, C.; Timsit, J.-F.; Schneider, D.; Maurin, M. Hidden Selection of Bacterial Resistance to Fluoroquinolones In Vivo: The Case of Legionella pneumophila and Humans. eBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, C.; Barton, R.; Farley, C.; Spiller, O.B.; Rodrigues, R.; Gonçalves, P. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Reveals Reduced Susceptibility to Azithromycin and Other Antibiotics in Legionella pneumophila Serogroup 1 Isolates from Portugal. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, M.; Lanni, A.; Mancini, F.; Girolamo, A.; Fillo, S.; Ciammaruconi, A.; Lista, F.; Cocuzza, C.E.; Musumeci, R.; Ginevra, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Epidemiological Types of Legionella pneumophila Human Isolates from Italy (1987–2020). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 41, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.B.; Marrafa, M.; Cruz, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Nunes, F.; Monteiro, S.; Santos, R.; Carneiro, R.N.; Neto, C.; Aguilar, J.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Legionella from Artificial Water Systems: Findings from a Two-Year Study. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.; Echahidi, F.; De Muylder, G.; Sewell, M.; Boostrom, I.; Denis, O.; Spiller, O.B.; Pierard, D. Occurrence of Macrolides Resistance in Legionella pneumophila ST188: Results of the Belgian Epidemiology and Resistome Investigation of Clinical Isolates. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 153, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-L.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, M.; Zhan, X.-Y. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles and Tentative Epidemiological Cutoff Values of Legionella pneumophila from Environmental Water and Soil Sources in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 924709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, O.; Chochlakis, D.; Sandalakis, V.; Dioli, C.; Psaroulaki, A.; Mavridou, A. Antibiotic Resistance of Legionella pneumophila in Clinical and Water Isolates—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, J.; Hallström, L.P.; Marrone, G.; Dias, J.G. Legionnaires’ Disease in the EU/EEA*: Increasing Trend from 2017 to 2019. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
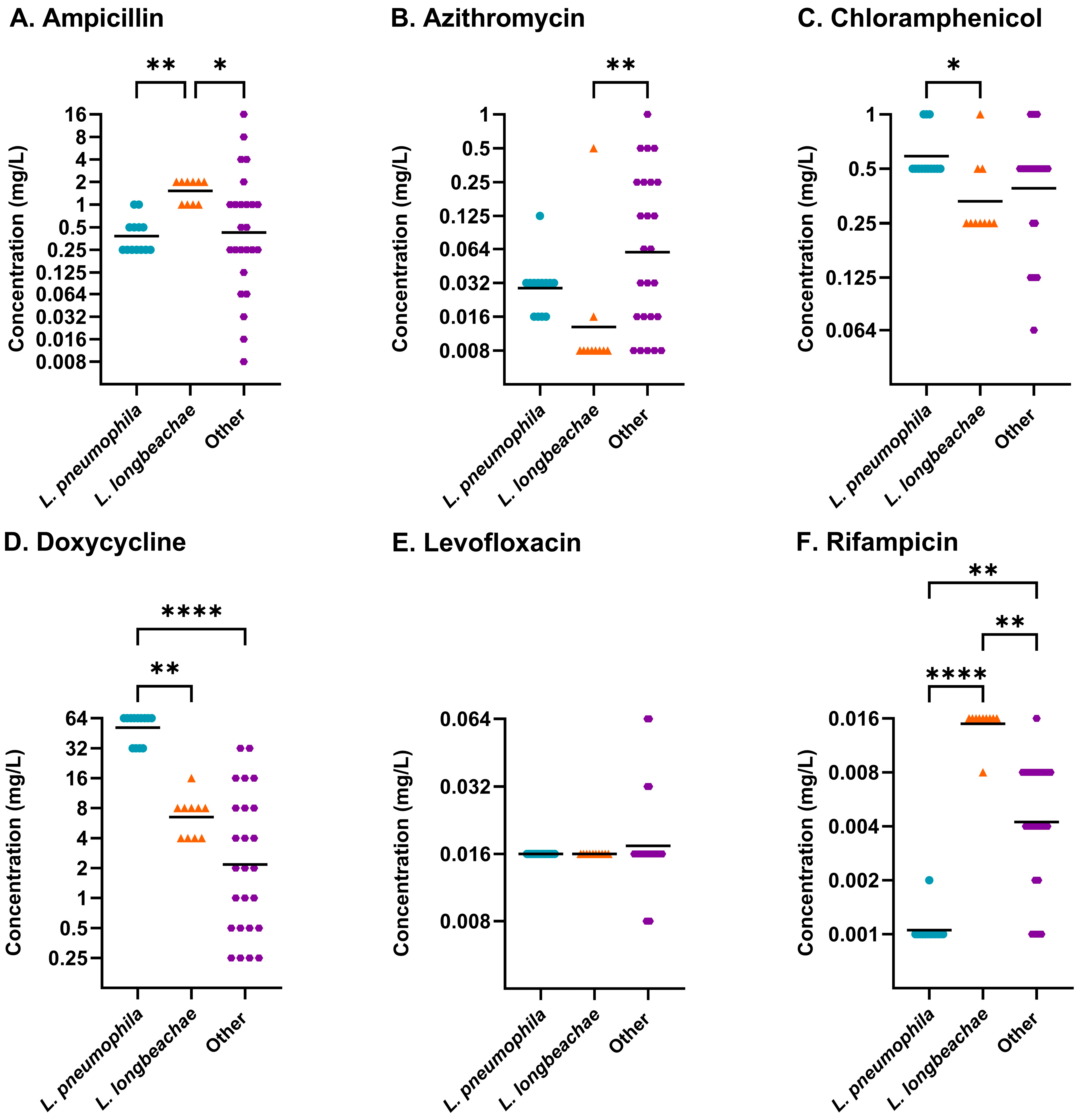

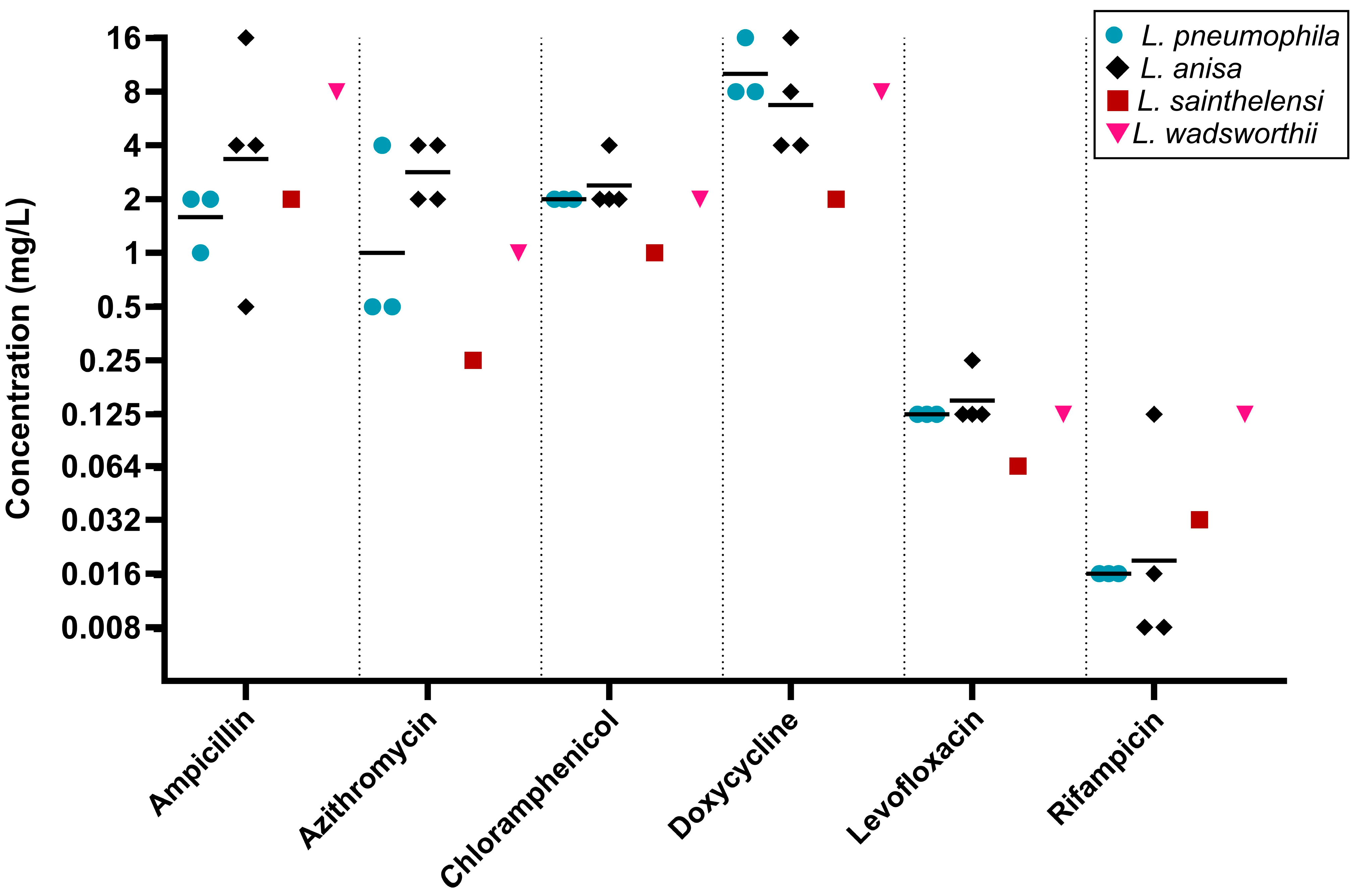
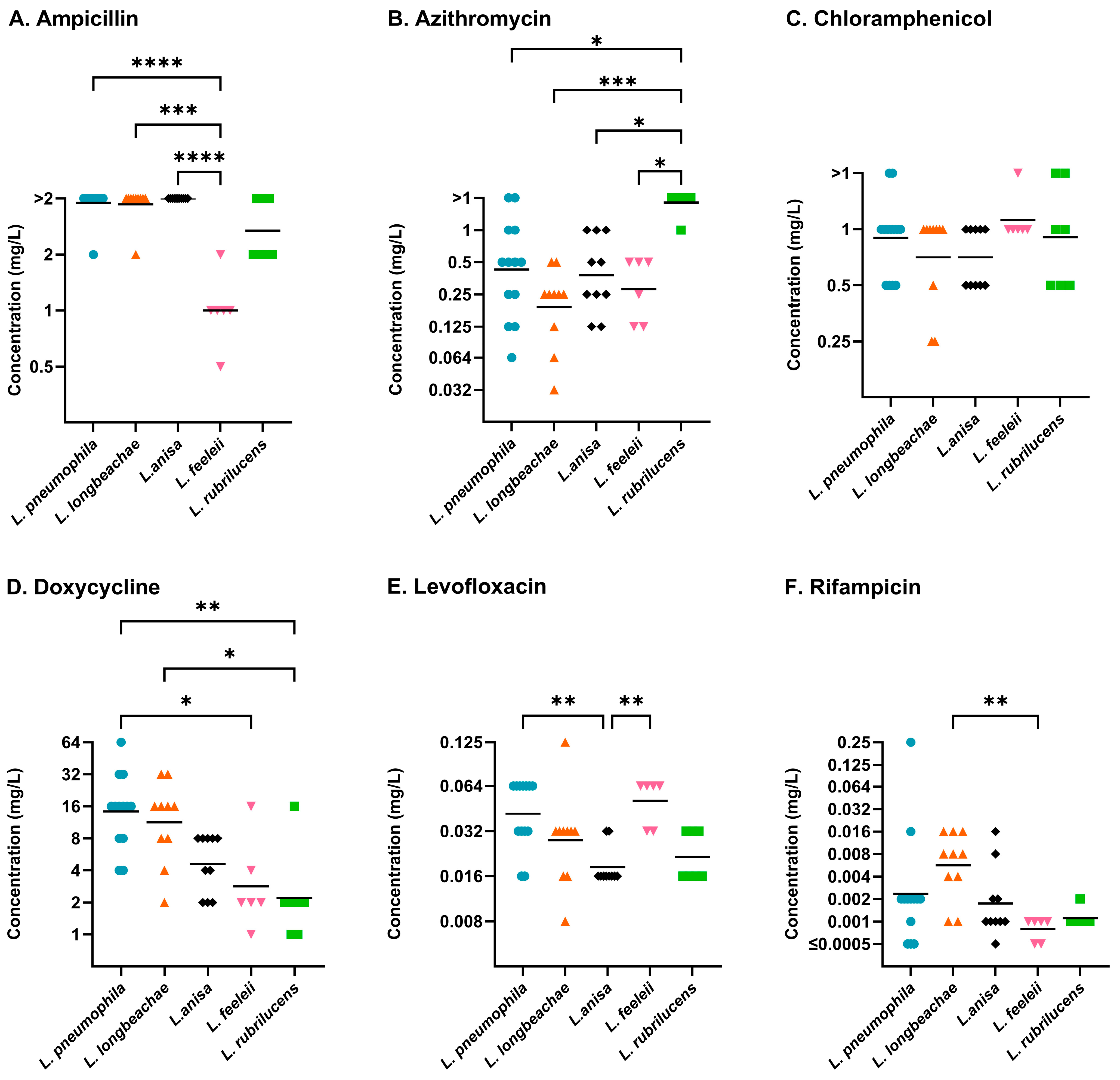


| Legionella Species | Isolates (n) | Susceptibility Profiles 1 (n (%)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LASARUS | Broth | BCYE | ||
| L. anisa | 14 | 1 (7.14) | 10 (83.33) | 4 (100) |
| L. beliardensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. birminghamensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. bozemanae | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. brunensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. busanensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. cherrii | 3 | - | 3 (100) | n/a |
| L. cincinnatiensis | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. donaldsonii | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. dresdenensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. dumoffii | 2 | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. erythra | 2 | 1 (50) | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. fairfieldensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. fallonii | 2 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. feeleii | 6 | 4 (66.67) | 6 (100) | n/a |
| L. gormanii | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. hackeliae | 2 | - | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. israelensis | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. jamestowniensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. jordanis | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. londiniensis | 2 | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. longbeachae | 10 | 10 (100) | 10 (100) | n/a |
| L. maceachernii | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. micdadei | 2 | 1 (50) | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. nautarum | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. oakridgensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. parisiensis | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. pneumophila | 13 | 13 (100) | 13 (100) | 3 (100) |
| L. quinlivanii | 2 | 1 (50) | 2 (100) | n/a |
| L. rubrilucens | 7 | 7 (100) | 7 (100) | n/a |
| L. sainthelensi | 2 | - | 1 (100) | 1 (100) |
| L. shakespearei | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. spiritensis | 1 | - | 1 (100) | n/a |
| L. wadsworthii | 1 | - | - | 1 (100) |
| ∑ | 89 | 48 (53.93) | 83 (93.26) | 9 (100) * |
| Organism (n) | Antibiotic | MIC (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 | MIC90 | Range | ||
| L. pneumophila (13) | Ampicillin | 0.25 | 1 | 0.25–1 |
| Azithromycin | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.016–0.125 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5–1 | |
| Doxycycline | 64 | 64 | 32–64 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001–0.002 | |
| L. longbeachae (10) | Ampicillin | 2 | 2 | 1–2 |
| Azithromycin | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.008–0.5 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25–1 | |
| Doxycycline | 8 | 8 | 4–16 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.008–0.016 | |
| Other Legionella species (25) | Ampicillin | 0.5 | 4 | 0.008–16 |
| Azithromycin | 0.064 | 0.5 | 0.008–1 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.5 | 1 | 0.064–1 | |
| Doxycycline | 2 | 16 | 0.25–32 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.008–0.064 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.001–0.016 | |
| Organism (n) | Antibiotic | MIC (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50 | MIC90 | Range | ||
| L. pneumophila (13) | Ampicillin | >2 | >2 | 2–>2 |
| Azithromycin | 0.5 | >1 | 0.064–>1 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 1 | >1 | 0.5–>1 | |
| Doxycycline | 16 | 32 | 4–64 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.016–0.064 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.002 | 0.016 | ≤0.0005–0.25 | |
| L. longbeachae (10) | Ampicillin | >2 | >2 | 2–>2 |
| Azithromycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.032–0.5 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 1 | 1 | 0.25–1 | |
| Doxycycline | 16 | 32 | 2–32 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.008–0.125 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.001–0.016 | |
| L. anisa (10) | Ampicillin | >2 | >2 | >2 |
| Azithromycin | 0.25 | 1 | 0.125–1 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5–1 | |
| Doxycycline | 4 | 8 | 2–8 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.016–0.032 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.001 | 0.008 | ≤0.0005–0.016 | |
| Other Legionella species (50) | Ampicillin | >2 | >2 | 0.016–>2 |
| Azithromycin | 0.5 | >1 | 0.016–>1 | |
| Chloramphenicol | 1 | >1 | 0.25–>1 | |
| Doxycycline | 4 | 16 | 0.5–32 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.032 | 0.125 | 0.016–0.25 | |
| Rifampicin | 0.002 | 0.008 | ≤0.0005–0.032 | |
| Legionella Group | Antibiotic | Friedman Test | Dunn’s Multiple Comparisons Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. longbeachae | Ampicillin | *** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | ** |
| Azithromycin | *** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | ** | |
| Chloramphenicol | * | ns | ||
| Doxycycline | * | BYE-BMD 72 h—BYE-BMD 96 h | * | |
| Levofloxacin | * | ns | ||
| Rifampicin | ** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 72 h | * | |
| Legionella spp. | Ampicillin | **** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 72 h | ** |
| LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | **** | |||
| Azithromycin | **** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 72 h | *** | |
| LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | **** | |||
| Chloramphenicol | **** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | *** | |
| Doxycycline | *** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | * | |
| BYE-BMD 72 h—BYE-BMD 96 h | *** | |||
| Levofloxacin | **** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 72 h | ** | |
| LASARUS—BYE-BMD 96 h | *** | |||
| Rifampicin | **** | LASARUS—BYE-BMD 72 h | *** | |
| BYE-BMD 72 h—BYE-BMD 96 h | * | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farley, C.; Price, A.; Sewell, M.; Barton, R.; Portal, E.A.R.; Boostrom, I.; Day, J.; Afshar, B.; Chalker, V.J.; Spiller, O.B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination of Less Frequently Isolated Legionella Species by Broth and Agar Dilution. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111165
Farley C, Price A, Sewell M, Barton R, Portal EAR, Boostrom I, Day J, Afshar B, Chalker VJ, Spiller OB. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination of Less Frequently Isolated Legionella Species by Broth and Agar Dilution. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111165
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarley, Caitlin, Amy Price, Max Sewell, Rachael Barton, Edward A. R. Portal, Ian Boostrom, Jessica Day, Baharak Afshar, Victoria J. Chalker, and Owen B. Spiller. 2025. "Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination of Less Frequently Isolated Legionella Species by Broth and Agar Dilution" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111165
APA StyleFarley, C., Price, A., Sewell, M., Barton, R., Portal, E. A. R., Boostrom, I., Day, J., Afshar, B., Chalker, V. J., & Spiller, O. B. (2025). Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination of Less Frequently Isolated Legionella Species by Broth and Agar Dilution. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111165






