Efflux-Mediated Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Streptococcus Isolates: A Comparative Molecular Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Characteristics and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
2.2. Species-Specific Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
2.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
2.4. Efflux Pump Activity Validation Using Ethidium Bromide Accumulation
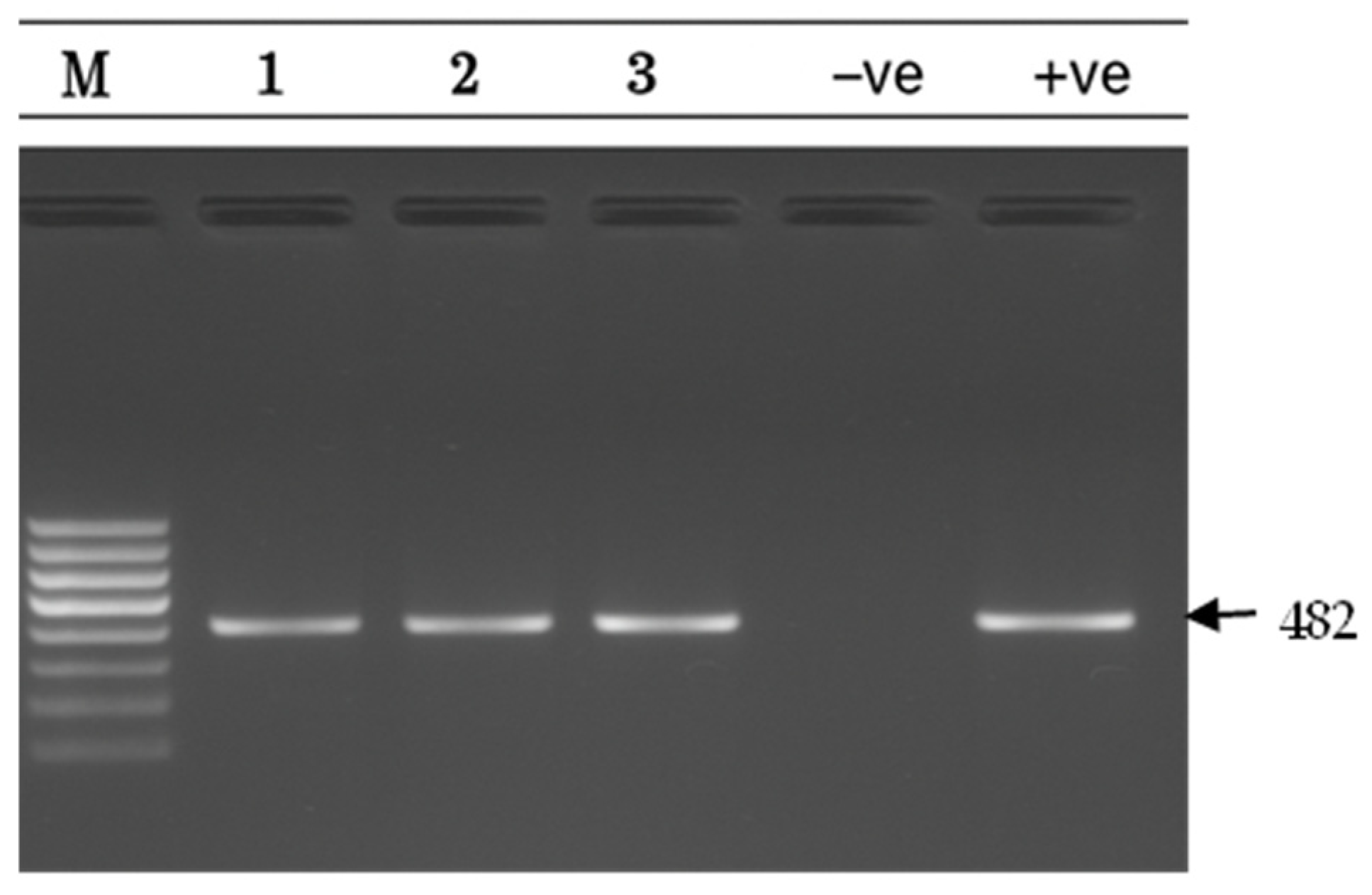
2.5. Detection of Efflux Resistance Genes (PCR)
2.6. Genotype–Phenotype Correlation
2.7. Predictors of Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Isolates
2.8. Regional Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance Patterns
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Identification and Characterization
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.3. Assessment of Efflux Pump Activity via Ethidium Bromide Accumulation Assay
3.4. Molecular Detection of Resistance Genes
3.4.1. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
3.4.2. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Streptococcus Isolates
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Limitations
4.2. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and European Economic Area in 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Coenen, S.; Van Herck, K.; Goossens, H. Effect of azithromycin and clarithromycin therapy on pharyngeal carriage of macrolide-resistant streptococci. Lancet 2007, 369, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.; Huikko, S.; Pihlajamäki, M.; Laippala, P.; Palva, E.; Huovinen, P.; Seppälä, H.; Finnish Study Group for Antimicrobial Resistance (FiRe Network). Effect of macrolide consumption on erythromycin resistance in Streptococcus pyogenes in Finland. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R. Mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, J.; Petitpas, J.; Dib-Hajj, F.; Yuan, W.; Cronan, M.; Kamath, A.V.; Bergeron, J.; Retsema, J.A. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of mefA from Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, C.; Grossman, T.H.; Kerstein, K.; Sutcliffe, J. Resistance to macrolide antibiotics in public health pathogens. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.M.; Doktor, S.; Flamm, R.; Shortridge, D. Characterization and prevalence of MefA, MefE, and MsrD in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3570–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancey, S.T.; Agrawal, S.; Schroeder, M.R.; Farley, M.M.; Tettelin, H.; Stephens, D.S. Composite mobile genetic elements disseminating macrolide resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, M.R.; Stephens, D.S. Macrolide resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C.; Soge, O.O.; No, D.B. Comparison of multi-drug resistant environmental MRSA. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636589. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, K.; Stephens, D.S. Structure and dissemination of chromosomal insertion elements encoding macrolide efflux. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaldo, P.E.; Montanari, M.P.; Giovanetti, E. Genetic elements responsible for erythromycin resistance in streptococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C. Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, F.; Starosta, A.L.; Arenz, S.; Sohmen, D.; Dönhöfer, A.; Wilson, D.N. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance mechanisms. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F.; Deleo, F.R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, G.A.; Raoult, D.; Dubourg, G. Antibiotic discovery: History, methods and perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2018, 53, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, E.; Kaur, P. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanafani, Z.A.; Zahreddine, N.; Tayyar, R. Macrolide resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae in Lebanon. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2018, 52, 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Shibl, A.M.; Memish, Z.A.; Al-Kattan, M. Antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2020, 41, 590–597. [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi, A.A.; Mahafzah, A.; Jarrad, N.; Hayajneh, W. Antimicrobial resistance patterns in Streptococcus pneumoniae in Jordan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Albrich, W.C.; Monnet, D.L.; Harbarth, S. Antibiotic selection pressure and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amhaz, P.M.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Kaplan, S.L.; Jacobs, M.R. Antimicrobial resistance in pediatric Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Piessens, J.; Goossens, H. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of macrolide and tetracycline resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4798–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochetti, I.; Vecchi, M.; Mingoia, M.; Tili, E.; Catania, M.R.; Manzin, A.; Varaldo, P.E.; Montanari, M.P. Molecular characterization of pneumococci with efflux-mediated erythromycin resistance and identification of a novel mef gene subclass, mef (I). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D.J.; Klugman, K.P.; Pichichero, M. Increased antimicrobial resistance among nonvaccine serotypes. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Chang, H.H.; Suh, J.Y.; Ko, K.S.; Jung, S.I.; Oh, W.S.; Peck, K.R.; Lee, N.Y.; Yang, Y.; Chongthaleong, A. Macrolide resistance and genotypic characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Asian countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhy, H.H.; El-Saed, A.; Al-Abri, S.S. Antimicrobial consumption in Gulf Cooperation Council countries. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Taiar, A.; Hammoud, M.S.; Cuiqing, L. Antibiotic prescribing in upper respiratory tract infections in UAE. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä, H.; Klaukka, T.; Vuopio-Varkila, J. The effect of changes in macrolide consumption on erythromycin resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.S.; Heilmann, K.P.; Dohrn, C.L.; Riahi, F.; Diekema, D.J.; Doern, G.V. Pneumococcal serotypes before and after conjugate vaccines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, A.C.; Law, I.; Matatolu, L.; Beall, B.W.; Carapetis, J.R. Global emm type distribution of group A streptococci. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Specimen Type | Group A | Group B | Group G | S. pneumoniae | Enterococcus | Group C/F | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throat swab | 42 (93.3%) | 2 (5.7%) | 3 (30%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 |
| Vaginal swab | 0 | 30 (83.3%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| Pus/wound | 2 (4.4%) | 2 (5.7%) | 4 (40%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0 | 2 (100%) | 11 |
| Ear swab | 1 (2.2%) | 0 | 3 (30%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Respiratory * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (33.3%) | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Blood culture | 0 | 1 (2.8%) | 0 | 1 (16.7%) | 1 (100%) | 0 | 3 |
| Other ** | 0 | 1 (2.8%) | 0 | 1 (16.7%) | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 45 | 36 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 100 |
| Species | n | ERY n (%) | CD n (%) | TET n (%) | Other Antibiotics n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | -- | CIP 1 (100); LEV 1 (100); PEN 1 (100); RIF 1 (100); TEI 1 (100) |
| Group A Strep | 45 | 45 (100) | 17 (37.8) | -- | -- |
| Group B Strep | 36 | 6 (16.7) | 33 (91.6) | -- | TEI 1 (2.9) |
| Group C Strep | 1 | -- | 1 (100) | -- | -- |
| Group F Strep | 1 | 1 (100) | -- | -- | -- |
| Group G Strep | 10 | 10 (100) | 2 (20) | -- | -- |
| S. pneumoniae | 6 | 4 (66.7) | 3 (50) | 1 (16.7) | OX 4 (66.7); COT 1 (16.7); TEI 2 (33.3); LEV 1 (16.7); PEN 1 (16.7) |
| Group/Species | n | Dominant Pattern | ERY Alone | CD Alone | ERY + CD | MDR (≥3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 45 | ERY-dominant | 28 (62.2%) | 0 | 17 (37.8%) | 0 |
| Group B | 36 | CD-dominant | 2 (5.56%) | 30 (83.3%) | 3 (8.33%) | 1 (2.78%) |
| Group G | 10 | ERY-dominant | 8 (80%) | 0 | 2 (20%) | 0 |
| S. pneumoniae | 6 | MDR | 0 | 0 | 3 (50%) | 4 (66.7%) |
| Group C/F | 2 | Variable | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 0 | 0 |
| Enterococcus | 1 | MDR | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 (100%) |
| Variable | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| mef(A/E) positive | 18.7 | 7.9–44.2 | <0.001 *** |
| Group A Streptococcus | 12.4 | 5.2–29.6 | <0.001 *** |
| Female gender | 2.9 | 1.3–6.8 | 0.012 * |
| Age 19–35 years | 2.3 | 1.1–4.9 | 0.028 * |
| Throat specimen | 3.1 | 1.4–6.9 | 0.005 ** |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Product (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| mef(A/E) | F: CGT CAA AGA CAC GTG AAA AAC T R: CTT CTG TGT ACA TAA TTA ACC AGA | 348 | [26] |
| msr(D) | F: ACA AAA CTT TGG GAA ATG TTT GG R: GTT TGC AGC TTC TGA TTA TCG | 482 | [27] |
| tet(K) | F: GCT GAT GAT GGT CAA TGA C R: CTT GAC CAA AGA GGA GTT G | 260 | [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moshewh, S.M.; Mohamed, S.E.; Kumar, P.; Eltom, A.E.; Jagdale, S.R.; Osman, E.A.; Ahmed, S.S.; Farajallah, N.A.M.; Ali, S. Efflux-Mediated Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Streptococcus Isolates: A Comparative Molecular Study. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111148
Moshewh SM, Mohamed SE, Kumar P, Eltom AE, Jagdale SR, Osman EA, Ahmed SS, Farajallah NAM, Ali S. Efflux-Mediated Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Streptococcus Isolates: A Comparative Molecular Study. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111148
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoshewh, Salsabeel M., Salma E. Mohamed, Praveen Kumar, Abdelgadir E. Eltom, Supriya R. Jagdale, Einas A. Osman, Saher S. Ahmed, Nour A. M. Farajallah, and Sara Ali. 2025. "Efflux-Mediated Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Streptococcus Isolates: A Comparative Molecular Study" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111148
APA StyleMoshewh, S. M., Mohamed, S. E., Kumar, P., Eltom, A. E., Jagdale, S. R., Osman, E. A., Ahmed, S. S., Farajallah, N. A. M., & Ali, S. (2025). Efflux-Mediated Macrolide Resistance in Clinical Streptococcus Isolates: A Comparative Molecular Study. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111148







