Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing System
Abstract
1. Introduction
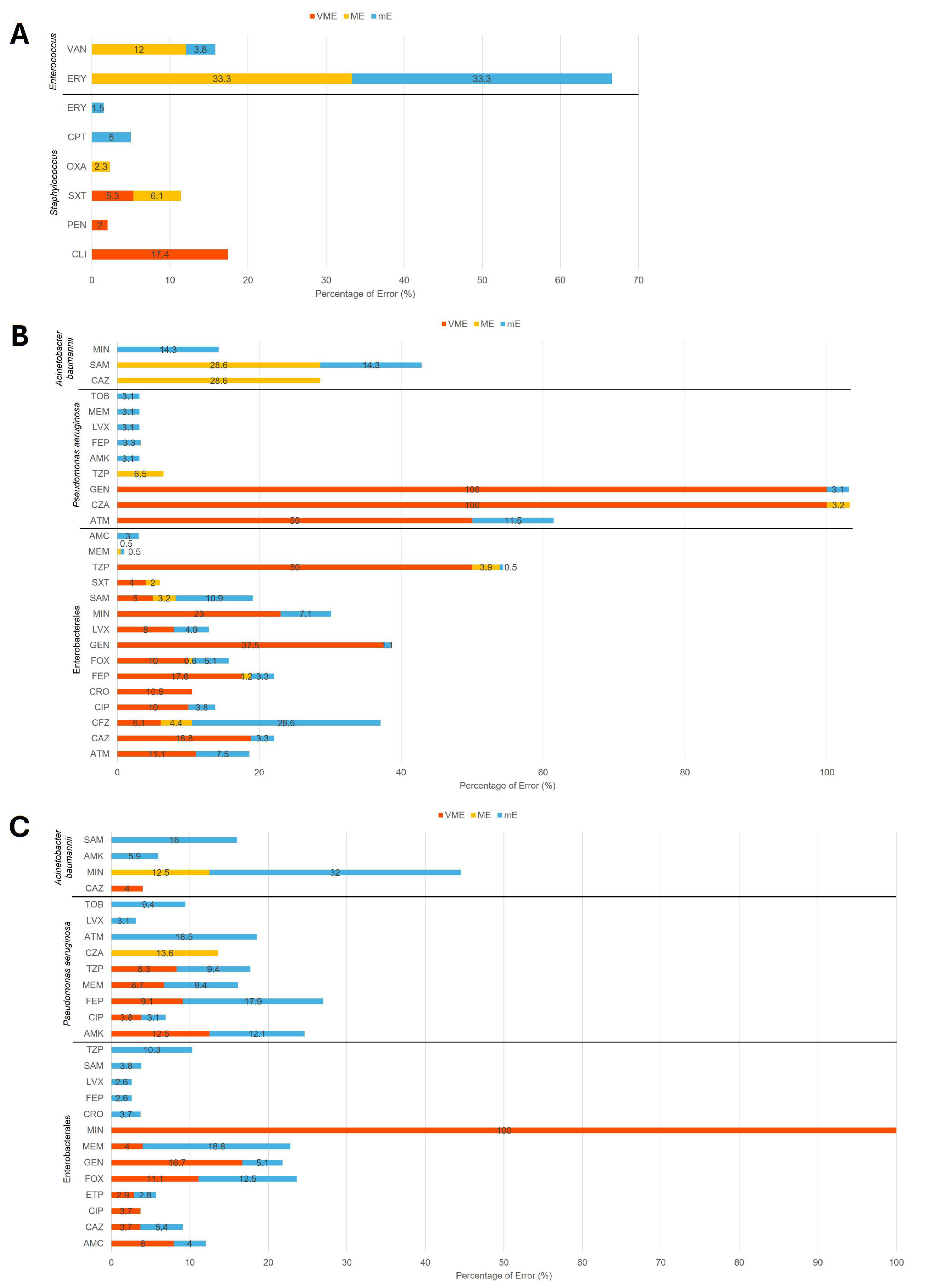
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Selux Next-Generation Phenotyping AST System
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Duin, D.; Paterson, D.L. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Community: Trends and Lessons Learned. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, T.; Chihara, S.; Costin, B.; Treggiari, M.M.; Bartz, R.R.; Raghunathan, K.; Krishnamoorthy, V. Association of Appropriate Empirical Antimicrobial Therapy with In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Bloodstream Infections in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2249353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.J.; Sorensen, J.; Jephson, A.; Mecham, I.; Dean, N.C. Broad-spectrum antibiotic use and poor outcomes in community-onset pneumonia: A cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.Y.; Khan, R.A.; Khalid, K.E.; Chong, C.W.; Bakhtiar, A. Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital: A 3-year observational study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Belkum, A.; Burnham, C.D.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Mallard, F.; Rochas, O.; Dunne, W.M., Jr. Innovative and rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, F.P.; Christner, M.; Hentschke, M.; Rohde, H. Advances in Rapid Identification and Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria in the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory: Implications for Patient Care and Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 9, 6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doern, C.D. The Slow March toward Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Are We There Yet? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galar, A.; Yuste, J.R.; Espinosa, M.; Guillen-Grima, F.; Hernaez-Crespo, S.; Leiva, J. Clinical and economic impact of rapid reporting of bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility results of the most frequently processed specimen types. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Lucy, I.B. Conventional methods and future trends in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, I.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Jovicevic, M.; Milenkovic, M.; Mitic Culafic, D.; Trudic, A.; Ranin, L.; Opavski, N. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: A Comprehensive Review of Currently Used Methods. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.R.; Colson, J.D.; Rhoads, D.D. Recent advances in rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing systems. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 563–578. [Google Scholar]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial resistance: Risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newswire. FDA Clears ‘Selux NGP System’ for Rapid Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. 2023. Available online: https://www.newswire.com/news/fda-clears-selux-ngp-system-for-rapid-antibiotic-susceptibility-testing-21933273 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Flentie, K.; Spears, B.R.; Chen, F.; Purmort, N.B.; DaPonte, K.; Viveiros, E.; Phelan, N.; Krebill, C.; Flyer, A.N.; Hooper, D.C.; et al. Microplate-based surface area assay for rapid phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, S.S.; Dominguez, E.L.; Hupp, A.A.; Griffis, M.; MacVane, S.H. Evaluation of MicroScan and VITEK 2 systems for susceptibility testing of Enterobacterales with updated breakpoints. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2025, 63, e0004825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.R.; Flentie, K.; Spears, B.R.; Mozharov, S.; Roberts, K.; El Ganbour, A.; Somers, M.; Calkwood, J.; Liu, J.; DaPonte, K.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of the Selux Next-Generation Phenotyping antimicrobial susceptibility testing system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e0054623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlich, D.; Bonnin, R.A.; Dortet, L.; Naas, T. Genetics of Acquired Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Proteus spp. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Bowler, S.L.; Kantz, S.F.; Mettus, R.T.; Guo, Y.; McElheny, C.L.; Doi, Y. Comparison of Minocycline Susceptibility Testing Methods for Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2937–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Tseng, K.C.; Huang, W.C.; Chuang, M.F.; Kuo, S.C.; Lauderdale, T.L.; Chen, T.L. In Vivo and In Vitro Efficacy of Minocycline-Based Combination Therapy for Minocycline-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4047–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Abdi, M.; Kouhsari, E.; Panahi, P.; Sholeh, M.; Sadeghifard, N.; Amiriani, T.; Ahmadi, A.; Maleki, A.; Gholami, M. Minocycline, focus on mechanisms of resistance, antibacterial activity, and clinical effectiveness: Back to the future. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K.; Development, C.M.; Standardization Working Group of the Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests. CLSI Methods Development and Standardization Working Group Best Practices for Evaluation of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry and FDA Class II Special Controls Guidance Document: Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test (AST) Systems; FDA: Silver Spring, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lippi, G.; Da Rin, G. Advantages and limitations of total laboratory automation: A personal overview. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.S.P.; Villegas, M.V.; Wenzler, E.; Rawson, T.M.; Oladele, R.O.; Doi, Y.; Apisarnthanarak, A. Rapid Diagnostic Test Value and Implementation in Antimicrobial Stewardship Across Low-to-Middle and High-Income Countries: A Mixed-Methods Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, F.; Leedahl, N.D.; Leedahl, D.D.; Guerrero, D.M. Clinical and Financial Impact of Rapid Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in Blood Cultures. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booton, R.D.; Agnew, E.; Pople, D.; Evans, S.; Bock, L.J.; Sutton, J.M.; Robotham, J.V.; Naylor, N.R. Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing for urinary tract infections in secondary care in England: A cost-effectiveness analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e081865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI M23. Development of In Vitro Susceptibility Testing Criteria and Quality Control Parameters, 6th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]


| Clinical Isolates | AR Bank Isolates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organisms | Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 24 | 22.0% | - | - |
| Enterococcus faecium | 2 | 1.8% | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 60 | 55.0% | - | - |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 2 | 1.8% | - | - |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 15 | 13.8% | - | - |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 1 | 0.9% | - | - |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 5 | 4.6% | - | - |
| Gram-Positive Total | 109 | - | - | |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 7 | 3.1% | 25 | 25.8% |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 0.4% | 1 | 1.0% |
| Citrobacter koseri | 5 | 2.2% | 4 | 4.1% |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 4 | 1.8% | 1 | 1.0% |
| Escherichia coli | 68 | 30.5% | 5 | 5.2% |
| Klebsiella aerogenes | 2 | 0.9% | 1 | 1.0% |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 3 | 1.3% | 1 | 1.0% |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 38 | 17.0% | 16 | 16.5% |
| Klebsiella variicola | 3 | 1.3% | - | - |
| Morganella morganii | 2 | 0.9% | 1 | 1.0% |
| Proteus mirabilis | 45 | 20.2% | 3 | 3.1% |
| Proteus vulgaris | 4 | 1.8% | - | - |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 32 | 14.3% | 33 | 34.0% |
| Serratia marcescens | 9 | 4.0% | 6 | 6.2% |
| Gram-Negative Total | 223 | 97 | ||
| Source | Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Abdomen fluid | 0 | 2 |
| Blood | 10 | 8 |
| Bone | 4 | 3 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | 1 | 1 |
| Sputum | 3 | 11 |
| Stool | 0 | 1 |
| Swab | 43 | 34 |
| Tissue | 6 | 5 |
| Urine | 23 | 141 |
| Wound | 19 | 17 |
| Total | 109 | 223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.-C.; Cerqueira, F.; Williams-Bouyer, N.; Ren, P. Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing System. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100962
Xue Y-C, Cerqueira F, Williams-Bouyer N, Ren P. Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing System. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100962
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yuan-Chao, Filipe Cerqueira, Natalie Williams-Bouyer, and Ping Ren. 2025. "Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing System" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100962
APA StyleXue, Y.-C., Cerqueira, F., Williams-Bouyer, N., & Ren, P. (2025). Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing System. Antibiotics, 14(10), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100962





