Looking for ESKAPE Bacteria: Occurrence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Wild Birds from Northern and Central Italy Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sampled Bird Population
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
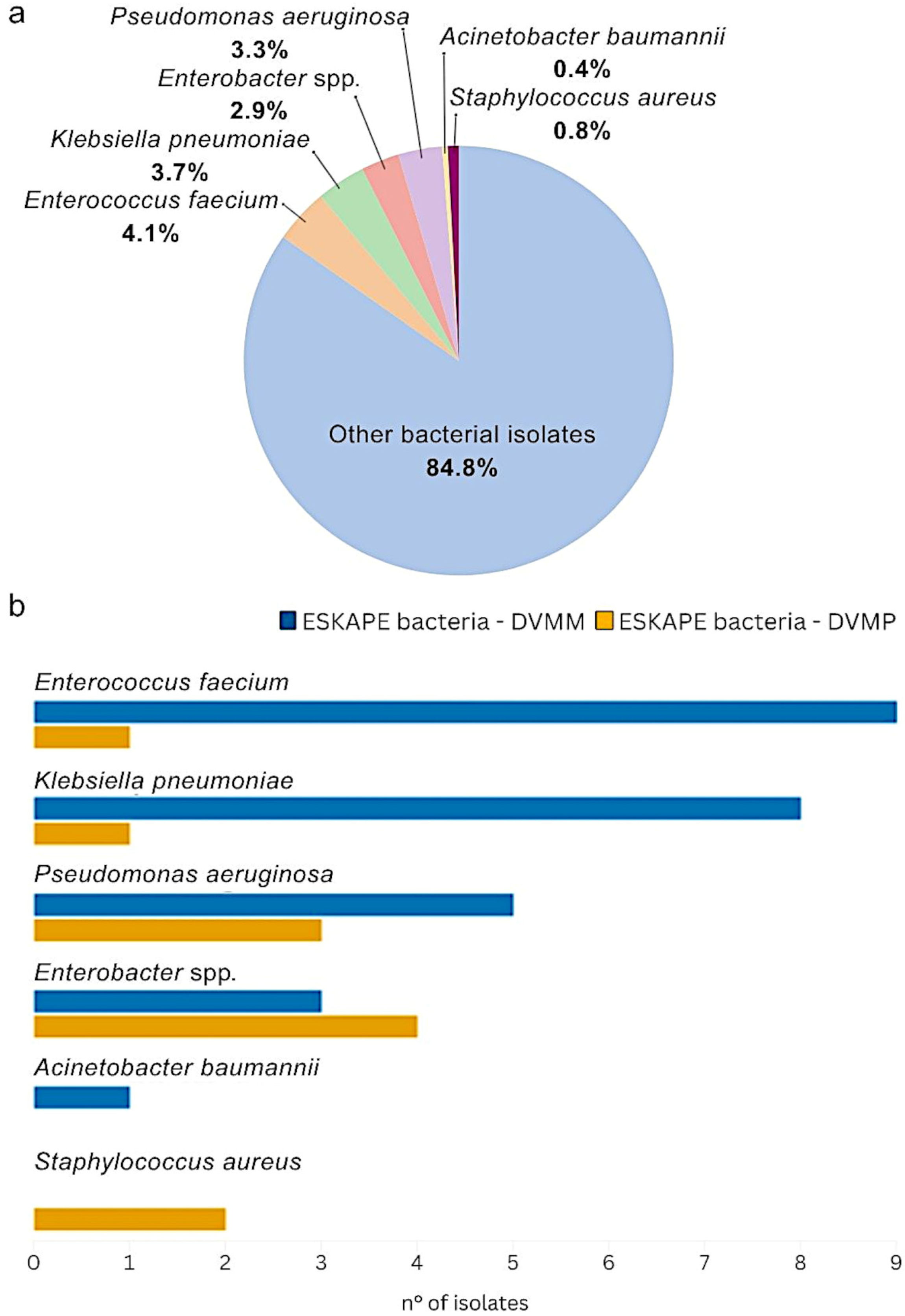
2.2.1. ESKAPE Bacteria Isolation in Both DVMM and DVMP
2.2.2. Distribution of ESKAPE Bacteria and Their Co-Occurrence with Other Bacterial Isolates at DVMM
2.2.3. Distribution of ESKAPE Bacteria and Their Co-Occurrence with Other Bacterial Isolates at DVMP
2.2.4. Non-ESKAPE Bacteria Isolation in Both DVMM and DVMP
2.3. Salmonella Serotyping
2.4. AMR Profiles of ESKAPE Bacteria by Minimun Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
2.4.1. MIC Results for Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at DVMM
2.4.2. MIC Results for Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at DVMP
2.4.3. MIC Results for Gram-Positive ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at DVMM
2.4.4. MIC Results for Gram-Positive ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at DVMP
2.5. MDR Profile Among ESKAPE Bacteria
2.5.1. MDR in Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at Both Sites
2.5.2. MDR in Gram-Positive ESKAPE Bacteria Isolated at Both Sites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. In The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial resistance: A growing serious threat for global public health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneschi, A.; Bardhi, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A. The use of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance in veterinary medicine, a complex phenomenon: A narrative review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navidinia, M. The clinical importance of emerging ESKAPE pathogens in nosocomial infections. Arch. Adv. Biosci. 2016, 7, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, R.C.; Founou, L.L.; Essack, S.Y. Clinical and economic impact of antibiotic resistance in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, J.; Reyneke, B.; Waso-Reyneke, M.; Havenga, B.; Barnard, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Prevalence of ESKAPE pathogens in the environment: Antibiotic resistance status, community-acquired infection and risk to human health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Webb, A.K.; Limbago, B.; Dudeck, M.A.; Patel, J.; Kallen, A.J.; Edwards, J.R.; Sievert, D.M. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011-2014. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.P.; Minichino, A.; Gargiulo, A.; Varriale, L.; Borrelli, L.; Pace, A.; Santaniello, A.; Pompameo, M.; Fioretti, A.; Dipineto, L. Prevalence and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance among ESKAPE bacteria and Enterobacterales strains in wild birds. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, J.A.; Salgado-Caxito, M.; Torres, C.; Godreuil, S. Public health implications of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife at the One Health interface. Med. Sci. Forum 2024, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in wildlife. In Antibiotic Resistance in the Environment: A Worldwide Overview; Manaia, C.M., Donner, E., Vaz-Moreira, I., Hong, P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 19–70. [Google Scholar]
- Laborda, P.; Sanz-García, F.; Ochoa-Sánchez, L.E.; Gil-Gil, T.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Martínez, J.L. Wildlife and Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 873989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Gulhan, T. Determination of antibiotic resistance patterns and genotypes of Escherichia coli isolated from wild birds. Microbiome 2024, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, B.M.C.; Bennett, M.; Waller, K.; Dodd, C.; Murray, A.; Gomes, R.L.; Humphreys, B.; Hobman, J.L.; Jones, M.A.; Whitlock, S.E.; et al. Anthropogenic environmental drivers of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayah, R.S.; Kaneene, J.B.; Johnson, Y.; Miller, R. Patterns of antimicrobial resistance observed in Escherichia coli isolates obtained from domestic-and wild-animal fecal samples, human septage, and surface water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittecoq, M.; Godreuil, S.; Prugnolle, F.; Durand, P.; Brazier, L.; Renaud, N.; Arnal, A.; Aberkane, S.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Silva, N.; Poeta, P.; Torres, C.; Correia, S.; Igrejas, G. Potential impact of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife, environment and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 66221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, L.E.; Campbell, A.; Zhang, L.; Gaze, W.H.; McDonald, R.A. Wild small mammals as sentinels for the environmental transmission of antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouani, H.; Poeta, P.; Goncalves, A.; Pacheco, R.; Sargo, R.; Igrejas, G. Wild birds as biological indicators of environmental pollution: Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Escherichia coli and enterococci isolated from common buzzards (Buteo buteo). J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezeau, N.; Kahn, L. Current understanding and knowledge gaps regarding wildlife as reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Araújo, S.; Caniça, M.; Pereira, J.E.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Caught in the ESKAPE: Wildlife as key players in the ecology of resistant pathogens in a One Health context. Diversity 2025, 17, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, T.; Ali, S.; Javid, A.; Sheikh, A.A. Occurrence, characteristics, and antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from wild birds in the Kasur district of Punjab, Pakistan. Vet. Res. Forum 2024, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnoli, G.; Bertelloni, F.; Interrante, P.; Ceccherelli, R.; Marzoni, M.; Ebani, V.V. Antimicrobial-resistant Enterococcus spp. in wild avifauna from Central Italy. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.B.; Hossain, H.; Roy, M.; Begum, R.; Ghosh, P.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Cho, H.S.; Hossain, M.M. Molecular identification and antimicrobial resistance characteristics of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from captive wild and migratory birds. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendecke, J.; Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Schmitz Ornés, A.; Guenther, S.; Heiden, S.E.; Schwabe, M.; Eger, E.; Schaufler, K. Multidrug-resistant high-risk Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal lineages occur in Black-Headed Gulls from two conservation islands in Germany. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Genomic analysis of Proteus mirabilis: Unraveling global epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance dissemination−emerging challenges for public health and biosecurity. Environ. Int. 2025, 199, 109487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibello, A.; Galán-Sánchez, F.; Blanco, M.M.; Rodríguez-Iglesias, M.; Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F. The zoonotic potential of Lactococcus garvieae: An overview on microbiology, epidemiology, virulence factors and relationship with its presence in foods. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 109, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabeen, I.; Islam, S.; Hassan, A.; Tasnim, Z.; Shuvo, S.R. A brief insight into Citrobacter species—A growing threat to public health. Front. Antibiot. 2023, 2, 1276982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 35th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025; Volume M100. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. Expected Resistant Phenotypes, Version 1.2; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Expert_Rules/2023/Expected_Resistant_Phenotypes_v1.2_20230113.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Kümmerer, K. Resistance in the environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, H.Y.; Jamshidi, S.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Current advances in developing inhibitors of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1062–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benskin, C.M.; Wilson, K.; Jones, K.; Hartley, I.R. Bacterial pathogens in wild birds: A review of the frequency and effects of infection. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2009, 84, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Pagès, J.M. Enterobacter spp.: Update on taxonomy, clinical aspects, and emerging antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzatesta, M.L.; Gona, F.; Stefani, S. Enterobacter cloacae complex: Clinical impact and emerging antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Phenotypic and genomic insights into the pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance of an Enterobacter roggenkampii strain isolated from diseased silver arowana (Osteoglossum bicirrhosum). J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Peirano, G.; Motyl, M.R.; Adams, M.D.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.; DeVinney, R.; Pitout, J.D. Global molecular epidemiology of IMP-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2017, 61, e02729-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, A.F.; Meyer, S.; Deenen, R.; Köhrer, K.; Kolbe-Busch, S.; Pfeffer, K.; Willmann, M.; Kaasch, A.J.; MacKenzie, C.R. Long-term, low-frequency cluster of a german-imipenemase-1-producing Enterobacter hormaechei ssp. steigerwaltii ST89 in a tertiary care hospital in Germany. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2018, 24, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, J.; Carretero, O.; Viedma, E.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Mingorance, J.; Chaves, F. Emergence of NDM-7-producing multi-drug-resistant Enterobacter hormaechei sequence type ST-78 in Spain: A high-risk international clone. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, K.; Nakamura, H.; Fukuda, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Kawahara, R. Molecular characterization of blaKHM-1 encoding plasmid in an Enterobacter hormaechei subsp. hoffmannii isolate from blood culture. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zha, L.; Wang, K.; Qi, K.; et al. Characterization of blaNDM-1- and blaSHV-12-positive IncX3 plasmid in an Enterobacter hormaechei new sequence type 1000 from China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, G.; Matsumura, Y.; Adams, M.D.; Bradford, P.; Motyl, M.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Pitout, J.D.D. Genomic epidemiology of global carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter spp., 2008–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, K.H.; Song, W.; Chung, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Yum, J.H.; Yi, H.N.; Chun, J.S.; Yong, D.; Lee, K.; Chong, Y. Chromosomal cephalosporinase in Enterobacter hormaechei as an ancestor of ACT-1 plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, E.M.; Boxall, A.B.; Cross, P.; Feil, E.J.; Gaze, W.H.; Hawkey, P.M.; Johnson-Rollings, A.S.; Jones, D.L.; Lee, N.M.; Otten, W.; et al. The role of the natural environment in the emergence of antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Rafailidis, P.I. Re-emergence of colistin in today’s world of multidrug-resistant organisms: Personal perspectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Jean-Michel, B.; Jean-Christophe, D.; Martine, R.-G.; Rolain, J.-M. Colistin: An update on the antibiotic of the 21st century. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, K.S.; Pogue, J.M.; Tran, T.B.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Agents of last resort: Polymyxin resistance. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Fisichella, V.; Fulco, E.; Orlandella, B.M.; Lo Piccolo, F. Antibiotic resistance assessment in bacteria isolated in migratory Passeriformes transiting through the Metaponto territory (Basilicata, Italy). Avian Res. 2017, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, V.; Gambino, D.; Oddo, A.M.; Pizzo, M.; Sucato, A.; Cammilleri, G.; La Russa, F.; Di Pasquale, M.L.; Parisi, M.G.; Cassata, G.; et al. Scolopax rusticola carrying Enterobacterales harboring antibiotic resistance genes. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Grosso, F.; Ricciardi, D.; Fisichella, V.; Piccolo, F.L. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Enterobacteriaceae in European wild bird species admitted in a wildlife rescue centre. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Métayer, V.; Jarry, R.; Drapeau, A.; Puech, M.-P.; Madec, J.-Y.; Keck, N. Wide spread of blaCTX–M–9/mcr-9 IncHI2/ST1 plasmids and CTX-M-9-producing Escherichia coli and Enterobacter cloacae in rescued wild animals. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 601317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.J.; Kuzel, T.M.; Shafikhani, S.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Infections, animal modeling, and therapeutics. Cells 2023, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso-Becerra, M.V.; Santos-Medellín, C.; González-Valdez, A.; Méndez, J.L.; Delgado, G.; Morales-Espinosa, R.; Servín-González, L.; Alcaraz, L.D.; Soberón-Chávez, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical and environmental isolates constitute a single population with high phenotypic diversity. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Causapé, C.; Cabot, G.; Del Barrio-Tofiño, E.; Oliver, A. The versatile mutational resistome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.G.C.; Nair, H.P.; O’Kane, C.; Walker, C.A. Prevalence of multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas spp. isolated from wild bird feces in an urban aquatic environment. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 14303–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, W.M.B.S.; Narciso, A.C.; Cayô, R.; Santos, S.V.; Fehlberg, L.C.C.; Ramos, P.L.; da Cruz, J.B.; Gales, A.C. SPM-1-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST277 clone recovered from microbiota of migratory birds. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan, A.; Mohamed, M.; Elhaig, M.M.; Al-Rasheed, M.; Abd-Allah, E.M. Genomic characterization and multidrug resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from peregrine falcons in Saudi Arabia: A One Health perspective. Vet. World 2025, 18, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolejska, M.; Masarikova, M.; Dobiasova, H.; Jamborova, I.; Karpiskova, R.; Havlicek, M.; Carlile, N.; Priddel, D.; Cizek, A.; Literak, I. High prevalence of Salmonella and IMP-4-producing Enterobacteriaceae in the silver gull on Five Islands, Australia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and emergence of OXA-48 producing Enterobacterales in wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaverini, A.; Cornacchia, A.; Centorotola, G.; Tieri, E.E.; Sulli, N.; Del Matto, I.; Iannitto, G.; Petrone, D.; Petrini, A.; Pomilio, F. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from wild animals in Central Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ji, F.; Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Qin, J.; Dong, G.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C. Genomic characteristics and molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains carried by wild birds. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0269122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO’s List of Medically Important Antimicrobials: A Risk Management Tool for Mitigating Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Non-Human Use; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopińska, A.; Indykiewicz, P.; Skiebe, E.; Pfeifer, Y.; Trček, J.; Jerzak, L.; Minias, P.; Nowakowski, J.; Ledwoń, M.; Betleja, J.; et al. Low occurrence of Acinetobacter baumannii in Gulls and Songbirds. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiru, M.; Enabulele, O.I. Acinetobacter baumannii in birds’ feces: A public health threat to vegetables and irrigation farmers. Adv. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ortiz, E.; Blanco Gutiérrez, M.D.; Calvo-Fernandez, C.; Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Pastor Tiburón, N.; Alvarado Piqueras, A.; Pablos-Tanarro, A.; Martín-Maldonado, B. Addressing challenges in wildlife rehabilitation: Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria from wounds and fractures in wild birds. Animals 2024, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrel, M.; Smith, M.; Shi, Q.; Hasegawa, S.; Clore, G.S.; Perencevich, E.N.; Goto, M. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of outpatient Staphylococcus aureus isolates. JAMA Netw. Open. 2024, 7, e2417199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Scarpellini, R.; Celli, G.; Marliani, G.; Zaghini, A.; Mondo, E.; Rossi, G.; Piva, S. Wild birds as potential bioindicators of environmental antimicrobial resistance: A preliminary investigation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 180, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutkowska, J.; Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Kucharczyk, M.; Kucharczyk, H.; Zalewska, J.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and glycopeptide-resistant enterococci in fecal samples of birds from South-Eastern Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, A.; Salvatore, D.; Bertelloni, F.; Ebani, V.V. Tetracycline resistance genes in wild birds from a wildlife recovery centre in central Italy. Animals 2023, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerek, Á.; Szabó, Á.; Jerzsele, Á. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from domestic pigeons in Hungary in 2022. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giulieri, S.G. Case commentary: The hidden side of oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e00716-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; de Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbeck, B.L.; Rice, L.B. Intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms in enterococcus. Virulence 2012, 3, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.R.; Murray, B.E.; Rice, L.B.; Arias, C.A. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci: Therapeutic challenges in the 21st century. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Lila, A.S.; Alharby, T.N.; Alanazi, J.; Alanazi, M.; Abdallah, M.H.; Rizvi, S.M.; Moin, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Tabrez, S.; Al Balushi, A.A.; et al. Clinical resistant strains of enterococci and their correlation to reduced susceptibility to biocides: Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C. Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Grasso, R.; Fisichella, V.; Mascetti, A.; Zafarana, M.A.; Colnaghi, M.; Grasso, M.; Spena, M.T. Analysis of Eurasian Stone curlew (Burhinus oedicnemus) microbial flora reveals the presence of multi-drug resistant pathogens in agro-pastoral areas of Sicily (Italy). Heliyon 2020, 6, e05401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA (ESAC-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-consumption-eueea-esac-net-annual-epidemiological-report-2023#:~:text=For%202023%2C%2027%20countries%20%2825%20European%20Union%20%28EU%29,doses%20%28DDD%29%20per%201%20000%20inhabitants%20per%20day (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- EMA. European Sales and Use of Antimicrobials for Veterinary Medicine (ESUAvet)—Annual Surveillance Report for 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/veterinary-regulatory-overview/antimicrobial-resistance-veterinary-medicine/european-sales-use-antimicrobials-veterinary-medicine-esuavet-annual-surveillance-reports (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Galimand, M.; Schmitt, E.; Panvert, M.; Desmolaize, B.; Douthwaite, S.; Mechulam, Y.; Courvalin, P. Intrinsic resistance to aminoglycosides in Enterococcus faecium is conferred by the 16S rRNA m5C1404-specific methyltransferase EfmM. RNA 2011, 17, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatfinski, N.; Kramer, C.N.; Goodman, S.D.; Bakaletz, L.O. ESKAPEE pathogens newly released from biofilm residence by a targeted monoclonal are sensitized to killing by traditional antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1202215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarde-López, M.; Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Godoy-Lozano, E.E.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.A.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Sassoé-González, A.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Saturno-Hernández, P.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Presence and persistence of ESKAPEE bacteria before and after hospital wastewater treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, P.P.; Sahoo, R.K. Blocking horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes: An effective strategy in combating antibiotic resistance. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souguir, M.; Châtre, P.; Drapeau, A.; François, P.; Azaiez, S.; Ncir, S.; Madec, J.Y.; Mansour, W.; Haenni, M. Molecular characterization of highly prevalent Escherichia coli and Escherichia marmotae resistant to extended-spectrum cephalosporins in European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) in Tunisia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0222023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Gorkina, N.; Pérez-Reyes, M.E.; Smith, S.A. Profiling toxin genes and antibiotic resistance in Bacillus cereus isolated from pre-launch spacecraft. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1231726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenk, S.; Rakovitsky, N.; Kon, H.; Rov, R.; Abramov, S.; Lurie-Weinberger, M.N.; Schwartz, D.; Pinco, E.; Lellouche, J.; Carmeli, Y. OXA-900, a novel OXA sub-family carbapenemase identified in Citrobacter freundii, evades detection by commercial molecular diagnostics tests. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, T.I. The role of Citrobacter in clinical disease of children: Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Singh, N.; Aggarwal, A.; Khanna, M. The antibiotic resistance pattern in Citrobacter species: An emerging nossocomial pathogen in a tertiary care hospital. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2012, 6, 642–644. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Stübner, S.; Kniehl, E. Transmission of extended-spectrum β-lactamase Klebsiella oxytoca via the breathing circuit of a transport ventilator: Root cause analysis and infection control recommendations. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamio, K.; Espinoza, J.L. The predominance of Klebsiella aerogenes among carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections in Japan. Pathogens 2022, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.d.M.S.; de Leon, C.M.C.G.; Silva, N.M.V.d.; Raso, T.F.; Serafini, P.P.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Oliveira, C.J.B.d. Staphylococcus sciuri as a reservoir of mecA to Staphylococcus aureus in non-migratory seabirds from a remote oceanic island. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 27, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, N.M.; Penati, M.; Fusar-Poli, S.; Addis, M.F.; Tola, S. Species identification by MALDI-TOF MS and gap PCR-RFLP of non-aureus Staphylococcus, Mammaliicoccus, and Streptococcus spp. associated with sheep and goat mastitis. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella serovars. Available online: https://www.pasteur.fr/sites/default/files/veng_0.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 12th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024; Volume M07. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. EUCAST Reading Guide for Broth Microdilution, Version 5.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/MIC_testing/Reading_guide_BMD_v_5.0_2024.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- EUCAST. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 15.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_15.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Yusuf, E.; Zeitlinger, M.; Meylan, S. A narrative review of the intermediate category of the antimicrobial susceptibility test: Relation with dosing and possible impact on antimicrobial stewardship. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 14.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_14.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021; Volume M100. [Google Scholar]
- CA-SFM/EUCAST. Comité de L’antibiogramme de la Societé Francaise de Microbiologie, Recommendations v.1.1; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2025. Available online: https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/CASFM2025_V1.1-JUILLET-2025.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- CA-SFM/EUCAST. Comité de L’antibiogramme de la Societé Francaise de Microbiologie, Recommendations v.1.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2014. Available online: https://www.departement-information-medicale.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/CASFM_EUCAST_V1_0_2014.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Parolini, F.; Ventura, G.; Rosignoli, C.; Rota Nodari, S.; D’incau, M.; Marocchi, L.; Santucci, G.; Boldini, M.; Gradassi, M. Detection and phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serotypes in dairy cattle farms in the Po valley, northern Italy. Animals 2024, 14, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Antimicrobial Wild Type Distributions of Microorganisms. Available online: https://mic.eucast.org/search/?search%5Bmethod%5D=mic&search%5Bantibiotic%5D=-1&search%5Bspecies%5D=-1&search%5Bdisk_content%5D=-1&search%5Blimit%5D=50 (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Lin, Y.W.; Yu, H.H.; Zhao, J.; Han, M.L.; Zhu, Y.; Akter, J.; Wickremasinghe, H.; Walpola, H.; Wirth, V.; Rao, G.G.; et al. Polymyxin B in combination with enrofloxacin exerts synergistic killing against extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00028-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.M.; Hadis, M.A.; Secker, B.; Shaw, S.C.; Cooper, P.R.; Palin, W.M.; Milward, M.R.; Atterbury, R.J. Exposure to blue light reduces antimicrobial resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from dog ear infections. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1414412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Order | Family | Species | Samples DVMM | Samples DVMP | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accipitriformes | Accipitridae | Eurasian Sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| Eurasian Common Buzzard (Buteo buteo Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 3 | 3 | ||
| Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Short-toed Snake Eagle (Circaetus gallicus Gmelin, 1788) | - | 3 | 3 | ||
| Anseriformes | Anatidae | Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos Linnaeus, 1758) | 6 | 1 | 7 |
| Swan (Cignus olor Gmelin, 1789) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Apodiformes | Apodidae | Alpine Swift (Tachymarptis melba Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 | - | 3 |
| Common Swift (Apus apus Linnaeus, 1758) | 8 | 1 | 9 | ||
| Bucerotiformes | Upupidae | Eurasian Hoopoe (Upupa epops Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Charadriiformes | Laridae | Common Gull (Larus canus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| European Herring Gull (Larus argentatus Pontoppidan, 1763) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Columbiformes | Columbidae | Common Woodpigeon (Columba palumbus Linnaeus, 1758) | 5 | - | 5 |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto Frivaldszky, 1838) | 5 | 3 | 8 | ||
| Common Pigeon (Columba livia Gmelin, 1789) | - | 3 | 3 | ||
| Falconiformes | Falconidae | Common Kestrel (Falco tinnunculus Linnaeus, 1758) | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| Eurasian Hobby (Falco subbuteo Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Galliformes | Phasianidae | Pheasant (Phasianus colchicus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| Gruiformes | Rallidae | Common Moorhen (Gallinula chloropus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| Passeriformes | Corvidae | Hooded Crow (Corvus cornix Linnaeus, 1758) | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| Eurasian Magpie (Pica pica Linnaeus, 1758) | 5 | 3 | 8 | ||
| Eurasian Jay (Garrulus glandarius Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Turdidae | Common Blackbird (Turdus merula Linnaeus, 1758) | 7 | 5 | 12 | |
| Paridae | Great Tit (Parus major Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Blue Tit (Cyanistes caeruleus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Muscicapidae | Common Redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| European Pied Flycatcher (Ficedula hypoleuca Pallas, 1764) | 1 | - | 1 | ||
| Fringillidae | Eurasian Siskin (Spinus spinus Linnaeus, 1766) | - | 1 | 1 | |
| European Greenfinch (Chloris chloris Linnaeus, 1758) | 4 | 1 | 5 | ||
| Hirundinidae | Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica Linnaeus, 1758) | 2 | - | 2 | |
| Sturnidae | European Starling (Sturnus vulgaris Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 4 | 4 | |
| Pelecaniformes | Ardeidae | Grey Heron (Ardea cinerea Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | - | 1 |
| Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Little Egret (Egretta garzetta Linnaeus, 1766) | 1 | - | 1 | ||
| Night Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Piciformes | Picidae | Green Woodpecker (Picus viridis Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| Podicipediformes | Podicipedidae | Great Crested Grebe (Podiceps cristatus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 1 | 1 |
| Strigiformes | Strigidae | Eurasian Scops-owl (Otus scops Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Little Owl (Athene noctua Scopoli, 1769) | 4 | 5 | 9 | ||
| Tawny Owl (Strix aluco Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 9 | 9 | ||
| Owl (Asio otus Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 3 | 3 | ||
| Tytonidae | Barn Owl (Tyto alba Scopoli, 1769) | - | 3 | 3 | |
| Suliformes | Phalacrocoracidae | Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo Linnaeus, 1758) | - | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 66 | 75 | 141 | ||
| AST Panel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Penicillins | Cephalosporins (1st–2nd) | Cephalosporins (3rd–4th) | Polymyxin | Fluoroquinolones | Phenicols | Quinolones | Sulphonamides | Tetracyclines | |||||||
| Site | Bird Species | ESKAPE Isolate | AN | GEN | KAN | AMP | AMC | CFZ | CTX | CL | ENR | FFC | FLU | SFX | SXT | TET |
| DVMM | Eurasian Magpie (Pica pica) | Acinetobacter baumannii | =2 | R | ≤2 | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | S | =64 | ≤1 | ≤128 | S | IR |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | Enterobacter hormaechei | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Little Egret (Egretta garzetta) | Enterobacter hormaechei | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| European Greenfinch (Chloris chloris) | Enterobacter roggenkampii | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | |
| Common Blackbird (Turdus merula) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Common Blackbird (Turdus merula) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | R | S | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | R | |
| Common Redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | R | R | S | R | S | R | R | S | S | |
| European Pied Flycatcher (Ficedula hypoleuca) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | R | S | IR | R | R | R | S | R | S | R | R | R | R | |
| Common Swift (Apus apus) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Alpine Swift (Tachymarptis melba) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | R | S | I | IR | S | R | R | S | R | S | R | R | R | R | |
| Alpine Swift (Tachymarptis melba) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | S | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| Great Tit (Parus major) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | I | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| Common Blackbird (Turdus merula) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | I | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | =8 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | R | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| European Greenfinch (Chloris chloris) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | I | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| DVMP | European Starling (Sturnus vulgaris) | Enterobacter hormaechei | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) | Enterobacter hormaechei | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | S | |
| Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | Enterobacter hormaechei | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | I | |
| Eurasian Hobby (Falco subbuteo) | Enterobacter hormaechei | R | S | I | IR | IR | IR | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | |
| Common Swift (Apus apus) | Klebsiella pneumoniae | S | S | S | IR | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Short-toed Snake Eagle (Circaetus gallicus) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | I | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | R | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >32 | S | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR | S | I | S | >16 | >512 | IR | IR | |
| AST Panel | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Cephalosporins (1st–2nd) | Cephalosporins (3rd–4th) | Lincosamides | Fluoroquinolones | Macrolides | Aminoglycosides | Phenicols | Ansamycins | Sulphonamides | Tetracyclines | ||||||||
| Site | Bird Species | ESKAPE Isolate | OX | P | AMP | AMC | CFZ | CTF | DA | ENR | ERY | TIL | KAN | FFC | RD | SFX | SXT | TET |
| DVMM | Common Woodpigeon (Columba palumbus) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | R | R | >32 | ≤250 | S | I | IR | IR | S |
| Eurasian Hoopoe (Upupa epops) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | R | I | ≤8 | ≤250 | S | I | IR | IR | S | |
| Common Woodpigeon (Columba palumbus) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | R | I | =16 | ≤250 | S | I | IR | IR | S | |
| Common Swift (Apus apus) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | I | I | =16 | ≤250 | S | S | IR | IR | S | |
| Eurasian Jay (Garrulus glandarius) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | I | =16 | =500 | S | I | IR | IR | R | |
| Common Swift (Apus apus) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | I | I | =16 | ≤250 | S | I | IR | IR | S | |
| Alpine Swift (Tachymarptis melba) | Enterococcus faecium | >4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | S | I | =16 | ≤250 | S | S | IR | IR | S | |
| Common Woodpigeon (Columba palumbus) | Enterococcus faecium | >16 | R | R | R | IR | IR | IR | R | R | >32 | >500 | S | I | IR | IR | R | |
| Eurasian Collared-dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | Enterococcus faecium | =1 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | I | I | =16 | ≤250 | S | S | IR | IR | R | |
| DVMP | Eurasian Sparrowhawk (Accipiter gentilis) | Enterococcus faecium | =4 | S | S | S | IR | IR | IR | I | S | =16 | ≤250 | S | S | IR | IR | R |
| Tawny Owl (Strix aluco) | Staphylococcus aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | ≤8 | S | S | S | R | S | S | |
| Common Blackbird (Turdus merula) | Staphylococcus aureus | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | ≤8 | S | S | S | R | S | R | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grilli, G.; Rapi, M.C.; Musa, L.; Di Giacinto, G.; Passamonti, F.; Raimondi, S.; Cianca, O.; Franciosini, M.P. Looking for ESKAPE Bacteria: Occurrence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Wild Birds from Northern and Central Italy Sites. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101025
Grilli G, Rapi MC, Musa L, Di Giacinto G, Passamonti F, Raimondi S, Cianca O, Franciosini MP. Looking for ESKAPE Bacteria: Occurrence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Wild Birds from Northern and Central Italy Sites. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrilli, Guido, Maria Cristina Rapi, Laura Musa, Giacomo Di Giacinto, Fabrizio Passamonti, Stefano Raimondi, Oriana Cianca, and Maria Pia Franciosini. 2025. "Looking for ESKAPE Bacteria: Occurrence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Wild Birds from Northern and Central Italy Sites" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101025
APA StyleGrilli, G., Rapi, M. C., Musa, L., Di Giacinto, G., Passamonti, F., Raimondi, S., Cianca, O., & Franciosini, M. P. (2025). Looking for ESKAPE Bacteria: Occurrence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Wild Birds from Northern and Central Italy Sites. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101025









