Silent Carriers: The Hidden Threat of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Seafood Across Poland’s Tri-City Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Contamination by S. aureus
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Characterization
3. Discussion
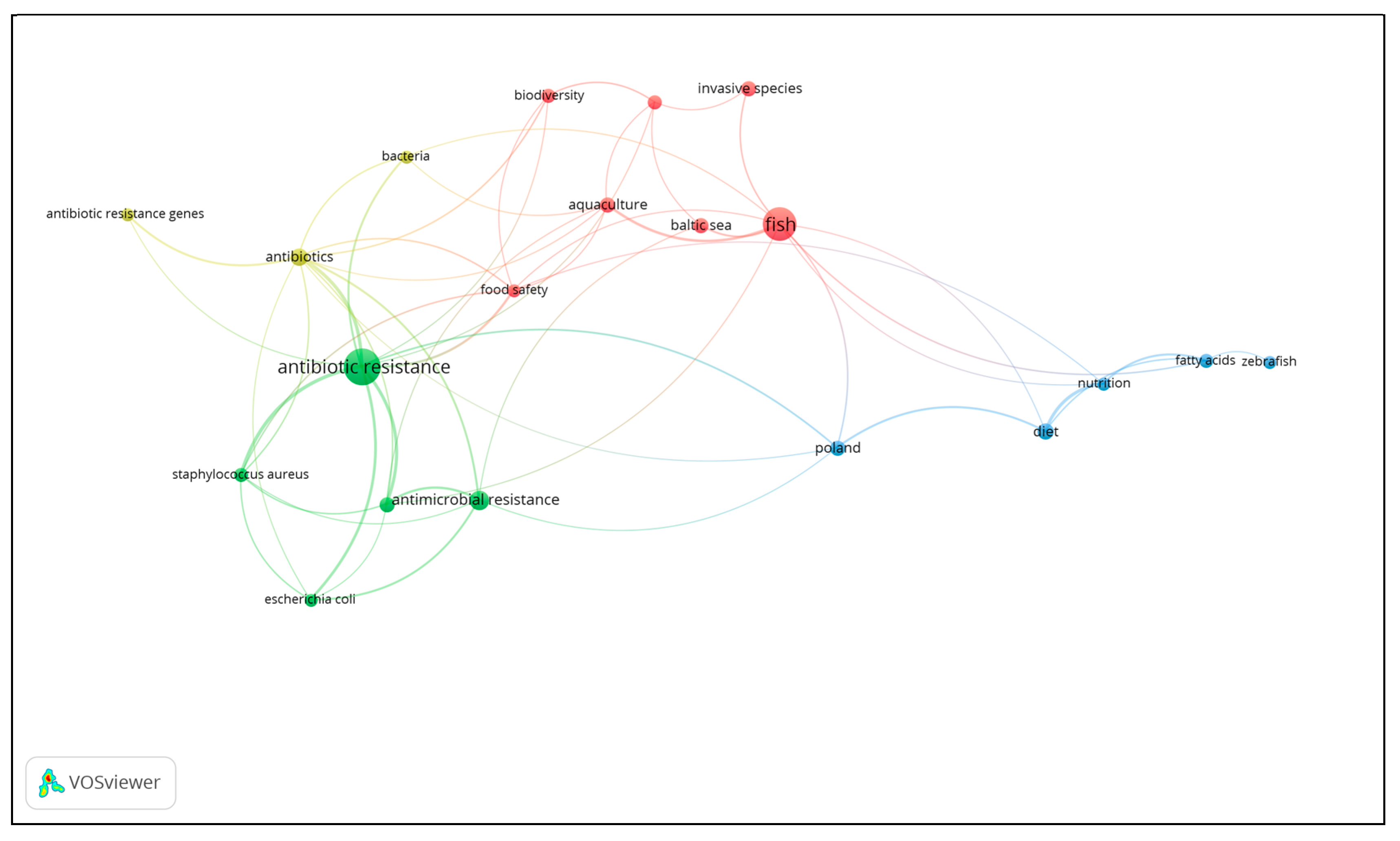
Network Analysis of Key Concepts
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Materials
4.3. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus
4.4. AntimicrobialSusceptibility Testing
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selamoglu, Z.; Naeem, M.Y. Fish as a significant source of nutrients. J. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.P.; Pradesh, U. Significance of fish nutrients for human health. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2020, 5, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Balami, S.; Sharma, A.; Karn, R. Significance of nutritional value of fish for human health. Makara J. Health Res. 2019, 2, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Roy, A.; Jeon, E.B.; DeWitt, C.A.M.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.Y. Comprehensive analysis of predominant pathogenic bacteria and viruses in seafood products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, J. Fish Consumption Worldwide—How Does Fish Consumption in Poland Compare to the Global Average? (In Polish: Spożycie Ryb Na Świecie—Jak Wypada Spożycie Ryb W Polsce Na Tle Świata?). 2022. Available online: https://wiadomoscispozywcze.pl/artykuly/11328/spozycie-ryb-na-swiecie-jak-wypada-spozycie-ryb-w-polsce-na-tle-swiata/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- OECD-FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031. 2022. Available online: https://www.agri-outlook.org/commodities/oecd-fao-agricultural-outlook-fish.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Pyz-Łukasik, R.; Paszkiewicz, W. Microbiological quality of farmed grass carp, bighead carp, Siberian sturgeon, and wels catfish from Eastern Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziarati, M.; Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Hassantabar, F.; Mehrabi, Z.; Dhawan, M.; Sharun, K.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Chaicumpa, W.; Shamsi, S. Zoonotic diseases of fish and their prevention and control. Vet. Q. 2022, 42, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitrus, A.A.; Peter, O.M.; Abbas, M.A.; Goni, M.D. Staphylococcus aureus: A review of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. Vet. Sci. Res. Rev. 2018, 4, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Gutama, K.P.; Koliopoulos, T. Staphylococcus aureus, an important pathogen of public health and economic importance: A comprehensive review. J. Emerg. Environ. Technol. Health Prot. 2021, 4, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi, G. Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Pathogenesis and Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, A. Role and significance of microorganisms in foods. In Food Microbiology; Ed-Tech Press: Waltham Abbey, UK, 2018; p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.S.; Lupindu, A.M.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mmoch, A.J. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus in fresh Indian mackerel fish. Tanz. Vet. J. 2019, 37, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Salman, A.E.B.; Lafi, S.Q. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in imported fish and correlations between antibiotic resistance and enterotoxigenicity. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, H.T.; Edarhoby, R.A.; Garbaj, A.M.; Azwai, S.M.; Abolghait, S.K.; Gammoudi, F.T.; Moawad, A.A.; Barbieri, I.; Eldaghayes, I.M. Occurrence, characterization, and antibiogram of Staphylococcus aureus in meat, meat products, and some seafood from Libyan retail markets. Vet. World. 2019, 12, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, J.; Mukherjee, S.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S.H.; Varela, M.F. Antibiotic resistance in fish-borne pathogens of public health significance: An emerging food safety issue. Curr. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 14, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz, W.; Strużycka, I. Antibiotic resistance—Where are we going (In Polish: Antybiotykooporność- dokąd zmierzamy?). Adv. Microbiol. 2023, 62, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzepkowska, A.; Zielińska, D.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Antibiotic resistance to bacteria of Lactobacillus genus isolated from food, as a criterion for probiotic (In Polish: Antybiotykooporność bakterii z rodzaju Lactobacillus pochodzących z żywności jako kryterium stawiane probiotykom). Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk. Rol. 2014, 578, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, L.; Ogugbue, C.J.; Okpokwasili, G.C. Antibiotic resistance profiles of bacteria associated with fresh and frozen shrimp (Palaemonetes sp.) and their public health significance. Int. J. Sci. Res. Knowl. 2013, 1, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Bauza-Kaszewska, J.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Budzyńska, A.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Skowron, K. Antibiotic Resistance in Selected Emerging Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens—An Issue of Concern? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, A.S.; Abou Elez, R.M.; El-Gazzar, N.; Elnahriry, S.S.; Alfifi, A.E.; Al-Harthi, H.F.; Ibrahim, D. Cross sectional analysis of risk factors associated with Mugil cephalus in retailed fish markets concerning methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1348973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu-Wu, J.W.F.; Guadamuz-Mayorga, C.; Oviedo-Cerdas, D.; Zamora, W.J. Antibiotic resistance and food safety: Perspectives on new technologies and molecules for microbial control in the food industry. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, V.; Mallea, A.; Bonilla, A.M.; Campos, J.; Rojas-García, P. Antibiotic-resistance profile of Staphylococcus aureus strains in the pork supply chain. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2022, 38, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Machado, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in different food groups and drinking water. Foods 2024, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.G.L.; Kasim, K.A.; Lekshmi, M.; Nayak, B.B.; Kumar, S. Incidence of methicillin-resistant staphylococci in fresh seafood. Adv. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, A.; Sergelidis, D.; Kirkoudis, I.; Anagnostou, V.; Kaitsa-Tsiopoulou, E.; Kazila, P.; Papa, A. Isolation and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus spp. in freshwater fish and Greek marketplaces. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2010, 19, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallal, M.M.S.; Fard, R.; Sharifi-Yazdi, R.M.N.; Sharifi-Yazdi, M.K. Prevalence of sea, seb, tsst, and mecA Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Shrimps Sold in Seafood Retailers in Tehran, Iran. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control 2018, 5, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fri, J.; Ndip, R.N.; Njom, H.A.; Clarke, A.M. First report of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in tank cultured dusky kob (Argyrosomus japonicus), and evaluation of tyree phenotypic methods in the detection of MRSA. J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.M.; Watanabe, W.; Fujii, T.; Shimamoto, T. Occurrence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant and-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from Japanese retail ready-to-eat raw fish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjusha, K.M.; Prejit, H.R.; Jess Vergis, A.K.; Vinod, V.K.; Prasanna, K.S. Assessment of post-harvest contamination of seafood with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in retail markets of Wayanad district, Kerala, India. Transit. Pathw. Initiat. 2022, 11, 6009–6013. [Google Scholar]
- Chon, J.; Sung, K.; Khan, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in food-producing and companion animals and food products. In Frontiers in Staphylococcus aureus; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraman, G.K.; Gupta, S.S.; Visnuvinayagam, S.; Muthulakshmi, T.; Elangovan, R.; Perumal, V.; Balasubramanium, G.; Lodha, T.; Yadav, A. Prevalence of S. aureus and/or MRSA from seafood products from Indian seafood products. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, E.M.; El-Sayed, M.; Ahmed, W.F.; El Barbary, M.L. Mycotic and bacterial evaluation for some fresh and frozen fish in Sharkia Governorate. Glob. J. Agric. Food Saf. Sci. 2014, 1, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Edris, M.A.; Hassanien, F.S.; Shaltout, F.A.E.; ELbaba, A.H.; Adel, N.M. Microbiological evaluation of some frozen and salted fish products in Egyptian markets. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2017, 33, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Odike, O. Investigation of bacterial spoilage of cooked food stored in freezer during thawing. Int. J. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2024, 3, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ariti, K.D.; Jabo, K.K. Determination of traditional and biologically viable methods for food preservation: A review. J. Vet. Health Sci. 2022, 3, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Stratev, D.; Stoyanchev, T.; Bangieva, D. Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Staphylococcus aureus in seafood. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2021, 10, 10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. 2005. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/2073/oj (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Marciniak, K.; Tyczewska, A.; Grzywacz, K. Genetics of antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). BioTechnologia 2024, 105, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brdová, D.; Ruml, T.; Viktorová, J. Mechanism of staphylococcal resistance to clinically relevant antibiotics. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 77, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilyk, B.L.; Panchal, V.V.; Tinajero-Trejo, M.; Hobbs, J.K.; Foster, S.J. An interplay of multiple positive and negative factors governs methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2022, 86, e0015921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska, B.; Kowalewski, C.; Krolak-Ulinska, A.; Marusza, W. Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.; Wu, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Prevalence, virulence genes, antimicrobial susceptibility, and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from retail aquatic products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léguillier, V.; Pinamonti, D.; Chang, C.-M.; Gunjan; Mukherjee, R.; Himanshu; Cossetini, A.; Manzano, M.; Anba-Mondoloni, J.; Malet-Villemagne, J.; et al. A review and meta-analysis of Staphylococcus aureus prevalence in foods. Microbe 2024, 4, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Shafee, M.; Iqbal, S.; Samad, A.; Khan, S.A.; Hasni, M.S.; Akbar, A. Enterotoxigenic methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus contamination in salted fish from Gwadar Balochistan. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e247701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onmaz, N.E.; Abay, S.; Karadal, F.; Hizlisoy, H.; Telli, N.; Al, S. Occurence and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella spp. in retail fish samples in Turkey. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharan, M.; Dhaka, P.; Bedi, J.S.; Mehta, N.; Singh, R. Assessment of biofilm-forming capacity and multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from animal-source foods: Implications for lactic acid bacteria intervention. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.; Takahisa, M.; Tong, T.A.N. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Pangasius fish and fish processing handlers in the Mekong Delta, Viet Nam. CTU J. Innov. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 15, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 6888-1:2001; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and Other Species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2022.
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- Wang, M.; Wei, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, L.; Di, L.; Lyu, C.; Liu, J. Analysis of multidrug-resistant bacteria in 3223 patients with hospital-acquired infections (HAI) from a tertiary general hospital in China. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 19, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalik, M.; Podbielska-Kubera, A.; Samet, A.; Konopka, W. Multidrug-resistant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from patients with chronic sinusitis–MDR, XDR, PDR strains. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2020, 74, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System); Version 13; StatSoft, Inc.: St Tulsa, OK, USA, 2013; Available online: www.statsoft.com (accessed on 20 September 2024).
| No. of Samples | M ± SD [CFU/g] | No. of Samples Positivefor S. aureus (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Place of origin | |||
| PL | 35 | 1.1 × 102 ± 6.6 × 101 | 25 (71.4) |
| ECs | 31 | 1.3 × 102 ± 6.4 × 101 | 20 (64.5) |
| ACs | 23 | 1.2 × 102 ± 6.9 × 101 | 16 (69.6) |
| Degree of processing | |||
| F | 47 | 1.2 × 102 ± 4.3 × 101 | 31 (66.0) |
| FS | 42 | 1.2 × 102 ± 6.6 × 101 | 30 (71.4) |
| Origin and processing | |||
| F/PL | 7 | 1.4 × 102 ± 1.6 × 101 | 5 (71.4) |
| F/ECs | 17 | 1.2 × 102 ± 4.7 × 101 | 10 (58.8) |
| F/ACs | 23 | 1.2 × 102 ± 6.9 × 101 | 16 (69.6) |
| FS/PL | 28 | 9.9 × 101 ± 7.2 × 101 | 20 (71.4) |
| FS/ECs | 14 | 1.5 × 102 ± 7.7 × 101 | 10 (71.4) |
| FS/ACs | 0 | - | 0 |
| Total | 89 | 1.2 × 102 ± 6.6 × 101 | 61 (68.5) |
| Antibiotic (Antibiotic Content in Disk) | Resistance (%) | MDR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Erythromycin (15 μg) | 30.5 | |
| Clindamycin (2 μg) | 22.2 | |
| Gentamicin (10 μg) | 8.3 | |
| Multidrug resistance | 0 |
| Place of Origin | |
| PL | n= 35 |
| ECs | n= 31 |
| ACs | n= 23 |
| Degree of Processing | |
| F | n= 47 |
| FS | n= 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kukułowicz, A.; Steinka, I.; Szelągowska, A. Silent Carriers: The Hidden Threat of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Seafood Across Poland’s Tri-City Area. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010073
Kukułowicz A, Steinka I, Szelągowska A. Silent Carriers: The Hidden Threat of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Seafood Across Poland’s Tri-City Area. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(1):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010073
Chicago/Turabian StyleKukułowicz, Anita, Izabela Steinka, and Aleksandra Szelągowska. 2025. "Silent Carriers: The Hidden Threat of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Seafood Across Poland’s Tri-City Area" Antibiotics 14, no. 1: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010073
APA StyleKukułowicz, A., Steinka, I., & Szelągowska, A. (2025). Silent Carriers: The Hidden Threat of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Seafood Across Poland’s Tri-City Area. Antibiotics, 14(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010073





