Pharmacokinetic Analysis of an Isoniazid Suspension Among Spanish Children Under 6 Years of Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
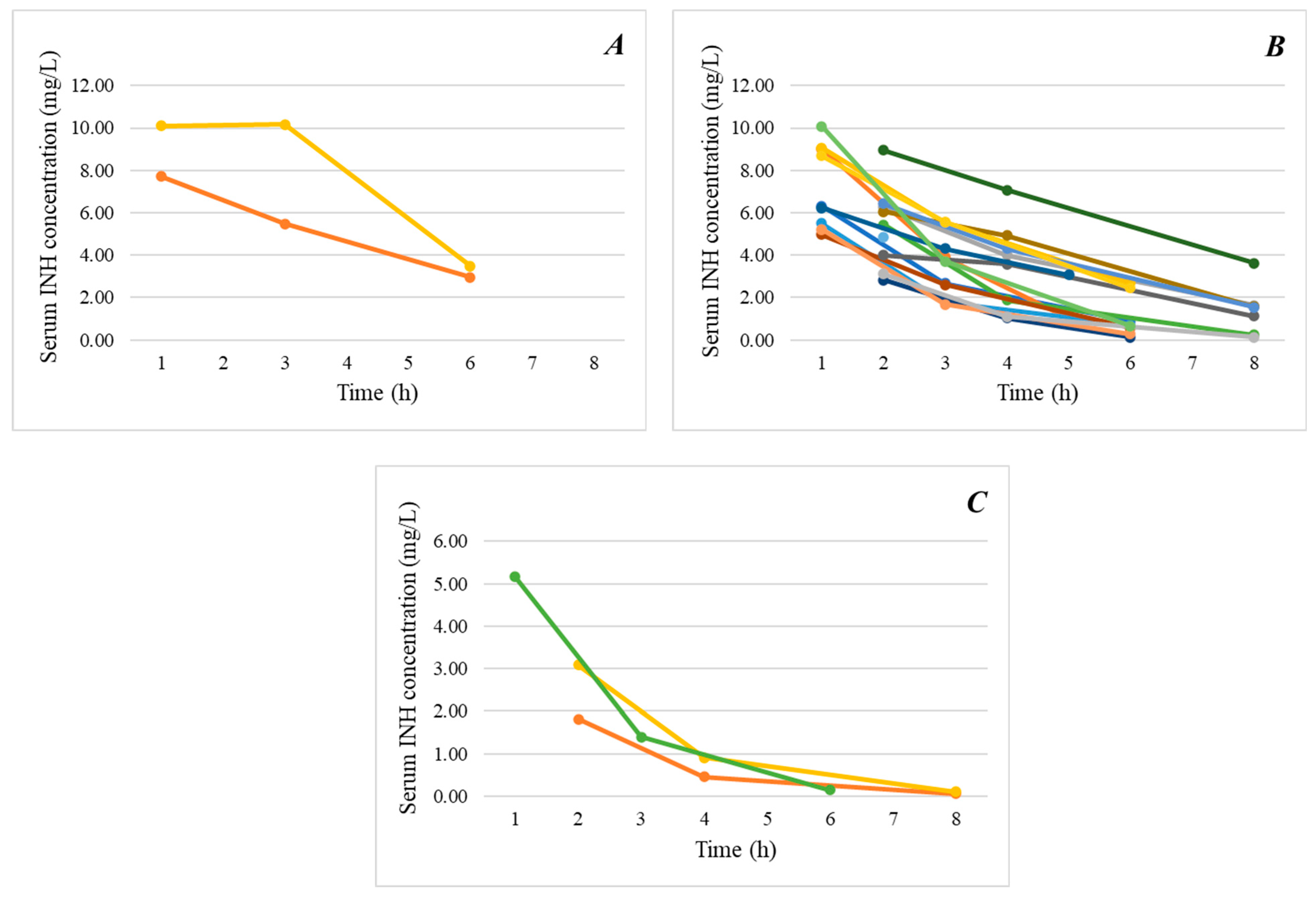
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design and Setting
4.2. Study Procedures
4.3. Drug Administration, Pharmacokinetic Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
4.4. Primary Outcomes
4.5. Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Roadmap Towards Ending TB in Children and Adolescents, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240084254 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica. Informe Epidemiológico Sobre la Situación de la Tuberculosis en España. Año 2022. Centro Nacional de Epidemiología. Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Available online: https://ens.isciii.es/documents/20119/531612/RENAVE_informe_Vigilancia+TB_+2022.pdf/89558149-e01d-0519-db27-44941311fc49 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Perez-Velez, C.M.; Marais, B.J. Tuberculosis in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thee, S.; Basu Roy, R.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Falcón-Neyra, L.; Neth, O.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Lillo, C.; Galli, L.; Venturini, E.; Buonsenso, D.; et al. Treatment and Outcome in Children with Tuberculous Meningitis: A Multicenter Pediatric Tuberculosis Network European Trials Group Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Roadmap for Childhood Tuberculosis: Towards Zero Deaths; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://www.tbonline.info/media/uploads/documents/roadmap_for_childhood_tuberculosis_%282013%29.compressed.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis Module 4: Treatment—Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240048126 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment—Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment, 2022 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240063129 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Updated and Consolidated Guidelines for Programmatic Management; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550239 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Dean, A.S.; Auguet, O.T.; Glaziou, P.; Zignol, M.; Ismail, N.; Kasaeva, T.; Floyd, K. 25 years of surveillance of drug-resistant tuberculosis: Achievements, challenges, and way forward. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e191–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix-Comellas, E.M.; Rozas-Quesada, L.; Velasco-Arnaiz, E.; Ferrés-Canals, A.; Estrada-Masllorens, J.M.; Force-Sanmartín, E.; Noguera-Julian, A. Impact of nursing interventions on adherence to treatment with antituberculosis drugs in children and young people: A nonrandomized controlled trial. J. Adv. Nurs. 2018, 74, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Dosing Instructions for the Use of Currently Available Fixed-Dose Combination TB Medicines for Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://stoptb.org/assets/documents/gdf/whatis/Interim%20Paediatric%20FDCs%20dosing%20instructions%20for%20prescribers_Sept09.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- WHO. Guidance for National Tuberculosis Programmes on the Management of Tuberculosis in Children, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/112360/9789241548748_eng.pdf?sequen (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Bartelink, I.H.; Rademaker, C.M.; Schobben, A.F.; van den Anker, J.N. Guidelines on paediatric dosing on the basis of developmental physiology and pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 1077–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.P.; Vandenplas, S.; Botha, F.J.; Vandenplas, M.L.; I Seifart, H.; van Helden, P.D.; van der Walt, B.J.; Donald, P.R.; van Jaarsveld, P.P. Trimodality of isoniazid elimination: Phenotype and genotype in patients with tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, B.P.; Béranger, A.; Radtke, K.; Mohamed, A.; Mirzayev, F.; Gegia, M.; Linh, N.N.; Schumacher, S.G.; Nahid, P.; Savic, R.M. Effectiveness and Pharmacokinetic Exposures of First-Line Drugs Used to Treat Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 76, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafar, F.; Wasmann, R.E.; McIlleron, H.M.; Aarnoutse, R.E.; Schaaf, H.S.; Marais, B.J.; Agarwal, D.; Antwi, S.; Bang, N.D.; Bekker, A.; et al. Global estimates and determinants of antituberculosis drug pharmacokinetics in children and adolescents: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2201596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsultan, A.; Peloquin, C.A. Therapeutic drug monitoring in the treatment of tuberculosis: An update. Drugs 2014, 74, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskapan, A.; Idrus, L.R.; Postma, M.J.; Wilffert, B.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Stienstra, Y.; Touw, D.J.; Andersen, A.B.; Bekker, A.; Denti, P.; et al. A systematic review on the effect of HIV infection on the pharmacokinetics of first-line tuberculosis drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, T.G.; Svensson, E.M.; Musiime, V.; Rojo, P.; E Dooley, K.; McIlleron, H.; E Aarnoutse, R.; Burger, D.M.; Turkova, A.; Colbers, A. Pharmacokinetics of antiretroviral and tuberculosis drugs in children with HIV/TB co-infection: A systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3433–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanz-Lobo, A.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Minguell, L.; López-Suárez, A.M.; Soriano-Arandes, A.; Espiau, M.; Gil, E.C.; Medina, E.M.L.; Bustillo-Alonso, M.; Aguirre-Pascual, E.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Children With Nonsevere Tuberculosis in Spain. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguera-Julian, A.; Buonsenso, D.; McKenna, L.; Seddon, J.A.; Ritz, N. Availability of fixed-dose, child-friendly formulations of first-line tuberculosis drugs in Europe. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguera-Julian, A.; Latre, C.; Flores, Á. Availability of paediatric dispersible fixed-dose combinations of tuberculosis drugs in Spain. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2400104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wademan, D.T.; Busakwe, L.; Nicholson, T.J.; van der Zalm, M.; Palmer, M.; Workman, J.; Turkova, A.; Crook, A.M.; Thomason, M.J.; Gibb, D.M.; et al. Acceptability of a first-line anti-tuberculosis formulation for children: Qualitative data from the SHINE trial. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2019, 23, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denti, P.; E Wasmann, R.; van Rie, A.; Winckler, J.; Bekker, A.; Rabie, H.; Hesseling, A.C.; E van der Laan, L.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C.; Zar, H.J.; et al. Optimizing Dosing and Fixed-Dose Combinations of Rifampicin, Isoniazid, and Pyrazinamide in Pediatric Patients With Tuberculosis: A Prospective Population Pharmacokinetic Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabala, C.; Turkova, A.; Hesseling, A.C.; Zimba, K.M.; van der Zalm, M.; Kapasa, M.; Palmer, M.; Chirehwa, M.; Wiesner, L.; Wobudeya, E.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of first-line drugs in children with tuberculosis using WHO-recommended weight band doses and formulations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, A.; Schaaf, H.S.; Seifart, H.I.; Draper, H.R.; Werely, C.J.; Cotton, M.F.; Hesseling, A.C. Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid in low-birth-weight and premature infants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Schaaf, H.S.; Draper, H.R.; van der Laan, L.; Murray, S.; Wiesner, L.; Donald, P.R.; McIlleron, H.M.; Hesseling, A.C. Pharmacokinetics of Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol in Infants Dosed According to Revised WHO-Recommended Treatment Guidelines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denti, P.; E Wasmann, R.; Francis, J.; McIlleron, H.; Sugandhi, N.; Cressey, T.R.; Mirochnick, M.; Capparelli, E.V.; Penazzato, M. One dose does not fit all: Revising the WHO paediatric dosing tool to include the non-linear effect of body size and maturation. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Velpandian, T.; Singla, M.; Kanhiya, K.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R. Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol in HIV-infected Indian children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero-Artigao, F.; Del Rosal, T.; Falcón-Neyra, L.; Ferreras-Antolín, L.; Gómez-Pastrana, D.; Hernanz-Lobo, A.; Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Pascual-Sánchez, M.T.; Rodríguez-Molino, P.; et al. Update on the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. An. Pediatría (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 98, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbo, T.; Louie, A.; Liu, W.; Brown, D.; Ambrose, P.G.; Bhavnani, S.M.; Drusano, G.L. Isoniazid bactericidal activity and resistance emergence: Integrating pharmacodynamics and pharmacogenomics to predict efficacy in different ethnic populations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaram, R.; Shandil, R.K.; Gaonkar, S.; Kaur, P.; Suresh, B.L.; Mahesh, B.N.; Jayashree, R.; Nandi, V.; Bharath, S.; Kantharaj, E.; et al. Isoniazid pharmacokinetics–pharmacodynamics in an aerosol infection model of tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafar, F.; Alffenaar, J.C. Is it time for new fixed-dose combinations and revised weight bands for children with drug-susceptible TB? Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2023, 27, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwara, A.; Yang, H.; Martyn-Dickens, C.; Enimil, A.; Amissah, A.K.; Ojewale, O.; Dompreh, A.; Bosomtwe, D.; Sly-Moore, E.; Opoku, T.; et al. Adequacy of WHO weight-band dosing and fixed-dose combinations for the treatment of TB in children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2023, 27, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.T.; Starke, J.R. Monitoring Treatment of Childhood Tuberculosis and the Role of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Marco-García, M.; Gamell, A.; Cusó, T.; Monsonís, M.; Latre, C.; Fortuny, C.; Noguera-Julian, A. Toxicity of the Increased Recommended Doses of First-line Anti-tuberculosis Oral Drugs in Children in a Reference Center in Spain. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkova, A.; Wills, G.H.; Wobudeya, E.; Chabala, C.; Palmer, M.; Kinikar, A.; Hissar, S.; Choo, L.; Musoke, P.; Mulenga, V.; et al. Shorter Treatment for Nonsevere Tuberculosis in African and Indian Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansumba, M.; Kumbakumba, E.; Orikiriza, P.; Bastard, M.; Mwanga, J.A.; Boum, Y.; de Beaudrap, P.; Bonnet, M. Treatment outcomes and tolerability of the revised WHO anti-tuberculosis drug dosages for children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, T.; Adjobimey, M.; Ruslami, R.; Trajman, A.; Sow, O.; Baah, J.O.; Marks, G.B.; Long, R.; Elwood, K.; Zielinski, D.; et al. Safety and Side Effects of Rifampin versus Isoniazid in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.-L.; D’Cunha, R.; Li, P.; Al-Shaer, M.H.; Alghamdi, W.A.; An, G.; Peloquin, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Isoniazid Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Tuberculosis. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, e220–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, J.; Ohno, M.; Kubota, R.; Yokota, S.; Nagai, T.; Tsuyuguchi, K.; Okuda, Y.; Takashima, T.; Kamimura, S.; Fujio, Y.; et al. NAT2 genotype guided regimen reduces isoniazid-induced liver injury and early treatment failure in the 6-month four-drug standard treatment of tuberculosis: A randomized controlled trial for pharmacogenetics-based therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.M.; Ahmed, T.; Amanullah, F.; Browning, R.; Cardenas, V.; Casenghi, M.; Cuevas, L.E.; Gale, M.; Gie, R.P.; Grzemska, M.; et al. Evaluation of tuberculosis diagnostics in children: 1. Proposed clinical case definitions for classification of intrathoracic tuberculosis disease. Consensus from an expert panel. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, S199–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsis, K.P.; Weber, W.W.; Bell, D.A.; Dupret, J.-M.; Evans, D.A.P.; Grant, D.M.; Hein, D.W.; Lin, H.J.; Meyer, U.A.; Relling, M.V.; et al. Nomenclature for N-acetyltransferases. Pharmacogenetics 1995, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| At inclusion (n = 24) | |
| Sex (female) | 12 (50.0) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Latin American | 12 (50.0) |
| Caucasian | 5 (20.8) |
| Maghrebi | 4 (16.7) |
| Asian | 2 (8.3) |
| Black | 1 (4.2) |
| Indication for INH treatment | |
| Primary chemoprophylaxis | 12 (50.0) |
| TB infection | 3 (12.5) |
| TB disease a | 9 (37.5) |
| ALT levels (IU/L) | 19.5 (16.0–27.5) |
| Hemoglobin levels (g/dL) | 12.4 (11.6–13.2) |
| Albumin levels (g/L) | 44 (43.5–46) |
| On the day of pharmacokinetic sampling (n = 24) | |
| Age (years) | 2.8 (1.8–4.2) |
| <2 years of age, Group A | 7 (29.2) |
| ≥2 years of age, Group B | 17 (70.8) |
| Weight (kg) | 13.3 (11.9–18.0) |
| Weight-for-length/height Z-score in patients < 5 years (mean, SD) | 0.60 (0.86) |
| Body mass index-for-age Z-score in patients ≥ 5 years (mean, SD) | 0.03 (0.45) |
| Malnutrition b | 0 (0) |
| Breastfeeding c | 2 (8.3) |
| INH dose (mg/kg) | 10 (10.0–10.0) |
| Concomitant medications | |
| Other anti-TB drugs (rifampicin in all cases) | 11 (45.8) |
| Steroids | 2 (8.3) |
| Time on INH treatment (weeks) | 12.4 (10.1–25.3) |
| ALT levels (IU/L) | 21.0 (15.5–27.3) |
| ALT levels > 50 IU/L | 3 (12.5) |
| Pre-dose fasting time (minutes) | 681 (591–760) |
| Post-dose fasting time (minutes) | 30 (30–35) |
| Median (IQR) | Patients Below/Within/Above the Recommended Range in Adults (In Brackets) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mg/L) | 6.1 (4.5–8.2) | 3/8/12 (3–6) [17] |
| Tmax (h) | 1.6 (1.2–2.0) | |
| AUC0–24h (h∙mg/L) | 23.0 (11.2–35.4) | 6/8/9 (11.6–26.3) [18] |
| t1/2 (h) | 1.7 (1.3–2.9) | |
| Cl/F (L/h) | 5.7 (4.4–12.5) | |
| Vd/F (L) | 21.7 (13.8–24.4) |
| n | Cmax (mg/L) | p | Tmax (h) | p | AUC0–24h (h∙mg/L) | p | t1/2 (h) | p | Cl/F (L/h) | p | Vd/F (L) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 12 | 6.1 (4.9–9.0) | 0.443 | 1.8 (1.3–2.0) | 0.630 | 24.7 (12.4–35.3) | 0.566 | 1.7 (1.3–3.0) | 0.608 | 5.0 (4.0–9.7) | 0.487 | 20.6 (12.6–24.3) | 0.651 |
| Male | 11 | 5.3 (4.4–6.7) | 1.6 (1.2–2.0) | 15.7 (10.8–36.7) | 1.7 (1.3–2.7) | 7.2 (4.8–12.5) | 21.8 (15.6–25.0) | ||||||
| <2 years | 7 | 6.3 (5.9–8.4) | 0.234 | 1.2 (1.1–1.5) | 0.075 | 23.0 (15.1–37.4) | 0.624 | 1.8 (1.5–2.9) | 0.413 | 4.6 (3.0–5.9) | 0.585 | 13.8 (11.9–14.3) | 0.003 |
| ≥2 years | 16 | 5.2 (4.0–6.4) | 2.0 (1.4–2.0) | 20.0 (9.8–35.3) | 1.5 (1.3–2.9) | 8.2 (5.0–16.0) | 22.9 (21.1–27.4) | ||||||
| NAT2 genotype SS | 2 | 8.9 (8.3–9.5) | 0.030 | 2.1 (1.6–2.5) | 0.592 | 50.0 (48.1–51.9) | 0.011 | 2.8 (2.4–3.2) | 0.026 | 2.4 (2.3–2.5) | 0.006 | 9.9 (8.0–11.8) | 0.024 |
| NAT2 genotype FS | 17 | 6.1 (5.0–8.1) | 1.5 (1.1–2.0) | 24.4 (15.2–35.3) | 1.8 (1.3–3.0) | 5.0 (4.6–9.9) | 21.7 (13.8–23.2) | ||||||
| NAT2 genotype FF | 3 | 3.1 (2.4–4.1) | 2.0 (1.7–2.0) | 8.3 (6.5–9.3) | 1.2 (1.1–1.2) | 17.5 (16.9–27.5) | 29.0 (26.7–48.1) | ||||||
| INH monotherapy | 12 | 5.5 (5.0–6.4) | 0.865 | 2.0 (1.3–2.0) | 0.531 | 16.4 (12.4–33.3) | 0.786 | 1.6 (1.3–2.2) | 0.651 | 6.8 (4.3–10.5) | 0.928 | 18.5 (13.4–23.5) | 0.608 |
| INH + rifampicin | 11 | 6.1 (3.6–8.2) | 1.4 (1.3–2.0) | 25.0 (10.2–37.3) | 2.6 (1.3–3.0) | 5.0 (4.4–14.4) | 21.8 (16.2–26.6) |
| Total (n = 26) | Group A, <2 Years (n = 9) | Group B, ≥2 Years (n = 17) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 8/26 (30.8%) | 3/9 (33.3%) | 5/17 (29.4%) |
| Any adverse event | 11 | 5 | 6 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Bronchospasm | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Headache | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Pneumonia | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Fever | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cough | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noguera-Julian, A.; Wilhelmi, E.; Cussó, M.; Aarnoutse, R.; Colbers, A.; Martorell, L.; López-Ramos, M.G.; Vinent, J.; Farré, R.; Soy, D.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of an Isoniazid Suspension Among Spanish Children Under 6 Years of Age. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010074
Noguera-Julian A, Wilhelmi E, Cussó M, Aarnoutse R, Colbers A, Martorell L, López-Ramos MG, Vinent J, Farré R, Soy D, et al. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of an Isoniazid Suspension Among Spanish Children Under 6 Years of Age. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010074
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoguera-Julian, Antoni, Emma Wilhelmi, Maria Cussó, Rob Aarnoutse, Angela Colbers, Loreto Martorell, Maria Goretti López-Ramos, Joan Vinent, Rosa Farré, Dolors Soy, and et al. 2025. "Pharmacokinetic Analysis of an Isoniazid Suspension Among Spanish Children Under 6 Years of Age" Antibiotics 14, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010074
APA StyleNoguera-Julian, A., Wilhelmi, E., Cussó, M., Aarnoutse, R., Colbers, A., Martorell, L., López-Ramos, M. G., Vinent, J., Farré, R., Soy, D., Simó-Nebot, S., & Fortuny, C. (2025). Pharmacokinetic Analysis of an Isoniazid Suspension Among Spanish Children Under 6 Years of Age. Antibiotics, 14(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010074





