Antimicrobial Resistance Elements in Coastal Water of Llanquihue Lake, Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
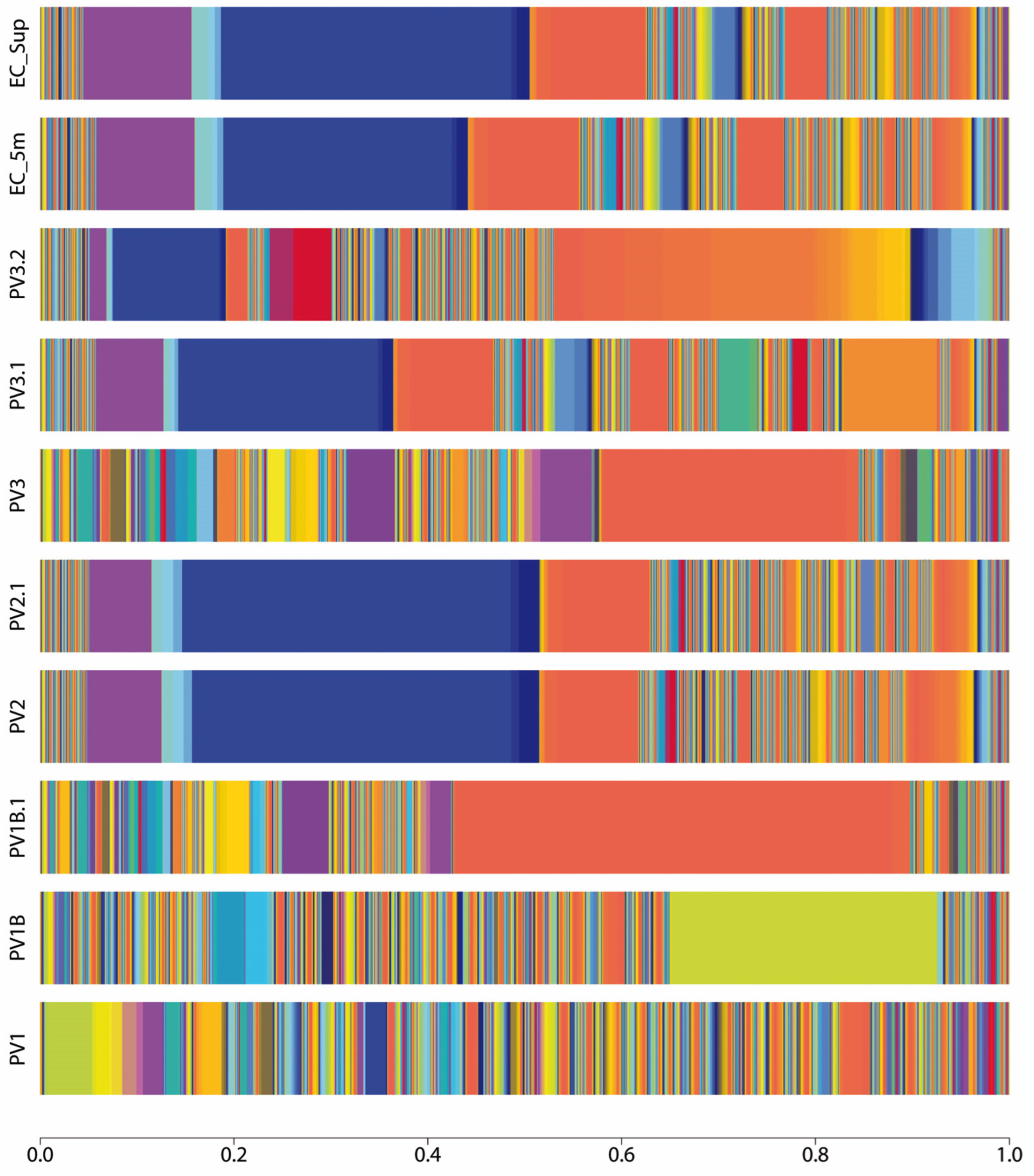
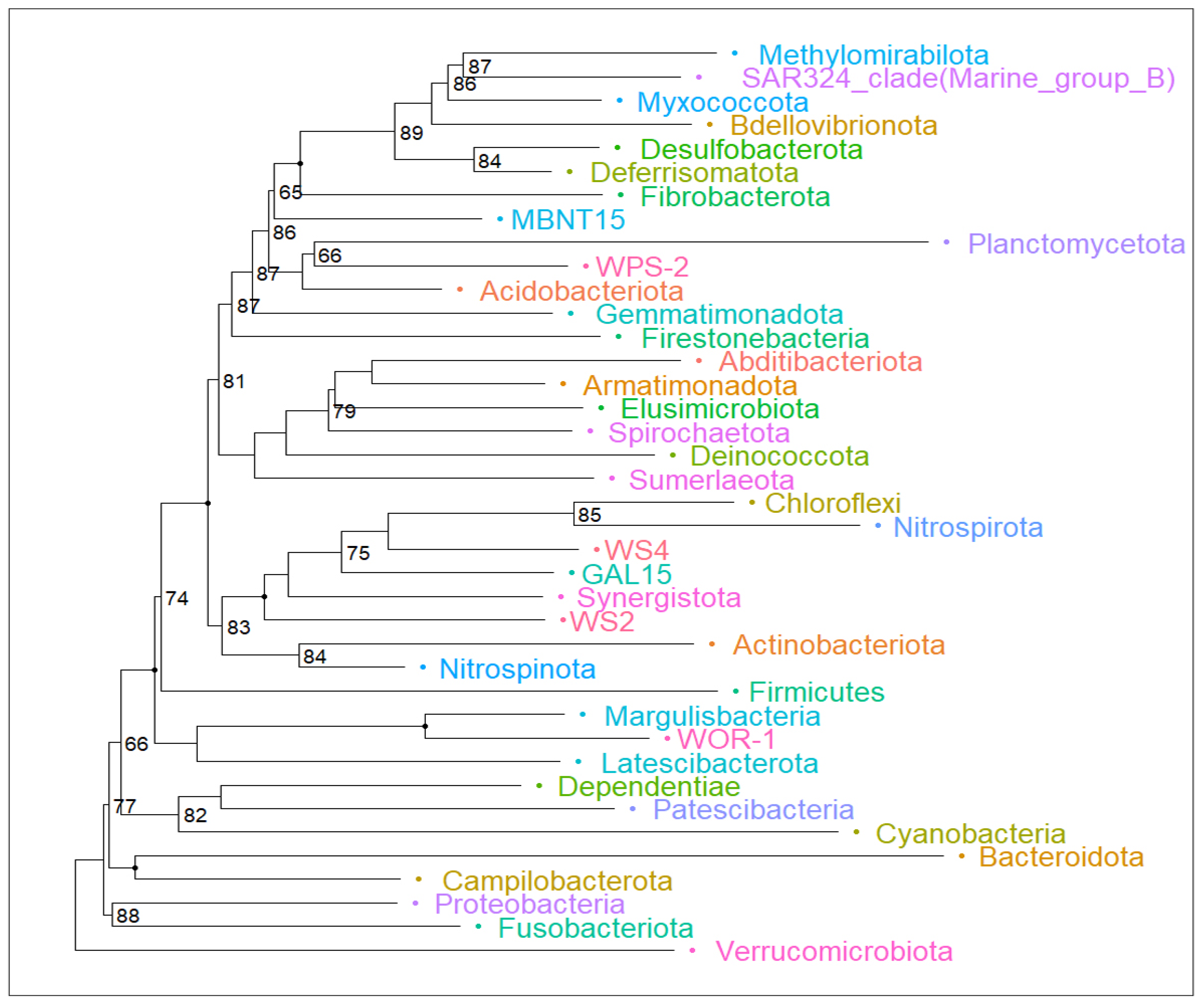
2.1. Composition of Bacterial Communities That Inhabit Llanquihue Lake
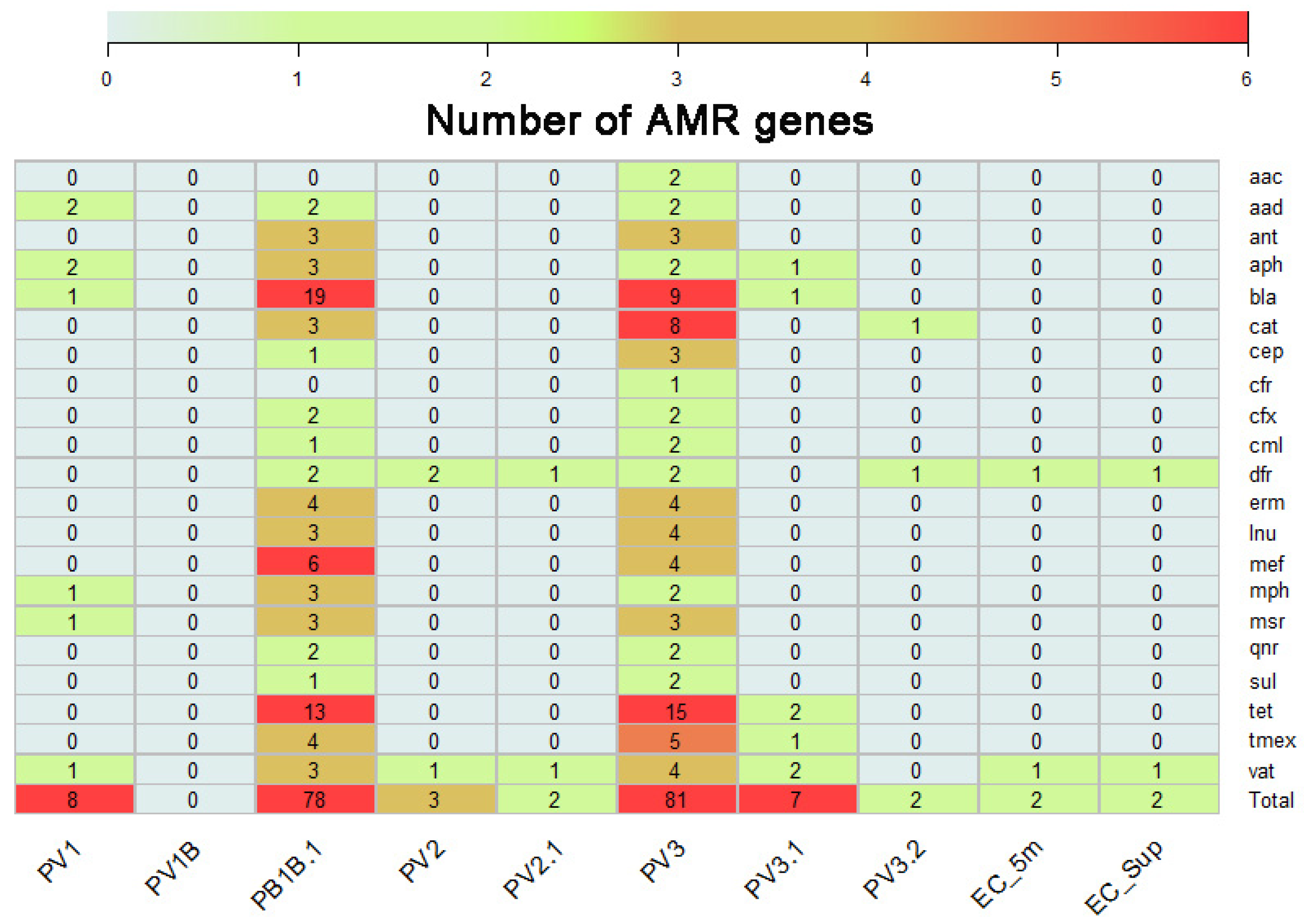
2.2. Identification of AMR Genes Present on DNA Recovered from Llanquihue Lake
2.3. Mobile Genetic Elements Carrying AMR Genes Are Related to Microbial Species of Health Interest
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests of Microbial Isolates Do Not Show the Presence of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Microbial Isolation
4.2. DNA Purification and Metagenomic Sequencing
4.3. Metagenomic Data Analysis and Identification of AMR Genes
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Multifaceted Phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.M.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in Microbes: History, Mechanisms, Therapeutic Strategies and Future Prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Committee on the Long-Term Health and Economic Effects of Antimicrobial Resistance; Palmer, G.H.; Buckley, G.J. The Health and Economic Burden of Resistance; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, A.N.; Zhu, S.; Cooper, N.; Little, P.; Tarrant, C.; Hickman, M.; Yao, G. The Economic Burden of Antibiotic Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Drug-Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Njoga, E.O.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter Species from Food-Producing Animals and Humans in Nigeria: Public Health Implications and One Health Control Measures. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 103, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, J.E., Jr. Economic Impact of Antimicrobial Resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S. Understanding the Contribution of Environmental Factors in the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2015, 20, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, P.M.C.; Blaak, H.; de Jong, M.C.M.; Graat, E.A.M.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Role of the Environment in the Transmission of Antimicrobial Resistance to Humans: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11993–12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Petersen, T.N. Importance of Mobile Genetic Elements for Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Metagenomic Sewage Samples across the World. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic Resistance in the Environment: A Link to the Clinic? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H.H.P. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Water Environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.-L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Water Environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The Vocabulary of Microbiome Research: A Proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.J.; Markey, B.K.; Leonard, F.C.; Hartigan, P.; Fanning, S.; Fitzpatrick, E.S. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781405158237. [Google Scholar]
- Requena, T.; Velasco, M. The Human Microbiome in Sickness and in Health. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2021, 221, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, M.; Szoboszlay, S.; Vörös, L.; Lovász, Z.; Méhes, N.; Mátyás, K.; Sebők, R.; Kaszab, E.; Háhn, J.; Tóth, G.; et al. Bacterial Community Dynamics along a River-Wetland-Lake System. Water 2022, 14, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, M.W.; Lanclos, V.C.; Faircloth, B.C.; Thrash, J.C. Cultivation and Genomics of the First Freshwater SAR11 (LD12) Isolate. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1846–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuenschwander, S.M.; Ghai, R.; Pernthaler, J.; Salcher, M.M. Microdiversification in Genome-Streamlined Ubiquitous Freshwater Actinobacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline Antibiotics and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025387. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, R.; Sami, M. Genetic Investigation of Beta-Lactam Associated Antibiotic Resistance among Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Water Sources. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, R.J.; Melander, C. Overcoming Resistance to β-Lactam Antibiotics. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 4207–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüthrich, D.; Brilhante, M.; Hausherr, A.; Becker, J.; Meylan, M.; Perreten, V. A Novel Trimethoprim Resistance Gene, DfrA36, Characterized from Escherichia coli from Calves. mSphere 2019, 4, e00255-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.P.; O’Mahony, R.; Buckley, J.F.; Shine, P.; Fidelma Boyd, E.; Gilroy, D.; Fanning, S. Investigation of a Global Collection of Nontyphoidal Salmonella of Various Serotypes Cultured between 1953 and 2004 for the Presence of Class 1 Integrons. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 266, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Schwarz, S. DfrA20, a Novel Trimethoprim Resistance Gene from Pasteurella multocida. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Doublet, B.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Resistance to Chloramphenicol and Florfenicol. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-X.; Lei, C.-W.; Zhang, A.-Y.; Wang, H.-N. Novel Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-7.1 in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1791–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madinier, I.; Fosse, T.; Giudicelli, J.; Labia, R. Cloning and Biochemical Characterization of a Class A β-Lactamase from Prevotella intermedia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2386–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karray, F.; Darbon, E.; Oestreicher, N.; Dominguez, H.; Tuphile, K.; Gagnat, J.; Blondelet-Rouault, M.-H.; Gerbaud, C.; Pernodet, J.-L. Organization of the Biosynthetic Gene Cluster for the Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Microbiology 2007, 153, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthje, P.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Schwarz, S. Identification and Characterization of Nine Novel Types of Small Staphylococcal Plasmids Carrying the Lincosamide Nucleotidyltransferase Gene lnu(A). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grosso, M.; Iannelli, F.; Messina, C.; Santagati, M.; Petrosillo, N.; Stefani, S.; Pozzi, G.; Pantosti, A. Macrolide Efflux Genes mef (A) and mef (E) Are Carried by Different Genetic Elements in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, F.; Santoro, F.; Santagati, M.; Docquier, J.-D.; Lazzeri, E.; Pastore, G.; Cassone, M.; Oggioni, M.R.; Rossolini, G.M.; Stefani, S.; et al. Type M Resistance to Macrolides Is Due to a Two-Gene Efflux Transport System of the ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Superfamily. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharatham, N.; Bhowmik, P.; Aoki, M.; Okada, U.; Sharma, S.; Yamashita, E.; Shanbhag, A.P.; Rajagopal, S.; Thomas, T.; Sarma, M.; et al. Structure and Function Relationship of OqxB Efflux Pump from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allignet, J.; Loncle, V.; Simenel, C.; Delepierre, M.; El Solh, N. Sequence of a Staphylococcal Gene, vat, Encoding an Acetyltransferase Inactivating the A-Type Compounds of Virginiamycin-like Antibiotics. Gene 1993, 130, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcillán-Barcia, M.P.; Redondo-Salvo, S.; de la Cruz, F. Plasmid Classifications. Plasmid 2023, 126, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard-Tenth Edition. Available online: https://clsi.org/media/1632/m07a10_sample.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H. Phylogenetic Identification and in Situ Detection of Individual Microbial Cells without Cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Moreira, I.; Egas, C.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Bacterial Diversity from the Source to the Tap: A Comparative Study Based on 16S RRNA Gene-DGGE and Culture-Dependent Methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miłobedzka, A.; Ferreira, C.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Calderón-Franco, D.; Gorecki, A.; Purkrtova, S.; Bartacek, J.; Dziewit, L.; Singleton, C.M.; Nielsen, P.H.; et al. Monitoring Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Environments: The Challenges of Filling a Gap in the One-Health Cycle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandra, S.; Alvarez-Uria, G.; Turner, P.; Joshi, J.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; van Doorn, H.R. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Progress and Challenges in Eight South Asian and Southeast Asian Countries. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00048-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in the Food Chain: Trade, One Health and Codex. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Bortolaia, V.; Tate, H.; Tyson, G.H.; Aarestrup, F.M.; McDermott, P.F. Using Genomics to Track Global Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, P.; Knudsen, B.E.; Lukjancenko, O.; Duarte, A.S.R.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Smit, L.A.M.; Schmitt, H.; Garcia, A.D.; Hansen, R.B.; et al. Abundance and Diversity of the Faecal Resistome in Slaughter Pigs and Broilers in Nine European Countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseem, H.; Williams, M.R.; Stedtfeld, T.; Chai, B.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Cole, J.R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Hashsham, S.A. Virulence Factor Activity Relationships (VFARs): A Bioinformatics Perspective. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. The New Science of Metagenomics; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780309106764. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, A.-D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T. Mobile Antibiotic Resistome in Wastewater Treatment Plants Revealed by Nanopore Metagenomic Sequencing. Microbiome 2019, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, S.; Machiyama, A.; Ijichi, M.; Inoue, K.; Oshima, K.; Hattori, M.; Yoshizawa, S.; Kogure, K.; Iwasaki, W. Genomic and Metagenomic Analysis of Microbes in a Soil Environment Affected by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake Tsunami. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Albrecht, B.; Bağcı, C.; Bessarab, I.; Górska, A.; Jolic, D.; Williams, R.B.H. MEGAN-LR: New Algorithms Allow Accurate Binning and Easy Interactive Exploration of Metagenomic Long Reads and Contigs. Biol. Direct 2018, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Shang, R. GLOBMAP SWF: A Global Annual Surface Water Cover Frequency Dataset during 2000–2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 14, 4505–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, W.; Hubeny, J.; Buta-Hubeny, M.; Rolbiecki, D.; Harnisz, M.; Paukszto, Ł.; Korzeniewska, E. Metagenomics Analysis of Probable Transmission of Determinants of Antibiotic Resistance from Wastewater to the Environment—A Case Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruti, I.; Nahim-Granados, S.; Abeledo-Lameiro, M.J.; Oller, I.; Polo-López, M.I. Peroxymonosulfate/Solar Process for Urban Wastewater Purification at a Pilot Plant Scale: A Techno-Economic Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, A.M.M.T.; Hassan, J.; Rahman, M.T. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase in Escherichia coli Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Environments in Bangladesh: A One Health Perspective Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. One Health 2023, 16, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, I.; Rozanah, U.N.; Nishiyama, M.; Mith, H.; Watanabe, T. Detection and Genetic Analysis of Escherichia coli from Tonle Sap Lake and Its Tributaries in Cambodia: Spatial Distribution, Seasonal Variation, Pathogenicity, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorlí, L.; Luque, S.; Li, J.; Campillo, N.; Danés, M.; Montero, M.; Segura, C.; Grau, S.; Horcajada, J.P. Colistin for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extremely Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Dose Is Critical. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanita, M.T.; Carrilho, C.M.D.d.M.; Garcia, J.P.; Festti, J.; Cardoso, L.T.Q.; Grion, C.M.C. Parenteral Colistin for the Treatment of Severe Infections: A Single Center Experience. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2013, 25, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Saravolatz, L.D. Colistin: The Revival of Polymyxins for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyman, Y.; Whitelaw, A.C.; Barnes, J.M.; Maloba, M.R.B.; Newton-Foot, M. Characterisation of Mobile Colistin Resistance Genes (mcr-3 and mcr-5) in River and Storm Water in Regions of the Western Cape of South Africa. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ichiyama, S.; Yoneda, M.; Matsumura, Y. Molecular Characterization of a Multidrug-Resistant IncF Plasmid Carrying Mcr-3.1 in an Escherichia coli Sequence Type 393 Strain of Wastewater Origin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Tian, Z.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S. Abundance and Distribution of Tetracycline Resistance Genes and Mobile Elements in an Oxytetracycline Production Wastewater Treatment System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7551–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; He, X.; Bu, Y.; Shi, P.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, X.-X. Environmental Fate of Tetracycline Resistance Genes Originating from Swine Feedlots in River Water. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2014, 49, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engemann, C.A.; Keen, P.L.; Knapp, C.W.; Hall, K.J.; Graham, D.W. Fate of Tetracycline Resistance Genes in Aquatic Systems: Migration from the Water Column to Peripheral Biofilms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5131–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, G.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; McGann, P.; Hiney, M.; Smith, P.; Pickup, R.W. Distribution of Oxytetracycline Resistance Plasmids between Aeromonads in Hospital and Aquaculture Environments: Implication of Tn1721 in Dissemination of the Tetracycline Resistance Determinant Tet A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, I.S.; Fonseca, F.; Alves, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Correia, A. Tetracycline-Resistance Genes in Gram-Negative Isolates from Estuarine Waters. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernapesca, P. Informe Sobre uso de Antimicrobianos en la Salmonicultura Nacional. Available online: http://www.sernapesca.cl/sites/default/files/informe_sobre_el_uso_de_antimicrobianos_en_la_salmonicultura_nacional_-_primer_semestre_-_ano_2022.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Ben Maamar, S.; Glawe, A.J.; Brown, T.K.; Hellgeth, N.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.-P.; Huttenhower, C.; Hartmann, E.M. Mobilizable Antibiotic Resistance Genes Are Present in Dust Microbial Communities. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Amézquita, A.; Collignon, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Graham, D.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Silley, P.; Snape, J.R.; et al. Management Options for Reducing the Release of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes to the Environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katusiime, J.; Schütt, B. Integrated Water Resources Management Approaches to Improve Water Resources Governance. Water 2020, 12, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalova, L.; Siegrist, H.; Singer, H.; Wittmer, A.; McArdell, C.S. Hospital Wastewater Treatment by Membrane Bioreactor: Performance and Efficiency for Organic Micropollutant Elimination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millanao, A.R.; Barrientos-Schaffeld, C.; Siegel-Tike, C.D.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Godfrey, H.P.; Dölz, H.J.; Buschmann, A.H.; Cabello, F.C. Resistencia a los antimicrobianos en Chile y el paradigma de Una Salud: Manejando los riesgos para la salud pública humana y animal resultante del uso de antimicrobianos en la acuicultura del salmón y en medicina. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2018, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerum, A.M.; Heuer, O.E.; Emborg, H.-D.; Bagger-Skjøt, L.; Jensen, V.F.; Rogues, A.-M.; Skov, R.L.; Agersø, Y.; Brandt, C.T.; Seyfarth, A.M.; et al. Danish Integrated Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring and Research Program. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, U.Q.; Dalcanale, F.; Kayser, G.; Bentley, P.; Bartram, J. Evidence-Based Decision-Making on Water Quality in Domestic Water Supply in Malawi, Ecuador, and Brazil. Water Policy 2018, 20, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, C.Z.; Garfan, S.; Talal, M.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Alamleh, A.; Ahmaro, I.Y.Y.; Sulaiman, S.; Ibrahim, A.B.; Zaidan, B.B.; Ismail, A.R.; et al. IoT-Based Water Monitoring Systems: A Systematic Review. Water 2022, 14, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Bandsode, V.; Singh, A.; Mendem, S.K.; Semmler, T.; Alam, M.; Ahmed, N. Genomic Insights into Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Adaptation Acumen of Escherichia coli Isolated from an Urban Environment. mBio 2024, 15, e0354523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Cortés, G.; Arenas-Hernández, M.M.P.; Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Rocha-Gracia, R.d.C.; Barrios-Villa, E. Editorial: Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Factors of Emerging and Re-Emerging Bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1387087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijsingh, N.; Munthe, C.; Larsson, D.G.J. Managing Pollution from Antibiotics Manufacturing: Charting Actors, Incentives and Disincentives. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kies, F.; De Los Rios-Escalante, P.; Matemilola, S.; Elegbede, I. Water Bodies Quality Assessment and Trophic Gradient Monitoring of the Llanquihue Lake-Maullin River in Chile from Years 1999–2014. Available online: https://www.jmaterenvironsci.com/Document/vol12/vol12_N7/JMES-2021-12076-Kies.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeau, A.M.; Douglas, G.M.; Langille, M.G.I. Microbiome Helper: A Custom and Streamlined Workflow for Microbiome Research. mSystems 2017, 2, e00127-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An Ultra-Fast Single-Node Solution for Large and Complex Metagenomics Assembly via Succinct de Bruijn Graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Abricate: Mag_right: Mass Screening of Contigs for Antimicrobial and Virulence Genes; Github: San Francisco, CA, USA.
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.; Ferrés, I.; Iraola, G. Improved Detection and Classification of Plasmids from Circularized and Fragmented Assemblies. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Scientific Research Publishing: Wuhan, China, 2021; Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=3131254 (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9783319242750. [Google Scholar]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol. Available online: https://asm.org/getattachment/2594ce26-bd44-47f6-8287-0657aa9185ad/Kirby-Bauer-Disk-Diffusion-Susceptibility-Test-Protocol-pdf.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Patel, J.B.; Cockerill, F.R.; Bradford, P.A. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Fifth Informational Supplement; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Family Gen | Antibiotic Family | Drug Example | Resistance Mechanism Example | Literature References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bla | Beta-lactams | Imipenem | Antibiotic Inactivation | [24] |
| cat | Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | Antibiotic Inactivation | [29] |
| cfx | Cefamycins | Cefoxitin | Antibiotic Inactivation | [31] |
| dfr | Diaminopyridines | Trimethoprim | Target modification | [26] |
| erm | Macrolides | Erythromycin | Target modification | [32] |
| inu | Lincosamides | Clindamicin | Antibiotic Inactivation | [33] |
| mef | Macrolides | Erythromycin | Efflux Pump | [34] |
| msr | Macrolides | Erythromycin | Efflux Pump | [35] |
| oqx | Multi-Drug | Multi-Drug | Efflux Pump | [36] |
| tet | Tetracyclines | Doxicycline | Efflux Pump, Target Modification, Antibiotic Inactivation | [23] |
| vat | Streptogramins | Virginiamycin | Antibiotic Inactivation | [37] |
| nº | Species | Antibiotic Drug Tested | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cefotaxime | Ampicillin /Sulbactam | Sulfamethoxazole /Trimethoprim | Gentamicin | Ciprofloxacin | Imipenem | ||||||||
| IZD (mm) | Int | IZD (mm) | Int | IZD (mm) | Int | IZD (mm) | Int | IZD (mm) | Int | IZD (mm) | Int | ||
| 23 | Citrobacter freundii | 36.3 ± 0.6 | S | 19.7 ± 0.6 | S | 26.0 ± 1.0 | S | 19.3 ± 0.6 | S | 39.0 ± 1.0 | S | 28.3 ± 1.5 | S |
| 55 | Citrobacter gillenii | 36.3 ± 1.5 | S | 32.0 ± 1.0 | S | 24.3 ± 0.6 | S | 24.0 ± 1.0 | S | 44.3 ± 1.2 | S | 27.3 ± 0.6 | S |
| 62 | Citrobacter gillenii | 32.7 ± 1.2 | S | 38.0 ± 2.0 | S | 22.7 ± 0.6 | S | 20.7 ± 0.6 | S | 50.0 ± 1.0 | S | 37.0 ± 1.7 | S |
| 2 | Enterobacter absuriae | 34.7 ± 2.9 | S | 29.7 ± 0.6 | S | 33.3 ± 0.6 | S | 19.3 ± 1.5 | S | 36.3 ± 0.6 | S | 27.3 ± 0.6 | S |
| 14 | Enterobacter cloacae | 35.7 ± 1.2 | S | 30.0 ± 0.0 | S | 32.7 ± 1.2 | S | 19.7 ± 1.2 | S | 40.3 ± 0.6 | S | 31.0 ± 1.0 | S |
| 39 | Enterobacter ludwigii | 34.0 ± 1.7 | S | 32.3 ± 1.2 | S | 31.3 ± 0.6 | S | 23.3 ± 0.6 | S | 47.3 ± 0.6 | S | 33.0 ± 1.0 | S |
| 41 | Enterobacter ludwigii | 35.0 ± 2.0 | S | 34.7 ± 0.6 | S | 35.7 ± 0.6 | S | 24.0 ± 0.0 | S | 49.0 ± 1.0 | S | 35.3 ± 1.2 | S |
| 21 | Escherichia coli | 36.7 ± 0.6 | S | 19.7 ± 0.6 | S | 24.7 ± 0.6 | S | 24.3 ± 0.6 | S | 34.0 ± 0.0 | S | 31.0 ± 1.0 | S |
| 22 | Escherichia coli | 35.3 ± 06 | S | 20.3 ± 1.2 | S | 26.3 ± 0.6 | S | 20.3 ± 0.6 | S | 41.3 ± 1.2 | S | 31.3 ± 1.5 | S |
| 26 | Escherichia coli | 37.3 ± 0.6 | S | 23.3 ± 0.6 | S | 28.3 ± 2.1 | S | 22.0 ± 1.0 | S | 38.3 ± 0.0 | S | 29.3 ± 1.5 | S |
| 27 | Escherichia coli | 34.0 ± 1.0 | S | 20.0 ± 0.0 | S | 27.0 ± 1.0 | S | 19.7 ± 2.1 | S | 35.3 ± 0.6 | S | 31.3 ± 1.5 | S |
| 28 | Escherichia coli | 33.0 ± 0.0 | S | 21.3 ± 1.5 | S | 27.3 ± 0.6 | S | 23.7 ± 0.6 | S | 41.0 ± 1.0 | S | 32.3 ± 1.5 | S |
| 42 | Escherichia coli | 36.7 ± 1.5 | S | 20.3 ± 1.2 | S | 24.7 ± 0.6 | S | 19.0 ± 1.0 | S | 38.3 ± 0.6 | S | 30.3 ± 2.3 | S |
| 3 | Rahnella aquatilis | 25.3 ± 3.1 | S | 18.7 ± 1.2 | S | 21.3 ± 1.5 | S | 15.3 ± 0.6 | S | 25.3 ± 0.6 | S | 23.3 ± 0.6 | S |
| ATCC 25922 | Escherichia coli | 31.3 ± 0.6 | ✓ | 20.7 ± 0.6 | ✓ | 24.7 ± 0.6 | ✓ | 24.3 ± 0.6 | ✓ | 45.0 ± 0.0 | ✓ | 34.7 ± 0.6 | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanini-Salinas, J.; Opitz-Ríos, C.; Sagredo-Mella, J.A.; Contreras-Sanchez, D.; Giménez, M.; Páez, P.; Tarifa, M.C.; Rubio, N.D.; Medina, D.A. Antimicrobial Resistance Elements in Coastal Water of Llanquihue Lake, Chile. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070679
Campanini-Salinas J, Opitz-Ríos C, Sagredo-Mella JA, Contreras-Sanchez D, Giménez M, Páez P, Tarifa MC, Rubio ND, Medina DA. Antimicrobial Resistance Elements in Coastal Water of Llanquihue Lake, Chile. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(7):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070679
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanini-Salinas, Javier, Catherine Opitz-Ríos, John A. Sagredo-Mella, Danilo Contreras-Sanchez, Matías Giménez, Paula Páez, María Clara Tarifa, Nataly D. Rubio, and Daniel A. Medina. 2024. "Antimicrobial Resistance Elements in Coastal Water of Llanquihue Lake, Chile" Antibiotics 13, no. 7: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070679
APA StyleCampanini-Salinas, J., Opitz-Ríos, C., Sagredo-Mella, J. A., Contreras-Sanchez, D., Giménez, M., Páez, P., Tarifa, M. C., Rubio, N. D., & Medina, D. A. (2024). Antimicrobial Resistance Elements in Coastal Water of Llanquihue Lake, Chile. Antibiotics, 13(7), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13070679






