Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
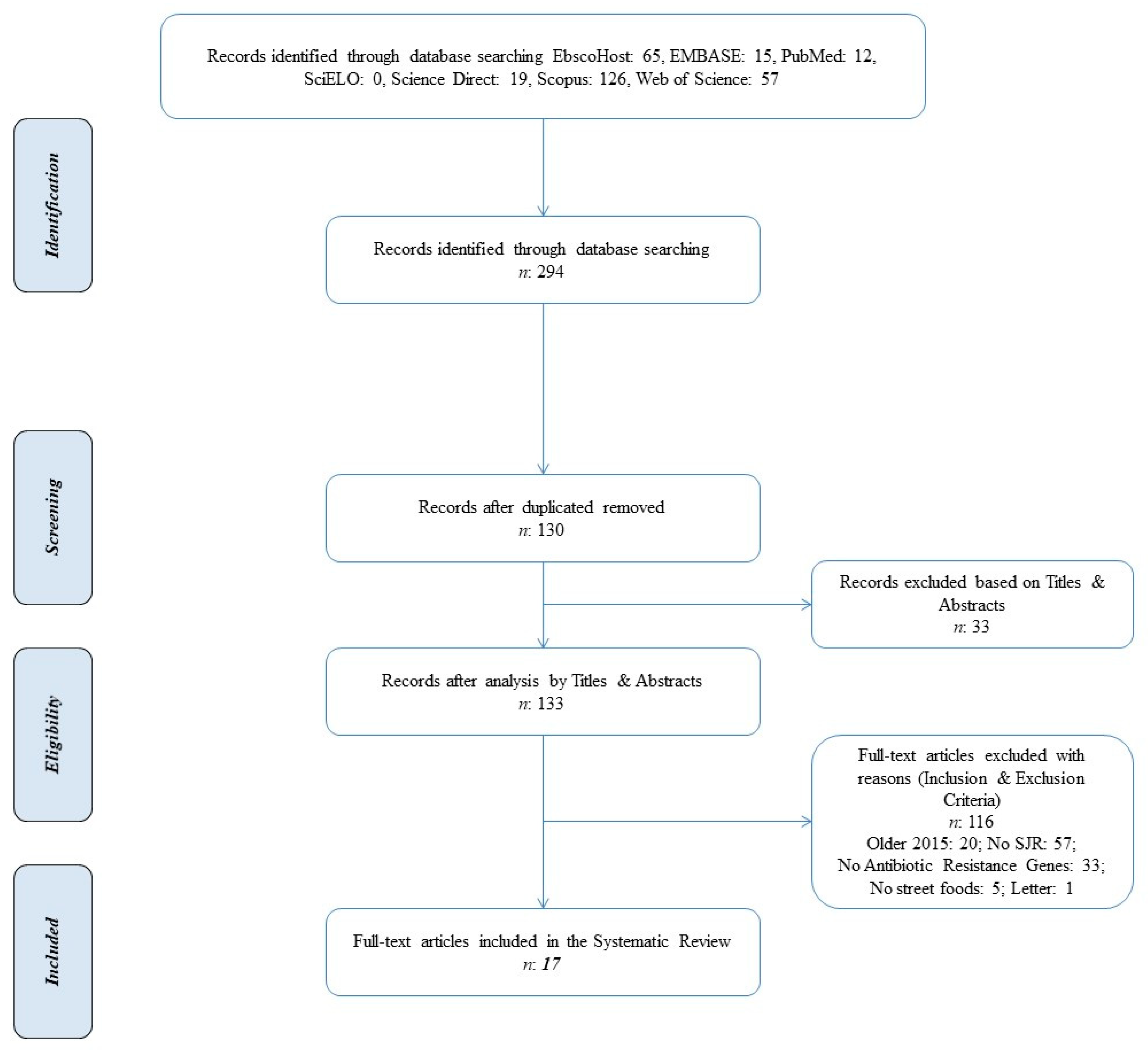
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Basic Characteristics of Selected Studies
2.3. Data on Antibiotic Resistance in Different Types of Food
2.4. Susceptibility to Antibiotics in the Selected Studies
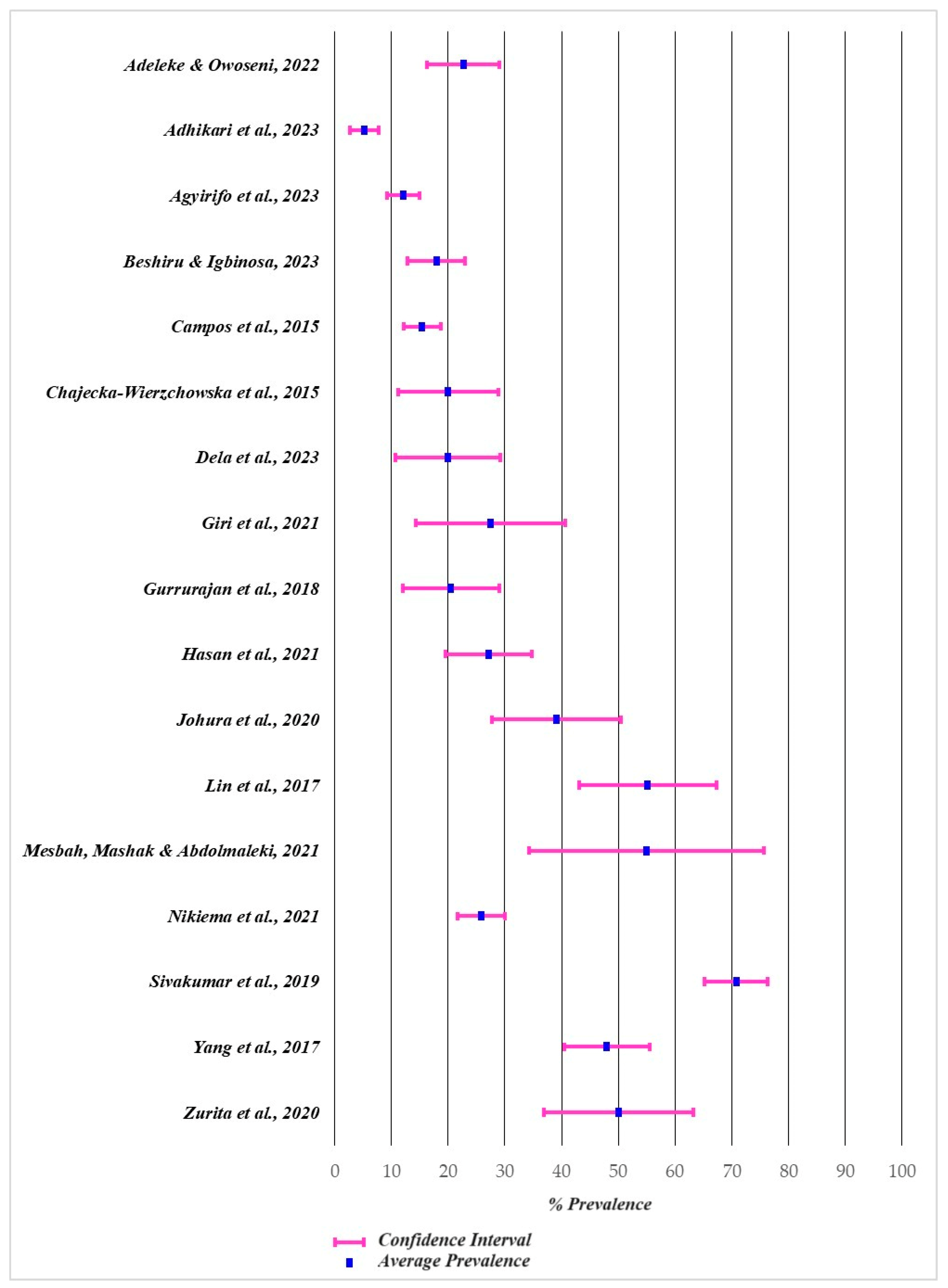
2.5. Reported Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Street Foods
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reporting
4.2. Search Strategy
4.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.4. Selection of Studies
4.5. Data Extraction and Analysis
4.6. Quality Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulati, D.; Chakraborty, D. Antibiogram of Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from One of the Most Popular Street Food (Panipuri) of Dehradun. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2017, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, B.; Sönmez, S.; Moore, S.; Auvil, D.P.; Parks, G.D. Exploring Safety of Food Truck Products in a Developed Country. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 81, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellia, C.; Bacarella, S.; Ingrassia, M. Interactions between Street Food and Food Safety Topics in the Scientific Literature—A Bibliometric Analysis with Science Mapping. Foods 2022, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiatrowski, M.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Trafiałek, J. Consumer Eating Behavior and Opinions about the Food Safety of Street Food in Poland. Nutrients 2021, 13, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peimani, N.; Kamalipour, H. Informal Street Vending: A Systematic Review. Land 2022, 11, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrasaigaran, P.; Kuan, C.H.; Radu, S.; Abidin, U.F.U.Z.; Rukayadi, Y.; New, C.Y.; Hasan, H. Multiple Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium in Ready-To-Eat Battered Street Foods, and Their Survival Under Simulated Gastric Fluid and Microwave Heating. Food Control 2023, 146, 109515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhun Sezgin, A.; Şanlıer, N. Street Food Consumption in Terms of the Food Safety and Health. Int. J. Human Sci. 2016, 13, 4072–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacardon, E.R.; Ong, A.K.S.; Gumasing, M.J.J. The Perception of Food Quality and Food Value among the Purchasing Intentions of Street Foods in the Capital of the Philippines. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, M.M.; Rahman, S.M.; Turin, T.C. Knowledge and Awareness of Children’s Food Safety among School-Based Street Food Vendors in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013, 10, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, H.; Yan, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W. Food Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behavior of Street Food Vendors and Consumers in Handan, A Third Tier City in China. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.; de Morais, I.L.; Albuquerque, G.; Gelormini, M.; Casal, S.; Pinho, O.; Motta, C.; Damasceno, A.; Moreira, P.; Breda, J.; et al. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Street Foods Purchased by Customers in Urban Areas of Central Asia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adane, M.; Teka, B.; Gismu, Y.; Halefom, G.; Ademe, M. Food Hygiene and Safety Measures among Food Handlers in Street Food Shops and Food Establishments of Dessie Town, Ethiopia: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoni Auad, L.; Cortez Ginani, V.; Stedefeldt, E.; Yoshio Nakano, E.; Costa Santos Nunes, A.; Puppin Zandonadi, R. Food Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Brazilian Food Truck Food Handlers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anukampa; Shagufta, B.; Sivakumar, M.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, R.K.; Bhilegaonkar, K.N.; Kumar, A.; Dubal, Z.B. Antimicrobial Resistance and Typing of Salmonella Isolated From Street Vended Foods and Associated Environment. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemechu, T.; Eshetu, T.; Kassa, T.; Jarso, H. Assessment of Intestinal Parasites, Enteric Bacterial Infections, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Among Street Food Handlers in Jimma Town, Southwest Ethiopia. J. Trop. Med. 2022, 2022, 5483367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, A.B.; Yang, H.; Feng, Y.; Xi, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Tang, J.; He, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, X. Presence and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli in ready-to-eat foods in Shaanxi, China. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, G.; Mitiku, H.; Teklemariam, Z.; Marami, D. Salmonella and Shigella among asymptomatic street food vendors in the Dire Dawa city, Eastern Ethiopia: Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility pattern, and associated factors. Environ. Health Insights 2019, 13, 1178630219853581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, X. Prevalence, genetic diversity, and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in retail ready-to-eat foods in China. Food Control 2016, 68, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria—A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria: Mechanisms, Evolution, and Persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial antibiotic resistance: The most critical pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.C.; Rodrigues, S.; Afonso, A.; Nogueira, A.; Coutinho, P. Antibiotic Resistance in the Drinking Water: Old and New Strategies to Remove Antibiotics, Resistant Bacteria, and Resistance Genes. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Galarde-López, M.; Carrillo-Quiróz, B.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Antimicrobial resistance: One Health approach. Vet. World 2022, 15, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Schweizer, H.P. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Active efflux and reduced uptake. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1486–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.A. Cellular impermeability and uptake of biocides and antibiotics in Gram-positive bacteria and mycobacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 92, 46S–54S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, S.; Queiroga, M.C.; Laranjo, M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Meat and Meat Products: A One Healt Perspective. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Anal, A.K. Isolation of Salmonella from ready-to-eat poultry meat and evaluation of its survival at low temperature, microwaving and simulated gastric fluids. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lekshmi, M.; Parvathi, A.; Nayak, B.B.; Varela, M.F. Antibiotic resistance in seafood-borne pathogens. In Foodborne Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance; Singh, O.V., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 17; pp. 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesh, J.; Hoey, L.; Jones, A.D.; Friedmann, H.; Perfecto, I. Development pathways toward “zero hunger”. World Dev. 2019, 118, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; Badulescu, D.; Bac, D.P. Achieving Zero Hunger Goal through Minimizing Waste in Food Supply Chain: Evidence from Asian Emerging Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Strategic Framework for Food Security and Nutrition. First Version. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/meeting/026/ME498E.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Gibson, M. Food Security—A Commentary: What Is It and Why Is It So Complicated? Foods 2012, 1, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.A.; Owoseni, A.A. CTXM and OXA Genes in Foodborne Bacteria from Cooked Street Foods Sold in the South Western States of Nigeria. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 6, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Regmi, R.S.; Sapkota, S.; Khadka, S.; Patel, N.; Gurung, S.; Thapa, D.; Bhattarai, P.; Sapkota, P.; Devkota, R.; et al. Multidrug Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Detection of Bla CTX-M and Bla VIM Genes in E. coli and Salmonella Isolates from Chutney Served at the Street-Food Stalls of Bharatpur, Nepal. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyirifo, D.S.; Mensah, T.A.; Senya, A.S.Y.; Hounkpe, A.; Dornyoh, C.D.; Otwe, E.P. Dynamics of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcal Species Isolated from Foods Traded in the Cape Coast Metropolitan and Elmina Municipality of Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshiru, A.; Igbinosa, E.O. Surveillance of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Pathogens Recovered from Ready-to-Eat Foods. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.; Gil, J.; Mourão, J.; Peixe, L.; Antunes, P. Ready-to-Eat Street-Vended Food as a Potential Vehicle of Bacterial Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance: An Exploratory Study in Porto Region, Portugal. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 206, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chajecka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Nalepa, B.; Sierpińska, M.; Laniewska-Trokenheim, L. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Food of Animal Origin—Phenotypic and Genotypic Antibiotic Resistance. Food Microbiol 2015, 46, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela, H.; Egyir, B.; Behene, E.; Sulemana, H.; Tagoe, R.; Bentil, R.; Bongo, R.N.A.; Bonfoh, B.; Zinsstag, J.; Bimi, L.; et al. Microbiological Quality and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria Species Recovered from Ready-to-Eat Food, Water Samples, and Palm Swabs of Food Vendors in Accra, Ghana. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 396, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Kudva, V.; Shetty, K.; Shetty, V. Prevalence and Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Ready-to-Eat Street Foods. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, G.; Srinivasan, I.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Balagurunathan, R. SHV and CTX-M Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamases (ESBL) Producing Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods in and around Chennai, India. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 11, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Siddika, F.; Kallol, M.A.; Sheikh, N.; Hossain, M.T.; Alam, M.M.; Rahman, M. Bacterial Loads and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Bacteria Isolated from the Most Popular Street Food (Phuchka) in Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2021, 8, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johura, F.-T.; Tasnim, J.; Barman, I.; Biswas, S.R.; Jubyda, F.T.; Sultana, M.; George, C.M.; Camilli, A.; Seed, K.D.; Ahmed, N.; et al. Colistin-Resistant Escherichia Coli Carrying Mcr-1 in Food, Water, Hand Rinse, and Healthy Human Gut in Bangladesh. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.-F.; Yang, T.-Y.; Hung, W.-C.; Chan, M.-Y.; Tseng, S.-P. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Diversity in Ceftazidime Non-Susceptible Bacterial Pathogens from Ready-to-Eat Street Foods in Three Taiwanese Cities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbah, A.; Mashak, Z.; Abdolmaleki, Z. A Survey of Prevalence and Phenotypic and Genotypic Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteria Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Food Samples Collected from Tehran Province, Iran. Trop. Med. Health 2021, 49, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiema, M.E.M.; La Gandara, M.P.D.; Compaore, K.A.M.; Ba, A.K.; Soro, K.D.; Nikiema, P.A.; Barro, N.; Sangare, L.; Weill, F.-X. Contamination of Street Food with Multidrugresistant Salmonella, in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Dubal, Z.B.; Kumar, A.; Bhilegaonkar, K.; Kumar, O.R.V.; Kumar, S.; Kadwalia, A.; Shagufta, B.; Grace, M.R.; Ramees, T.P.; et al. Virulent Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Street Vended Foods. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2019, 56, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-Y.; Hung, W.-W.; Lin, L.; Hung, W.-C.; Tseng, S.-P. MecA-Related Structure in Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Street Food in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita, J.; Yánez, F.; Sevillano, G.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; y Miño, A.P. Ready-to-Eat Street Food: A Potential Source for Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Epidemic Clones in Quito, Ecuador. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Joji, R.M.; Shahid, M. Evolution and implementation of One Health to control the dissemination of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes: A review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1065796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Ma, L.; Yu, Q.; Yang, J.; Su, W.; Hilal, M.G.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, H. The source, fate and prospect of antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 976657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, J. Emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant foodborne pathogens from farm to table. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1481–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, D.; Du, L.; Song, B.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Huang, H.; Zeng, G. Antibiotic resistance in soil-plant systems: A review of the source, dissemination, influence factors, and potential exposure risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlaja, A.; Ogunlaja, O.O.; Olukanni, O.D.; Taylor, G.O.; Olorunnisola, C.G.; Dougnon, V.T.; Mousse, W.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Unuabonah, E.I. Antibiotic resistomes and their chemical residues in aquatic environments in Africa. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 119783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Dong, D.; Fang, H.; Wang, C.; Dong, Y.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Zhu, P.; et al. Antibiotic resistant bacteria: A bibliometric review of literature. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1002015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Shah, D.; Dalai, P.; Agrawal-Rajput, R. The tale of antibiotics beyond antimicrobials: Expanding horizons. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadgir, C.A.; Biswas, D.A. Antibiotic Resistance and Its Impact on Disease Management. Cureus 2023, 15, e38251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Thakur, B.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Khatri, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. Nanomaterial-based fluorescent biosensors for the detection of antibiotics in foodstuffs: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Taguchi, M.; Kawahara, R.; Kanki, M.; Kawatsu, K. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial pathogens in ready-to-eat foods retailed in Osaka prefecture, Japan. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayode, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Antibiotic resistance profile of listeria monocytogenes recovered from ready-to-eat foods surveyed in South Africa. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Occurrence, serovars and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp. in retail ready-to-eat food products in some Chinese provinces. LWT 2022, 154, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; Lei, T.; Chen, M.; Ye, Q.; Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. High prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and first detection of IncHI2/IncX4-plasmid carrying mcr-1 E. coli in retail ready-to-eat foods in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 355, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Moola, S.; Lisy, K.; Riitano, D.; Tufanaru, C. Methodological guidance for systematic reviews of observational epidemiological studies reporting prevalence and cumulative incidence data. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Country | SJR | Risk of Bias | JBI Score | Collection Period | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | Q4 | Moderate | 6/9 66.6% | March–August 2021 | Adeleke and Owoseni, 2022 [43] |
| Nepal | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | September 2019–March 2020 | Adhikari et al., 2023 [44] |
| Ghana | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | January–April 2021 | Agyirifo et al., 2023 [45] |
| Nigeria | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | July 2021–February 2022 | Beshiru and Igbinosa, 2023 [46] |
| Portugal | Q1 | Low | 7/9 77.7% | January–February 2013 | Campos et al., 2015 [47] |
| Poland | Q1 | Low | 7/9 77.7% | ND | Chaje˛cka-Wierzchowska et al., 2015 [48] |
| Ghana | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | January 2019–March 2020 | Dela et al., 2023 [49] |
| India | Q2 | Low | 9/9 100% | June–October 2019 | Giri et al., 2021 [50] |
| India | Q2 | Low | 7/9 77.7% | ND | Gurrurajan et al., 2018 [51] |
| Bangladesh | Q2 | Low | 7/9 77.7% | ND | Hasan et al., 2021 [52] |
| Bangladesh | Q2 | Low | 7/9 77.7% | June 2018 | Johura et al., 2020 [53] |
| Taiwan | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | June–November 2014 | Lin et al., 2017 [54] |
| Iran | Q2 | Low | 9/9 100% | April–November 2018 | Mesbah, Mashak, and Abdolmaleki, 2021 [55] |
| Burkina Faso | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | June 2017–July 2018 | Nikiema et al., 2021 [56] |
| India | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | September 2015–May 2016 | Sivakumar et al., 2019 [57] |
| Taiwan | Q1 | Low | 9/9 100% | June–November 2014 | Yang et al., 2017 [58] |
| Ecuador | Q3 | Moderate | 6/9 66.6% | November 2016–January 2017 | Zurita et al., 2020 [59] |
| Food Type | Type of Antibiotic Used | Method of Testing | Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria | Antibiotic Resistance | Antibiotic Resistance Genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooked Street Foods | CAZ, CXM, GEN, CIP, OFX, CFM, AX, NFT, AUG | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ, NFT | β-lactam (CTXM, OXA) | Adeleke and Owoseni, 2022 [43] |
| Shigella | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ | |||||
| Staphylococcus | ||||||
| Klebsiella | ||||||
| Bacillus | ||||||
| Proteus | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ | β-lactam (CTXM) | ||||
| Salmonella | ||||||
| Lactobacillus | ||||||
| Citrobacter | ||||||
| Streptococcus | CAZ, CXM, GEN, CIP, OFX, CFM, AX, NFT, AUG | β-lactam (OXA) | ||||
| Acinetobacter | CXM, GEN, AX, CAZ | |||||
| Vibrio | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ | |||||
| Clostridium | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ | |||||
| Bifidobacterium | CXM, AUG, AX, CAZ | |||||
| Chutney | STX, CAZ, C, CIP, AZT, AM, GEN, IMP, AX, NA | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | AM, AX | β-lactam (blaCTX-M, blaVIM) | Adhikari et al., 2023 [44] |
| Salmonella | ||||||
| Cooked Street Foods (Beans, Fish, Fufu, Kenkey, Pepper sauce, Salad, Soup, Waakye) Vegetables (Cabbage, Carrot, Tomato) Fruit (Apple, Banana, Orange, Pineapple) | AKN, CIP, TE, CRO, CTX, GEN, LEV, NOR, NA, NFT, Zosyn, CF | Disk diffusion | Staphylococcus | AKN, CIP, TE, GEN, LEV, NOR | β-lactam (mecA, blaTEM) Tetracycline (tetA, tetB) Aminoglycoside (strA, aacC3) Macrolide (ermA, ermB) Fluoroquinolones (acrA) Vancomycine (vanA) | Agyirifo et al., 2023 [45] |
| Agidi jollof, Jollof rice, Fried rice, White ukodo, Soup | AM, TE, C, STX, CIP, CTX, NA, AZ, CAZ, SMN, SAM, GEN, IMP | Disk diffusion | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | AM, TE, C, STX, CIP, CTX, NA, AZ, CAZ, SMN, SAM | Sulfonamide (sul1, sul2) Tetracycline (tetA, tetB, tetM) Trimethoprim (dfrA1) β-lactam (blaTEM) Aminoglycoside (aadA) | Beshiru and Igbinosa, 2023 [46] |
| Hamburgers, Hotdogs | AX, CIP, C, GEN, K, NA, SMN, SMZ, TE, TMP | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | AX, CIP, C, K, NA, SMN, SMZ, TE, TMP | Sulfonamide (sul1, sul2) Tetracycline (tetA, tetB) Phenicols (floR, catA) β-lactam (blaTEM) Aminoglycoside (aadA, strA-strB) Trimethoprim (dfrA1) | Campos et al., 2015 [47] |
| Cheeses, Cured meats, Smoked fish | ERM, CLI, GEN, FOX, NOR, CIP, TE, TGC, RFP, NFT, Lzd, TMP, STX, C, Q/D | Disk diffusion | Staphylococcus | ERM, CLI, GEN, FOX, NOR, CIP, TE, TGC, RFP, NFT, Lzd, TMP, STX, C, Q/D | Tetracycline (tetL, tetK, tetM) Macrolide (ermA, ermB, ermC) β-lactam (mecA) | Chaje˛cka-Wierzchowska et al., 2015 [48] |
| Ampesi, Banku, Beans, Rice, Salad, Waakye, Soup, Kenkey, Jollof, Spaghetti, Porridge | CRO, STX, Zosyn, TIM, TE, AKN, GEN, CIP, MEM, AZM, C, NFT, NA, CAZ, AMC, ERM, RFP, PG, Lzd | Disk diffusion | Citrobacter freundii | STX, TE, NFT, AMC | β-lactam (blaTEM, blaSHV) | Dela et al., 2023 [49] |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | ||||||
| Chutney, Dressings, Pickles, Cutlets, Vegetables, Noodles, Pasta, Muffins, Eggs, Chicken, Salami | AM, AKN, AMC, CAZ, CACL, CRO, CTX, CXM, FEP, CFS, COT, C, CIP, ETP, ERM, GEN, IMP, MEM, NA, NFT, Zosyn, TE, TGC | Disk diffusion | Klebsiella pneumoniae | AM, CTX, FEP, CFS, ETP, ERM; IMP, MEM | β-lactam (blaTEM, blaCTX) | Giri et al., 2021 [50] |
| Vegetables, Chicken, Samosa, Panipuri water, Bhelpuri | AM, CAZ, CTX, FEP, Zosyn, IMP, GEN, AKN, TOB | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | AM, CAZ, CTX, FEP, Zosyn, GEN, AKN, TOB | β-lactam (blaCTX-M, blaSHV) | Gurrurajan et al., 2018 [51] |
| Klebsiella | ||||||
| Pseudomonas | ||||||
| Phuchka, Eggs | AM, AX, CIP, C, GEN, K, PG, NA, TE, OX | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | AM, AX, K, TE | Tetracycline (tetA) | Hasan et al., 2021 [52] |
| Juice, Velpuri, Fruit (Guava, Pineapple, Cucumber) | CRO, CET, FEP, CFM, FOS, MEL, TE, STX, LEV, ERM, AZM, IMP, AM, NA, CIP, GEN, C, AZT | Disk diffusion | Escherichia coli | CRO, CET, CFM, MEL, TE, STX, LEV, ERM, AZM, AM, NA, GEN, C, AZT | Polymyxins (mcr-1) β-lactam (blaTEM) Macrolide (mphA) | Johura et al., 2020 [53] |
| Spring rolls, Noodles, Fruit | CTX, CAZ, C, CST, GEN, LEV, MEM, TIC, TIM, TE, STX | Disk diffusion | Acinetobacter spp. | CTX, CAZ, C, CST, GEN, MEM, TIC, TIM, TE, STX, LEV | Aminoglycoside (aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacC4) | Lin et al., 2017 [54] |
| Pseudomonas spp. | CTX, CAZ, C, CST, GEN, MEM, TIC, TIM, TE, STX | Aminoglycoside (aacC2) Phenicols (cmlA) | ||||
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | CAZ, C, LEV, TIM, STX | Phenicols (catIII) | ||||
| Enterobacteriaceae | CTX, CAZ, C, CST, GEN, MEM, TIC, TIM, TE, STX, LEV | Aminoglycoside (aacC4 ) Tetracycline (tetA, tetC, tetD) | ||||
| Hamburgers, Chicken nuggets, Salad, Salami, Falafel, Grilled mushrooms, Mexican corn | AKN, GEN, LEV, CIP, CLI, ERM, AZ, PG, DCN, TE, C, STX, RFP | Disk diffusion | Staphylococcus aureus | GEN, CIP, ERM, PG, TE, STX | Tetracycline (tetK) β-lactam (blaZ) Aminoglycoside (aacA-D) Macrolide (ermA) Fluroquinolones (gyrA) | Mesbah, Mashak, and Abdolmaleki, 2021 [55] |
| Sandwiches | AM, AMC, FOX, CTX, CAZ, FEP, SMN, SPT, GEN, AKN, TGC, K, SSS, TMP, STX, C, TE, NA, CIP, MEM, AZM | Disk diffusion | Salmonella | AM, SMN, SPT, GEN, SSS, TMP, STX, C, TE, NA, CIP | Aminoglycoside (strA, strB) Sulfonamide (sul1, sul2) β-lactam (blaTEM-1B) Phenicol (catA1) Tetracycline (tetA) Aminoglycoside (aad7) Fluoroquinolones (gyrA, parC) Phosphonics (fosA7) | Nikiema et al., 2021 [56] |
| Chicken, Eggs, Milk, Paneer, Fish, Lassi, Salad, Chutney, Masala | OX, FOX, PG | Disk diffusion | Staphylococcus aureus | OX, FOX, PG | β-lactam (mecA, blaZ) | Sivakumar et al., 2019 [57] |
| Spring rolls, Noodles | ERM, GEN, LEV, OX, TE, VAN | ND | Staphylococcus | ERM, GEN, LEV, OX, TE | β-lactam (mecA) Macrolide (ermA, ermC) Tetracycline (tetM, tetK, tetO) Aminoglycoside (aac(6′)Ie-aph(2″)Ia) | Yang et al., 2017 [58] |
| Chili pepper sauce, Ceviche, Salad, Cheeses | STX, AM, SAM, FOX, CAZ, CTX, FEP, AKN, GEN, Zosyn, DOR, ETP, IMP, MEM, CIP, TGC, CST | VITEK®2 Compact System Broth Microdilution Assay | Escherichia coli | STX, AM, SAM, FOX, CAZ, CTX, FEP, AKN, GEN | β-lactam (blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaSHV) | Zurita et al., 2020 [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusaro, C.; Miranda-Madera, V.; Serrano-Silva, N.; Bernal, J.E.; Ríos-Montes, K.; González-Jiménez, F.E.; Ojeda-Juárez, D.; Sarria-Guzmán, Y. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060481
Fusaro C, Miranda-Madera V, Serrano-Silva N, Bernal JE, Ríos-Montes K, González-Jiménez FE, Ojeda-Juárez D, Sarria-Guzmán Y. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(6):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060481
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusaro, Carmine, Valentina Miranda-Madera, Nancy Serrano-Silva, Jaime E. Bernal, Karina Ríos-Montes, Francisco Erik González-Jiménez, Dennys Ojeda-Juárez, and Yohanna Sarria-Guzmán. 2024. "Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review" Antibiotics 13, no. 6: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060481
APA StyleFusaro, C., Miranda-Madera, V., Serrano-Silva, N., Bernal, J. E., Ríos-Montes, K., González-Jiménez, F. E., Ojeda-Juárez, D., & Sarria-Guzmán, Y. (2024). Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics, 13(6), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060481







