Abstract
Elderly patients (age ≥ 65 years) are susceptible to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections, with potential for more adverse treatment outcomes or complications compared to younger adults (18–64 years). This study compared vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity and efficacy in elderly and adult patients and investigated the correlation between vancomycin pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) indices and clinical outcomes. A prospective study was conducted in 10 hospitals in Shanghai from October 2012 to November 2019. A total of 164 patients with MRSA infections were enrolled, including 83 elderly and 81 adult patients. Vancomycin therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) was performed in all patients, indicating significantly higher vancomycin trough concentrations (Ctrough), 24-h area under the curve (AUC24) values, and AUC24/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC24/MIC) values in elderly patients compared to adult patients. The incidence of vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity was nearly three times higher in elderly patients (18.1% vs. 6.2%, p = 0.020), despite similar clinical and microbiological efficacy. Of particular importance, a Ctrough > 20 mg/L was found as an independent factor of nephrotoxicity in elderly patients. Further analysis of patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 also revealed that elderly patients had significantly higher vancomycin-related PK/PD indices and more nephrotoxicity than adult patients. In conclusion, elderly patients receiving vancomycin therapy face a higher risk of nephrotoxicity, which requires close vancomycin TDM, especially when the Ctrough exceeds 20 mg/L.
1. Introduction
Elderly patients (age ≥ 65 years), often with diminished immunity and multiple comorbidities, are particularly susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection, a common cause of hospitalization with a rising incidence [1]. Notably, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) bacteremia and pneumonia disproportionately affect elderly patients compared to younger adult patients (aged 18–64 years), with higher mortality rates [2].
Vancomycin, a first-line therapy for MRSA treatment, has been applied in clinical practice since the 1950s. It is a time-dependent antibiotic with an optimal pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) index of the 24-h area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC24/MIC) [3]. The revised 2020 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Guidelines [4] prioritize monitoring the AUC24/MIC ratio of 400–600 over a vancomycin trough concentration (Ctrough) of 15–20 mg/L for optimal clinical efficacy and patient safety. The 2020 Chinese evidence-based guideline for therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin [5], however, continues to recommend monitoring both the steady-state Ctrough (10–20 mg/L for MRSA infections) and AUC24 (400–650 mg·h/L). Despite recommending therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of vancomycin in elderly patients, the supporting evidence in the guideline [5] is of low quality and lacks high-quality and specific literature.
A cohort study [6] demonstrated that applying a standardized dosing regimen in MRSA patients led to significantly higher Ctrough and AUC24/MIC values in older patients (≥65 years) compared to younger adults (18–64 years), while the incidence of nephrotoxicity was similar between the two groups. However, it was well known that higher levels of both Ctrough and AUC24 were strongly associated with nephrotoxicity risk [7,8], and further comparative analyses of two patient groups are necessary. Additionally, the study was retrospective, and the MIC was determined using two different methods, which may affect the calculation of the AUC24/MIC [9]. Hence, prospective clinical studies and harmonized methods for MIC determination are also needed to further validate these findings.
To evaluate the impact of age on vancomycin-related treatment efficacy and nephrotoxicity, we conducted a prospective clinical trial in elderly and younger adult patients. Additionally, an analysis of the factors influencing these clinical outcomes, including patient clinical characteristics and vancomycin PK/PD indices, was conducted to identify the corresponding risk factors in both groups.
2. Results
2.1. Patient Enrollment and Characteristics
The study enrolled 164 patients with MRSA infections, including 83 patients aged ≥65 years, with a median age of 80 years (interquartile range [IQR]: 75–85), and 81 patients aged 18–64 years, with a median age of 53 years (IQR: 40–60).
While initial creatinine levels were similar between older and adult patients, the two groups exhibited significant differences in initial and final eGFR, final creatinine, and creatinine change (Table 1). Elderly patients with MRSA infections exhibited significantly higher rates of comorbidities compared to adult patients, including cardiovascular disease (51.8% vs. 16.0%, p < 0.001), diabetes mellitus (26.5% vs. 6.2%, p < 0.001), stroke (43.4% vs. 21.0%, p = 0.002), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (10.8% vs. 0.0%, p = 0.003). Furthermore, elderly patients were less likely to undergo surgery (26.5% vs. 66.7%, p < 0.001) and were more susceptible to pneumonia (77.1% vs. 60.5%, p = 0.022). However, adult patients were more prone to skin and soft tissue infections (18.5% vs. 3.6%, p = 0.002) and received treatment with quinolones more frequently (7.4% vs. 0.0%, p = 0.013).

Table 1.
Characteristics and outcomes of elderly versus adult patients.
2.2. Vancomycin Treatment and Clinical Outcomes
Despite receiving a lower daily vancomycin dose [1.4 (1.0, 2.0) g vs. 2.0 (1.8, 2.2) g, p < 0.001], elderly patients still exhibited significantly higher vancomycin Ctrough [14.69 (10.58, 20.71) mg/L vs. 7.82 (4.52, 12.57) mg/L, p < 0.001], AUC24 [461.65 (353.01, 609.10) mg·h/L vs. 387.56 (283.53, 462.09) mg·h/L, p = 0.006], and AUC24/MIC [647.97 (461.65, 913.42) vs. 463.54 (330.09, 718.28), p = 0.007] values than adult patients (Table 1 and Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials). There was no difference in vancomycin peak concentrations (Cpeak) and MIC values between the two groups (Table 1 and Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials).
Clinical and microbiological success rates did not differ significantly between the two groups. However, the incidence of nephrotoxicity was significantly higher in the older group (18.1% vs. 6.2%, p = 0.02), with a nearly 3-fold increase (Table 1). In addition, 3 out of 15 patients in the elderly group experienced nephrotoxicity within 48 h, while 2 out of 5 patients in the adult group developed nephrotoxicity within the same timeframe.
2.3. Risk Factor for Nephrotoxicity
Risk factors for nephrotoxicity were analyzed in the older and adult groups. Among the older patients, 15 experienced nephrotoxicity following vancomycin therapy (Table 2). A univariate analysis identified the following factors associated with nephrotoxicity (p < 0.1): surgery, drainage tube, ICU admission, Ctrough, Cpeak, and AUC24. In the subsequent multivariate logistic analysis, only a Ctrough > 20 mg/L still had a significant association with nephrotoxicity (Table 3).

Table 2.
Differences in clinical and vancomycin parameters between elderly and young adult patients classified according to nephrotoxicity.

Table 3.
Multivariate analysis of risk factors for vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity in elderly patients.
In contrast, for the adult group, significant differences were observed in initial serum creatinine, initial eGFR, daily dose, Ctrough, Cpeak, AUC24, and AUC24/MIC (Table 2), but the multivariate analysis did not reveal any significant associations between these factors and nephrotoxicity (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials).
2.4. Associations between Nephrotoxicity and Vancomycin Exposures
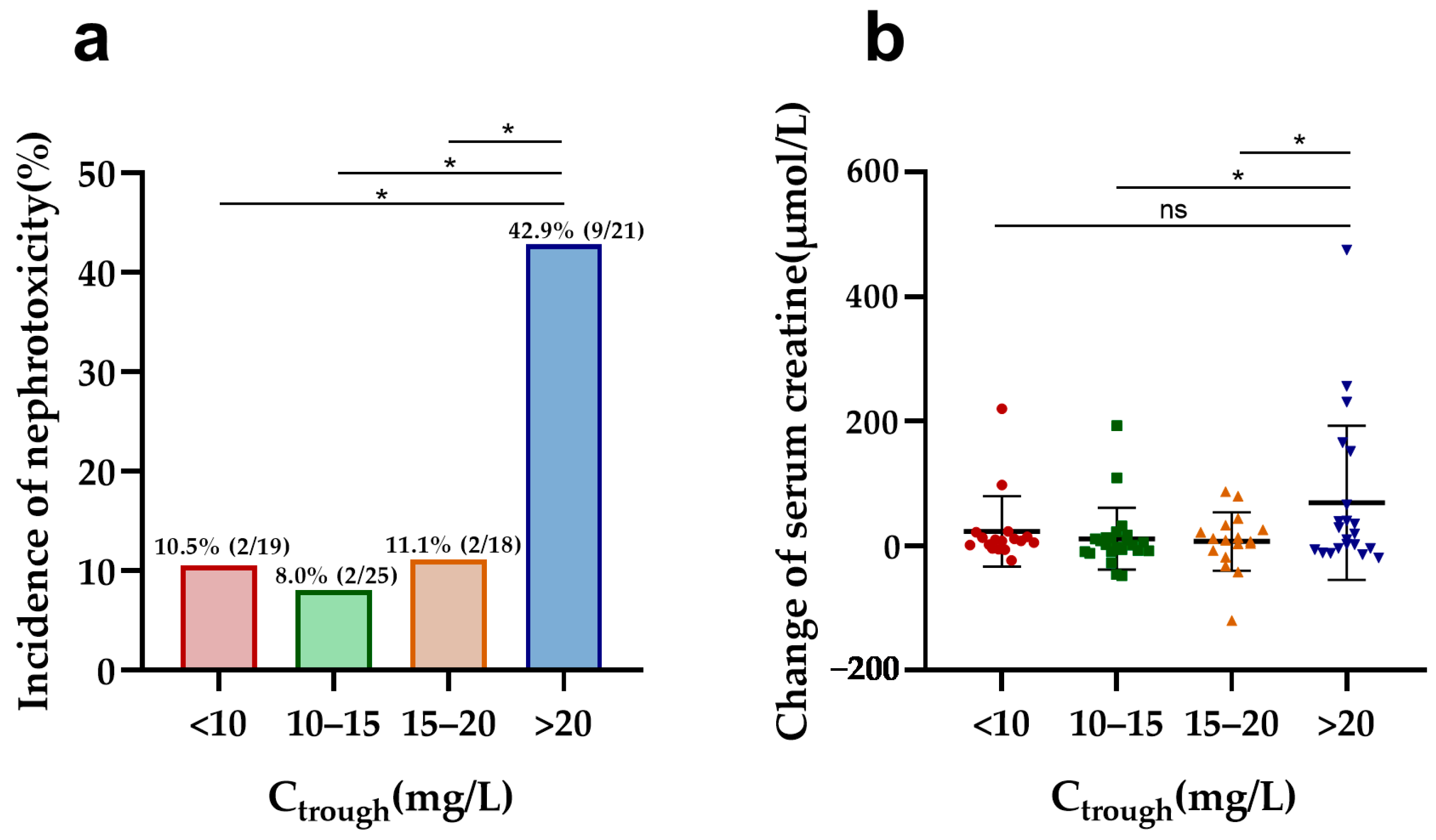
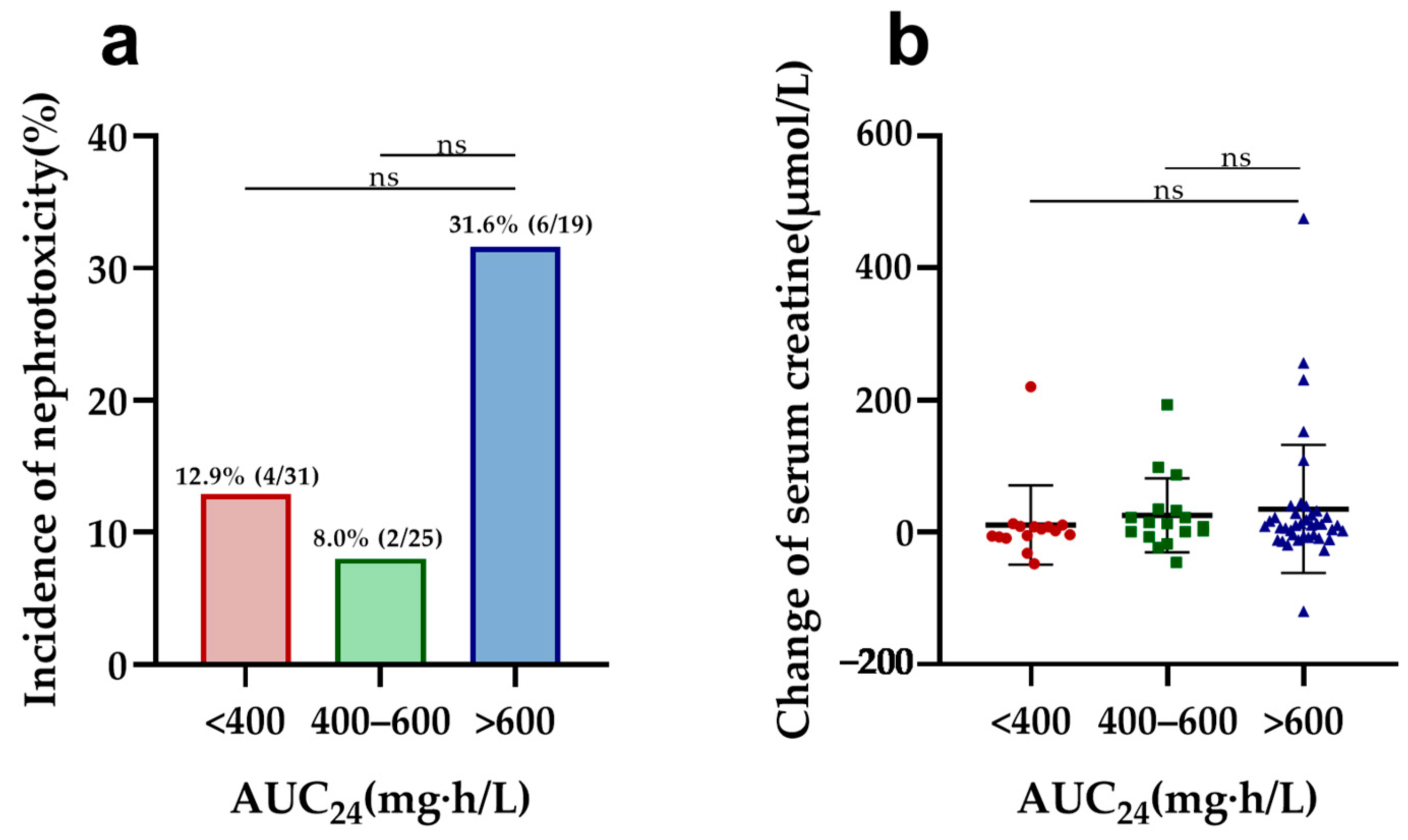
In vancomycin therapy, Ctrough and AUC24, identified as markers of nephrotoxicity, were further evaluated in both elderly and adult patients. Elderly patients with a higher vancomycin Ctrough (>20 mg/L) had a significantly increased risk of nephrotoxicity compared to other trough concentrations (Ctrough < 10, 10–15, and 15–20 mg/L) and a more pronounced elevation in serum creatinine compared to those with Ctrough values of 10–15 and 15–20 mg/L (Figure 1). Furthermore, Ctrough was also found to be a good predictor of nephrotoxicity in elderly patients, with an AUC of 0.740 (95%CI, 0.588–0.891, p = 0.004) using the ROC analysis (Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials). The optimal cutoff value was 20.78 mg/L, with a sensitivity of 60.0% and a specificity of 83.8%. However, there was no difference in nephrotoxicity and creatine changes between the different AUC24 groups (Figure 2). Also, the cutoff values of the AUC24 were not significant for predicting nephrotoxicity in older patients (p > 0.05).
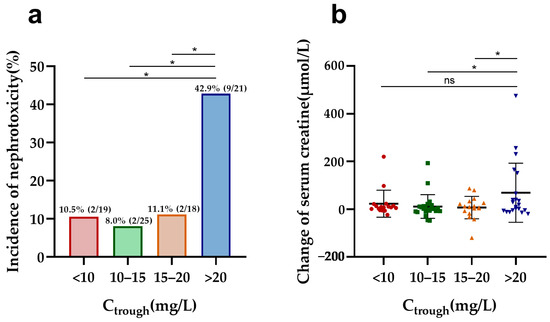
Figure 1.
Nephrotoxicity and serum creatine changes in elderly patients by different Ctrough groups: (a) comparison of the incidence of nephrotoxicity among different Ctrough groups in elderly patients; (b) comparison of change in serum creatine levels during vancomycin treatment across different Ctrough groups in elderly patients. * p < 0.5; ns: no significance.
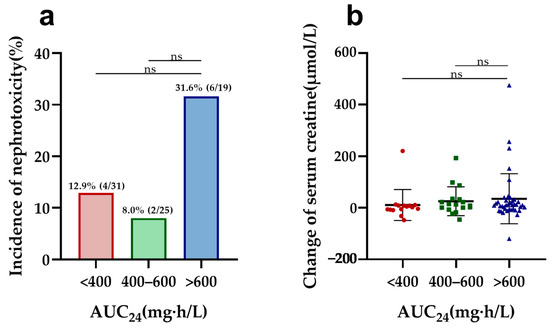
Figure 2.
Nephrotoxicity and serum creatine changes in elderly patients by different AUC24 groups: (a) comparison of the incidence of nephrotoxicity among different AUC24 groups in elderly patients; (b) comparison of change in serum creatine levels during vancomycin treatment across different AUC24 groups in elderly patients. ns: no significance.
While significant changes in nephrotoxicity and SCr rise were also observed among young adults, categorized by Ctrough and AUC24, further analysis revealed limitations due to the overall low incidence of nephrotoxicity in this group. The small number of cases, combined with the fact that nearly all nephrotoxicity occurred in the high-exposure group (Ctrough > 20 mg/L and AUC24 > 600 mg·h/L), restricted the ability to identify statistically significant associations in the multivariate analysis.
2.5. Associations between Nephrotoxicity and Renal Function
Considering age-related differences in renal function, patients with normal renal function were compared between the elderly and adult groups. Consistent with the findings in the entire cohort, the subgroup analysis of patients with an eGFR exceeding 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 yielded similar results. Elderly patients consistently exhibited significantly higher vancomycin Ctrough, AUC24, and AUC24/MIC values compared to adult patients. Remarkably, elderly patients with normal renal function exhibited a significantly higher incidence of nephrotoxicity compared to adult patients (15.4% vs. 2.7%, p = 0.007). Importantly, no significant differences in clinical and microbiological outcomes were observed between the two groups (Table 4). Overall, all data suggest that elderly patients, even with normal renal function, may remain more susceptible to vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity compared to adult patients.

Table 4.
Characteristics of elderly versus adult patients in subgroup of patients with eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
3. Discussion
In this study, we compared the efficacy and nephrotoxicity of vancomycin therapy in MRSA-infected patients between elderly (≥65 years) and adult patients (18–64 years). A notable finding was the significantly higher incidence of nephrotoxicity among elderly patients (18.1% vs. 6.2%), despite comparable clinical success and microbiological clearance rates. Previous studies have demonstrated that reduced albumin, a higher volume of distribution, decreased renal function, and a longer half-life in elderly patients can alter the PK/PD of vancomycin [10,11]. However, current vancomycin dosage and monitoring guidelines fail to consider elderly groups. Our findings underscore the need for age-tailored dosing strategies and the comprehensive monitoring of vancomycin therapy in elderly patients to minimize the risk of adverse events, particularly nephrotoxicity.
Currently, there is still a lack of cohort studies comparing vancomycin treatment in elderly and adult patients with MRSA infections. Only Yahav et al. has conducted such a comparison to date, who reported no significant differences in nephrotoxicity between elderly and adult patients. However, we observed a three-fold higher incidence of nephrotoxicity in elderly patients compared to adults. This discrepancy may be attributable to differences in nephrotoxicity assessment criteria: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) in our study vs. Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, End-Stage Kidney Disease (RIFLE) criteria in their study [12,13]. Additionally, baseline creatinine levels of both groups in Yahav’s study were higher than that of our study, which may affect the risk of nephrotoxicity occurrence.
In our study, elderly patients exhibited significantly higher vancomycin Ctrough, AUC24, and AUC24/MIC values compared to adult patients. Our multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that a Ctrough > 20 mg/L is an independent risk factor for nephrotoxicity, with an optimal cutoff of 20.78 mg/L for elderly patients based on ROC analysis. Moreover, elderly patients with a Ctrough exceeding 20 mg/L exhibited a significant increase in nephrotoxicity incidence and serum creatinine changes compared to those with lower Ctrough values. While a significant correlation exists between serum vancomycin Ctrough and the incidence of vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity [14], the specific Ctrough threshold for increased risk remains inconsistent among elderly patients. Wang et al. suggested that a vancomycin Ctrough ≥ 20 mg/L seems to indicate a poorer prognosis in patients ≥80 years [15], while Fukumori et al. proposed that nephrotoxicity risk increases with a Ctrough in excess of 15 mg/L [3]. Dai et al. further recommended different Ctrough thresholds based on renal function, with 21.5 mg/L and 16.5 mg/L associated with increased nephrotoxicity risk in chronic kidney disease at Stage 3a and 3b-5, respectively [16]. The Ctrough threshold for vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in elderly patients may require further research for determination.
The 2020 IDSA Guideline and some reports [17,18] concluded that Ctrough was a poor predictor of AUC24. However, our study revealed a correlation between Ctrough and AUC24 in both groups, indicating that to some extent, Ctrough can reflect the situation of AUC24 (Figure S4 in Supplementary Materials). In clinical practice, actively monitoring Ctrough levels proves beneficial and effective for elderly patients at risk of nephrotoxicity, especially when Ctrough is maintained above 20 mg/L.
During vancomycin treatment, close monitoring of serum creatinine levels is essential in elderly patients, as they exhibit a significantly higher rise in serum creatinine compared to adult patients. This increased susceptibility to vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity is attributed to microanatomical structural changes in the aging kidney, including a reduction in the number of functional glomeruli due to an increased prevalence of nephrosclerosis, a compensatory hypertrophy of remaining nephrons [19], and a diminished kidney functional reserve compared to adult patients. Renal function is strongly related to vancomycin Ctrough [20]. In elderly patients, lower empiric vancomycin doses and shorter duration are advised due to reduced clearance from enhanced tissue binding and overall decreased systemic and renal clearance [21]. Hence, vigilant monitoring of vancomycin levels and renal function is crucial for elderly patients. Additionally, considering that some patients may develop AKI within 48 h after vancomycin administration, it is preferable to initiate monitoring as early as possible (within 48 h).
Despite receiving a lower daily vancomycin dose, elderly patients still exhibited significantly higher vancomycin Ctrough, AUC24, and AUC24/MIC values compared to adult patients. The difference is likely attributed to complexities of renal function assessment in older patients, potentially influenced by factors such as sarcopenia [6] and hypoalbuminemia, which can impact vancomycin pharmacokinetics. These findings were consistent even in a subgroup analysis of patients with normal eGFRs (eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), suggesting that creatinine-based GFR estimation in elderly patients may not accurately reflect their true renal function.
In addition to vancomycin-associated indices, ICU residence was associated with nephrotoxicity in elderly patients [22]. This increased susceptibility likely stems from altered vancomycin pharmacokinetics [23,24,25], sepsis, hemodynamic instability, contrast exposure, and concurrent nephrotoxic medication [26].
The limitations of this study are that patients with only one measured concentration were excluded from the AUC24 calculation, and no adjustment was made for prognostic factors such as Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score and frailty status. Future studies are needed to confirm the findings using larger sample sizes and more comprehensive data collection.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Data Collection
This cohort was obtained from two prospective, multicenter, clinical observational studies conducted between October 2012 and November 2019 that were registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (Registration numbers: ChiCTR-OPC-16007920 and ChiCTR-OPC-17012567). The study was approved by the ethics committees of Fudan University-affiliated Huashan Hospital and various sub-centers. All participants signed informed consent before being enrolled in the study.
Patients were classified into elderly patients (≥65 years) and younger adult patients (18–64 years). Demographic information from patients, including gender, age, body mass index (BMI), renal function, comorbidities (such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, malignancy, hematological malignancy, etc.), types of medical intervention (venous catheters, tracheal cannula, tracheostomy, urinary catheters, drainage tubes, surgery, ICU admission, etc.), infection sites, duration of vancomycin treatment, vancomycin daily dosage, and concomitant use of other antibiotics were collected. The eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) was calculated by the modification of diet in renal disease equation. The change in serum creatinine was determined by subtracting the serum creatinine measured either on the day before or on the initial day of vancomycin therapy from the maximum serum creatinine recorded during the course of therapy. These data were extracted from medical records and verified by two physicians.
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Patients included in the study had bloodstream infections, pulmonary infections, central nervous system infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and other infections caused by MRSA, confirmed by clinical symptoms, physical signs, laboratory tests, and microbiological examinations. Patients were aged 18 years or older and treated with vancomycin for at least 5 days.
Individuals were excluded from this study if they had received effective anti-MRSA agents such as linezolid, norvancomycin, or daptomycin for more than 24 h within 72 h before inclusion, were colonized with MRSA, received less than 5 days of vancomycin treatment, underwent dialysis, were pregnant or lactating, or lacked a microbiological diagnosis of infection.
4.3. Microbiological Detection
Pathogens were identified using the Mérieux Vitek2 GP identification card (version number: 21342) and the VITEK 2 Compact system (BIOMÉRIEUX, Marcy l′Etoile, France). The MICs of vancomycin and oxacillin were determined using the agar dilution method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institutes (CLSI) standards [27,28], with ATCC29213 as the quality control strain. S. aureus with an oxacillin MIC of ≥4 mg/L was classified as MRSA.
4.4. Vancomycin TDM and PK/PD Analysis
Clinicians initiate vancomycin therapy based on the patient’s renal function. For patients with normal renal function, 15–20 mg/kg of vancomycin is administered based on actual body weight every 8–12 h as an intravenous infusion [29]. Vancomycin TDM and PK/PD analysis were conducted to enhance the efficacy and safety of treatment for all enrolled patients. For patients with normal kidney function, Ctrough samples were collected 0–0.5 h before the 4th or 5th dose, and peak concentration samples were collected at 0.5–1 h after the end of vancomycin infusion. For patients with impaired or severe kidney function (i.e., eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2), serum Ctrough and peak concentration samples were collected before and after the second vancomycin dose, respectively. If the patient’s dosage was adjusted, TDM could be repeated after 3–4 days of vancomycin therapy, depending on how the patient’s infection was responding to treatment.
Vancomycin concentrations were measured using chemiluminescent immunoassay or fluorescence polarization immunoassay, with a linear range of 3–100 mg/L. Quality control and external quality assurance samples were performed to monitor assay differences. The vancomycin AUC24 was calculated using Fan’s method [30]. Specifically, a one-compartment model in Phoenix WinNonlin 8.0 software (Pharsight, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) was utilized to simulate the vancomycin concentration–time profiles for each patient. Subsequently, Matlab 7.0 software (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) was employed to calculate the AUC24 for each individual patient. The AUC24/MIC ratio was calculated based on the vancomycin MIC values of the strains.
4.5. Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy
Clinical success of vancomycin treatment was defined as disappearance of or improvement in clinical symptoms and signs of infection (such as fever and chills), return of laboratory results (such as white blood cell count and neutrophil count) to normal or pre-infection levels, and no need for vancomycin for at least 7 days after discontinuation. Clinical ineffectiveness was defined as the lack of improvement in infection-related symptoms and signs after vancomycin treatment or worsening of laboratory results. Specific auxiliary examinations, such as chest X-rays or CT scans indicating a reduction or disappearance of pulmonary lesions, are essential for evaluating clinical efficacy, especially in pneumonia cases.
The microbiological success of vancomycin treatment was defined as negative bacterial cultures after completing vancomycin treatment, or clinical success, even if microbiological examination specimens could not be repeated. Microbiological ineffectiveness was defined as positive bacterial cultures after completing vancomycin treatment, or clinical ineffectiveness, even if bacterial cultures could not be repeated.
4.6. Evaluation of Nephrotoxicity
Vancomycin nephrotoxicity indicates the occurrence of acute kidney injury (AKI). The definition of AKI, according to the KDIGO criteria [31], includes any of the following conditions (not graded): (a) an increase in serum creatinine (SCr) ≥26.5 μmol/L within 48 h; (b) a known or presumed increase in SCr 1.5 times the baseline value within the past 7 days; (c) urine output less than 0.5 mL/kg/h within 6 to 12 h.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 25.0 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Continuous variables were presented as median (interquartile range, IQR) and compared using an independent sample t-test or non-parametric tests. Categorical variables were expressed as number of cases (%) and compared using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Logistic regression analysis was used to calculate the odds ratio (OR) and corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) for risk factors related to nephrotoxicity. Clinically significant variables with p < 0.1 in univariate regression were included in the multivariate logistic regression analysis, and adjusted odds ratios (aOR) were calculated. A significance level of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the incidence of vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity was nearly three times higher in elderly patients than adult patients, but with similar clinical and microbiological efficacy. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity included Ctrough, AUC24, ICU admission, surgery, and drainage tube placement. Of these, a Ctrough > 20 mg/L was an independent factor in elderly patients. In adult patients, vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity was related to renal function and vancomycin levels. These findings suggest that renal function and vancomycin concentration need to be closely monitored in elderly patients to prevent nephrotoxicity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics13040324/s1, Figure S1. Comparison of Ctrough, AUC24, and AUC24/MIC in elderly and adult patients; Figure S2. Distribution of vancomycin MIC value in MRSA of elderly and adult patients; Figure S3: ROC analysis of vancomycin and Ctrough in elderly patients; Figure S4. Correlation of Ctrough and AUC24 of elderly and adult patients; Table S1: Multivariate analysis of risk factors for nephrotoxicity in subgroup of adult patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and J.Z.; methodology, L.X., X.H., S.L. and Y.F.; formal analysis, L.X. and Y.F.; investigation, M.C., Y.F., M.Y., X.L. (Xin Li), N.C., H.W., X.B., X.L. (Xiaoyu Liang) and N.L.; data curation, L.X., Q.B. and Y.F.; resources, B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.X.; writing—review and editing, Y.F., S.L., Q.B. and J.Z.; visualization, L.X.; supervision, B.G.; project administration, Y.F.; funding acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82204467), the Research Startup Fund of Huashan Hospital, Fudan University (2021QD033), the Municipal Hospital Emerging Frontier Technology Joint Research Project of Shanghai Shenkang Development Center (SHDC12020106), and the Community infectious disease research capacity building project (BCF-XC-SQ-20221206-07).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, and various sub-centers (Registration numbers: ChiCTR-OPC-16007920 and ChiCTR-OPC-17012567).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Vancomycin Collaborative Group for their contribution to their case collection. We also thank Naiqing Zhao, Siping Zhou, and Jianfeng Luo for providing advice on the statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Garduno, A.; Povoa, P.; Nseir, S. Choosing antibiotic therapy for severe community-acquired pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 35, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Pop-Vicas, A.E.; D’Agata, E.M. Increased mortality among elderly patients with meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 64, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumori, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Mizoguchi, A.; Kasai, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Iwamura, N.; To, H. Association of the clinical efficacy of vancomycin with the novel pharmacokinetic parameter area under the trough level (AUTL) in elderly patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, M.J.; Le, J.; Lodise, T.P.; Levine, D.P.; Bradley, J.S.; Liu, C.; Mueller, B.A.; Pai, M.P.; Wong-Beringer, A.; Rotschafer, J.C.; et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A revised consensus guideline and review by the American society of health-system pharmacists, the infectious diseases society of America, the pediatric infectious diseases society, and the society of infectious diseases pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Su, S.; Ye, Z.; Du, G.; He, B.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Evidence-based guideline for therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin: 2020 update by the division of therapeutic drug monitoring, Chinese pharmacological society. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71 (Suppl. S4), S363–S371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahav, D.; Abbas, M.; Nassar, L.; Ghrayeb, A.; Shepshelovich, D.; Kurnik, D.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Attention to age: Similar dosing regimens lead to different vancomycin levels among older and younger patients. Age Ageing 2019, 49, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodise, T.P.; Drusano, G. Vancomycin area under the curve-guided dosing and monitoring for adult and pediatric patients with suspected or documented serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: Putting the safety of our patients first. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljefri, D.M.; Avedissian, S.N.; Rhodes, N.J.; Postelnick, M.J.; Nguyen, K.; Scheetz, M.H. Vancomycin area under the curve and acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, N.E.; Turnidge, J.D.; Munckhof, W.J.; Robinson, J.O.; Korman, T.M.; O’Sullivan, M.V.; Anderson, T.L.; Roberts, S.A.; Warren, S.J.; Gao, W.; et al. Vancomycin AUC/MIC ratio and 30-day mortality in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, K.E.; Bell, A.M.; Stover, K.R.; Wagner, J.L. Intravenous vancomycin dosing in the elderly: A focus on clinical issues and practical application. Drugs Aging 2016, 33, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, D.R.; Vance-Bryan, K.; Gilliland, S.; Rodvold, K.; Rotschafer, J. Comparison of vancomycin pharmacokinetics in hospitalized elderly and young patients using a Bayesian forecaster. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 33, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Uchino, S.; Takinami, M.; Bellomo, R. Validation of the kidney disease improving global outcomes criteria for AKI and comparison of three criteria in hospitalized patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Jiang, L.; Du, B.; Wen, Y.; Wang, M.; Xi, X. A comparison of different diagnostic criteria of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffres, M.N. The Whole price of vancomycin: Toxicities, troughs, and time. Drugs 2017, 77, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, N.; Wei, W.; Jiang, C. Outcomes and nephrotoxicity associated with vancomycin treatment in patients 80 years and older. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, N.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Relationship between vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity and vancomycin trough concentration in older adults: A retrospective observational study. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 55, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Pai, M.P.; Rodvold, K.A.; Lomaestro, B.; Drusano, G.L.; Lodise, T.P. Vancomycin: We can’t get there from here. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drennan, P.G.; Begg, E.J.; Gardiner, S.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.J.; Chambers, S.T. The dosing and monitoring of vancomycin: What is the best way forward? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, A.; Glassock, R.J.; Rule, A.D. Structural and functional changes with the aging kidney. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2016, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.W.; Ji, S.M.; He, X.R.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Lu, W. Influences of renal function descriptors on population pharmacokinetic modeling of vancomycin in Chinese adult patients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, N.R.; Narang, P.K.; Lesko, L.J.; Ninos, M.; Power, M. Vancomycin disposition: The importance of age. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1984, 36, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lim, N.R.; Park, H.J.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.; In, Y.W.; Lee, Y.M. Evaluation of risk factors for vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 40, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, T.; Miljkovic, B.; Kovacevic, P.; Dragic, S.; Momcicevic, D.; Avram, S.; Jovanovic, M.; Vucicevic, K. Population pharmacokinetic model of vancomycin based on therapeutic drug monitoring data in critically ill septic patients. J. Crit. Care 2020, 55, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugel, B.; Nowack, M.C.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Umgelter, A.; Schultheiss, C.; Thies, P.; Phillip, V.; Eyer, F.; Schmid, R.M.; Huber, W. Continuous intravenous administration of vancomycin in medical intensive care unit patients. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.H.; Nguyen, D.A.; Delattre, I.K.; Ho, T.T.; Do, H.G.; Pham, H.N.; Dao, X.C.; Tran, N.T.; Nguyen, G.B.; Van Bambeke, F.; et al. Determination of optimal loading and maintenance doses for continuous infusion of vancomycin in critically ill patients: Population pharmacokinetic modelling and simulations for improved dosing schemes. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippone, E.J.; Kraft, W.K.; Farber, J.L. The nephrotoxicity of vancomycin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wang, J.L.; Chiang, W.C.; Lai, M.S.; Chie, W.C.; Chang, S.C.; Hsueh, P.R. Method-specific performance of vancomycin MIC susceptibility tests in predicting mortality of patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M100: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: Executive summary. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.X.; Chen, M.T.; Li, N.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Yang, M.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Liang, X.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Guo, B.N.; Song, S.C.; et al. Sequence Type 5 (ST5) as a Possible Predictor of Bacterial Persistence in Adult Patients with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia Treated with Vancomycin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0134822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, S.; Shoyinka, A.; Chen, A.; Jacobsen, G.; Zervos, M. Evaluation of vancomycin serum trough concentrations and out comes in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).