Anti-Staphylococcal Biofilm Effects of a Liposome-Based Formulation Containing Citrus Polyphenols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Activity against Planktonic Staphylococci
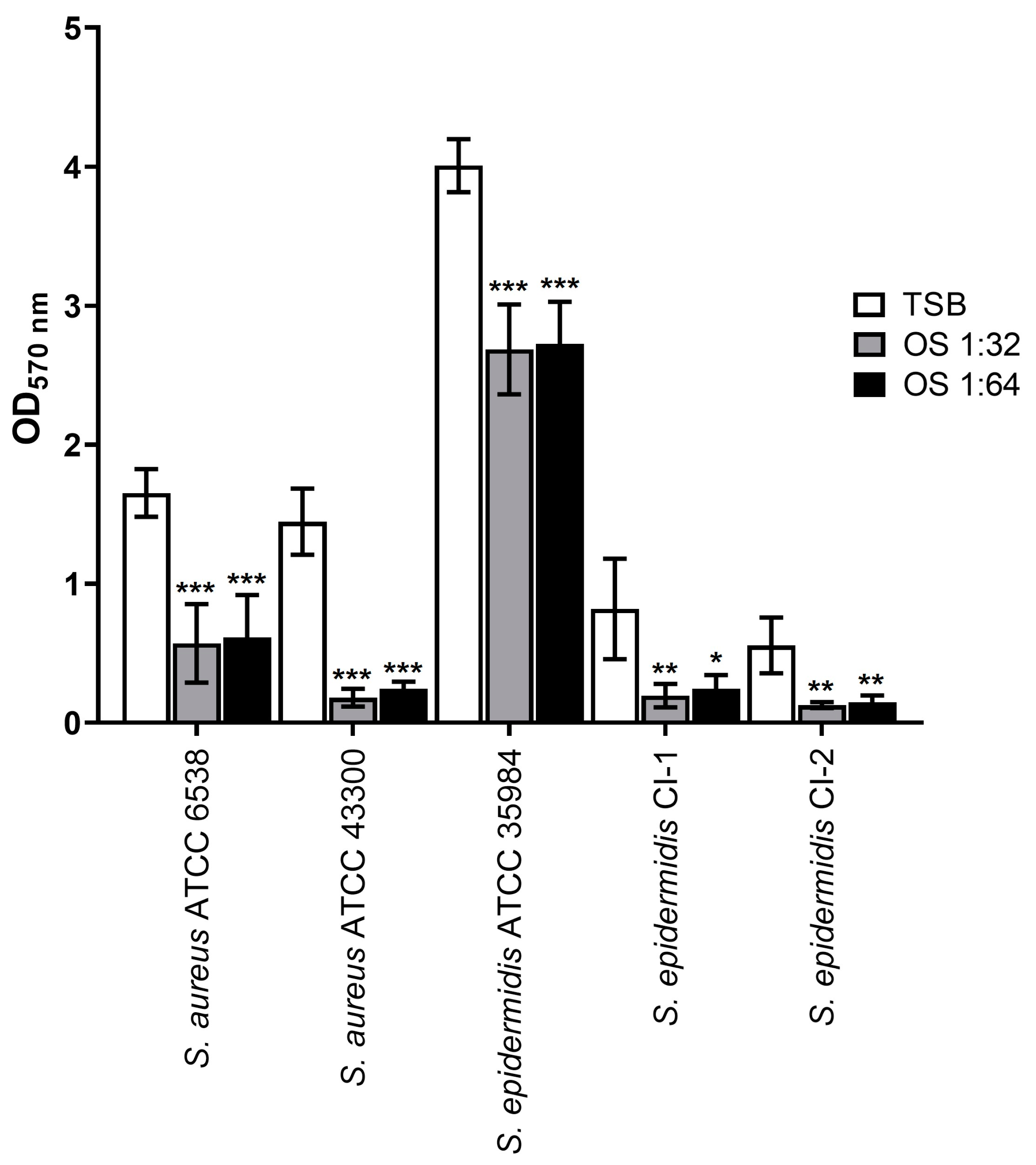
2.2. Inhibitory Effect on Biofilm Formation
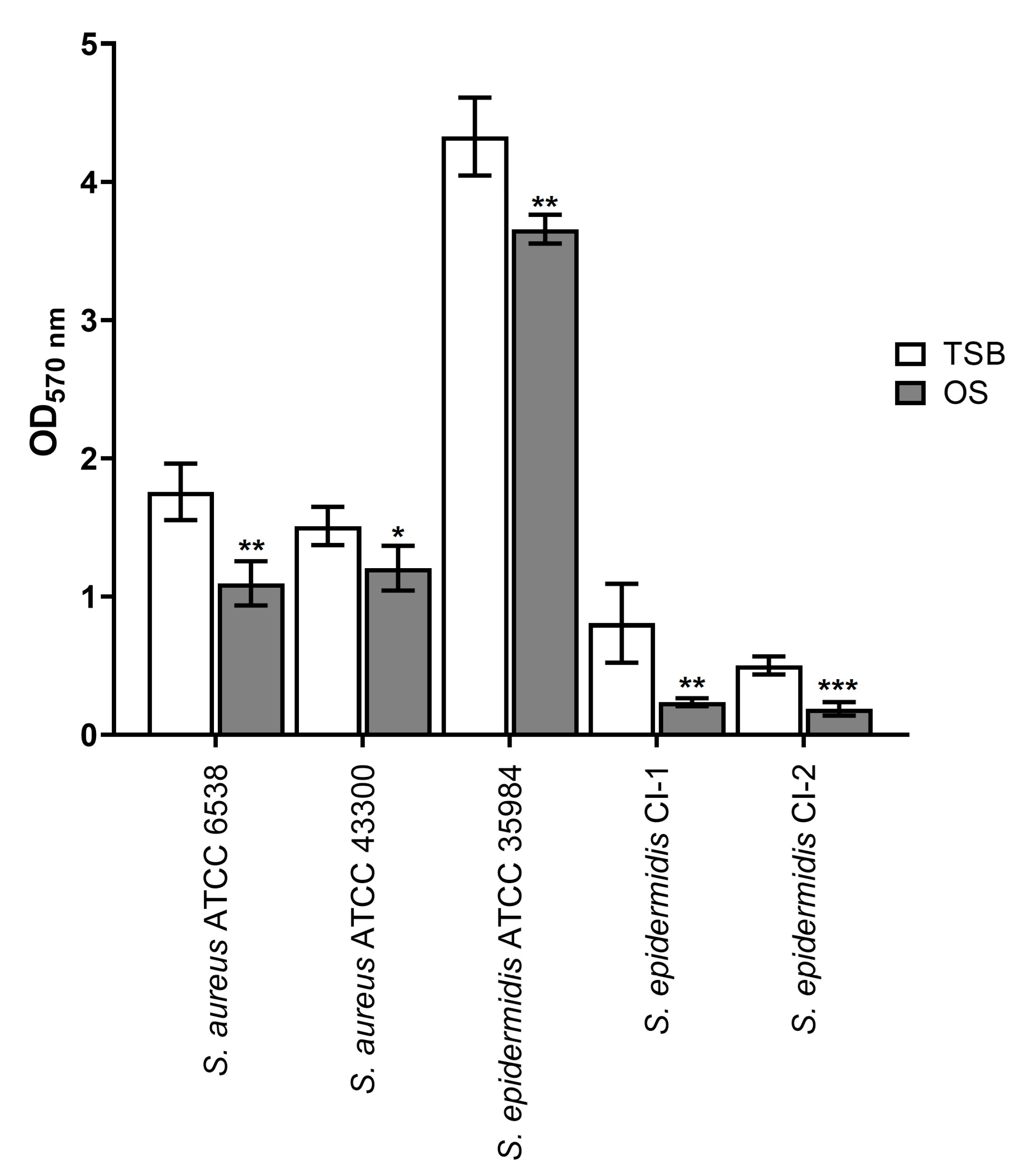
2.3. Eradicating Effect on Mature Biofilms
2.4. Activity of OS in Combination with Levofloxacin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Culture Conditions, and Chemicals
4.2. MIC and MBC
4.3. Growth Curves
4.4. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
4.5. Eradication of Mature Biofilms
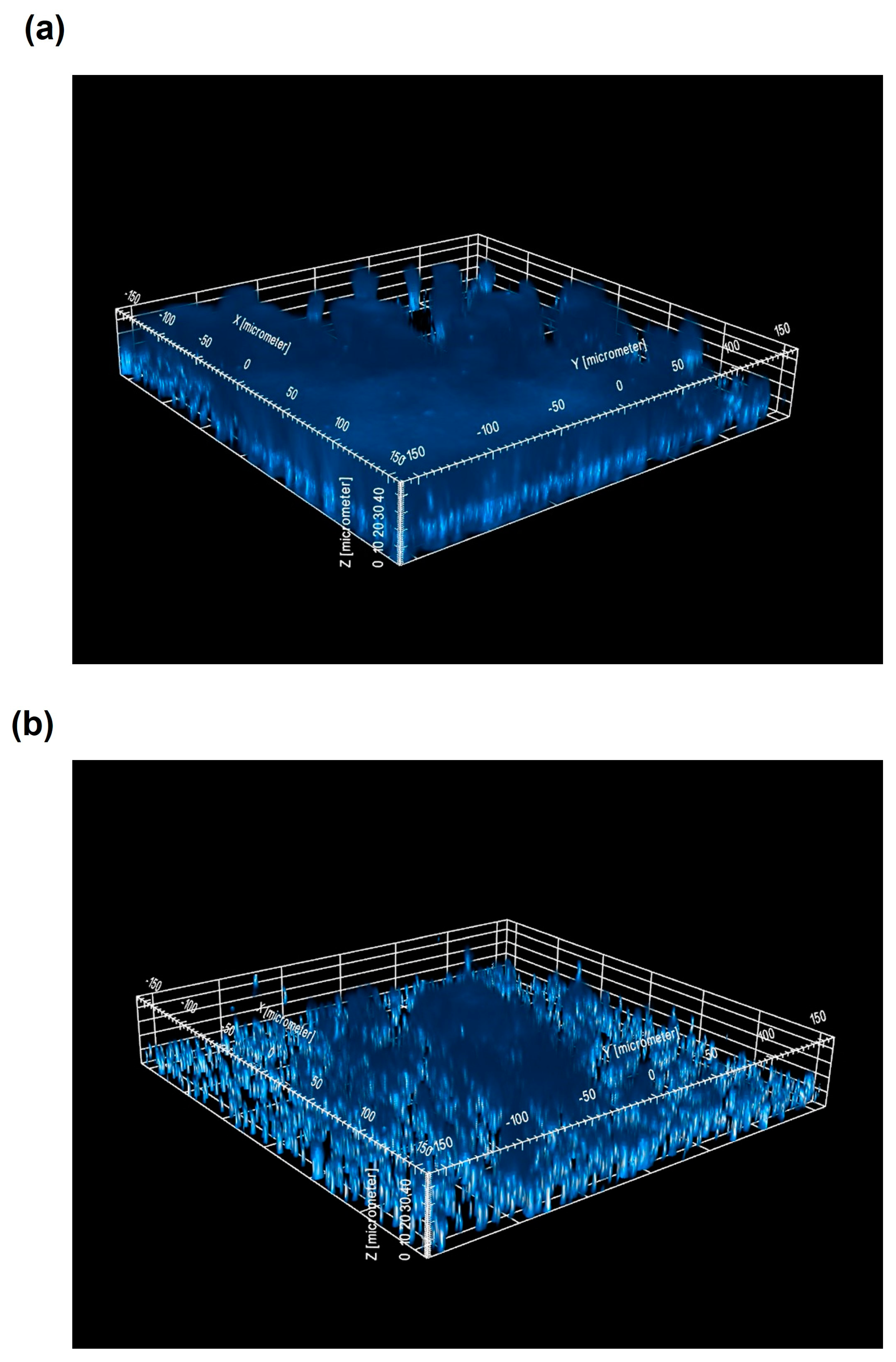
4.6. CLSM Analysis of Staphylococcal Biofilms
4.7. Analysis of Synergism
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, M.C.; Chern, E. Ocular surface microbiota: Ophthalmic infectious disease and probiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 952473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepthi, K.G.; Prabagaran, S.R. Ocular bacterial infections: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 145, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.L.; Barshak, M.B.; Sobrin, L. Eye Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, R.; Miller, F.C.; Mursalin, M.H.; Coburn, P.S.; Callegan, M.C. An Eye on Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: Roles in Ocular Damage and Inflammation. Toxins 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, R.A.; Mursalin, M.H.; Coburn, P.S.; Livingston, E.T.; Nightengale, J.W.; Bagaruka, E.; Hunt, J.J.; Callegan, M.C. Ocular Bacterial Infections: A Ten-Year Survey and Review of Causative Organisms Based on the Oklahoma Experience. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.; Dehari, D.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kumar, D.N.; Kumar, D.; Singh, S.; Nath, G.; Agrawal, A.K. Recent advancements in nanotechnology-based bacteriophage delivery strategies against bacterial ocular infections. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 273, 127413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, F.; Petrillo, A.; Sasso, F.P.; Schettino, A.; Maione, A.; Galdiero, M. Viral Infection and Antiviral Treatments in Ocular Pathologies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginatto, P.; Agostinetto, G.J.; Fuentefria, R.D.N.; Marinho, D.R.; Pizzol, M.D.; Fuentefria, A.M. Eye fungal infections: A mini review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bispo, P.J.; Haas, W.; Gilmore, M.S. Biofilms in infections of the eye. Pathogens 2015, 4, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, D. Chloramphenicol Resurrected: A Journey from Antibiotic Resistance in Eye Infections to Biofilm and Ocular Microbiota. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urwin, L.; Okurowska, K.; Crowther, G.; Roy, S.; Garg, P.; Karunakaran, E.; MacNeil, S.; Partridge, L.J.; Green, L.R.; Monk, P.N. Corneal Infection Models: Tools to Investigate the Role of Biofilms in Bacterial Keratitis. Cells 2020, 9, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Mandal, M. Microbial biofilm: Formation, architecture, antibiotic resistance, and control strategies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Amod, A.; Pandey, P.; Bose, P.; Pingali, M.S.; Shivalkar, S.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Bacterial biofilm infections, their resistance to antibiotics therapy and current treatment strategies. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slobodníková, L.; Fialová, S.; Rendeková, K.; Kováč, J.; Mučaji, P. Antibiofilm Activity of Plant Polyphenols. Molecules 2016, 21, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, M.S.; Ghannam, I.A.Y.; El-Azzouny, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, M.N. Synthetic non-toxic anti-biofilm agents as a strategy in combating bacterial resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 262, 115867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Chakrabartty, I.; Mishra, A.K.; Chopra, H.; Mahanta, S.; Avula, S.K.; Patowary, K.; Ahmed, R.; Mishra, B.; Mohanta, T.K.; et al. Nanotechnology in combating biofilm: A smart and promising therapeutic strategy. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1028086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Gomez, A.; Hosseinidoust, Z. Liposomes for Antibiotic Encapsulation and Delivery. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Awsi, G.R.L.; Alameri, A.A.; Al-Dhalimy, A.M.B.; Gabr, G.A.; Kianfar, E. Application of nano-antibiotics in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. Braz. J. Biol. 2023, 84, e264946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, V.; Strazzabosco, G.; Salgari, N.; Mancini, A.; Rizzo, S.; Beltrami, S.; Schiuma, G.; Casciano, F.; Alogna, A.; Passarella, D.; et al. Ozonated Oil in Liposome Eyedrops Reduces the Formation of Biofilm, Selection of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria, and Adhesion of Bacteria to Human Corneal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. GRAS Notice No 475. Available online: https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=GRASNotices (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Patent Application Publication No US 2017/0079281 A1. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/56/f9/54/9c37ac82687411/US20170079281A1.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Turuvekere Vittala Murthy, N.; Agrahari, V.; Chauhan, H. Polyphenols against infectious diseases: Controlled release nano-formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 161, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.Y.; Seo, Y.H.; Oh, S.W. Antibacterial activities of polyphenols against foodborne pathogens and their application as antibacterial agents. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge, R. Targeting Bacterial Biofilms by the Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG. Molecules 2019, 24, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabska-Kobyłecka, I.; Szpakowski, P.; Król, A.; Książek-Winiarek, D.; Kobyłecki, A.; Głąbiński, A.; Nowak, D. Polyphenols and Their Impact on the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Hou, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Biofilm-forming capacity of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa from ocular infections. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5624–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramón-Peréz, M.L.; Diaz-Cedillo, F.; Ibarra, J.A.; Torales-Cardeña, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S.; Jan-Roblero, J.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C. D-Amino acids inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from ocular infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kıvanç, S.A.; Kıvanç, M.; Kılıç, V.; Güllülü, G.; Özmen, A.T. Comparison of Biofilm Formation Capacities of Two Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis with and without icaA and icaD Genes on Intraocular Lenses. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 47, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kłos, M.; Pomorska-Wesołowska, M.; Romaniszyn, D.; Chmielarczyk, A.; Wójkowska-Mach, J. Epidemiology, Drug Resistance, and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Ocular Infections in Polish Patients. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, R.; Saiabhilash, C.R.; Shivaji, S. Biofilm-Forming Potential of Ocular Fluid Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis on Ex Vivo Human Corneas from Attachment to Dispersal Phase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjith, K.; Nagapriya, B.; Shivaji, S. Polymicrobial biofilms of ocular bacteria and fungi on ex vivo human corneas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, H.C.; Ma, D.H.K.; Yeh, L.K.; Hung, K.H.; Hsiao, C.H. Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Ocular Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates in Taiwan. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kıvanç, S.A.; Akova, B.; Kıvanç, M. Effects of the Dibenzofuran, Usnic Acid, on Inhibition of Ocular Biofilm Formation Due to Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Med. Sci. Monit. 2023, 29, e940266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagge, A.; Ferro Desideri, L.; Carnevali, A.; Del Noce, C.; Camposampiero, D.; Agrusta, M.; Ponzin, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Vaccaro, S.; Nicolò, M.; et al. Efficacy of a New Commercial Ocular Spray Containing Oftasecur Citrus Extract for Reducing Microbial Load in the Conjunctiva of Patients Receiving Intravitreal Injections. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2021, 10, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencucci, R.; Ghelardi, E.; Celandroni, F.; Mazzantini, C.; Vecchione, A.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Favuzza, E.; Landucci, E. Antiseptics and the Ocular Surface: In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Effects on Conjunctival and Corneal Epithelial Cells of a New Liposomal Ocular Spray Containing Biosecur® Citrus Extract. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2022, 11, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Annunziata, F.; Morone, M.V.; Gioia, M.; Cione, F.; Galdiero, M.; Rosa, N.; Franci, G.; De Bernardo, M.; Folliero, V. Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity of Oftasecur and Visuprime Ophthalmic Solutions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tamimi, A.; Alfarhan, A.; Rajagopal, R. Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities of polyphenols extracted from different Saudi Arabian date cultivars against human pathogens. J. Infect. Public. Health 2021, 14, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simina, D.S.; Larisa, I.; Otilia, C.; Ana Cristina, G.; Liliana, M.V.; Aurelian, M.G. The ocular surface bacterial contamination and its management in the prophylaxis of post cataract surgery endophthalmitis. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 65, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Aguas, M.; Khoo, P.; Watson, S.L. Infectious keratitis: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 50, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiltunen, A.K.; Savijoki, K.; Nyman, T.A.; Miettinen, I.; Ihalainen, P.; Peltonen, J.; Fallarero, A. Structural and Functional Dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms and Biofilm Matrix Proteins on Different Clinical Materials. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Thomas, N.; Thierry, B.; Vreugde, S.; Prestidge, C.A.; Wormald, P.J. Distribution and Inhibition of Liposomes on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhlouf, Z.; Ali, A.A.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Liposomes-Based Drug Delivery Systems of Anti-Biofilm Agents to Combat Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukavina, Z.; Šegvić Klarić, M.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Lovrić, J.; Vanić, Ž. Azithromycin-loaded liposomes for enhanced topical treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus aureus (MRSA) infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkash, Y.; Feldman, M.; Ginsburg, I.; Steinberg, D.; Shalish, M. Polyphenols Inhibit Candida albicans and Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Formation. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Chu, X.; Lou, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, B.; Chu, W. Tea polyphenols inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances resistance to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in Caenorhabditis elegans model. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, A.K.; Belalekar, T.S.; Poojary, A.; Rohra, S. Combination drug strategies for biofilm eradication using synthetic and natural agents in KAPE pathogens. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1155699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelardi, E.; Mazzantini, D.; Celandroni, F.; Calvigioni, M.; Panattoni, A.; Lupetti, A.; Bois De Fer, B.; Perez, M., 3rd. Analysis of the microbial content of probiotic products commercialized worldwide and survivability in conditions mimicking the human gut environment. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Media Preparation for EUCAST Disk Diffusion Testing and for Determination of MIC Values by the Broth Microdilution Method. Version 7.0. 2022. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria/media_preparation (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Kwiecinski, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Jin, T. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus isolates from skin and soft tissue infections. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, L.D.R.; Pinto, G.; Oliveira, F.; Vilas-Boas, D.; Almeida, C.; Sillankorva, S.; Cerca, N.; Azeredo, J. The Protective Effect of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Matrix against Phage Predation. Viruses 2020, 12, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST Reading Guide for Broth Microdilution. Version 5.0. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/MIC_testing/Reading_guide_BMD_v_5.0_2024.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Liu, J.Y.; Jia, J.J.; Liu, M.; Duan, H.; Hu, M.L.; Liu, C.; Xue, R.Y.; Jin, Z.L.; Zhang, S.S.; Li, G.C.; et al. A novel indolylbenzoquinone compound HL-J6 suppresses biofilm formation and α-toxin secretion in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batoni, G.; Catelli, E.; Kaya, E.; Pompilio, A.; Bianchi, M.; Ghelardi, E.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Esin, S.; Maisetta, G. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipin, C.; Saptami, K.; Fida, F.; Mujeeburahiman, M.; Rao, S.S.; Athmika Arun, A.B.; Rekha, P.D. Potential synergistic activity of quercetin with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Levofloxacin Concentration (µg/mL) | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | S. aureus ATCC 43300 | S. epidermidis ATCC 35984 | S. epidermidis CI-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 18.81 ± 6.80 | 11.13 ± 3.83 | 11.26 ± 5.80 | 7.07 ± 3.04 |
| 1 | 27.91 ± 8.78 | 11.42 ± 5.29 | 12.26 ± 5.13 | 14.50 ± 3.77 |
| 2 | 31.80 ± 10.32 | 12.36 ± 4.19 | 12.46 ± 4.04 | 18.00 ± 10.50 |
| 4 | 36.36 ± 4.67 | 27.33 ± 7.57 | 13.10 ± 4.19 | 21.35 ± 4.34 |
| 8 | 41.48 ± 6.02 | 28.93 ± 6.09 | 13.49 ± 2.74 | 23.44 ± 5.16 |
| 16 | 43.77 ± 7.11 | 33.26 ± 6.29 | 17.70 ± 5.93 | 33.67 ± 11.23 |
| 32 | 46.79 ± 9.00 | 34.29 ± 4.01 | 17.83 ± 1.43 | 34.85 ± 4.82 |
| 64 | 52.97 ± 4.51 | 35.41 ± 8.16 | 18.68 ± 3.42 | 35.38 ± 6.09 |
| 128 | 54.27 ± 10.62 | 35.49 ± 4.07 | 24.85 ± 12.65 | 35.43 ± 6.35 |
| 256 | 96.43 ± 0.985 | 36.98 ± 5.83 | 45.94 ± 3.15 | 37.75 ± 12.99 |
| 512 | 98.52 ± 0.468 | 37.22 ± 6.68 | 65.91 ± 4.92 | 46.30 ± 6.29 |
| S. aureus ATCC 6538 | S. epidermidis CI-1 | |
|---|---|---|
| TSB a | 1.99 ± 0.14 | 1.10 ± 0.09 |
| OS | 1.25 ± 0.14 (37.48 ± 5.58) | 0.374 ± 0.03 (65.83 ± 2.00) |
| Levofloxacin 8 b or 128 c µg/mL | 1.161 ± 0.14 (41.36 ± 10.82) | 0.719 ± 0.04 (33.93 ± 8.35) |
| Levofloxacin 16 b or 256 c µg/mL | 1.086 ± 0.04 (45.37 ± 5.08) | 0.694 ± 0.02 (36.36 ± 5.60) |
| Levofloxacin 32 b or 512 c µg/mL | 1.046 ± 0.19 (47.52 ± 9.52) | 0.594 ± 0.02 (45.58 ± 4.45) |
| OS + levofloxacin 8 b or 128 c µg/mL | 1.16 ± 0.06 (41.46 ± 6.46) | 0.39 ± 0.05 (64.42 ± 2.09) |
| OS + levofloxacin 16 b or 256 c µg/mL | 1.02 ± 0.02 (48.62 ± 4.77) | 0.380 ± 0.06 (64.92 ± 7.94) |
| OS + levofloxacin 32 b or 512 c µg/mL | 1.019 ± 0.01 (48.75 ± 3.99) | 0.372 ± 0.04 (65.84 ± 4.74) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzantini, D.; Massimino, M.; Calvigioni, M.; Rossi, V.; Celandroni, F.; Lupetti, A.; Batoni, G.; Ghelardi, E. Anti-Staphylococcal Biofilm Effects of a Liposome-Based Formulation Containing Citrus Polyphenols. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040318
Mazzantini D, Massimino M, Calvigioni M, Rossi V, Celandroni F, Lupetti A, Batoni G, Ghelardi E. Anti-Staphylococcal Biofilm Effects of a Liposome-Based Formulation Containing Citrus Polyphenols. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzantini, Diletta, Mariacristina Massimino, Marco Calvigioni, Virginia Rossi, Francesco Celandroni, Antonella Lupetti, Giovanna Batoni, and Emilia Ghelardi. 2024. "Anti-Staphylococcal Biofilm Effects of a Liposome-Based Formulation Containing Citrus Polyphenols" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040318
APA StyleMazzantini, D., Massimino, M., Calvigioni, M., Rossi, V., Celandroni, F., Lupetti, A., Batoni, G., & Ghelardi, E. (2024). Anti-Staphylococcal Biofilm Effects of a Liposome-Based Formulation Containing Citrus Polyphenols. Antibiotics, 13(4), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040318







