Fusion Partner Facilitates Expression of Cell-Penetrating Peptide L2 in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
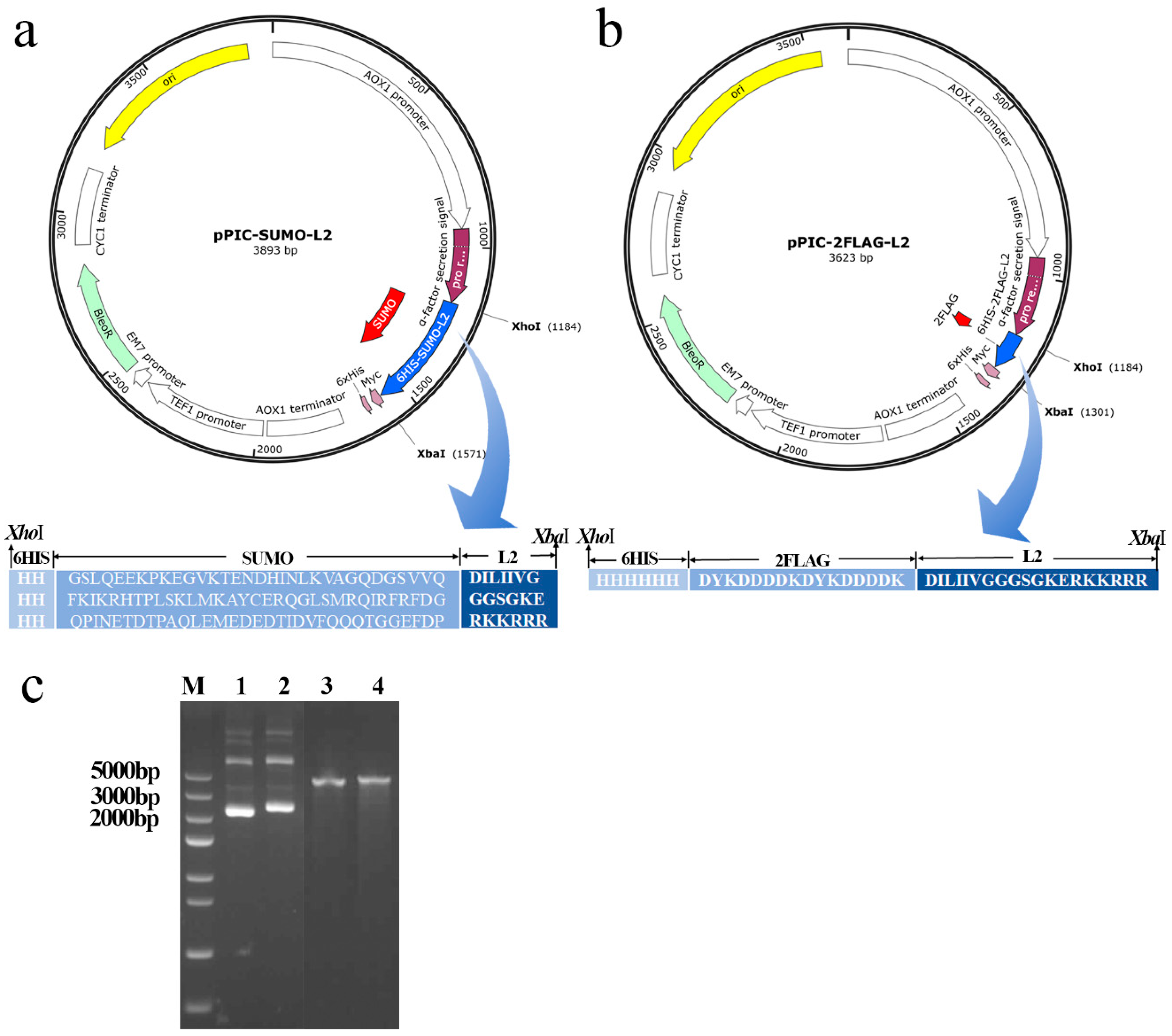
2.1. Design and Construction of the Recombinant Expression Plasmids pPIC-SUMO-L2 and pPIC-2FLAG-L2
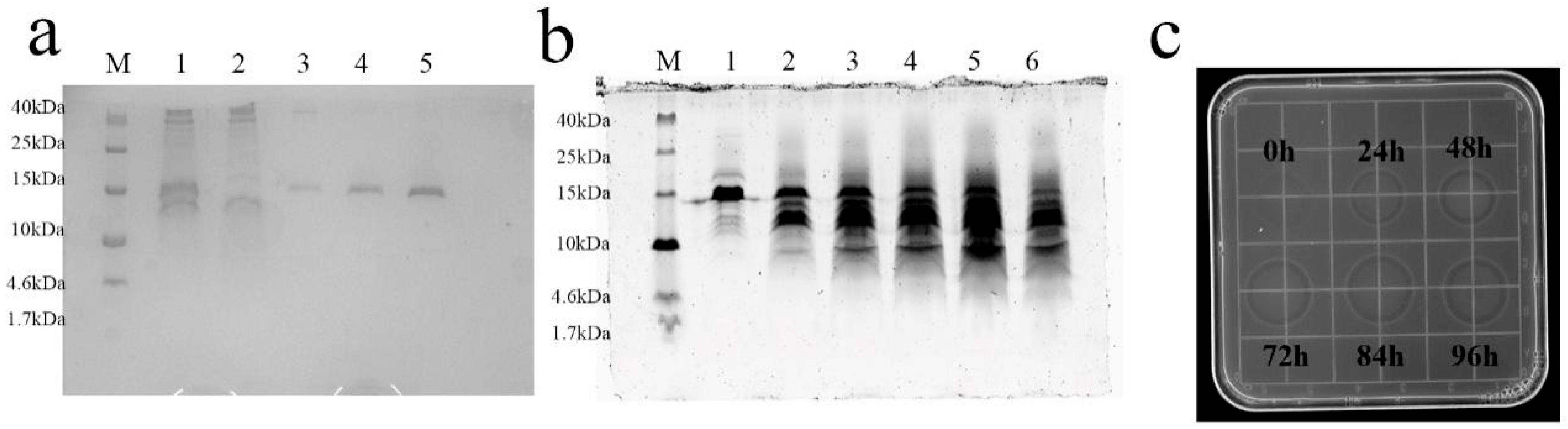
2.2. Methanol-Induced Screening Expression of Recombinant SUMO-L2 and 2FLAG-L2
2.3. Purification and Cleavage of SUMO-L2 Fusion Proteins
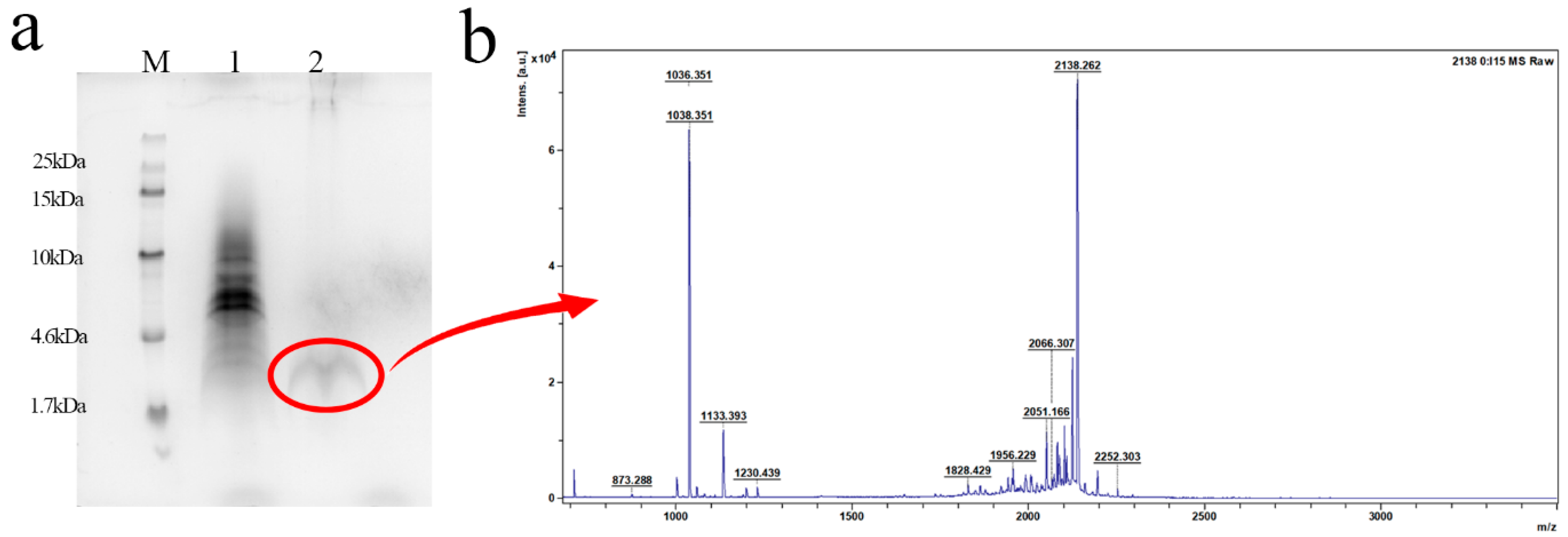
2.4. Purification and Identification of the Activity of L2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Vectors and Reagents
4.2. Design and Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
4.3. Transformation of P. pastoris X-33 and Screening of Positive Transformants
4.4. Expression of SUMO-L2 and 2FLAG-L2 in P. pastoris in 48-Well Plates, Shake Flasks and A 5 L Fermenter Level
4.5. Purification and Cleavage of the SUMO-L2
4.6. Purification and Identification of L2
4.7. Antimicrobial Activity of L2
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- do Nascimento, C.S.; dos Santos, N.F.B.; Ferreira, R.C.C.; Taddei, C.R. Streptococcus agalactiae in pregnant women in Brazil: Prevalence, serotypes, and antibiotic resistance. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, C.A.G.; Queiroz, G.A.; Pereira, F.L.; Tavares, G.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Streptococcus agalactiae Sequence Type 283 in Farmed Fish, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Chu, S.-M.; Wang, H.-C.; Yang, P.-H.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, J.-F. Complicated Streptococcus agalactiae sepsis with/without meningitis in young infants and newborns: The clinical and molecular characteristics and outcomes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppegaard, O.; Skrede, S.; Mylvaganam, H.; Kittang, B.R. Emerging threat of antimicrobial resistance in β-hemolytic Streptococci. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Jia, Y.; Li, R.; He, C.; Chen, H. The structure-mechanism relationship and mode of actions of antimicrobial peptides: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 109, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, G.; Li, S.; Chen, A.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Antibacterial peptide NP-6 affects Staphylococcus aureus by multiple modes of action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desale, K.; Kuche, K.; Jain, S. Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs): An overview of applications for improving the potential of nanotherapeutics. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1153–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shang, L.; Lan, J.; Chou, S.; Feng, X.; Shi, B.; Wang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Shan, A. Targeted and intracellular antibacterial activity against S. agalactiae of the chimeric peptides based on pheromone and cell-penetrating peptides. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44459–44474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushahba, M.F.N.; Mohammad, H.; Thangamani, S.; Hussein, A.A.A.; Seleem, M.N. Impact of different cell penetrating peptides on the efficacy of antisense therapeutics for targeting intracellular pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parachin, N.S.; Mulder, K.C.; Viana, A.A.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Expression systems for heterologous production of antimicrobial peptides. Peptides 2012, 38, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hirz, M.; Pichler, H.; Schwab, H. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: Recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5301–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Ai, Y.-H.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-W. High-level expression of Aspergillus niger lipase in Pichia pastoris: Characterization and gastric digestion in vitro. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.-C. Fusion protein linkers: Property, design and functionality. ADV Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Gu, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, F.; Song, H.; Nian, R.; Liu, W. A novel silk fibroin protein-based fusion system for enhancing the expression of nanobodies in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Gao, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Fusion expression of cecropin B-like antibacterial peptide in Pichia GS115 and its antibacterial mechanism. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.D.; Sun, H.C.; Hu, S.M.; Chiu, C.F.; Homhuan, A.; Liang, S.M.; Leng, C.H.; Wang, T.F. An improved SUMO fusion protein system for effective production of native proteins. Protein Sci. 2009, 17, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, R.; Wen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, L. Molecular chaperones (TrxA, SUMO, Intein, and GST) mediating expression, purification, and antimicrobial activity assays of plectasin in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2015, 62, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, M.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Hang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, G. Soluble expression of antimicrobial peptide BSN-37 from Escherichia coli by SUMO fusion technology. Protein J. 2023, 42, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, N.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Hao, Y.; Lu, H.; Mao, R.; Wang, J. High-yield preparation of american oyster defensin (AOD) via a small and acidic fusion tag and its functional characterization. Mar. Drugs 2023, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Tiwari, R.; Gugjoo, M.B.; Iqbal Yatoo, M.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; Karthik, K.; Khurana, S.K.; Singh, R.; et al. Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenhagen, B.A.; Köster, G.; Wallmann, J.; Heuwieser, W. Prevalence of mastitis pathogens and their resistance against antimicrobial agents in dairy cows in Brandenburg, Germany. J. Dairy. Sci. 2006, 89, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbel, D.; González-díaz, A.; López de Egea, G.; Càmara, J.; Ardanuy, C. An overview of macrolide resistance in Streptococci: Prevalence, mobile elements and dynamics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Jayaraman, A.; Van Deventer, J.A.; Lee, K. Engineering selectively targeting antimicrobial peptides. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 23, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Ji, W.; Zhou, H.; Gong, X.; Miao, B.; Meng, S.; Duan, L.; Shi, Q.; et al. Molecular characteristics and antibiotic resistance mechanisms of clindamycin-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae isolates in China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1138039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pascual, D.; Gaudu, P.; Fleuchot, B.; Besset, C.; Rosinski-Chupin, I.; Guillot, A.; Monnet, V.; Gardan, R. RovS and its associated signaling peptide form a cell-to-cell communication system required for Streptococcus agalactiae pathogenesis. mBio 2015, 6, e02306-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucataru, C.; Ciobanasu, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Opportunities and challenges in overcoming resistance. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 286, 127822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Pitta, A.; Broset, E.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Probiotic engineering strategies for the heterologous production of antimicrobial peptides. Adv. Drug Deliver Rev. 2021, 176, 113863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Rao, B.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y. A Method for rapid screening, expression, and purification of antimicrobial peptides. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.H.; Pei, C.; Yeh, J.Y.; Shih, C.H.; Chung, Y.C.; Hung, L.T.; Ou, B.R. Production of bioactive human alpha-defensin 5 in Pichia pastoris. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Popa, C.; Shi, X.; Ruiz, T.; Ferrer, P.; Coca, M. Biotechnological production of the cell penetrating antifungal PAF102 peptide in Pichia pastoris. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Teng, D.; Tian, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Expression of plectasin in Pichia pastoris and its characterization as a new antimicrobial peptide against Staphyloccocus and Streptococcus. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 78, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Ma, X.; Teng, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, J. Effect of NZ2114 against Streptococcus dysgalactiae biofilms and its application in murine mastitis model. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1010148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Shen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, S. Disruption of YPS1 and PEP4 genes reduces proteolytic degradation of secreted HSA/PTH in Pichia pastoris GS115. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-S.; Kan, S.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Shieh, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C. Antibacterial peptide CecropinB2 Production via various host and construct systems. Molecules 2016, 21, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVallie, E.R.; McCoy, J.M. Gene fusion expression systems in Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1995, 6, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Teng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R.Y.; Wang, J.H. Recombinant production of the antimicrobial peptide NZ17074 in Pichia pastoris using SUMO3 as a fusion partner. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, V.; Saffar, B.; Emamzadeh, R. Functional expression and purification of recombinant Hepcidin25 production in Escherichia coli using SUMO fusion technology. Gene 2017, 610, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Hu, M.; Fang, Y.; Dong, N.; Shan, A. Heterologous expression of the novel dimeric antimicrobial peptide LIG in Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 381, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.R.; Edavettal, S.C.; Hall, J.P.; Mattern, M.R. SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein Expres Purif. 2005, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Carrier proteins boost expression of PR-39-derived peptide in Pichia pastoris. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyarajan, S.; Peter, A.S.; Sathyan, A.; Ranjith, S.; Kandasamy, I.; Duraisamy, S.; Chidambaram, P.; Kumarasamy, A. Expression and purification of epinecidin-1 variant (Ac-Var-1) by acid cleavage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, J.; Cao, L.; Jia, G.; Long, D.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Shang, H. Characterization of bioactive recombinant antimicrobial peptide parasin I fused with human lysozyme expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris system. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2015, 77, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, D.P.; Almeida, J.F.; Goulart, L.R.; Nicolau-Junior, N.; Ueira-Vieira, C. Heterologous expression of abaecin peptide from Apis mellifera in Pichia pastoris. Microb. Cell Factories 2017, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Gene cloning, expression and polyclonal antibody preparation of Rab3A for protein interaction analysis. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popitool, K.; Wataradee, S.; Wichai, T.; Noitang, S.; Ajariyakhajorn, K.; Charoenrat, T.; Boonyaratanakornkit, V.; Sooksai, S. Potential of Pm11 antimicrobial peptide against bovine mastitis pathogens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Peptide | Number of Amino Acids | Theoretical Molecular Weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Positively Charged Residues | Negatively Charged Residues | Instability Index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2 | 19 | 2138.55 | 11.57 | 7 | 2 | 96.65 | −0.926 |
| SUMO | 98 | 11,180.48 | 4.98 | 13 | 18 | 37.78 | −0.965 |
| FLAG | 8 | 1012.98 | 3.97 | 2 | 5 | −1.86 | −3.325 |
| SUMO-L2 | 123 | 14,123.86 | 7.27 | 20 | 20 | 44.15 | −1.068 |
| 2FLAG-L2 | 41 | 4951.33 | 6.63 | 11 | 12 | 46.01 | −2.195 |
| Positive Transformants | Total Protein Levels (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| SUMO-L2 25 | 129 |
| SUMO-L2 44 | 86 |
| SUMO-L2 52 | 92 |
| 2FLAG-L2 50 | 81 |
| 2FLAG-L2 51 | 90 |
| 2FLAG-L2 52 | 77 |
| Strains | MIC (μg/mL) | MBC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| S. agalactiae ATCC 13813 | 4 | 8 |
| S. agalactiae CAU-FRI 2 | 8 | 8 |
| S. agalactiae CAU-FRI 3 | 8 | 8 |
| S. agalactiae CAU-FRI 4 | 8 | 16 |
| S. agalactiae ACCC 61733 | 8 | 8 |
| S. agalactiae PBSA0903 | 8 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yang, N.; Fang, Y.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Teng, D.; Dong, N.; Shan, A.; Wang, J. Fusion Partner Facilitates Expression of Cell-Penetrating Peptide L2 in Pichia pastoris. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121207
Li X, Yang N, Fang Y, Mao R, Hao Y, Teng D, Dong N, Shan A, Wang J. Fusion Partner Facilitates Expression of Cell-Penetrating Peptide L2 in Pichia pastoris. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(12):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121207
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuan, Na Yang, Yuxin Fang, Ruoyu Mao, Ya Hao, Da Teng, Na Dong, Anshan Shan, and Jianhua Wang. 2024. "Fusion Partner Facilitates Expression of Cell-Penetrating Peptide L2 in Pichia pastoris" Antibiotics 13, no. 12: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121207
APA StyleLi, X., Yang, N., Fang, Y., Mao, R., Hao, Y., Teng, D., Dong, N., Shan, A., & Wang, J. (2024). Fusion Partner Facilitates Expression of Cell-Penetrating Peptide L2 in Pichia pastoris. Antibiotics, 13(12), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121207










