Optimizing the Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) over Exposure Time for the Control of Salmonella spp. In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
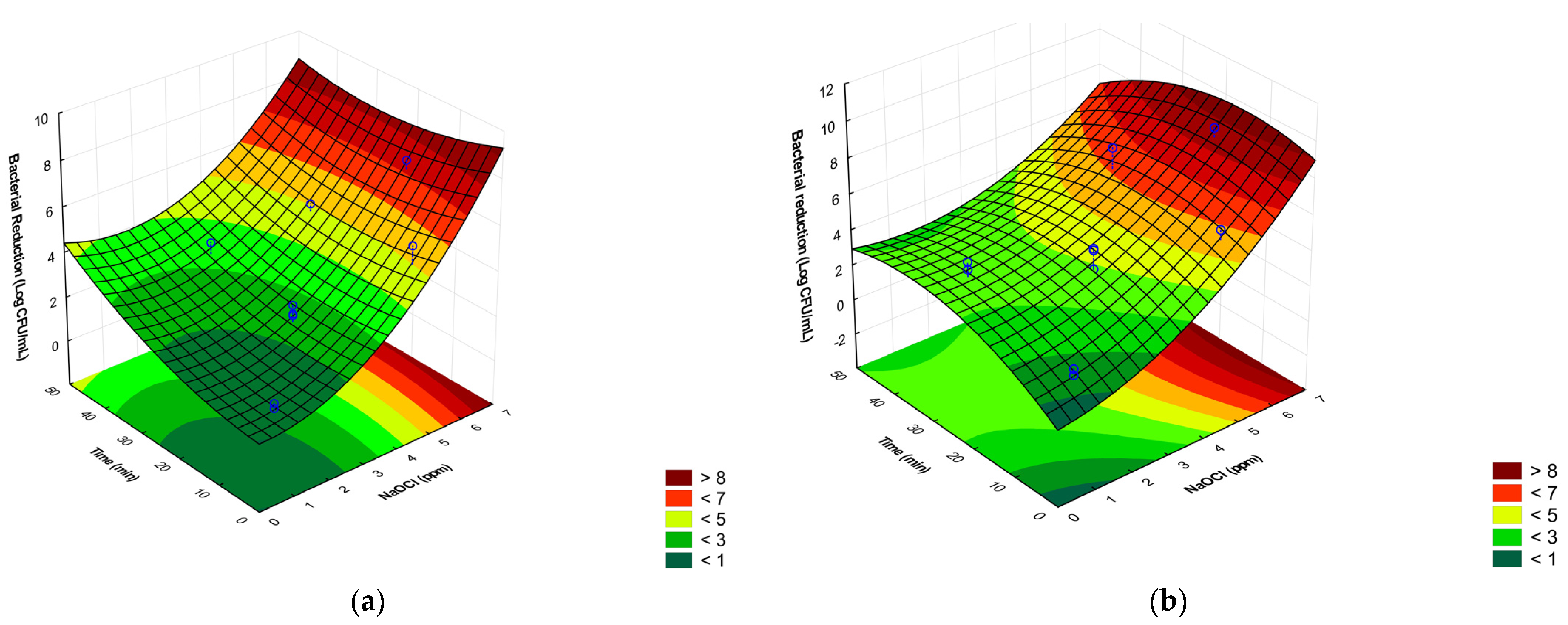
2.1. Central Composite Rotatable Design (CCRD)
2.2. Validation of the Inactivation Model of Salmonella Enteritidis ATCC 13076 and Salmonella Schwarzengrund
2.3. Performance of the Experimental Model and Data Adjustment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Preparation of the Strains
4.3. Central Composite Rotatable Design (CCRD)
4.4. Model of Inactivation and Validation of Salmonella Enteritidis ATCC 13076 and Salmonella Schwarzengrund
4.5. Performance of the Experimental Model and Data Adjustment
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Racki, A.S. Riscos Ambientais em um Frigorífico De Peixes. Monografia de Especialização. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Paraná, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Ed.) Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; ISBN 978-92-5-109185-2. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, A.C.; Lopes, A.L.; Pedrini, B.; Dellova, D.; França, D.; Souza, F.; Almeida, G.; Nascimento, G.; Borielo, G.; Dias, I.; et al. Veículo Oficial da Associação Brasileira da Piscicultura. 2022. Available online: https://www.peixebr.com.br/anuario2022/ (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- de Oliveira Sartori, A.G.; Amancio, R.D. Pescado: Importância nutricional e consumo no Brasil. Segur. Aliment. Nutr. 2012, 19, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, W.; Xia, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Rao, Z.; Du, L.; Zhao, R.; Yi, M.; et al. Fish Consumption and Multiple Health Outcomes: Umbrella Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, L.P.; Ferreira, L.P.; Freitas, M.F.U.; Nunes, C.d.R. Análise Microbiologica de Alimentos Minimamente Processados Comercializados em Campos Dos Goytacazes—RJ. Rev. Interdiscip. Pensamento Cient. 2020, 6, 187–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinitz, M.L.; Ruble, R.D.; Wagner, D.E.; Tatini, S.R. Incidence of Salmonella in Fish and Seafood. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Sant’Ana, A. Introduction to the Special Issue: Salmonella in Foods: Evolution, Strategies and Challenges. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, D.F.M.; Sellera, F.P.; Lopes, R.; Keelara, S.; Landgraf, M.; Greene, S.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Thakur, S. Class 1 integron-borne cassettes harboring blaCARB-2 gene in multidrug-resistant and virulent Salmonella Typhimurium ST19 strains recovered from clinical human stool samples, United States. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.G.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Cunha Neto, A.; Mano, S.B.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Worldwide Epidemiology of Salmonella Serovars in Animal-Based Foods: A Meta-Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.C.; Grass, J.E.; Richardson, L.C.; Nisler, A.L.; Bicknese, A.S.; Gould, L.H. Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella That Caused Foodborne Disease Outbreaks: United States, 2003–2012. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.V.G.S.; Carvalho, R.C.T.; Castro, V.S.; Cunha Neto, A.; Muller, B.; Carvalho, F.T.; dos Prazeres Rodrigues, D.; Vieira, B.S.; de Souza Figueiredo, E.E. Salmonella in the Processing Line of Farmed Tambatinga (Colossoma Macropomum x Piaractus Brachypomus) in Mato Grosso, Brazil: Serotypes of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Profile. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha Neto, A.; Panzenhagen, P.; Carvalho, L.; Rodrigues, D.; Conte Junior, C.; Figueiredo, E. Occurrence and Antimicrobial Resistance profile of Salmonella Isolated from Native Fish Slaughtered and Commercialised in Brazil. Arch. Leb. 2019, 70, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Data dictionaries—Guidelines for reporting data on zoonoses, antimicrobial resistance and food-borne outbreaks using the EFSA data models for the Data Collection Framework (DCF). EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2014. EFSA J. 2015, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.R.; Xavier, R.G.C.; de Oliveira, T.F.; Leite, R.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Leal, C.A.G. Occurrence, Genetic Diversity, and Control of Salmonella Enterica in Native Brazilian Farmed Fish. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.; Wong, W.; Chai, L.; Tunung, R.; Jeyaletchumi, P.; Hidayah, N.; Ubong, A.; Farinazleen, M.; Cheah, Y.; Son, R. Salmonella: A Foodborne Pathogen. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Dróżdż, M.; Małaszczuk, M.; Paluch, E.; Pawlak, A. Zoonotic Potential and Prevalence of Salmonella Serovars Isolated from Pets. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2021, 11, 1975530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Ed.) Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130562-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tong Thi, A.N.; Sampers, I.; Van Haute, S.; Samapundo, S.; Ly Nguyen, B.; Heyndrickx, M.; Devlieghere, F. Decontamination of Pangasius Fish (Pangasius Hypophthalmus) with Chlorine or Peracetic Acid in the Laboratory and in a Vietnamese Processing Company. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 208, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Manual de Procedimentos para Implantação de Estabelecimento Industrial de Pescado: Produtos Frescos e Congelados; Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento: Brasília, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, L.-S.; Schade, J.E.; Molyneux, B.T. Chlorination of Poultry Chiller Water: Chlorine Demand and Disinfection Efficiency. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.R.M.; Malheiros, P.S.; Brandelli, A.; Tondo, E.C. Avaliação da resistência de Salmonella à ação de desinfetantes ácido peracético, quaternário de amônio e hipoclorito de sódio. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 2010, 69, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkitanarayanan, K.S.; Lin, C.M.; Bailey, H.; Doyle, M.P. Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enteritidis, and Listeria monocytogenes on apples, oranges, and tomatoes by lactic acid with hydrogen peroxide. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.-H.; Han, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Efficacy of Chlorine-Based Disinfectants (Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorine Dioxide) on Salmonella Enteritidis Planktonic Cells, Biofilms on Food Contact Surfaces and Chicken Skin. Food Control 2021, 123, 107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, V.S.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Mutz, Y.S.; Paletta, A.C.C.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Modelling Inactivation of Wild-Type and Clinical Escherichia coli O26 Strains Using UV-C and Thermal Treatment and Subsequent Persistence in Simulated Gastric Fluid. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, A.A.M. Avaliação da Eficácia de Desinfectantes da Indústria Agro-Alimentar. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.; Cookson, B. Does Microbial Resistance or Adaptation to Biocides Create a Hazard in Infection Prevention and Control. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 76, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, S.; Matthews, K.R. Failure of Foodborne Pathogens to Develop Resistance to Sanitizers Following Repeated Exposure to Common Sanitizers. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegaro, A.; Flores, A.F.; Simer, P.; Silva, F.I.; Sbardelotto, P.R.R.; Pinto, E.P. Sanitizantes: Concentrações e Aplicabilidade na Indústria de Alimentos. Sci. Agrar. Parana. 2016, 15, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, S.B.P.; de Arruda Sucasas, L.F.; Oetterer, M. Resíduos da Comercialização de Pescado Marinho—Volume De Descarte E Aspectos Microbiológicos. Rev. Bras. Tecnol. Agroind. 2016, 10, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- te Giffel, M.C.; Zwietering, M.H. Validation of Predictive Models Describing the Growth of Listeria Monocytogenes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 46, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, T. Indices for Performance Evaluation of Predictive Models in Food Microbiology. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1996, 81, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyi, J.; Pin, C.; Ross, T. Validating and Comparing Predictive Models. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T. Predictive Modelling of the Growth and Survival of Listeria in Fishery Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 62, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.F.; Finan, C. Linear Regression and the Normality Assumption. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 98, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Points | Chlorine (ppm) | Time (m) | Temperature (°C) | S. Enteritidis ATCC 13076 (log N0 − N) | S. Schwarzengrund (log N0 − N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.36 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 1.33 | 1.9 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 1.28 | 1.6 |
| 3 | 1 | 30 | 5 | 2 | 4.17 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 30 | 1.5 | 1.95 |
| 5 | 1 | 30 | 30 | 1.97 | 3.74 |
| 6 | 3 | 17.5 | 3.52 | 3.15 | 4.99 |
| 7 | 3 | 17.5 | 38.52 | 1.39 | 3.49 |
| 8 | 3 | 3.52 | 17.5 | 2.16 | 2.02 |
| 9 | 3 | 38.52 | 17.5 | 3.8 | 3.41 |
| 10 | 3 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 2.08 | 3.43 |
| 11 | 3 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 2.04 | 4.89 |
| 12 | 3 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 2.7 | 3.51 |
| 13 | 3 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 2.76 | 3.85 |
| 14 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5.8 * | 4.59 |
| 15 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 3.59 | 7.28 * |
| 16 | 5 | 5 | 30 | 4.05 | 6.1 * |
| 17 | 5 | 30 | 30 | 5.19 | 5.1 |
| 18 | 6.36 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 7.52 * | 8.96 * |
| Points | Treatments | Salmonella Enteritidis ATCC 13076 | Salmonella Schwarzengrund | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorine ppm | Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | * Observed | * Predicted | * Observed | * Predicted | |
| 1 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 17.5° | 2.84 | 3.400821 | 4.24 | 4.08 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 8 | 17.5° | 2.579784 | 2.397442 | 3.06694679 | 2.82 |
| 3 | 4 | 3.5 | 17.5° | 3.826391 | 4.036951 | 3.903089987 | 3.74 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 25 | 17.5° | 2.253022 | 1.983209 | 3.678766618 | 3.17 |
| 5 | 3 | 19 | 17.5° | 3.051153 | 2.641538 | 4.293204658 | 3.98 |
| Models | Normality of Data (p Value) * | Normality of Residuals (p Value) * | R2adj | MSE | Bf | Af | Lack of Fit (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Enteritidis ATCC 13076 | 0.2971 | 0.1519 | 0.82337 | 0.1265 | 1.13 | 1.42 | 0.1100 |
| S. Schwarzengrund | 0.296 | 0.4504 | 0.83952 | 0.094 | 1.1 | 1.36 | 0.3956 |
| Factors | Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorine (ppm) | Time (m) | Temperature (°C) | |
| −1.44 | 0.36 | 3.52 | 3.52 |
| −1 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 0 | 3 | 17.5 | 17.5 |
| 1 | 5 | 30 | 30 |
| 1.44 | 6.36 | 38.5 | 38.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, N.B.; Reis, J.O.d.; Castro, V.S.; Machado, M.A.M.; Cunha-Neto, A.d.; Figueiredo, E.E.d.S. Optimizing the Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) over Exposure Time for the Control of Salmonella spp. In Vitro. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010068
Nunes NB, Reis JOd, Castro VS, Machado MAM, Cunha-Neto Ad, Figueiredo EEdS. Optimizing the Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) over Exposure Time for the Control of Salmonella spp. In Vitro. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Nathaly Barros, Jaqueline Oliveira dos Reis, Vinicius Silva Castro, Maxsueli Aparecida Moura Machado, Adelino da Cunha-Neto, and Eduardo Eustáquio de Souza Figueiredo. 2024. "Optimizing the Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) over Exposure Time for the Control of Salmonella spp. In Vitro" Antibiotics 13, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010068
APA StyleNunes, N. B., Reis, J. O. d., Castro, V. S., Machado, M. A. M., Cunha-Neto, A. d., & Figueiredo, E. E. d. S. (2024). Optimizing the Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) over Exposure Time for the Control of Salmonella spp. In Vitro. Antibiotics, 13(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010068








