Abstract
With the increase in carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB) infections, there has been a resurgence in the use of polymyxins, specifically colistin (COL). Since the reintroduction of COL-based regimens in treating CRAB infections, several COL-resistant A. baumannii isolates have been identified, with the mechanism of resistance heavily linked with the loss of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer of the bacterial outer membrane through mutations in lpxACD genes or the pmrCAB operon. SPR206, a novel polymyxin derivative, has exhibited robust activity against multidrug-resistant (MDR) A. baumannii. However, there is a dearth of knowledge regarding its efficacy in comparison with other A. baumannii-active therapeutics and whether traditional polymyxin (COL) mediators of A. baumannii resistance also translate to reduced SPR206 activity. Here, we conducted susceptibility testing using broth microdilution on 30 A. baumannii isolates (17 COL-resistant and 27 CRAB), selected 14 COL-resistant isolates for genomic sequencing analysis, and performed time-kill analyses on four COL-resistant isolates. In susceptibility testing, SPR206 demonstrated a lower range of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) compared with COL, with a four-fold difference observed in MIC50 values. Mutations in lpxACD and/or pmrA and pmrB genes were detected in each of the 14 COL-resistant isolates; however, SPR206 maintained MICs ≤ 2 mg/L for 9/14 (64%) of the isolates. Finally, SPR206-based combination regimens exhibited increased synergistic and bactericidal activity compared with COL-based combination regimens irrespective of the multiple resistance genes detected. The results of this study highlight the potential utility of SPR206 in the treatment of COL-resistant A. baumannii infections.
1. Introduction
Acinetobacter baumannii is an opportunistic, non-fermenting Gram-negative organism associated with high all-cause mortality rates [1,2]. Typically, A. baumannii manifests in nosocomial infections, with outbreaks identified in numerous countries and treatment settings globally [1,3]. A. baumannii shows a propensity for developing resistance against commonly used antimicrobials, including fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, and beta-lactams. The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) A. baumannii isolates has led to a resurgence in using polymyxin agents, such as polymyxin B and colistin (COL, also known as polymyxin E) [4,5]. However, the increased use and the absence of optimal dosing for COL have resulted in reports of COL-resistant strains [2,5].
The mode of action for COL, a part of the polymyxin class of antimicrobials, involves an interaction with the polyanionic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) present within the bacterial outer membrane, leading to membrane destabilization [6]. Resistance of Gram-negative pathogens to COL is most commonly attributed to the modification of the lipid anchor of LPS, or lipid A. Consequently, mutations in the first three genes in the lipid A biosynthesis pathway, namely lpxACD, are frequently implicated as the basis for polymyxin resistance in A. baumannii [6,7]. Apart from lpxACD gene mutation, various studies have highlighted that modifications of the target LPS, driven by the addition of phosphoethanolamine moieties to lipid A through the pmrCAB operon, also play a role in A. baumannii COL resistance [8,9]. Of note, investigators have reported detection of mutations, specifically in the pmrA and pmrB genes, in COL- and carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB) isolates [5,10]. When evaluated against MDR A. baumannii isolates, including those with pmrA and pmrB gene mutations, COL-based combination regimens (alongside other A. baumannii-active agents including meropenem, MEM, or minocycline, MIN) can be effective [11]. Nevertheless, conflicting data exists on whether these combinations are associated with improved patient outcomes or a reduction in the emergence of COL resistance [2,12]. Given the potentially detrimental spread of A. baumannii resistance to COL—a last-line agent—and dose-limiting toxicities associated with COL-based combination regimens, there is an urgent need to identify new agents to treat serious MDR A. baumannii infections.
SPR206, a novel polymyxin derivative, has shown robust activity against A. baumannii in both in vitro and in vivo studies [13,14]. While maintaining a similar pharmacophore to COL, SPR206 has undergone structural modifications to include a fatty acyl tail with an aryl chloride group-substituted aminobutyryl N-termini and a shortened nanopeptide cyclic core with L-Dap residues attached to the peptide ring [13,15]. These modifications have been attributed to a reduction in cytotoxicity and nephrotoxicity compared with COL, as observed in in vivo studies [16]. Additionally, in vitro studies have revealed that SPR206 has more potent activity compared with COL (nearly eight-fold lower MICs) when evaluated against MDR A. baumannii isolates [15]. Although these findings indicate the potential utility of SPR206 in MDR (including COL-resistant) A. baumannii infections, critical gaps remain. Namely, the potential mediators of SPR206 resistance need elucidation and whether these genes associated with A. baumannii COL resistance (i.e., lpxACD and/or pmrA, pmrB) exert the same impact on the novel polymyxin derivative remains unclear. Furthermore, there is a need to investigate whether similar or enhanced activity, comparative to COL, would be seen with SPR206 when tested in combination with other A. baumannii-active antimicrobials against MDR isolates.
In this study, our primary aims were to delineate the antibacterial activity of SPR206 against MDR A. baumannii isolates and to describe the effect of COL resistance on SPR206 susceptibility. The specific objectives of this study were to (i) evaluate the comparative activity of SPR206 and other A. baumannii-active agents against MDR A. baumannii isolates through minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) testing, (ii) conduct genomic sequencing analysis to determine mutations present in 14 A. baumannii isolates (both COL-resistant and CRAB), and (iii) investigate and compare the in vitro synergistic activity, employing time-kill analysis (TKA), of COL and SPR206 alone as well as in combination regimens with other antimicrobials against four MDR A. baumannii isolates.
2. Results
2.1. Susceptibility Testing
Thirty isolates underwent MIC testing revealing that 17/30 (57%) were COL-resistant, with six isolates registering COL MIC values of 32 mg/L or higher [17]. In the MIC testing performed on A. baumannii strains, SPR206 inhibited the growth of (22/30) 73% of the isolates at concentrations of <2 mg/L and 83% (25/30) at concentrations of <4 mg/L. Two isolates exhibited an SPR206 MIC value of 32 mg/L. A four-fold increase in potency was shown in the MIC50 and MIC90 values of SPR206 compared with COL. Additionally, 87% (27/30) of the A. baumannii isolates demonstrated resistance to meropenem (MEM), with MIC values of ≥ 8 mg/L. Amikacin (AMK) and sulbactam (SUL) were largely ineffective in inhibiting A. baumannii growth, with 90% (27/30) presenting AMK MICs at >16 mg/L and with 77% (23/30) presenting SUL MICs at > 8 mg/L. Minocycline (MIN) and tigecycline (TGC) yielded more favorable MIC results, inhibiting A. baumannii growth at a MIN concentration of <4 mg/L in 77% (21/30) of the isolates and at a TGC concentration of <4 mg/L in 60% (18/30) of the isolates. Individual MIC values for each of the 30 tested isolates, alongside the MIC50 and MIC90 values of SPR206 and the comparative antimicrobials tested, can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Broth microdilution susceptibility testing results (mg/L).
2.2. Genomic Sequencing Analysis
Genomic sequencing was conducted on 14 COL-resistant and CRAB isolates collected from different geographical regions. Three were from Thailand (21%), one from Taiwan (7%), one from Israel (7%), and nine from Michigan (64%). The identified isolates exhibited elevated MICs and various resistance genes were detected, including aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (notably APH (3′)-Vla) in all isolates. Beta-lactamases of classes A, C, and D, were present, with ADC-2 (an Acinetobacter-derived cephalosporinase) and blaOXA-23 in all isolates. Additionally, the endogenous presence of efflux pumps specific to the tetracycline agents (MIN and TGC) and the lpxA and lpxC genes was also confirmed in all A. baumannii isolates.
Compared with a reference strain (CP043953.1), mutations in pmrA were detected, with missense single-nucleotide variants (SNV) encoding S119T and A144T mutations detected in pmrA for three of the 14 isolates (21%). Alterations in pmrB were more commonly detected with mutations detected in 13 of the 14 (93%) included isolates. Strain typing revealed that the isolates belonged to five unique clonal groups based on Oxford and Pasteur multilocus sequence typing (MLST) schemes for A. baumannii (Table 2). The most common sequence type among the strains was Pasteur ST2, followed by Pasteur ST3, Oxford ST106, ST195, and ST281. Figure 1 illustrates the mutations in the 14 sequenced isolates (COL-resistant and CRAB) and pmrCAB operon amino acid variations (and MLST sequence type) are provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
pmrA and pmrB amino acid variations for 14 COL-resistant and CRAB isolates.
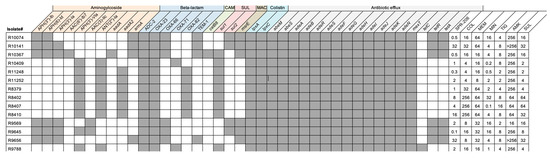
Figure 1.
Resistance Genes Detected in 14 COL-resistant and CRAB isolates. Shown in Figure 1 are the resistance genes and MICs detected in the 14 COL-resistant and CRAB isolates. Gray boxes indicate the presence of given resistance genes in each isolate and white boxes indicate the gene was not detected. MICs for each isolate and antibiotic are indicated to the right.
2.3. Time-Kill Analysis
In the in vitro synergy evaluation of four COL-resistant and CRAB A. baumannii isolates, single agents did not sustainably reduce the bacterial burden over 24 h. However, the SPR206 + MEM combination displayed synergistic and bactericidal activity against all isolates, achieving an average −5.6 log10 CFU/mL reduction from the most active single agent. The SPR206 + MIN combination regimen was synergistic against all isolates exhibiting bactericidal activity against R10141. Despite elevated MICs for SPR206 and COL against R10141 with a detected pmrB mutation, SPR206-based combinations outperformed COL-based regimens with an average −5.25 log10 cfu/mL reduction compared with a −3.2 log10 cfu/mL reduction. COL + MEM showed synergistic activity against all isolates but achieved bactericidal activity against only two (R11252 and R9645). COL + MIN combinations were synergistic but yielded lower average log reductions (−2.78 log10 vs. −3.77 log10 reduction in cfu/mL from the most active single agent) compared with COL + MEM. Overall, the SPR206 plus MIN or MEM combinations demonstrated an average 3-log10 reduction in CFU/mL compared with the 2-log10 log reduction observed in the COL-plus-MEM or MIN combinations. The 24-h TKA results for the A. baumannii strains are shown in Figure 2.
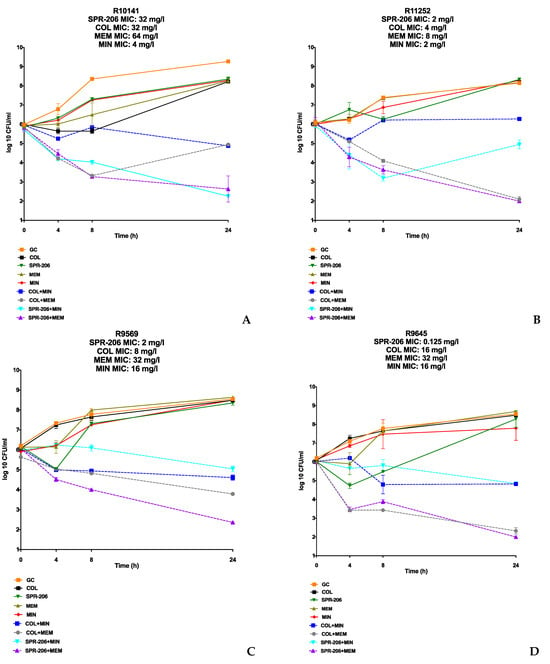
Figure 2.
TKA Results of COL-resistant and CRAB Isolates. (A–D) are SPR206, COL, MEM, and MIN tested alone and in combination through TKA against COL-resistant and CRAB isolates. All individual agents were tested at 0.5× MIC or at the biological peak concentration (whichever was lower) alone and then in SPR-206- and COL-based combination regimens.
3. Discussion
Given the escalating global threat of antimicrobial resistance, particularly in the context of COL-resistant CRAB infections, an increase in the utilization of COL is inevitable [1,18]. However, this heightened usage raises concerns about increased drug-related toxicities, including nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, and the continued dissemination of COL-resistant A. baumannii pathogens [1]. Identifying novel therapeutics becomes imperative to address this treatment gap. Our in vitro study highlights the robust activity of SPR206 against CRAB even in isolates with substantially elevated MICs to COL. Furthermore, our study suggests that traditional resistance mechanisms leading to elevated COL MICs, such as mutations in lpxACD or pmrAB, may not exert a similar impact on SPR206 susceptibility. Additionally, our results demonstrate enhanced activity when SPR206 is used in combination with other antimicrobials, even in the presence of resistance genes to either agent. This underscores the potential of SPR206 as a promising therapeutic option against COL-resistant A. baumannii infections.
In the last decade, several polymyxin derivatives have been developed, each featuring modifications to integral areas of the traditional polymyxin structure [13,19]. These modifications primarily involve changes to the N-terminal fatty acyl chain length, alterations in the hydrophobic domain of the COL, and substitutions of the Dab side chains and amino acids [20,21]. Of note, polymyxin derivative compounds with alterations in the hydrophobic domain of the N-terminus chain, such as SPR206, have demonstrated increased susceptibility compared with COL, a trend corroborated in our study [21]. SPR206 exhibited lower MICs in comparison to COL when evaluated against MDR A. baumannii isolates. Other studies have similarly reported lower MICs against MDR Gram-negative organisms compared with other polymyxin derivatives and polymyxin B. This improved activity may potentially be attributed to SPR206′s observed high LPS binding and permeabilization capabilities [21].
This heightened LPS binding and permeability capacity observed in SPR206 may contribute to its sustained activity even in the presence of COL resistance mediated by the loss of LPS genes (lpxACD and pmrAB) [22,23]. Each CRAB and COL-resistant isolate, characterized by the presence of multiple beta-lactamases, exhibited a mutation in either lpxA, lpxC, pmrA, or pmrB. This suggests that SPR206 may possess a higher barrier to resistance against LPS loss compared with COL. While lpxACD is more extensively studied in the context of COL resistance, the impact of the pmrCAB operon on A. baumannii-elevated MICs to COL is less understood [5,10,23,24]. It has been proposed that pmrB mutations could lead to the constitutive activation of pmrA, resulting in increased pmrCAB op-ron expression and COL resistance [25,26]. In our study, pmrA mutations were less common, while pmrB mutations were prevalent, potentially contributing to increased COL MICs. Nonetheless, SPR206 MICs remained relatively low, with 62% (9/14) of isolates having MICs at < 2 mg/L. In particular, isolates with elevated SPR206 MICs (>4 mg/L) exhibited pmrB mutations at A138T and/or amino acid substitutions, showing region-specific patterns. This regional variability is important for tailoring A. baumannii treatment strategies based on predominant clonal types in specific geographic regions [2,27,28]. Identifying molecular characteristics associated with elevated MICs to SPR206 is critical for informing the best practices in the treatment of A. baumannii infections.
In addition to SPR206 demonstrating retained susceptibility in the presence of multiple resistance genes, our study revealed similar and—in some cases—increased in vitro synergistic activity when SPR206 was combined with other antimicrobials compared with COL-based combination regimens. The enhanced membrane permeability attributed to polymyxins, including derivatives, has been hypothesized to facilitate the binding of drugs (such as MEM or MIN) when in combination irrespective of elevated MICs or gene mutations to either agent [2,11,29,30]. Given that SPR206 has demonstrated superior permeability compared with traditional polymyxins, this could explain why the SPR206-based combination regimens resulted in a greater reduction in CFU/mL compared with COL-based combinations [21]. Notably, the enhanced activity of MEM-containing combinations (SPR206 + MEM and COL + MEM) compared with MIN-containing combinations (SPR206 + MIN and COL + MIN) can be attributed to the fact that tetracyclines (MIN) are bacteriostatic agents, while carbapenems (MEM) are bactericidal [31,32]. This difference may influence the attenuated antimicrobial activity with MIN combinations compared with MEM combinations. Previous studies have also demonstrated increased activity with polymyxins in combination with carbapenems compared with combinations with tetracyclines, even in isolates with pmrA mutations [11,33].
Despite providing valuable insights about SPR206 activity, several limitations should be noted. First, only a select number of isolates underwent genomic sequencing analysis, potentially restricting the generalizability of the findings to a broader clinical applicability of the findings. Considering the epidemiological variations in A. baumannii infections, future studies should investigate SPR206 activity against prominent clonal ST types. Furthermore, polymyxin resistance in A. baumannii can be mediated through various factors, including other regulatory and effector mechanisms such as mutations in the mcr-1 gene or in genes encoding OmpA family proteins. While each strain sequenced did have mutations in genes encoding OmpA family proteins (shown in Supplemental Table S1), the mcr-1 gene was not detected in the selected sequenced strains [10,11]. Lastly, the MIC testing and TKA experiments were short-duration and used static concentrations, differing from humanized pharmacokinetic exposure conditions.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
A total of 30 A. baumannii clinical isolates were included in the study; the isolates were representative of different geographical areas including Thailand, Israel, Taiwan, Michigan, and California. A portion (14/30) (46%) of the isolates were collected from patients who were enrolled in an NIH-funded clinical trial evaluating the treatment outcomes of extremely drug-resistant Gram-negative pathogen infections [34]. A total of 28/30 of the isolates were CRAB, indicated through the meropenem (MEM) MIC of ≥8 mg/L, and 15/30 were COL-resistant, indicated through the colistin (COL) MIC OF ≥4 mg/L [35]. To further present resistance mechanisms, genomic sequencing analyses were completed on 14 A. baumannii isolates, all of them being COL-resistant and CRAB isolates.
4.2. Antimicrobials
The comparator antibiotics that were utilized for susceptibility testing versus SPR206 in A. baumannii were as follows: MEM, COL, minocycline (MIN), sulbactam (SUL), amikacin (AMK), and tigecycline (TGC). MEM, COL, MIN, SUL, AMK, and TGC were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA) and SPR206 was obtained from its manufacturer (SPERO Therapeutics Cambridge, MA, USA).
4.3. Susceptibility Testing
Susceptibility testing for COL, MEM, MIN, AMK, TGC, SUL, and MEM was performed for each strain in 96-well microtiter plates (Corning Costar®, obtained through Sigma-Aldrich®, Warren, MI, USA). Organism susceptibility (minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC) was evaluated through broth microdilution testing using cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth (CAMHB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) supplemented with 25 mg/L Ca2+ and 12.5 µg/mL Mg2+ as stated in the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines. Freshly prepared Mueller–Hinton broth was used to prevent the oxidative degradation of TGC in aqueous solution and SUL was tested in combination with ampicillin (AMP) and supplemented at a 4:1 ratio. The microtiter, 96-well plates were incubated at 37 °C for 18–24 h before recording the results and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) reductions were measured using serial two-fold dilutions. Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was used as the internal quality control strain.
4.4. Genomic Sequencing Analyses
Fourteen CRAB and COL-resistant isolates were selected to undergo whole genome sequencing (WGS). The total genomic DNA was extracted and used as input material for the library construction. DNA libraries were prepared using the Nextera XT™ library construction protocol and index kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) and sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer (Illumina). Libraries were multiplexed and sequenced with 100 base-pair (bp) paired end reads (PE100) on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Samples were demultiplexed using bcl2fastq conversion software (v1.8.4) (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Illumina genome sequencing reads were used for de novo genome assembly and annotation as well as re-sequencing analyses. The comprehensive genome analysis tool from the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC) was used to generate de novo assemblies and annotations for all genomes [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Beta-lactamase genes were identified through similarity to genes in the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database (CARD) [44]. Breseq (v0.37.1) was used for re-sequencing analysis to determine pmrA and pmrB single nucleotide variants [45]. Breseq was run in consensus mode to align sequencing reads according to the complete A. baumannii K09-14 reference genome sequence (Genbank accession CP043953.1).
4.5. Time-Kill Analyses
Time-kill analyses (TKAs) were performed against four isolates (CRAB and COL-resistant) in Mueller–Hinton broth (MHB) as growth media and each TKA was performed in duplicate for all antibiotic regimens to ensure reproducibility. In the TKA against the four A. baumannii isolates, each well was treated without a drug, SPR206, COL, MEM, MIN, SPR206 + MEM, SPR206 + MIN, COL + MEM, and COL + MIN, at a concentration of 0.5× MIC or the biological free peak (MEM fCmax at 30 mg/L per 1 g q 8 h dosing, COL fCmax at 2 mg/L per 4.5 million IU q 12 h dosing, and MIN fCmax at 8 mg/L per 200 mg IV q 12 h dosing), utilizing whichever was lower [32,46,47]. The experiments were conducted at a starting inoculum of ~1 × 106 for each isolate and were conducted in a shaker incubator at 37 °C for 24 h and aliquots of 0.1 mL were obtained from each well at the 0-, 4-, 8-, and 24-h time intervals.
The samples were serially diluted in 0.9% normal saline according to the appropriate concentrations and plated using automatic spiral plating (EasySpiral Pro Intersciences, Worburn, MA, USA); then, the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h before colony enumeration using an automated colony counter (Scan 1200, Interscience Laboratories Inc., Woburn, MA, USA). The time-kill curves were made by plotting mean colony counts remaining from duplicate experiments against each time point using Prism® (v10.1.2)(Graphpad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Bactericidal activity was defined as ≥3 log10 CFU/mL reduction from baseline and synergistic activity was defined as a ≥2 log10 CFU/mL reduction from the most active single agent. Antagonistic activity was defined as a ≥2 log10 CFU/mL decrease in killing from the most active single agent.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study reveals that SPR206 has robust activity against A. baumannii isolates, including those characterized by CRAB and COL-resistance. Importantly, SPR206 MIC values consistently outperformed COL MIC results when evaluated against A. baumannii. Traditional mechanisms of polymyxin-resistance, mediated through LPS loss and the modification of lpxACD or the pmrCAB operon, may not significantly impact SPR206 activity. Further research is warranted to assess the viability of SPR206 as a broadly applicable treatment option for MDR A. baumannii infections and its diverse potential mediators of resistance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics13010047/s1, Supplementary Table S1—Mutations in Genes Encoding for OmpA family Proteins for 14 COL-resistant and CRAB isolates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.A.-M. and H.M.F.; methodology, J.C.A.-M., H.M.F., K.K.T., N.S.O. and P.J.; software, J.C.A.-M. and P.J.; validation, J.C.A.-M., N.S.O. and P.J.; formal analysis, J.C.A.-M., N.S.O. and P.J.; investigation, J.C.A.-M., N.S.O., P.J. and K.K.T.; resources, J.C.A.-M., H.M.F., V.N., K.S.K. and M.J.R.; data curation, J.C.A.-M., N.S.O. and P.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.A.-M.; writing—review and editing, N.S.O., H.M.F., K.K.T., V.N., K.S.K. and M.J.R.; visualization, J.C.A.-M. and P.J.; supervision, J.C.A.-M., H.M.F., V.N. and M.J.R.; project administration, J.C.A.-M.; funding acquisition, J.C.A.-M. and H.M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and supplementary materials.
Acknowledgments
This publication includes data generated at the UC San Diego IGM Genomics Center utilizing an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 that was purchased with funding from a National Institutes of Health SIG grant (#S10 OD026929). J.C.A.-M. receives support from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development (NICHD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under Award Number K12HD113189. The content is solely the authors’ responsibility and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. A portion of this work was supported by the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP) under the early career research grant awarded to J.C.A.-M.
Conflicts of Interest
J.C.A.-M. has served on advisory boards and received an honorarium for Shionogi, GSK, NovaVax, CSL Sequiris, Innoviva Specialty Therapeutics, and Abbvie. She has also received research support from CSL Sequiris. M.J.R. has received research grant support and consulted or provided lectures for AbbVie, Innoviva Specialty Therapeutics, Melinta, Merck, Paratek, and Shionogi. M.J.R. is also supported in part by NIAID R21 AI163726. K.S.K. is supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (DMID Protocol Number: 10-0065 and R01-AI119446-01) and has served as a consultant for Xellia and Merck. All other authors have no financial disclosures to make.
References
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Hittle, L.E.; O’Hara, J.A.; Rivera, J.I.; Syed, A.; Shields, R.K.; Pasculle, A.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Doi, Y. Colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Beyond carbapenem resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, E.L.; Claeys, K.C.; Kline, E.G.; Rogers, T.M.; Squires, K.M.; Iovleva, A.; Doi, Y.; Banoub, M.; Noval, M.M.; Luethy, P.M.; et al. Early initiation of three-drug combinations for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii among COVID-19 patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, T.; Chopra, T.; Marchaim, D.; Pogue, J.M.; Alangaden, G.; Salimnia, H.; Boikov, D.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Akins, R.; Selman, P.; et al. Trends in antimicrobial resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a metropolitan Detroit health system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2235–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.A.; Hamouda, A.; Amyes, S.G. The rise of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.D.; Nickel, G.C.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Lavender, H.; Murthy, A.R.; Jacobs, M.R.; Bonomo, R.A. Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.; Hale, J.D.; Vinogradov, E.; Seemann, T.; Henry, R.; Crane, B.; St Michael, F.; Cox, A.D.; et al. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Boyce, J.D. Mechanisms of Polymyxin Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, L.A.; Herrera, C.M.; Fernandez, L.; Hankins, J.V.; Trent, M.S.; Hancock, R.E. The pmrCAB operon mediates polymyxin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 and clinical isolates through phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Llobet, E.; Aranda, J.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Hornsey, M.; Dhanji, H.; Chart, H.; Bou, G.; Livermore, D.M.; et al. Phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A in colistin-resistant variants of Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by the pmrAB two-component regulatory system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3370–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novović, K.; Jovčić, B. Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Molecular Mechanisms and Epidemiology. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Yim, J.; Nguyen, L.; Maassen, P.T.; Stamper, K.; Shiekh, Z.; Kebriaei, R.; Shields, R.K.; Castanheira, M.; Kaye, K.S.; et al. In Vitro Synergy of Colistin in Combination with Meropenem or Tigecycline against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Yahav, D.; Carmeli, Y.; Benattar, Y.D.; Skiada, A.; Andini, R.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Nutman, A.; et al. Colistin alone versus colistin plus meropenem for treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Abbott, E.; Abdulle, O.; Boakes, S.; Coleman, S.; Divall, N.; Duperchy, E.; Moss, S.; Rivers, D.; Simonovic, M.; et al. Design of Next Generation Polymyxins with Lower Toxicity: The Discovery of SPR206. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Boakes, S.; Duperchy, E.; Abdulle, O.; Rivers, D.; Simonovic, M.; Singh, J.; Coleman, S.; Dawson, M.J. Optimisation of Next-Generation Polymyxins Leading to SPR206 as a Development Candidate. In Proceedings of the ASM Microbe, San Francisco, CA, USA.
- Arends, S.J.R.; Rhomberg, P.; Lister, T.; Cotoreno, N.; Flamm, R.K.; Mendes, R.E. Activity of Investigiational Ploymyxib-B-Like Compound (SPR206) against Set of Gram-negative Bacilli Responsible for Human Infections. In Proceedings of the ASM Microbe, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grosser, L.; Heang, K.; Teague, J.; Warn, P.; Corbett, D.; Dawson, M.J.; Rubio, A. In Vivo Efficacy of SPR206 in Murine Lung and Thigh Infection Models Caused by Multidrug Resistant Pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumanii. ASM Microbe, 2019; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; M100-S33; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Deveson Lucas, D.; Crane, B.; Wright, A.; Han, M.L.; Moffatt, J.; Bulach, D.; Gladman, S.L.; Powell, D.; Aranda, J.; Seemann, T.; et al. Emergence of High-Level Colistin Resistance in an Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolate Mediated by Inactivation of the Global Regulator H-NS. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02442-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaara, M. Polymyxin Derivatives that Sensitize Gram-Negative Bacteria to Other Antibiotics. Molecules 2019, 24, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, J.; Fang, S.; Qiu, J. Antibacterial mechanisms of polymyxin and bacterial resistance. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 679109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundsadegh, N.; Belanger, C.R.; Hancock, R.E.W. Outer Membrane Interaction Kinetics of New Polymyxin B Analogs in Gram-Negative Bacilli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00935-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Velkov, T. Polymyxins: Mode of Action. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, J.; Kumaran, S.; Gobbo, M.; Zerbe, O. Interactions of lipopolysaccharide and polymyxin studied by NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11498–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.T.; Akova, M.; Paterson, D.L. Next-Generation Polymyxin Class of Antibiotics: A Ray of Hope Illuminating a Dark Road. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, O.; Sarrou, S.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Georgiadou, S.; Mantzarlis, K.; Zakynthinos, E.; Dalekos, G.N.; Petinaki, E. Rapid dissemination of colistin and carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Central Greece: Mechanisms of resistance, molecular identification and epidemiological data. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Aurosree, B.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Pancholi, V.; Pancholi, P. The role of LpxA/C/D and pmrA/B gene systems in colistin-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Lab. Med. 2017, 1, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams-Haduch, J.M.; Paterson, D.L.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Pasculle, A.W.; Potoski, B.A.; Muto, C.A.; Harrison, L.H.; Doi, Y. Genetic basis of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates at a tertiary medical center in Pennsylvania. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3837–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, A.; Glick, R.; Temkin, E.; Hoshen, M.; Edgar, R.; Braun, T.; Carmeli, Y. A case-control study to identify predictors of 14-day mortality following carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteraemia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O1028–O1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochado, A.R.; Telzerow, A.; Bobonis, J.; Banzhaf, M.; Mateus, A.; Selkrig, J.; Huth, E.; Bassler, S.; Zamarreno Beas, J.; Zietek, M.; et al. Species-specific activity of antibacterial drug combinations. Nature 2018, 559, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Efficacy of tigecycline monotherapy versus combination therapy with other antimicrobials against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii sequence type 2 in Heilongjiang Province. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2019, 8, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codjoe, F.S.; Donkor, E.S. Carbapenem Resistance: A Review. Med. Sci. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agwuh, K.N.; MacGowan, A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batirel, A.; Balkan, I.I.; Karabay, O.; Agalar, C.; Akalin, S.; Alici, O.; Alp, E.; Altay, F.A.; Altin, N.; Arslan, F.; et al. Comparison of colistin-carbapenem, colistin-sulbactam, and colistin plus other antibacterial agents for the treatment of extremely drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, K.S.; Marchaim, D.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Carmeli, Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Daikos, G.; Dhar, S.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Gikas, A.; Kotanidou, A.; et al. Colistin monotherapy versus combination therapy for carbapenem-resistant organisms. NEJM Evid. 2022, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M100-S25 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Eigth Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.J.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Shukla, M.; Vonstein, V.; Wattam, A.R.; Yoo, H. PATtyFams: Protein Families for the Microbial Genomes in the PATRIC Database. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.G.; Waglechner, N.; Nizam, F.; Yan, A.; Azad, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Bhullar, K.; Canova, M.J.; De Pascale, G.; Ejim, L.; et al. The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deatherage, D.E.; Barrick, J.E. Identification of mutations in laboratory-evolved microbes from next-generation sequencing data using breseq. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1151, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markou, N.; Markantonis, S.L.; Dimitrakis, E.; Panidis, D.; Boutzouka, E.; Karatzas, S.; Rafailidis, P.; Apostolakos, H.; Baltopoulos, G. Colistin serum concentrations after intravenous administration in critically ill patients with serious multidrug-resistant, gram-negative bacilli infections: A prospective, open-label, uncontrolled study. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, J.W.; van den Anker, J.N. Meropenem clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 28, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).