Recovery of Staphylococci from Teatcups in Milking Parlours in Goat Herds in Greece: Prevalence, Identification, Biofilm Formation, Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Predictors for Isolation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Significance of the Milking Parlour in the Development of Mastitis
1.2. Importance of Biofilm-Formation in Staphylococci Associated with Mastitis
1.3. Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococci Recovered from Goat Milk in Greece
1.4. Objectives of the Study
2. Results
2.1. Recovery of Staphylococcal Isolates from Teatcups
2.2. Identification of Staphylococcal Isolates from Teatcups
2.3. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococci Recovered from Teatcups
2.4. Variables Associated with Recovery of Staphylococcal Isolates from Teatcups
2.5. Associations with Total Bacterial Counts and Somatic Cell Counts in Bulk-Tank Milk
2.6. Isolation of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococci
2.7. Variables Associated with Recovery of Resistant or Multi-Resistant Staphylococcal Isolates from Teatcups
2.7.1. Isolation of Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcal Isolates
2.7.2. Isolation of Staphylococcal Isolates Resistant to at Least One Antibiotic
2.7.3. Isolation of Multi-Resistant Staphylococcal Isolates
3. Discussion
3.1. Isolation of Staphylococci from Teatcups
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcal Isolates
4. Materials and Methods
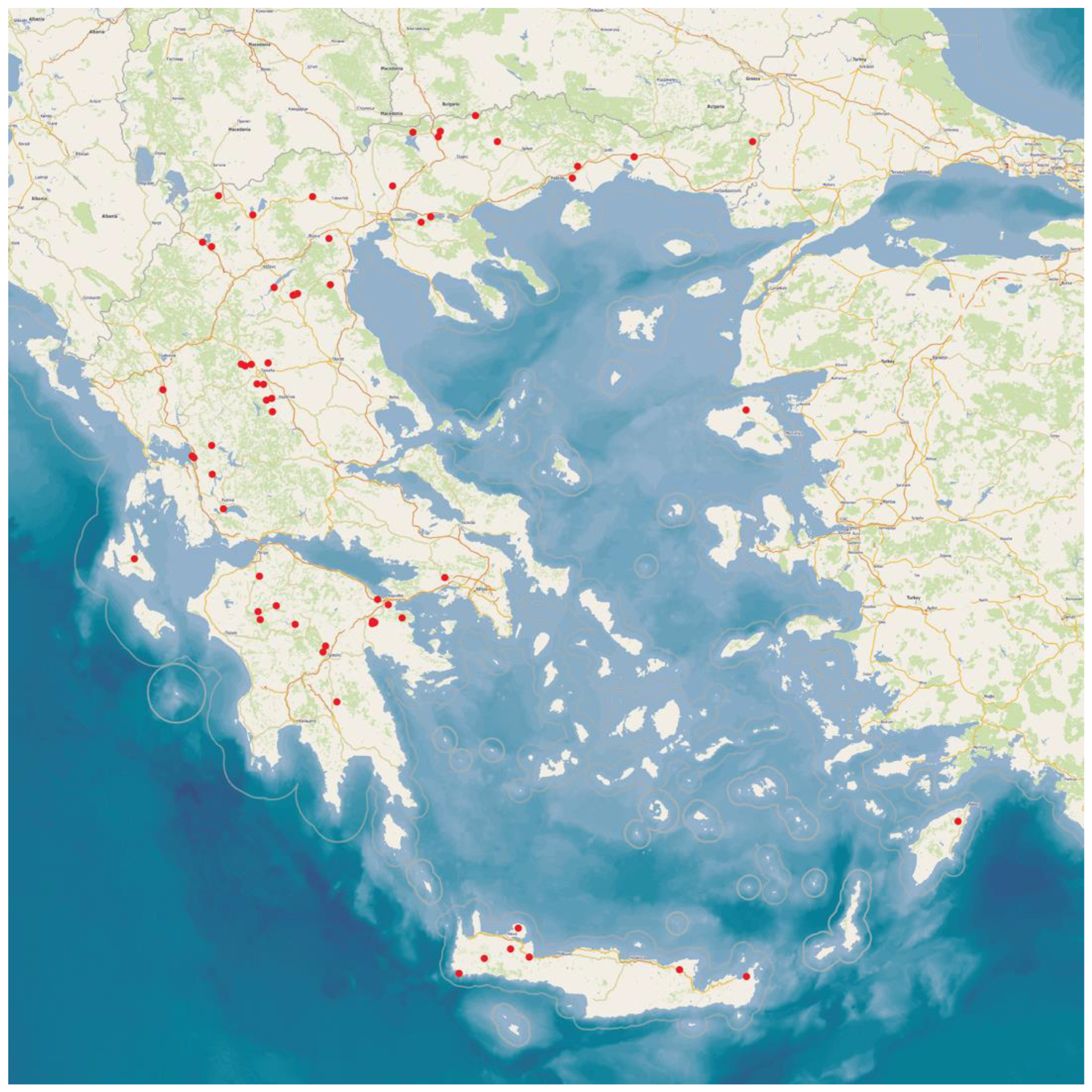
4.1. Goat Herds
4.2. Samplings
4.3. Laboratory Examinations
4.3.1. Somatic Cell Counting and Total Bacterial Counting in Bulk-Tank Milk Samples
4.3.2. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcal Isolates
4.3.3. Evaluation of Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcal Isolates
4.3.4. Testing for Susceptibility to Antibiotics
4.4. Data Management and Analysis
4.4.1. Data Management
4.4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edmondson, P. The milking machine and mastitis. In Pract. 1993, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caria, M.; Todde, G.; Pazzona, A. Influence of the milking units on the pulsation curve in dairy sheep milking. Animals 2020, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liagka, D.V.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Cripps, P.J.; Michael, C.K.; Kalonaki, S.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Kantas, D.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Spyrou, V.; Vasileiou, N.G.C. Bacterial entry into the teat of dairy ewes during the milking process. Animal Sci. Proc. 2023, 14, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonier, D.; Berthelot, X. New advances in epizootiology and control of ewe mastitis. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2003, 79, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.R.; Foster, S.J. Surface adhesins of Staphylococcus aureus. Adv. Microbial Physiol. 2006, 51, 187–225. [Google Scholar]
- Melchior, M.B.; Vaarkamp, H.; Fink–Gremmels, J. Biofilms: A role in recurrent mastitis infections? Vet. J. 2006, 171, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal biofilms. Cur. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, M.M.; Prenafeta, A.; Valle, J.; Penadés, J.; Rota, C.; Solano, C.; Marco, J.; Grillo, M.J.; Lasa, I.; Irache, J.M.; et al. Protection from Staphylococcus aureus mastitis associated with poly-N-acetyl β-1,6 glycosamine specific antibody production using biofilm-embedded bacteria. Vaccine 2009, 27, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianou, D.T.; Petinaki, E.; Cripps, P.J.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Michael, C.K.; Tsilipounidaki, K.; Skoulakis, A.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Giannoulis, T.; et al. Prevalence, patterns, association with biofilm formation, effects on milk quality, and risk factors for antibiotic resistance of staphylococci from bulk-tank milk of goat herds. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Sarrou, S.; Fragkou, I.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Role of staphylococci in mastitis in sheep. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; McEntire, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Doyle, M. The transfer of antibiotic resistance from food to humans: Facts, implications and future directions. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 2012, 31, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Loeffler, A.; Kadlec, K. Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents and its impact on veterinary and human medicine. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 28, 82-e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Leyssene, D.; Chacornac, J.P.; Kostrzewa, M.; Schmit, P.O.; Talon, R.; Bonnet, R.; Delmaset, J. Identification of a variety of staphylococcus species by Matrix-Assisted La-ser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmmod, Y.S.; Nonnemann, B.; Svennesen, L.; Pedersen, K.; Klaas, I.C. Typeability of MALDI-TOF assay for identification of non-aureus staphylococci associated with bovine intramammary infections and teat apex colonization. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9430–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergonier, D. Mastitis of dairy small ruminants. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 689–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, A.; Padfield, D.; Lear, L.; Bendall, R.; Vos, M. A comprehensive list of bacterial pathogens infecting humans. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkou, I.A.; Papaioannou, N.; Cripps, P.J.; Boscos, C.M.; Fthenakis, G.C. Teat lesions predispose to invasion of the ovine mammary gland by Mannheimia haemolytica. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 139, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, Y.; Aslantas, O.; Kirecci, E.; Ozturk, F.; Ceylan, A.; Boyar, Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility, presence of resistance genes and biofilm formation in coagulase negative staphlococci isolated from subclinical sheep mastitis. Kafkas Univer. Veter. Fakult. Derg. 2012, 18, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tel, O.Y.; Aslantas, O.; Keskin, O.; Yilmaz, E.S.; Demir, C. Investigation of the antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from gangrenous mastitis of ewes. Acta Vet. Hung. 2012, 60, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simojoki, H.; Hyvonen, P.; Plumed Ferrer, C.; Taponen, S.; Pyorala, S. Is the biofilm formation and slime producing ability of coagulase negative staphylococci associated with the persistence and severity of intramammary infection? Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Sarrou, S.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Spyrou, V.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Slime-producing staphylococci as causal agents of subclinical mastitis in sheep. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 224, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, E.I.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Karakasidis, T.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Lianou, D.T.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis on the surface of teatcups from milking parlours. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, B. Effect of Long Pasteurization Run Times on Bacterial Numbers in Milk. Master’s Thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT, USA, 2020; 79p. [Google Scholar]
- Lianou, D.T.; Michael, C.K.; Solomakos, N.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Petinaki, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Tzora, A.; Voidarou, C.; Fthenakis, G.C. Isolation of biofilm-forming staphylococci from the bulk-tank milk of small ruminant farms in Greece. Foods 2023, 12, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Sarrou, S.; Papagiannitsis, C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Malli, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Antimicrobial agent susceptibility and typing of staphylococcal isolates from subclinical mastitis in ewes. Microb. Drug Res. 2019, 25, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, D.T.; Fthenakis, G.C. Use of antibiotics against bacterial infections on dairy sheep and goat farms: Patterns of usage and associations with health management and human resources. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadgir, C.A.; Biswas, D.A. Antibiotic resistance and its impact on disease management. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2023, 15, 38251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehberg, L.; Frontzek, A.; Melhus, Å.; Bockmühl, D.P. Prevalence of β-lactamase genes in domestic washing machines and dishwashers and the impact of laundering processes on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A. Detergents. In Environmental Micropollutants; Hashmi, M.Z., Wang, S., Ahmed, Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Baquero, F.; Negri, M.C. Strategies to minimize the development of antibiotic resistance. J. Chemother. 1997, 9 (Suppl. S3), 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanquart, F. Evolutionary epidemiology models to predict the dynamics of antibiotic resistance. Evol. Appl. 2019, 12, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L.; Baquero, F. Mutation frequencies and antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L.; Rojo, F. Metabolic regulation of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 768–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandegren, L.; Andersson, D.I. Bacterial gene amplification: Implications for the evolution of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K. Mechanisms and clinical relevance of bacterial heteroresistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.Q.; Fan, F.Y.; Broach, J.R. Microbial adaptive evolution. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 49, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, R.B. The importance of hygienic procedures in controlling mastitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Large Anim. Pract. 1984, 6, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogianni, V.S.; Menzies, P.I.; Fragkou, I.A.; Fthenakis, G.C. Principles of mastitis treatment in sheep and goats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, D.T.; Chatziprodromidou, I.P.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Michael, C.K.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Politis, A.P.; Kordalis, N.G.; Billinis, C.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; et al. A detailed questionnaire for the evaluation of health management in dairy sheep and goats. Animals 2020, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.T.; Gambrel-Lenarz, S.A.; Scher, F.M.; Graham, T.E.; Reddy, R. Microbiological Count Methods. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products, 17th ed.; Wehr, H.M., Frank, J.F., Eds.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 153–186. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, G.I.; Feltham, R.K.A. Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Euzeby, J.P. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: A folder available on the Internet. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.J.; Falkiner, F.R.; Keane, C.T. New method of detecting slime production by coagulase negative staphylococci. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 42, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabres-Klein, M.H.; Santos, M.J.C.; Klein, R.C.; de Souza, G.N.; Ribon, A.D.B. An association between milk and slime increases biofilm production by bovine Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, P.; Nair, M.K.M.; Annamalai, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K.S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of bovine mastitis isolates of Staphylococcus aureus for biofilm formation. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 92, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall | Upper Part of Teatcups | Lower Part of Teatcups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcal Species | n | Staphylococcal Species | n | Staphylococcal Species | n |
| S. aureus | 6 | S. aureus | 4 | S. aureus | 5 |
| S. auricularis | 1 | S. auricularis | 1 | S. capitis | 5 |
| S. capitis | 11 | S. capitis | 6 | S. cohnii subsp. urealyticum | 1 |
| S. caprae | 1 | S. caprae | 1 | S. epidermidis | 1 |
| S. cohnii subsp. urealyticum | 1 | S. epidermidis | 1 | S. equorum | 3 |
| S. epidermidis | 1 | S. equorum | 8 | S. haemolyticus | 6 |
| S. equorum | 10 | S. haemolyticus | 4 | S. kloosii | 1 |
| S. haemolyticus | 7 | S. kloosii | 1 | S. lentus | 3 |
| S. kloosii | 1 | S. lentus | 5 | S. pasteuri | 1 |
| S. lentus | 6 | S. pasteuri | 3 | S. pettenkoferi | 1 |
| S. pasteuri | 4 | S. pettenkoferi | 2 | S. saprophyticus | 3 |
| S. pettenkoferi | 2 | S. saprophyticus | 6 | S. sciuri | 1 |
| S. saprophyticus | 6 | S. sciuri | 2 | S. warneri | 1 |
| S. sciuri | 3 | S. simulans | 2 | ||
| S. simulans | 2 | S. warneri | 4 | ||
| S. warneri | 4 | S. xylosus | 1 | ||
| S. xylosus | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcal Species | Proportion of Biofilm-Forming Isolates |
|---|---|
| S. aureus | 100% (6/6) |
| S. auricularis | 100% (1/1) |
| S. capitis | 81.8% (9/11) |
| S. caprae | 0.0% (0/1) |
| S. cohnii subsp. urealyticum | 100% (1/1) |
| S. epidermidis | 100% (1/1) |
| S. equorum | 80.0% (8/10) |
| S. haemolyticus | 71.4% (5/7) |
| S. kloosii | 100% (1/1) |
| S. lentus | 66.7% (4/6) |
| S. pasteuri | 75.0% (3/4) |
| S. pettenkoferi | 100% (2/2) |
| S. saprophyticus | 100% (6/6) |
| S. sciuri | 100% (3/3) |
| S. simulans | 100% (2/2) |
| S. warneri | 50.0% (2/4) |
| S. xylosus | 100% (1/1) |
| Total | 82.1% (55/67) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio 1 (95% Confidence Intervals) | p |
|---|---|---|
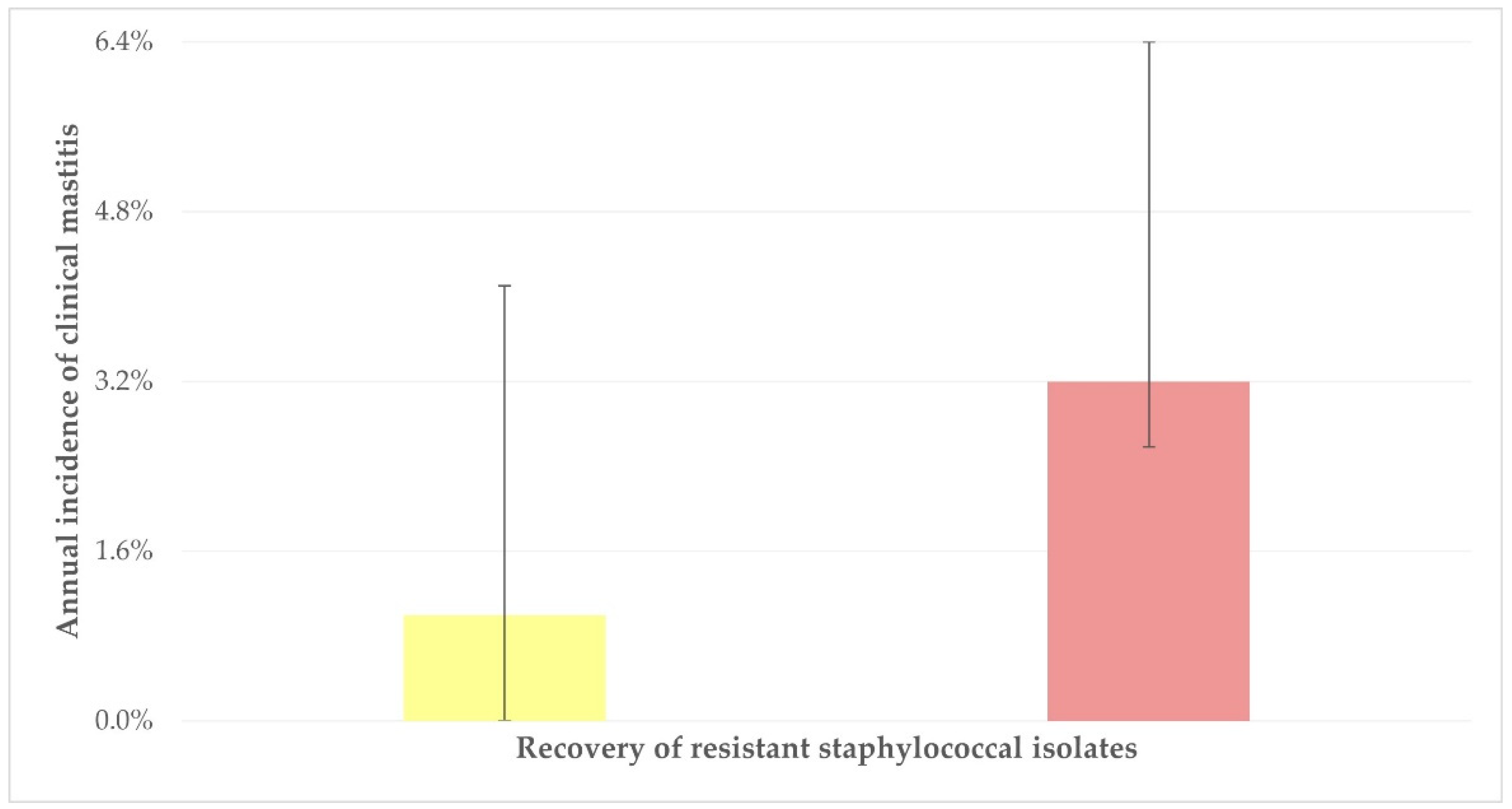
| Annual incidence of clinical mastitis | 0.043 | |
| ≤1% (12/29, 41.4%) | reference | - |
| >1% (23/37, 62.2%) | 2.327 (0.862–6.287) | 0.09 |
| Total Bacterial Counts in Bulk-Tank Milk | |
| ≤2000 × 103 cfu mL−1 (n = 55 herds) | >2000 × 103 cfu mL−1 (n = 11 herds) |
| 24.8% (61/246 teatcups) a | 45.6% (26/57) a |
| Somatic Cell Counts in Bulk-tank Milk | |
| ≤1.250 × 106 cells mL−1 (n = 49 herds) | >1.250 × 106 cells mL−1 (n = 17 herds) |
| 25.6% (57/223 teatcups) b | 37.5% (30/80 teatcups) b |
| Staphylococcal Species | Resistant Isolates | Multi-Resistant Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (n = 6 1) | 1 (16.7% 2) | 0 (0.0% 2) |
| S. auricularis (n = 1) | 1 (100%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. capitis (n = 11) | 3 (27.3%) | 1 (9.1%) |
| S. caprae (n = 1) | 1 (100%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. cohnii subsp. urealyticum(n = 1) | 1 (100%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. epidermidis (n = 1) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. equorum (n = 10) | 5 (50.0%) | 5 (50.0%) |
| S. haemolyticus (n = 7) | 2 (28.6%) | 1 (14.3%) |
| S. kloosii (n = 1) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. lentus (n = 6) | 2 (33.3%) | 2 (33.3%) |
| S. pasteuri (n = 4) | 1 (25.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. pettenkoferi (n = 2) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. saprophyticus (n = 6) | 3 (50.0%) | 2 (33.3%) |
| S. sciuri (n = 3) | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (33.3%) |
| S. simulans (n = 2) | 1 (50.0%) | 1 (50.0%) |
| S. warneri (n = 4) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| S. xylosus (n = 1) | 1 (100%) | 1 (100%) |
| Variables | Odds Ratios 1 (95% Confidence Intervals) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Annual incidence of clinical mastitis | 0.017 | |
| ≤1% (3/29, 10.3%) | reference | - |
| >1% (11/37, 29.7%) | 3.667 (0.916–14.685) | 0.07 |
| Use of detergent for parlour cleaning after the milking sessions | 0.034 | |
| Yes (13/65, 20.0%) | reference | - |
| No (1/1, 100.0%) | 11.667 (0.450–302.720) | 0.14 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio 1 (95% Confidence Intervals) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Use of detergent for parlour cleaning afterthe milking sessions | 0.035 | |
| Yes (10/65, 15.4%) | reference | - |
| No (1/1, 100%) | 15.857 (0.604–416.359) | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michael, C.K.; Lianou, D.T.; Tsilipounidaki, K.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Giannoulis, T.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Recovery of Staphylococci from Teatcups in Milking Parlours in Goat Herds in Greece: Prevalence, Identification, Biofilm Formation, Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Predictors for Isolation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091428
Michael CK, Lianou DT, Tsilipounidaki K, Gougoulis DA, Giannoulis T, Vasileiou NGC, Mavrogianni VS, Petinaki E, Fthenakis GC. Recovery of Staphylococci from Teatcups in Milking Parlours in Goat Herds in Greece: Prevalence, Identification, Biofilm Formation, Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Predictors for Isolation. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(9):1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091428
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichael, Charalambia K., Daphne T. Lianou, Katerina Tsilipounidaki, Dimitris A. Gougoulis, Themistoklis Giannoulis, Natalia G. C. Vasileiou, Vasia S. Mavrogianni, Efthymia Petinaki, and George C. Fthenakis. 2023. "Recovery of Staphylococci from Teatcups in Milking Parlours in Goat Herds in Greece: Prevalence, Identification, Biofilm Formation, Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Predictors for Isolation" Antibiotics 12, no. 9: 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091428
APA StyleMichael, C. K., Lianou, D. T., Tsilipounidaki, K., Gougoulis, D. A., Giannoulis, T., Vasileiou, N. G. C., Mavrogianni, V. S., Petinaki, E., & Fthenakis, G. C. (2023). Recovery of Staphylococci from Teatcups in Milking Parlours in Goat Herds in Greece: Prevalence, Identification, Biofilm Formation, Patterns of Antibiotic Susceptibility, Predictors for Isolation. Antibiotics, 12(9), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091428










