Molecular Cloning, Expression Analyses, and Physiological Roles of Cathelicidins in the Bursa of Fabricius of the Japanese Quail, Coturnix japonica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the cDNA of CATH-1, -2, and -3
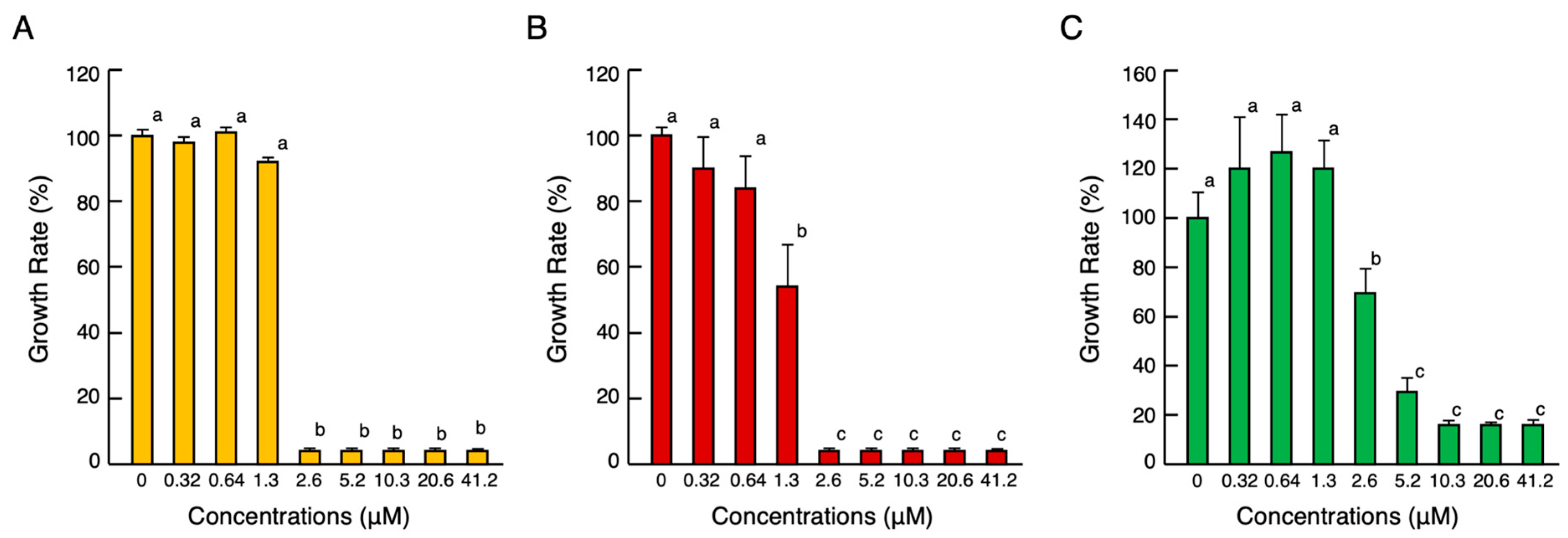
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of cjCATH-1
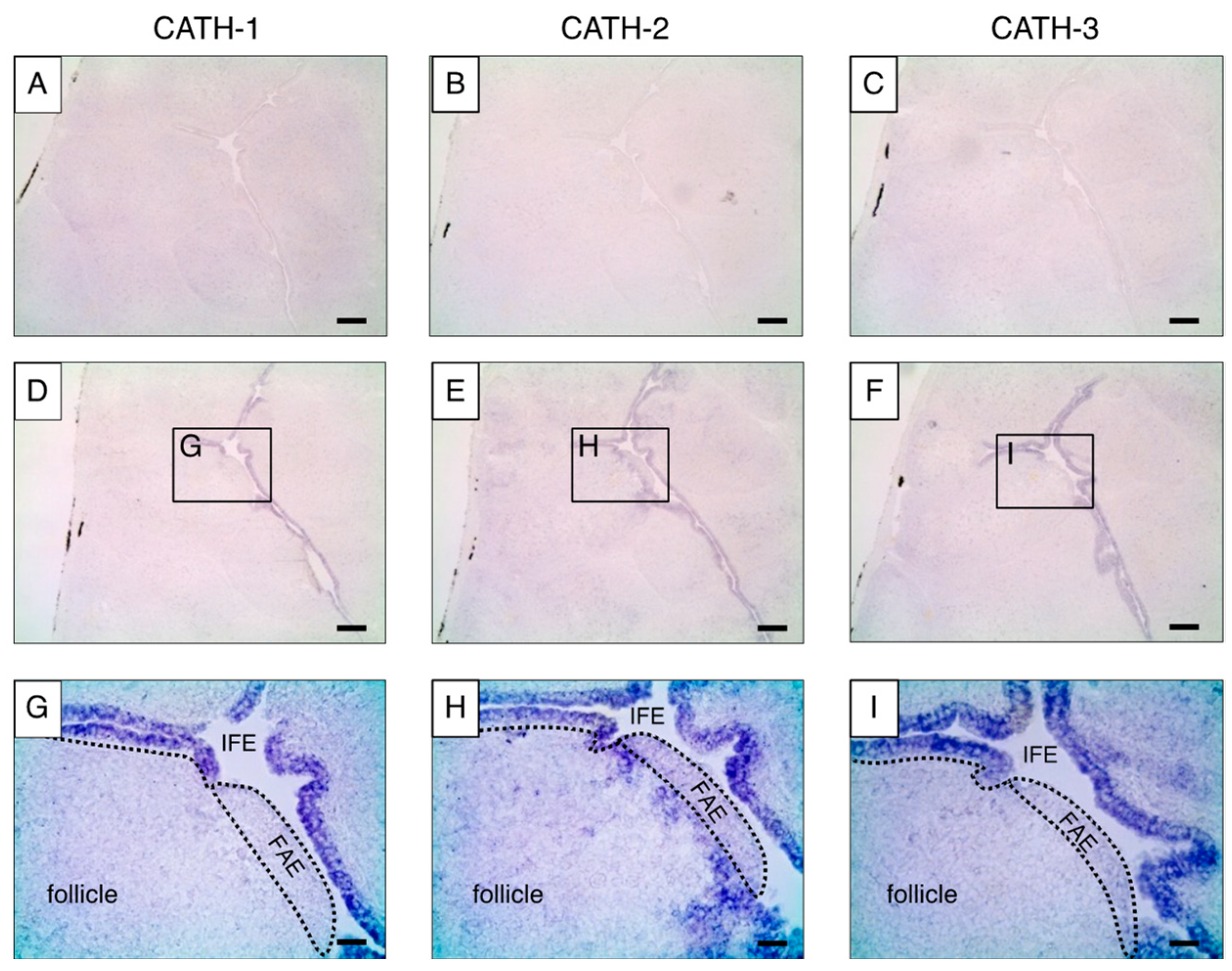
2.3. Localization of cjCATH mRNAs and Peptides in the BF
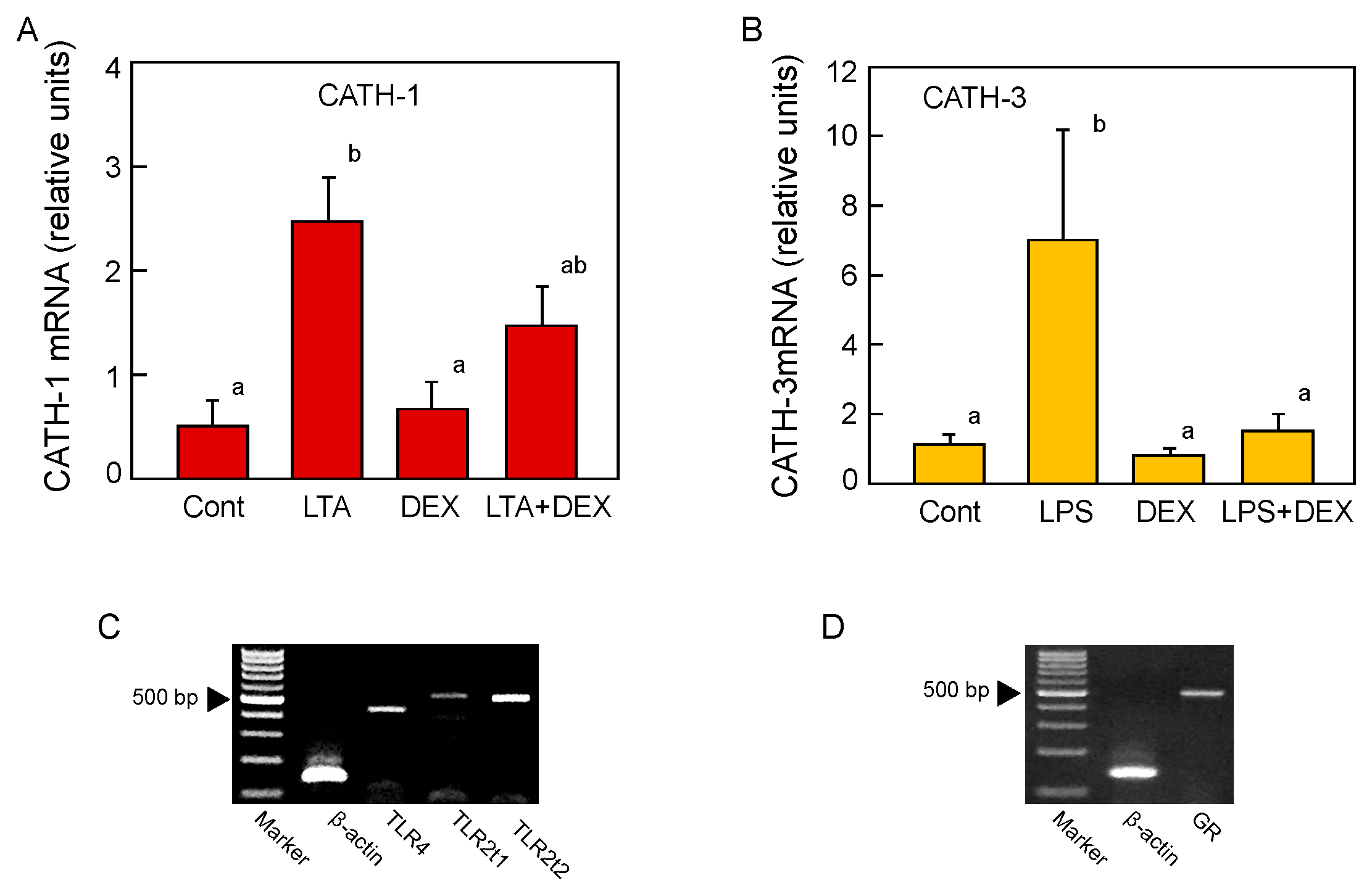
2.4. Endotoxin-Inducible cjCATH mRNA Expression in the BF and Suppression by Dexamethazone (DEX)
2.5. Influence of cjCATHs on Antibody Production
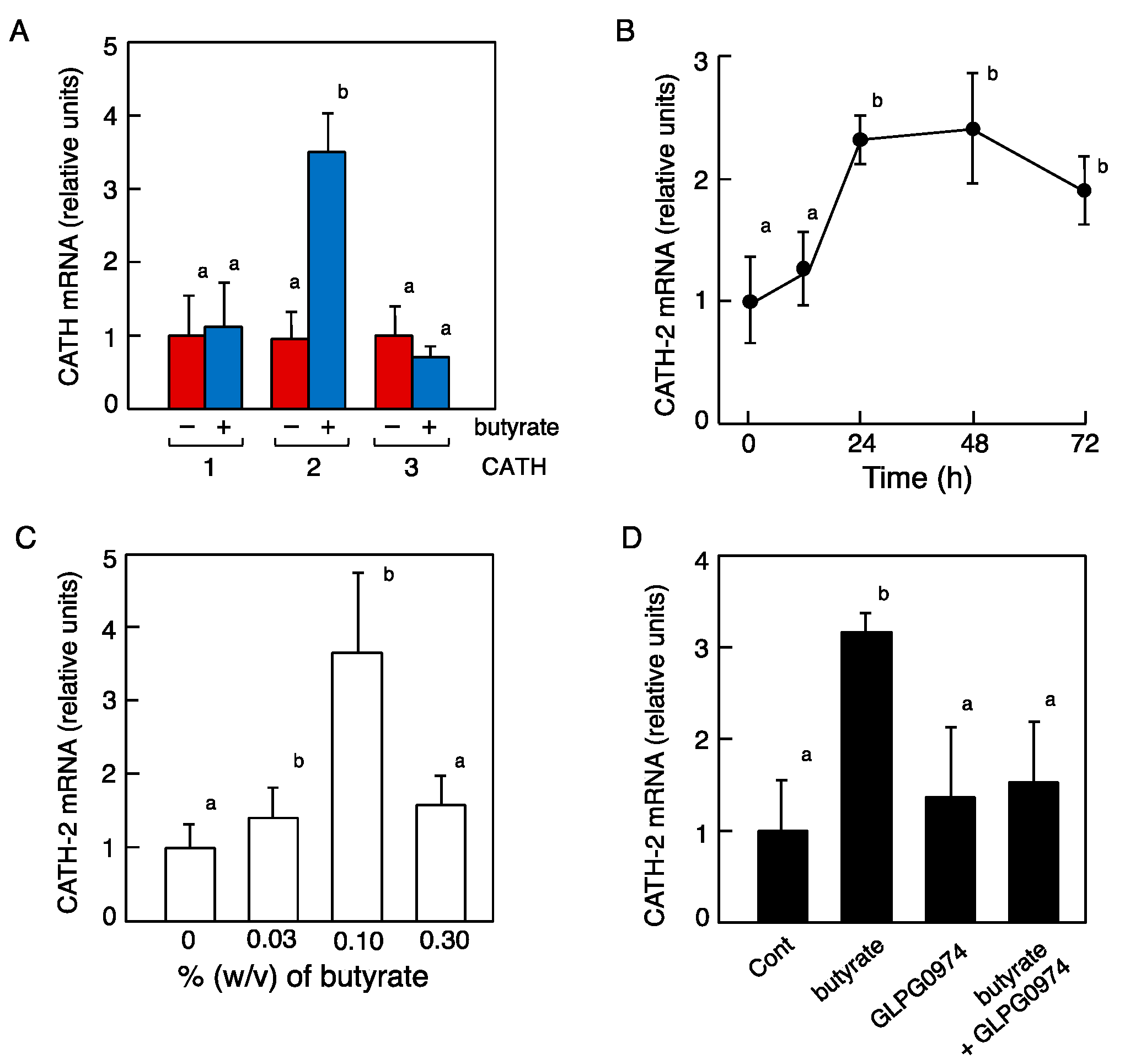
2.6. Promotion of CATH mRNA Expression by SCFAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Total RNA Extraction
4.2. Amplification of the cjCATH Precursor cDNA by 3′-RACE
4.3. Antimicrobial Assay
4.4. In Situ Hybridization Analysis
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Quantification of CATH mRNA Expression Levels by Real-Time PCR
4.7. Amplification of Partial cDNAs of TLR and GR by RT-PCR
4.8. Antibody Production-Promotion Assay
4.9. Promotion of CATH mRNA Expression by SCFAs
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auvynet, C.; Rosenstein, Y. Multifunctional host defense peptides: Antimicrobial peptides, the small yet big players in innate and adaptive immunity. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6497–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Song, Y. Mechanism of antimicrobial peptides: Antimicrobial, anti-Inflammatory and antibiofilm activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpantathan, M.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rajendhran, J. Antimicrobial peptides: Versatile biological properties. Int. J. Pept. 2013, 2013, 675391. [Google Scholar]
- van Harten, R.M.; van Woudenbergh, E.; van Dijk, A.; Haagsman, H.P. Cathelicidins: Immunomodulatory antimicrobials. Vaccines 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Antimicrobial peptides therapy: An emerging alternative for treating drug-resistant bacteria. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 445–463. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Sunkara, L.T. Avian antimicrobial host defense peptides: From biology to therapeutic applications. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 220–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasina, Y.O.; Obanla, T.; Dosu, G.; Muzquiz, S. Significance of endogenous antimicrobial peptides on the health of food animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 585266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Bommineni, Y.R.; Fernando, S.C.; Prakash, O.; Gilliland, S.E.; Zhang, G. Identification and functional characterization of three chicken cathelicidins with potent antimicrobial activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goitsuka, R.; Chen, C.L.; Benyon, L.; Asano, Y.; Kitamura, D.; Cooper, M.D. Chicken cathelicidin-B1, an antimicrobial guardian at the mucosal M cell gateway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15063–15068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Avian host defense cathelicidins: Structure, expression, biological functions, and potential therapeutic applications. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6434–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Chen, C.; Zhu, W.; He, W.; Guang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gene cloning, expression and characterization of avian cathelicidin orthologs, Cc-CATHs, from Coturnix coturnix. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishige, T.; Hara, H.; Hirano, T.; Kono, T.; Hanzawa, K. Characterization of the cathelicidin cluster in the Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veistinen, E.; Lassila, O. Bursa of Fabricius. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences Chichester; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, J.P.; Chrząstek, K.; Piasecki, T.; Wieliczko, A. New insight into the structure, development, functions and popular disorders of bursa Fabricii. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2013, 42, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvari, R.; Sorvari, T.E. Bursa Fabricii as a peripheral lymphoid organ. Transport of various materials from the anal lips to the bursal lymphoid follicles with reference to its immunological importance. Immunology 1977, 32, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Davani, D.; Pancer, Z.; Ratcliffe, M.J. Ligation of surface Ig by gut-derived antigen positively selects chicken bursal and peripheral B cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3218–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, L.T.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, G. Modulation of antimicrobial host defense peptide gene expression by free fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnesr, S.S.; Ropy, A.; Abdel-Razik, A.H. Effect of dietary sodium butyrate supplementation on growth, blood biochemistry, haematology and histomorphometry of intestine and immune organs of Japanese quail. Animal 2019, 13, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.K.; Seo, C.H.; Luchian, T.; Park, Y. Pse-T2, an antimicrobial peptide with high-level, broad-spectrum antimicrobial potency and skin biocompatibility against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01493-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, H.; Hamill, P.; Hancock, R.E. Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaní-Guerra, E.; Santos-Mendoza, T.; Lugo-Reyes, S.O.; Terán, L.M. Antimicrobial peptides: General overview and clinical implications in human health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Chai, J.; Deng, Z.; Ye, T.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Xu, X. Functional characterization of a novel lipopolysaccharide-binding antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory peptide in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10709–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Reyes, I.; Pérez-Hernández, E.G.; Delgado-Coello, B.; Mas-Oliva, J. Peptides as therapeutic molecules to neutralize Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides in sepsis and septic shock. Arch. Med. Res. 2001, 52, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Kang, Y.; Shang, D. Antimicrobial peptide temporin-1CEa isolated from frog skin secretions inhibits the proinflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 murine macrophages through the MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 132, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, C.E.; Demaries, S.L.; Pike, K.A.; Friedman, J.E.; Ratcliffe, M.J. The chicken B-cell receptor complex and its role in avian B-cell development. Immunol Rev. 2000, 175, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Han, Q.; Dai, C.; Li, Y. Forsythiaside attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in the bursa of Fabricius of chickens by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, K.; Isobe, N.; Nishibori, M.; Yoshimura, Y. Changes in the expression of gallinacins, antimicrobial peptides, in ovarian follicles during follicular growth and in response to lipopolysaccharide in laying hens (Gallus domesticus). Reproduction 2007, 133, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Tsubaki, T.; Sagae, N.; Onda, Y.; Inada, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; Okumura, K.; Kikuyama, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwamuro, S. Bacterial toxin-inducible gene expression of cathelicidin-B1 in the chicken bursal lymphoma-derived cell line DT40: Functional characterization of cathelicidin-B1. Peptides 2014, 59, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, R.L.; Hooper, L.V. Epithelial antimicrobial defence of the skin and intestine. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.C.; Schorey, J.S.; Johnson, A.L. Toll-like receptor signaling in hen ovarian granulosa cells is dependent on stage of follicle maturation. Reproduction 2009, 137, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Prefontaine, K.E. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-κB and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Domenico, J.; Jia, Y.; Lucas, J.J.; Gelfand, E.W. NF-κB-dependent induction of cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide in murine mast cells by lipopolysaccharide. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 150, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kin, N.W.; Chen, Y.; Stefanov, E.K.; Gallo, R.L.; Kearney, J.F. Cathelin-related antimicrobial peptide differentially regulates T- and B-cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, P.; Peh, C.A. LL-37 promotes rapid sensing of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides by B lymphocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraaij, M.D.; van Dijk, A.; Scheenstra, M.R.; van Harten, R.M.; Haagsman, H.P.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A. Chicken CATH-2 increases antigen presentation markers on chicken monocytes and macrophages. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, L.T.; Achanta, M.; Schreiber, N.B.; Bommineni, Y.R.; Dai, G.; Jiang, W.; Lamont, S.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Beker, A.; Teeter, R.G.; et al. Butyrate enhances disease resistance of chickens by inducing antimicrobial host defense peptide gene expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Nii, T.; Isobe, N.; Yoshimura, Y. Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus reuteri and Clostridium butyricum on the expression of toll-like receptors, pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and antimicrobial peptides in broiler chick intestine. J. Poult. Sci. 2020, 57, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Bilotta, A.J.; Yao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Eaves-Pyles, T.D.; Golovko, G.; et al. GPR43 mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamuro, S.; Kobayashi, T. An efficient protocol for DNA amplification of multiple amphibian skin antimicrobial peptide cDNAs. In Peptidomics; Soloviev, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 615, pp. 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yamanaka, N.; Koyano, I.; Hasunuma, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Kikuyama, S.; Iwamuro, S. Dual roles of extracellular histone H3 in host defense: Its differential regions responsible for antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties and their modes of action. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeda, T.; Kondo, H.; Nunomura, D.; Sato, G.; Ito, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Iwamuro, S.; Hasunuma, I.; Kikuyama, S.; Kobayashi, T. Molecular Cloning, Expression Analyses, and Physiological Roles of Cathelicidins in the Bursa of Fabricius of the Japanese Quail, Coturnix japonica. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081341
Ikeda T, Kondo H, Nunomura D, Sato G, Ito M, Yamanaka N, Iwamuro S, Hasunuma I, Kikuyama S, Kobayashi T. Molecular Cloning, Expression Analyses, and Physiological Roles of Cathelicidins in the Bursa of Fabricius of the Japanese Quail, Coturnix japonica. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(8):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081341
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeda, Takumi, Hirotada Kondo, Daiki Nunomura, Genki Sato, Machi Ito, Nanako Yamanaka, Shawichi Iwamuro, Itaru Hasunuma, Sakae Kikuyama, and Tetsuya Kobayashi. 2023. "Molecular Cloning, Expression Analyses, and Physiological Roles of Cathelicidins in the Bursa of Fabricius of the Japanese Quail, Coturnix japonica" Antibiotics 12, no. 8: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081341
APA StyleIkeda, T., Kondo, H., Nunomura, D., Sato, G., Ito, M., Yamanaka, N., Iwamuro, S., Hasunuma, I., Kikuyama, S., & Kobayashi, T. (2023). Molecular Cloning, Expression Analyses, and Physiological Roles of Cathelicidins in the Bursa of Fabricius of the Japanese Quail, Coturnix japonica. Antibiotics, 12(8), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081341




