Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A Global Perspective of a Rare Serovar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolate and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.2. Acquisition of Complementary Genomic Data
2.3. Genome Assembly and Quality Filtering
2.4. In Silico Genome Characterization
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
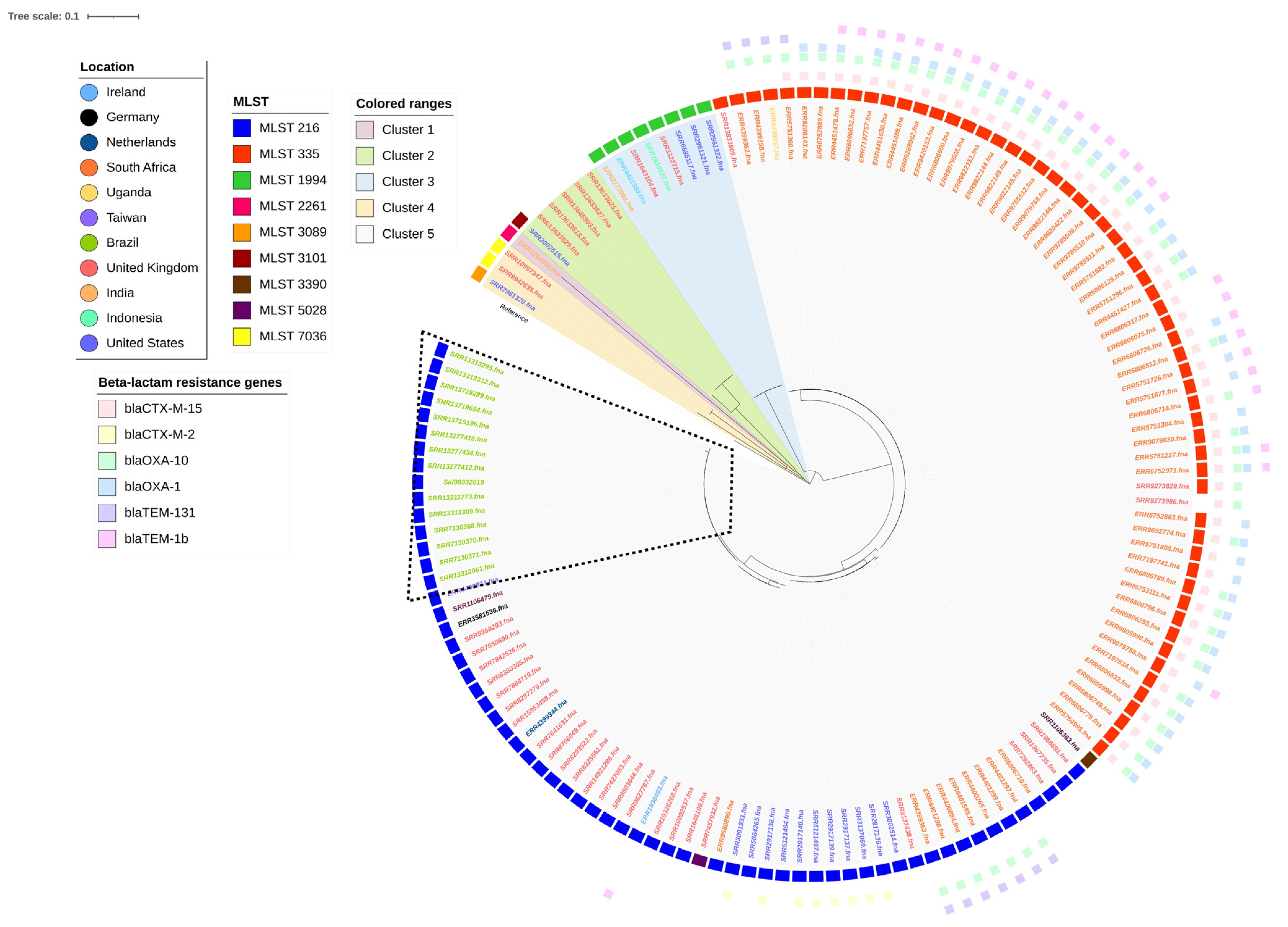
3.1. Data Collection and MLST Distribution
3.2. Resistome
3.3. Virulome
3.4. Phylogenetics and Characterization of Salmonella Isangi Lineages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tankson, J.D.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Jackson, C.R.; Headrick, M. Genetic relatedness of a rarely isolated Salmonella: Salmonella enterica serotype Niakhar from NARMS animal isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Karlsmose, S.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.A.; Jensen, A.B.; Wegener, H.C.; Aarestrup, F.M. Global Monitoring of Salmonella Serovar Distribution from the World Health Organization Global Foodborne Infections Network Country Data Bank: Results of Quality Assured Laboratories from 2001 to 2007. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govinden, U.; Mocktar, C.; Moodley, P.; Sturm, A.; Essack, S. CTX-M-37 in Salmonella enterica serotype Isangi from Durban, South Africa. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 28, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleyman, G.; Perri, M.; Vager, D.; Samuel, L.; Zervos, M.J.; Alangaden, G.; Tibbetts, R.J. Characterization of Salmonella Isangi possessing a CTX-M15 ESBL associated with an outbreak in a US Hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-P.; Gao, R.-H.; Hou, P.-B.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.-N.; Jiang, K.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Qi, Z.-G.; Xu, M.; Bi, Z.-W. Characterization of the Salmonella enterica Serotype Isangi Isolated from Patients for the First Time in China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, T.; Szabo, D.; Keddy, K.H.; Deeley, K.; Marsh, J.W.; Hujer, A.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Paterson, D.L. Infections with Nontyphoidal Salmonella Species Producing TEM-63 or a Novel TEM Enzyme, TEM-131, in South Africa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4263–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasman, H.; Mevius, D.; Veldman, K.; Olesen, I.; Aarestrup, F.M. β-Lactamases among extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-resistant Salmonella from poultry, poultry products and human patients in The Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.; Ajantha, G.; Shubhada, C.; Jain, P. Isolation of salmonella enterica serotype isangi from a suspected case of enteric encephalopathy. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 27, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, D.F.; Nethery, M.A.; Barrangou, R.; Landgraf, M.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Whole-genome sequencing analysis and CRISPR genotyping of rare antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from food and related sources. Food Microbiol. 2021, 93, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardine, B.; Riemer, C.; Hardison, R.C.; Burhans, R.; Elnitski, L.; Shah, P.; Zhang, Y.; Blankenberg, D.; Albert, I.; Taylor, J.; et al. Galaxy: A platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ramazzotti, D.; De Sano, L.; Zhu, J.; Pierson, E.; Batzoglou, S. SIMLR: A Tool for Large-Scale Genomic Analyses by Multi-Kernel Learning. Proteomics 2018, 18, 1700232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, A.M.; Panzenhagen, P.; Ferrari, R.G.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Large-scale genomic analysis reveals the pESI-like megaplasmid presence in Salmonella Agona, Muenchen, Schwarzengrund, and Senftenberg. Food Microbiol. 2022, 108, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, A.M.; Panzenhagen, P.; Ferrari, R.G.; Rodrigues, G.L.; Conte-Junior, C.A. The pESI megaplasmid conferring virulence and multiple-drug resistance is detected in a Salmonella Infantis genome from Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.L.; Panzenhagen, P.; Ferrari, R.G.; dos Santos, A.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Frequency of Antimi-crobial Resistance Genes in Salmonella From Brazil by in silico Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis: An Overview of the Last Four Decades. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzenhagen, P.; Portes, A.B.; dos Santos, A.M.P.; Duque, S.d.S.; Junior, C.A.C. The Distribution of Campylobacter jejuni Virulence Genes in Genomes Worldwide Derived from the NCBI Pathogen Detection Database. Genes 2021, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissman, A.I.; Mau, B.; Biehl, B.S.; Darling, A.E.; Glasner, J.D.; Perna, N.T. Reordering contigs of draft genomes using the Mauve Aligner. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2071–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.E.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Laing, C.R.; Lingohr, E.J.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Nash, J.H.E.; Taboada, E.N. The Salmonella In Silico Typing Resource (SISTR): An Open Web-Accessible Tool for Rapidly Typing and Subtyping Draft Salmonella Genome Assemblies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.E.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Dallman, T.J.; Zhou, Z.; Grant, K.; Maiden, M.C. Comparative analysis of core genome MLST and SNP typing within a European Salmonella serovar Enteritidis outbreak. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 274, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A novel web tool for WGS-based detection of antimicrobial resistance associated with chromosomal point mutations in bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcìa-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Voldby Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids. Antimicrob using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Taylor, B.; Delaney, A.J.; Soares, J.; Seemann, T.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. SNP-sites: Rapid efficient extraction of SNPs from multi-FASTA alignments. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, 038190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleyman, G.; Tibbetts, R.; Perri, M.B.; Vager, D.; Xin, Y.; Reyes, K.; Samuel, L.; Chami, E.; Starr, P.; Pietsch, J.; et al. Nosocomial Outbreak of a Novel Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Salmonella enterica Serotype Isangi Among Surgical Patients. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadava, R.; Prasad, M.; Narayan, K.G.; Jayasheela, M.; John, P.C.; Mago, M.L.; Saxena, S.N. Isolation of Salmonella isangi (6, 7, 14:d:l, 5) for the first time in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 1986, 84, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fassin, D.; Schneider, H. The politics of AIDS in South Africa: Beyond the controversies. BMJ 2003, 326, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.B.; Rubin, R.H. The Spectrum of Salmonella Infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1988, 2, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: Temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahérault, A.-C.; Kemble, H.; Magnan, M.; Gachet, B.; Roche, D.; Le Nagard, H.; Tenaillon, O.; Denamur, E.; Branger, C.; Landraud, L. Advantage of the F2:A1:B- IncF Pandemic Plasmid over IncC Plasmids in In Vitro Acquisition and Evolution of blaCTX-M Gene-Bearing Plasmids in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01130-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance Plasmid Families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leflon-Guibout, V.; Blanco, J.; Amaqdouf, K.; Mora, A.; Guize, L.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H. Absence of CTX-M Enzymes but High Prevalence of Clones, Including Clone ST131, among Fecal Escherichia coli Isolates from Healthy Subjects Living in the Area of Paris, France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3900–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. Analysis of the Resistome of a Multidrug-Resistant NDM-1-Producing Escherichia coli Strain by High-Throughput Genome Sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4224–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briales, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Velasco, C.; de Alba, P.D.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Pachón, J.; Pascual, A. In Vitro Effect of qnrA1, qnrB1, and qnrS1 Genes on Fluoroquinolone Activity against Isogenic Escherichia coli Isolates with Mutations in gyrA and parC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.H.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanism of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5638–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paglietti, B.; Falchi, G.; Mason, P.; Chitsatso, O.; Nair, S.; Gwanzura, L.; Uzzau, S.; Cappuccinelli, P.; Wain, J.; Rubino, S. Diversity among human non-typhoidal salmonellae isolates from Zimbabwe. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Jiang, H.-X.; Liao, X.-P.; Liu, J.-H.; Li, S.-J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Chen, C.-X.; Lü, D.-H.; Liu, Y.-H. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in poultry and swine clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Veter. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.C.; Shaw, H.; Rhodes, V.; Hart, A. Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment and Its Relevance to Environmental Regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Galiana, A.; Cremades, R.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Magnani, M.; Tognim, M.C.B.; Oliveira, T.C.R.M.; Royo, G. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance by genes qnrA1 and qnrB19 in Salmonella strains isolated in Brazil. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2011, 5, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Fortini, D.; Veldman, K.; Mevius, D.; Carattoli, A. Characterization of plasmids harbouring qnrS1, qnrB2 and qnrB19 genes in Salmonella. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, G.H.; Li, C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Bodeis-Jones, S.; McDermott, P.F. Diverse Fluoroquinolone Resistance Plasmids From Retail Meat E. coli in the United States. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyl, D.; Hoszowski, A.; Zając, M. Prevalence and characterisation of quinolone resistance mechanisms in Salmonella spp. Veter. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, F.; Araque, M. Association of Transferable Quinolone Resistance Determinant qnrB19 with Extended-Spectrumβ-Lactamases in Salmonella Give and Salmonella Heidelberg in Venezuela. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 628185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarczyk, M.; Martins, M.; McCusker, M.; Mattar, S.; Amaral, L.; Leonard, N.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Fanning, S. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica food and animal isolates from Colombia: Identification of a qnrB19-mediated quinolone resistance marker in two novel serovars. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 313, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, A.H.; Okeke, I.N.; Dalsgaard, A.; Menéndez, V.G.; Olsen, J.E. Genomic Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance and Resistance Plasmids in Salmonella Serovars from Poultry in Nigeria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, K.; Cavaco, L.M.; Mevius, D.; Battisti, A.; Franco, A.; Botteldoorn, N.; Bruneau, M.; Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Cerny, T.; Escobar, C.D.F.; et al. International collaborative study on the occurrence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli isolated from animals, humans, food and the environment in 13 European countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, F.M.; Carmo-Rodrigues, M.S.; Oliveira, V.G.S.; Gaspari, M.V.; dos Santos, A.; de Freitas, J.B.; Pignatari, A.C. β-Lactam Resistance Genes: Characterization, Epidemiology, and First Detection of blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-14 in Salmonella spp. Isolated from Poultry in Brazil—Brazil Ministry of Agriculture’s Pathogen Reduction Program. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.A.; Camargo, C.H.; Francisco, G.R.; Bueno, M.F.C.; Garcia, D.O.; Doi, Y.; Casas, M.R.T. Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases CTX-M-8 and CTX-M-2-Producing Salmonella Serotypes from Clinical and Nonhuman Isolates in Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, L.R.; Van Der Graaf-Van Bloois, L.; Donado-Godoy, P.; León, M.; Clavijo, V.; Arévalo, A.; Bernal, J.F.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Zomer, A.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Salmonella enterica in the Colombian Poultry Chain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, A.P.; Martins, B.T.F.; Barreiros, M.A.B.; Yamatogi, R.S.; Nero, L.A.; Bersot, L.d.S. Occurrence, quantification, pulse types, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella sp. isolated from chicken meat in the state of Paraná, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, A.; Pallecchi, L.; Riccobono, E.; Mantella, A.; Magnelli, D.; Di Maggio, T.; Villagran, A.; Lara, Y.; Saavedra, C.; Strohmeyer, M.; et al. Relentless increase of resistance to fluoroquinolones and expanded-spectrum cephalosporins in Escherichia coli: 20 years of surveillance in resource-limited settings from Latin America. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, C.; Clemente, L.; Moura, L.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Hansen, I.M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Amaro, A. Emergence and Clonal Spread of CTX-M-65-Producing Escherichia coli From Retail Meat in Portugal. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 653595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, J.P.R.; Lopes, R.; Ramos, M.S.; dos Santos, L.D.R.; Rosa, R.d.S.; Savazzi, E.A.; Stehling, E.G. Colistin-resistant mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli ST1775-H137 co-harboring blaCTX-M-2 and blaCMY-2 recovered from an urban stream. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, J.D.; Ferreira, H.; Madec, J.-Y.; Haenni, M. Draft genome of a ST443 mcr-1—And bla CTX-M-2 -carrying Escherichia coli from cattle in Brazil. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 13, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.P.J.; Botelho, J.; Cazares, A.; Baltrus, D.A. What makes a megaplasmid? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 377, 20200472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann, S.R.; Sherwood, J.S.; Logue, C.M. The Yersinia high pathogenicity island is present in Salmonella enterica Subspecies I isolated from turkeys. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.M.; Ferrari, R.G.; Panzenhagen, P.; Rodrigues, G.L.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Virulence genes identification and characterization revealed the presence of the Yersinia High Pathogenicity Island (HPI) in Salmonella from Brazil. Gene 2021, 787, 145646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Zhang, D.; Schubert, S.; Carniel, E.; Rabsch, W.; Karch, H.; Hacker, J. The High-Pathogenicity Island Is Absent in Human Pathogens of Salmonella enterica Subspecies I but Present in Isolates of Subspecies III and VI. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
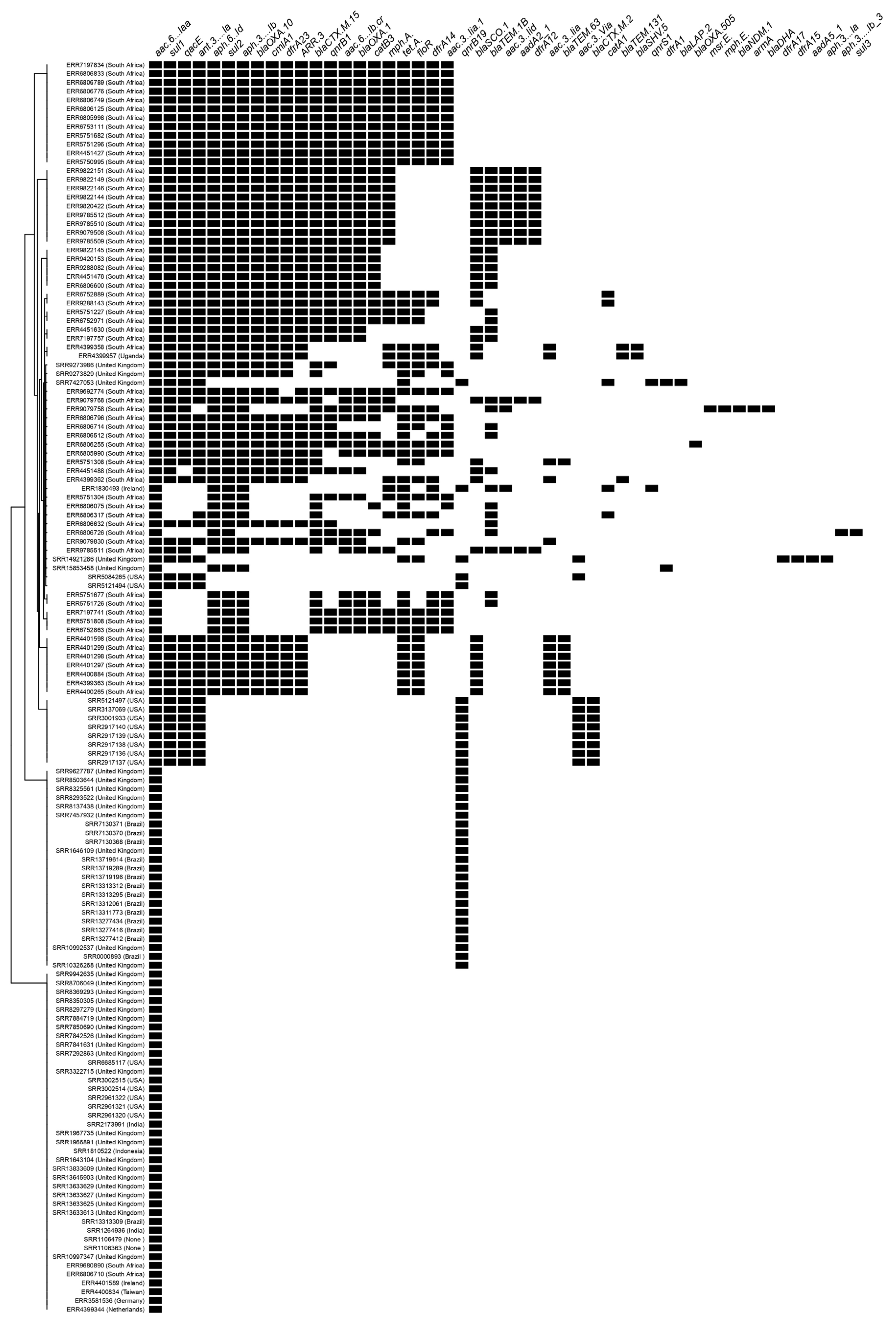
| Isolate ID | Location | Year of Isolation | Resistome | Gene | Mutation | Predicted Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERR4399363 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4400265 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4400834 | Tawain | 2007 | gyrA (S83F) | TCC→TTC (S→F) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid | |
| ERR4400884 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4401297 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4401298 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4401299 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR4401598 | South Africa | 2001 | aac(3)-IIa, ant(3″)-Ia, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, ARR-3, blaOXA-10, blaSCO-1, blaTEM-63, cmlA1, dfrA23, floR, gyrA (D87N), qacE, sul1, sul2, tet(A) | gyrA (D87N) | GAC→AAC (D→N) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid |
| ERR6806075 | South Africa | 2020 | aac(3)-IIa, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM-1B, catB3, gyrB (S464F), sul2 | gyrB (S464F) | TCT→TTC (S→F) | ciprofloxacin I/R |
| SRR1106479 | Unknown | gyrA (S83F) | TCC→TTC (S→F) | ciprofloxacin I/R, nalidixic acid | ||
| SRR1264936 | India | 2011 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR13633613 | United Kingdom | 2021 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR13633625 | United Kingdom | 2021 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR13633627 | United Kingdom | 2021 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR13633629 | United Kingdom | 2021 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR13645903 | United Kingdom | 2021 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
| SRR3002515 | United States | 2009 | parC (T57S) | parC (T57S) | ACC→AGC (T→S) | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, A.M.P.; Panzenhagen, P.; Ferrari, R.G.; de Jesus, A.C.S.; Portes, A.B.; Ochioni, A.C.; Rodrigues, D.d.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A Global Perspective of a Rare Serovar. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081309
dos Santos AMP, Panzenhagen P, Ferrari RG, de Jesus ACS, Portes AB, Ochioni AC, Rodrigues DdP, Conte-Junior CA. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A Global Perspective of a Rare Serovar. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(8):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081309
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Anamaria Mota Pereira, Pedro Panzenhagen, Rafaela G. Ferrari, Ana Carolina S. de Jesus, Ana Beatriz Portes, Alan Clavelland Ochioni, Dalia dos Prazeres Rodrigues, and Carlos Adam Conte-Junior. 2023. "Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A Global Perspective of a Rare Serovar" Antibiotics 12, no. 8: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081309
APA Styledos Santos, A. M. P., Panzenhagen, P., Ferrari, R. G., de Jesus, A. C. S., Portes, A. B., Ochioni, A. C., Rodrigues, D. d. P., & Conte-Junior, C. A. (2023). Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A Global Perspective of a Rare Serovar. Antibiotics, 12(8), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12081309









