Resveratrol as an Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump and Resistance Modulator in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
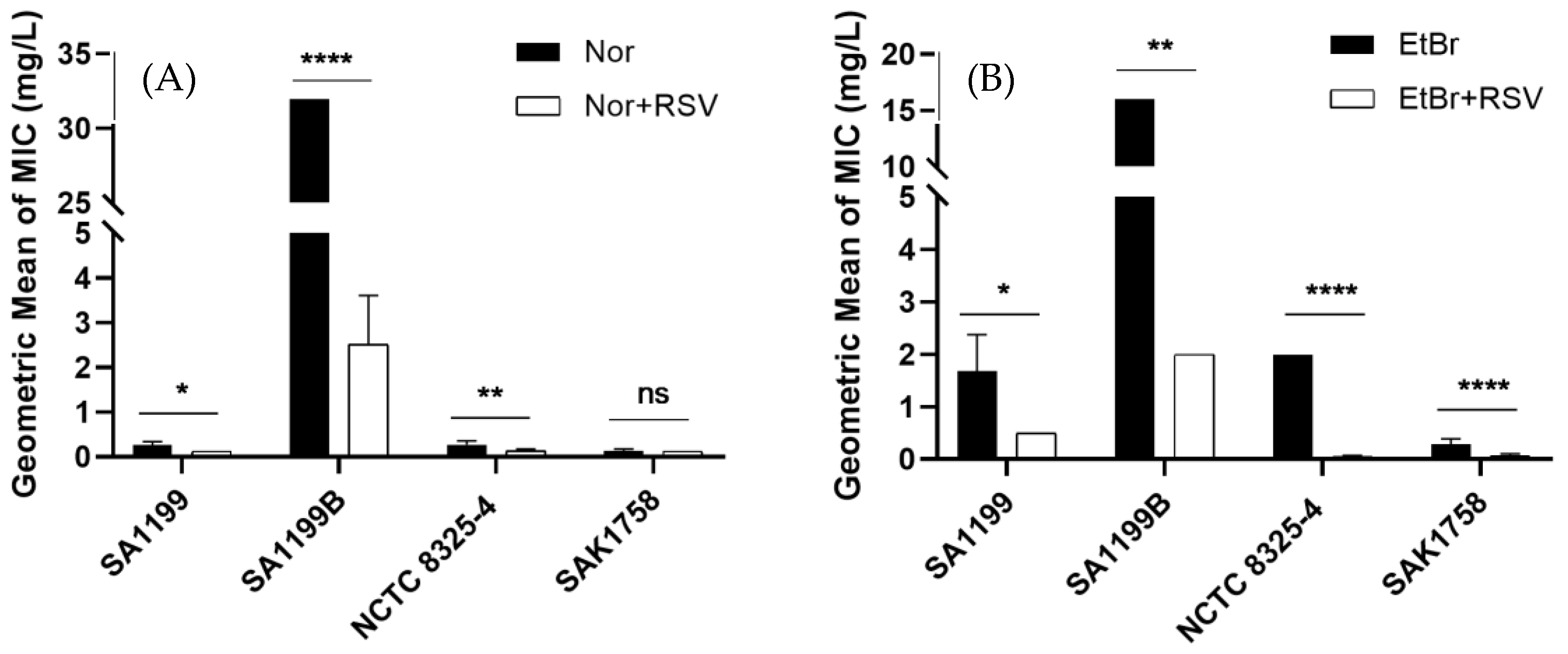
2.1. Evaluation of the Modulatory Effect of Resveratrol
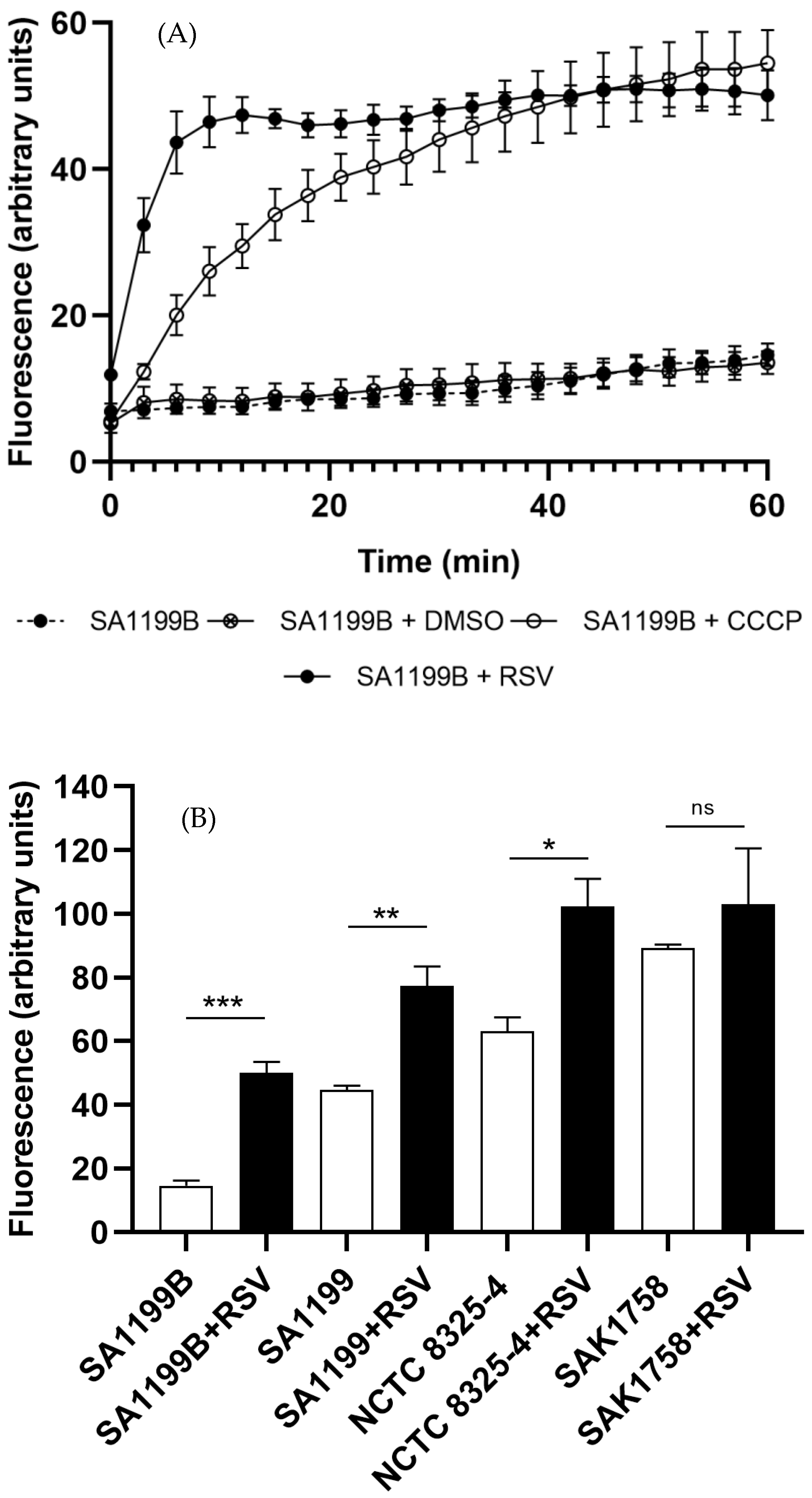
2.2. Ethidium Bromide Accumulation
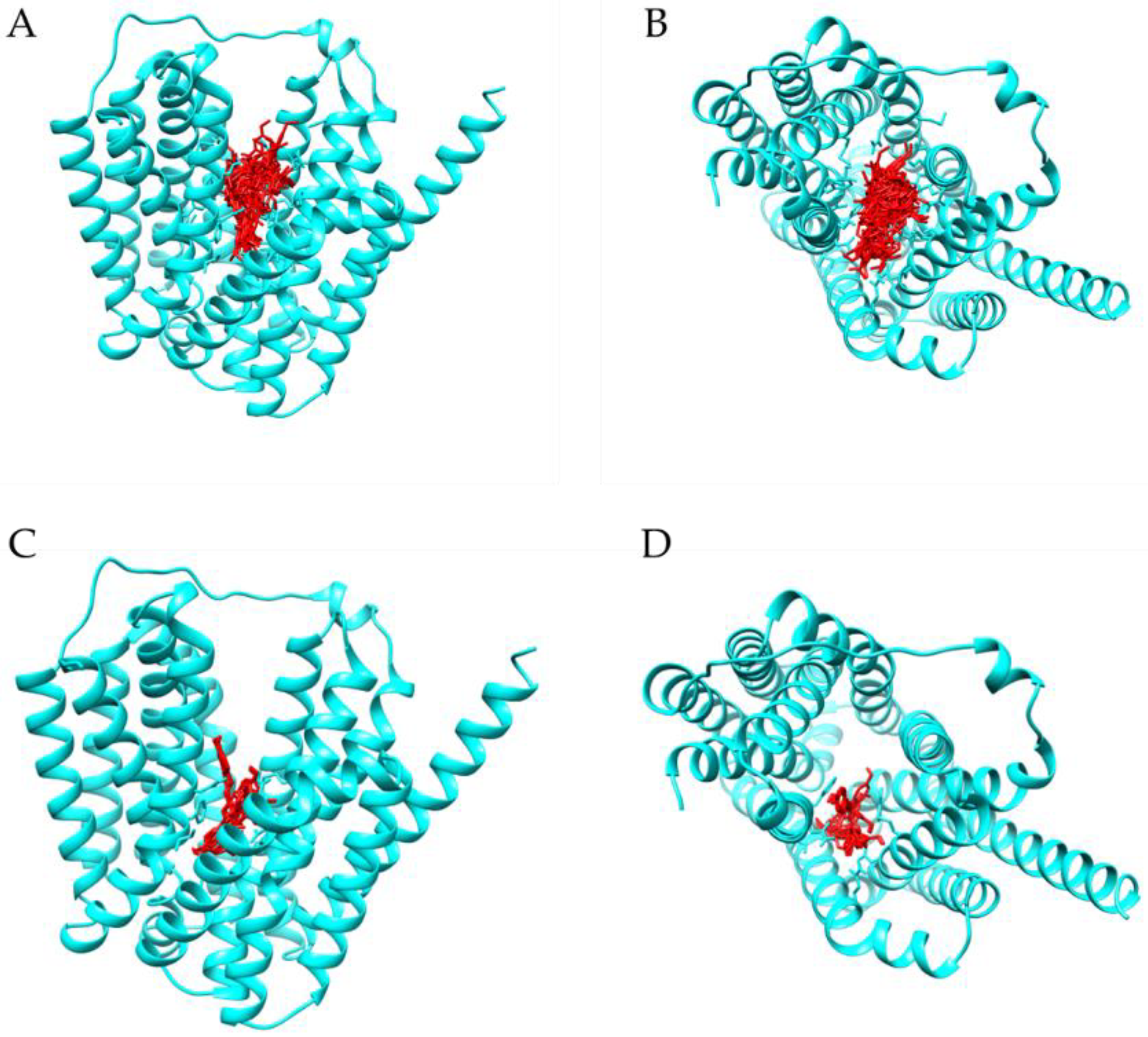
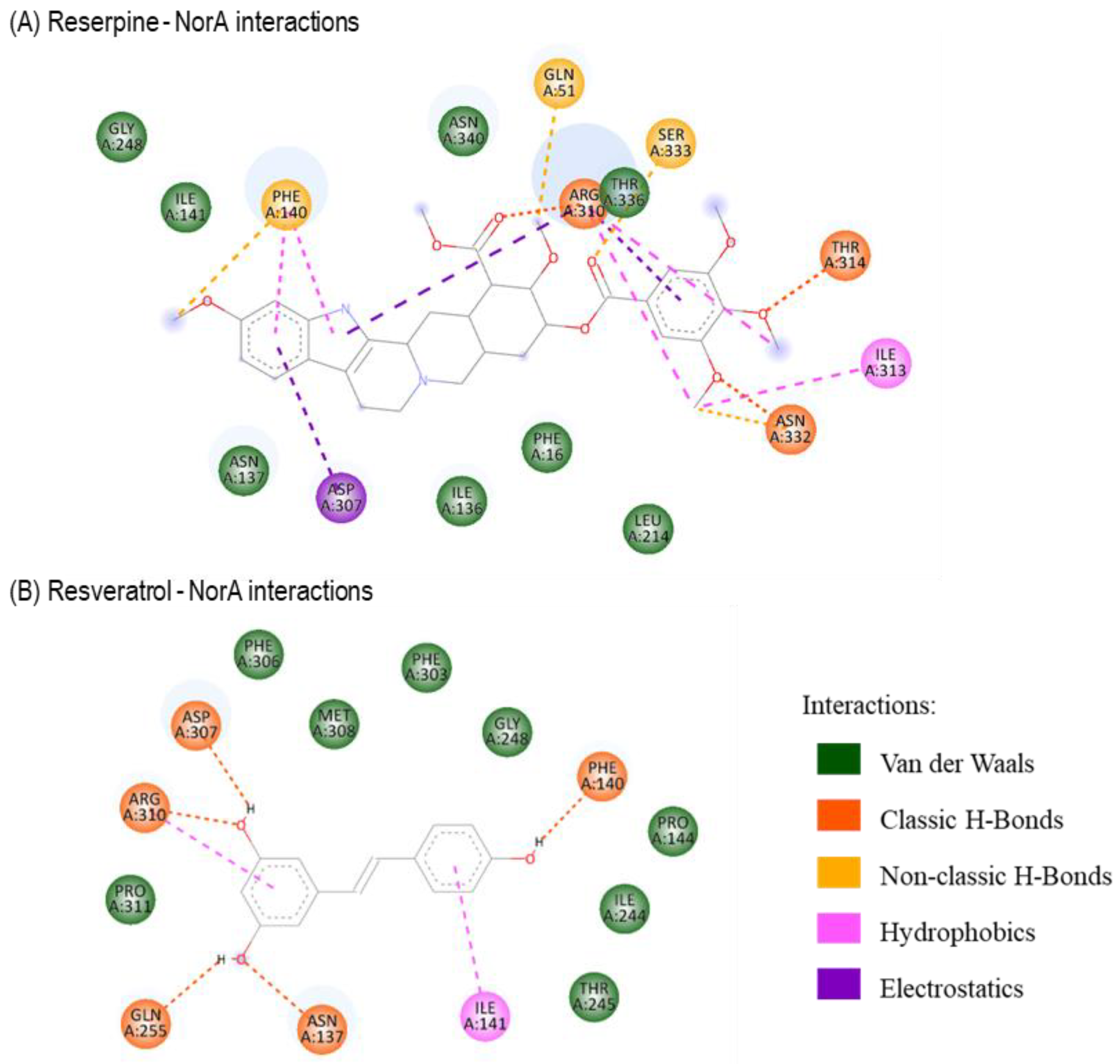
2.3. Molecular Docking Studies with Resveratrol
2.4. Impact on Mutation Frequency and Post-Antibiotic Effect (PAE)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Antimicrobial Agents
4.2. Antibacterial Activity Analysis through Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Modulatory Activity of Resveratrol
4.3. Ethidium Bromide Accumulation Assay
4.4. Molecular Docking Studies with Resveratrol
4.5. Impact on Frequency of Resistance
4.6. Post-Antibiotic Effect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madhaiyan, M.; Wirth, J.; Saravanan, V. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Tintino, S.; Silva, A.; Cristina, B.; Scherf, J.; Silveira, Z.; Freitas, T.; Neto, L.; Barros, L.; Menezes, I.; et al. Enhancement of the antibiotic activity by quercetin against Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2021, 53, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, D.; Barbosa, C.; Menezes, I.; Sousa, E.; Pereira, R.; Júnior, J.; Pereira, P.; Matos, Y.; Costa, R.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.; et al. In vitro and in silico inhibitory effects of synthetic and natural eugenol derivatives against the NorA efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howden, B.; Giulieri, S.; Lung, T.; Baines, S.; Sharkey, L.; Lee, J.; Hachani, A.; Monk, I.; Stinear, T. Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Ne Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus Genetic Background, Virulence Factors, agr Groups (Alleles), and Human Disease. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Srirama, K.; Dirisala, V. An Update on Clinical Burden, Diagnostic Tools, and Therapeutic Options of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2017, 10, 1179916117703999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.; Urzúa, A.; Sanhueza, L.; Walter, M.; Fincheira, P.; Muñoz, P.; Mendoza, L.; Wilkens, M. Essential Oil, Extracts, and Sesquiterpenes Obtained from the Heartwood of Pilgerodendron uviferum Act as Potential Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus aureus NorA Multidrug Efflux Pump. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, World Health Organization, Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe—2022: 2020 Data, Publications Office of the European Union. 2022. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2900/112339 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Sipahi, O. Economics of antibiotic resistance. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouwakeh, A.; Kincses, A.; Nové, M.; Mosolygó, T.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C.; Kiskó, G.; Spengler, G. Nigella sativa essential oil and its bioactive compounds as resistance modifiers against Staphylococcus aureus. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchiappan, A.; Chatterji, D. Antibiotic resistance: Current perspectives. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7400–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, V.; Kumar, A. Update on multidrug resistance efflux pumps in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handzlik, J.; Matys, A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Recent Advances in Multi-Drug Resistance (MDR) Efflux Pump Inhibitors of Gram-positive Bacteria S. aureus. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderon, J.; Corona, F.; Lira, F.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Bernardini, A.; Sanchez, M.; Martinez, J. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps: Much More Than Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, J.; Salam, F.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S.; Varela, M. The Major Facilitator Superfamily and Antimicrobial Resistance Efflux Pumps of the ESKAPEE Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, Z.; Macêdo, N.; Santos, J.; Freitas, T.; Barbosa, C.; Júnior, D.; Muniz, D.; Oliveira, L.; Júnior, J.; Cunha, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Molecules 2020, 25, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekshmi, M.; Stephen, J.; Ojha, M.; Kumar, S.; Varela, M. Staphylococcus aureus antimicrobial efflux pumps and their inhibitors: Recent developments. AIMS Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Ingmer, H. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of resveratrol. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, L.; Ferreira, S.; Gallardo, E.; Queiroz, J.A.; Domingues, F. Antimicrobial activity and effects of resveratrol on human pathogenic bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Silva, F.; Queiroz, J.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F. Resveratrol against Arcobacter butzleri and Arcobacter cryaerophilus: Activity and effect on cellular functions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 180, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nøhr-Meldgaard, K.; Ovsepian, A.; Ingmer, H.; Vestergaard, M. Resveratrol enhances the efficacy of aminoglycosides against Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seukep, J.; Sandjo, L.; Ngadjui, B.; Kuete, V. Antibacterial and antibiotic-resistance modifying activity of the extracts and compounds from Nauclea pobeguinii against Gram-negative multi-drug resistant phenotypes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, A.; Stabile, M.; Bagattini, M.; Triassi, M.; Berisio, R.; Gregorio, E.; Zarrilli, R. Resveratrol Reverts Tolerance and Restores Susceptibility to Chlorhexidine and Benzalkonium in Gram-Negative Bacteria, Gram-Positive Bacteria and Yeasts. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Lim, Y.-H. Resveratrol controls Escherichia coli growth by inhibiting the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.; Luís, Â.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.; Ferreira, S. Polyphenols as resistance modulators in Arcobacter butzleri. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkham-In, U.; Higgins, P.G.; Wannigama, D.L.; Hongsing, P.; Chatsuwan, T. Rescued chlorhexidine activity by resveratrol against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii via down-regulation of AdeB efflux pump. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, A.; Esposito, E.; Bagattini, M.; Berisio, R.; Triassi, M.; Gregorio, E.; Zarrilli, R. Inhibition of AdeB, AceI, and AmvA Efflux Pumps Restores Chlorhexidine and Benzalkonium Susceptibility in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 790263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, N.; Mahajan, P.; Mehra, R.; Nargotra, A.; Sharma, J.; Koul, S.; Khan, I. Capsaicin, a novel inhibitor of the NorA efflux pump, reduces the intracellular invasion of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Tintino, C.; Tintino, S.; Limaverde, P.; Figueredo, F.; Campina, F.; Cunha, F.; Costa, R.; Pereira, P.; Lima, L.; Matos, Y.; et al. Inhibition of the essential oil from Chenopodium ambrosioides L. and α-terpinene on the NorA efflux-pump of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Silva, H.; Magnani, M.; Siqueira, S.; Souza, E.; Siqueira-Júnior, J. Fruit flavonoids as modulators of norfloxacin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus that overexpresses norA. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kalia, N.P.; Joshi, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.R.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B.; Khan, I.A. Boeravinone B, A Novel Dual Inhibitor of NorA Bacterial Efflux Pump of Staphylococcus aureus and Human P-Glycoprotein, Reduces the Biofilm Formation and Intracellular Invasion of Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.; Oliveira, A.; Ferreira, A.; Silva, E.; Sousa, L.; Rocha, M.; Júnior, J.; Kaatz, G.; Almeida, J.; Souza, J.; et al. Modulation of the resistance to norfloxacin in Staphylococcus aureus by Bauhinia forficata link. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Patel, D.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Pal, A.; Tandon, S.; Darokar, M.P. Citral, a monoterpenoid aldehyde interacts synergistically with norfloxacin against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100-Ed32; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacterial Strains | MIC (mg/L) of Resveratrol |
|---|---|
| SA1199 (wildtype) | 200 |
| SA1199B (norA++) | 100 |
| NCTC 8325-4 (wildtype) | 400 |
| SAK1758 (ΔnorA) | 200 |
| Ligand | Reserpine | Resveratrol | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | −7.39 | −6.19 | |
| Interactions | Van der Waals | LEU214 PHE16 ILE136 ASN137 GLY248 ILE141 ASN340 THR336 | PHE306 MET308 PHE303 GLY248 PRO144 ILE244 THR245 PRO311 |
| Classic H-Bonds | ASN332 THR314 ARG310 | ASP307 ARG310 GLN255 ASN137 PHE140 | |
| Non-classic H-Bonds | PHE140 GLN51 SER333 | ---- | |
| Hydrophobics | ILE313 ARG310 PHE140 | ILE141 ARG310 | |
| Electrostatics | ASP307 ARG310 | ---- | |
| Resveratrol (mg/L) | Mutation Frequency with Norfloxacin (±SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4× MIC (1 mg/L) | 8× MIC (2 mg/L) | 16× MIC (4 mg/L) | |
| 0 | 1.87 (±0.39) × 10−5 | 5.27 (±6.07) × 10−7 | 4.03 (±1.98) × 10−8 |
| 50 | 2.16 (±1.27) × 10−7 | 1.93 (±1.33) × 10−8 | <5.31 × 10−10 |
| Regimen | Mean PAE (h) ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25× MIC Nor (8 mg/L) | 0.5× MIC Nor (16 mg/L) | 1× MIC Nor (32 mg/L) | |
| Nor | 0.04 ± 0.08 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.48 ± 0.14 |
| Nor + RSV (25 mg/L) | 0.75 ± 0.09 *** | 0.63 ± 0.06 *** | 0.93 ± 0.22 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, M.; Santos, R.; Soeiro, P.; Silvestre, S.; Ferreira, S. Resveratrol as an Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump and Resistance Modulator in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071168
Santos M, Santos R, Soeiro P, Silvestre S, Ferreira S. Resveratrol as an Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump and Resistance Modulator in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071168
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Madalena, Raquel Santos, Pedro Soeiro, Samuel Silvestre, and Susana Ferreira. 2023. "Resveratrol as an Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump and Resistance Modulator in Staphylococcus aureus" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071168
APA StyleSantos, M., Santos, R., Soeiro, P., Silvestre, S., & Ferreira, S. (2023). Resveratrol as an Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump and Resistance Modulator in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071168










