Discovery of Novel Myristic Acid Derivatives as N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Analysis, Computational Studies and Antifungal Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
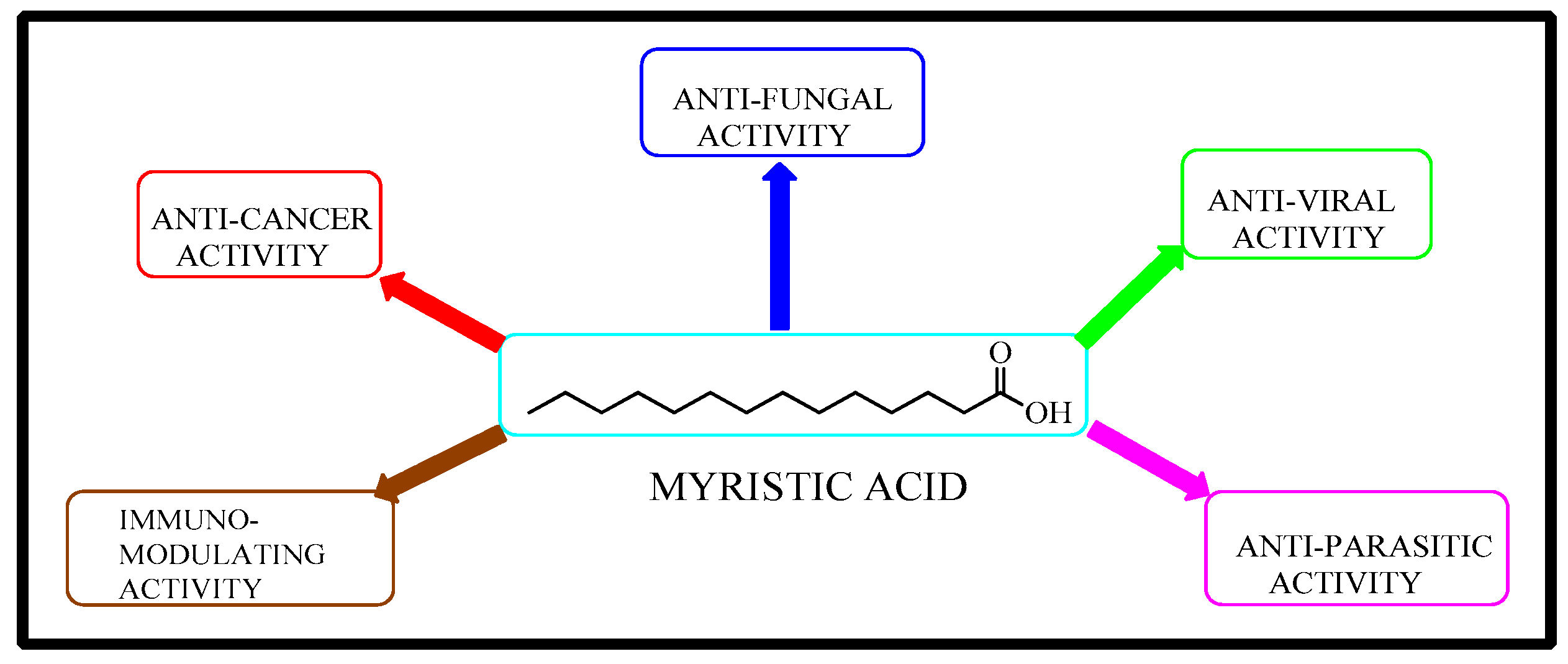
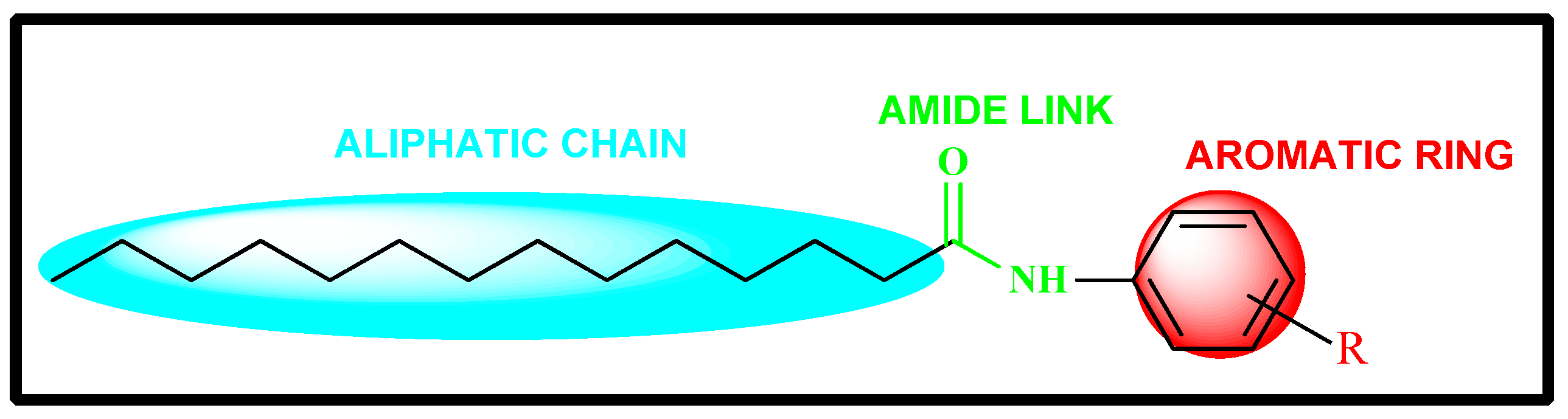
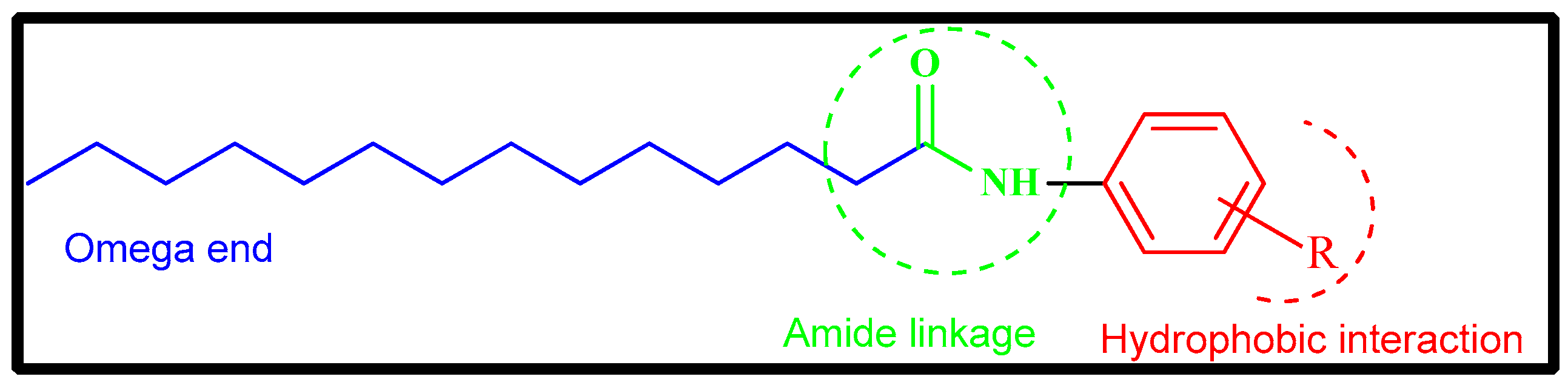
2.1. Rational Design of Myristic Acid Derivatives
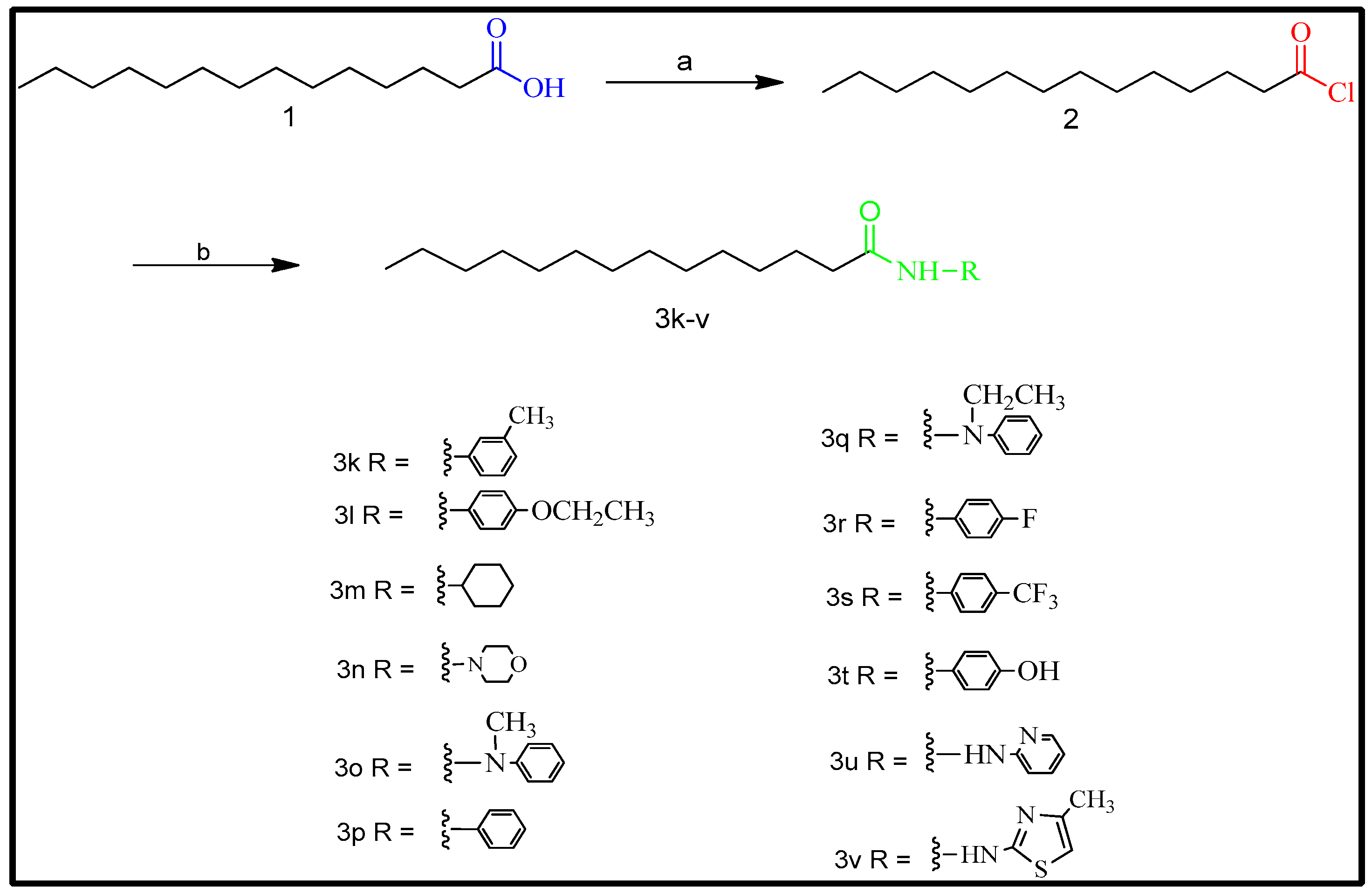
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. High-Throughput Virtual Screening of Designed Myristic Acid Derivatives
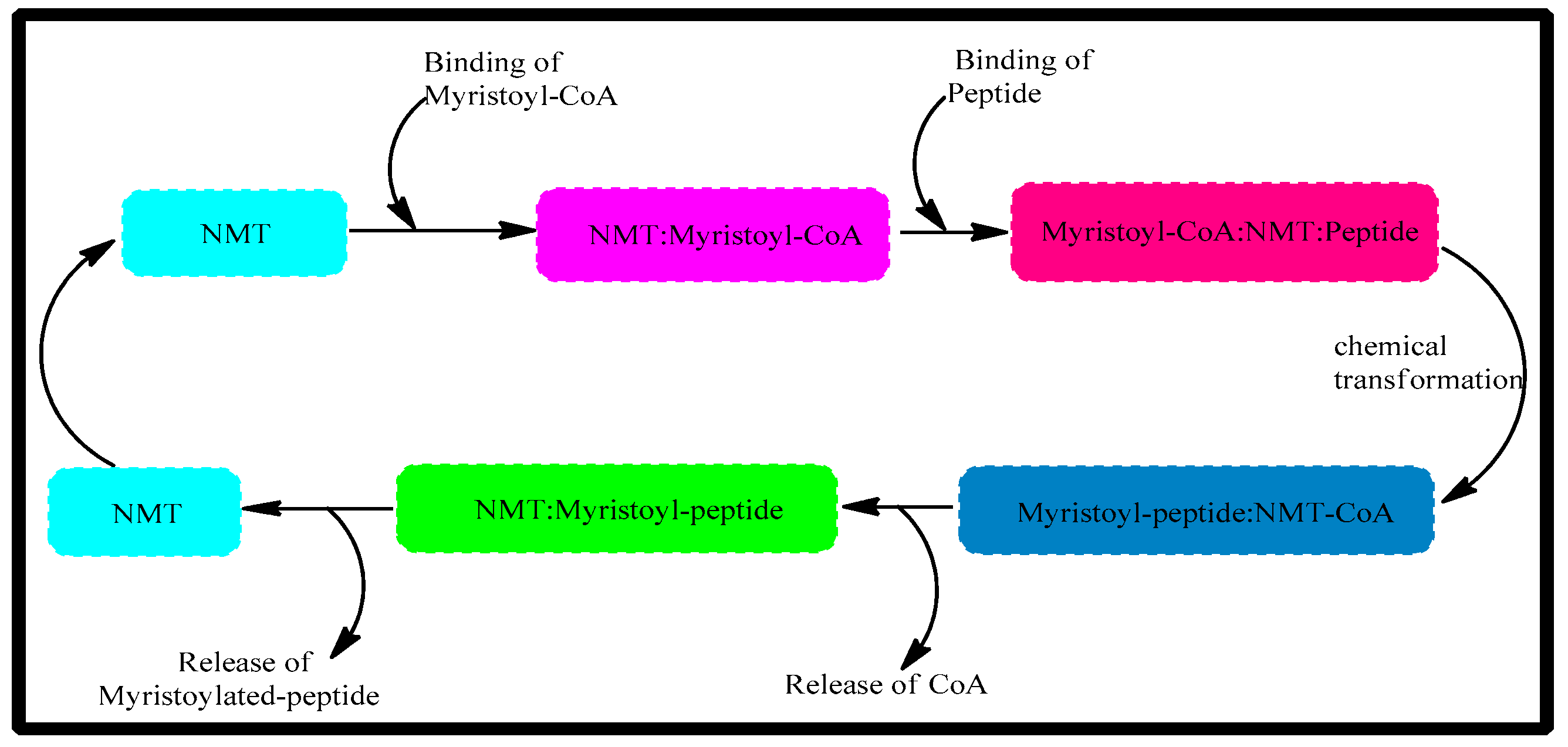
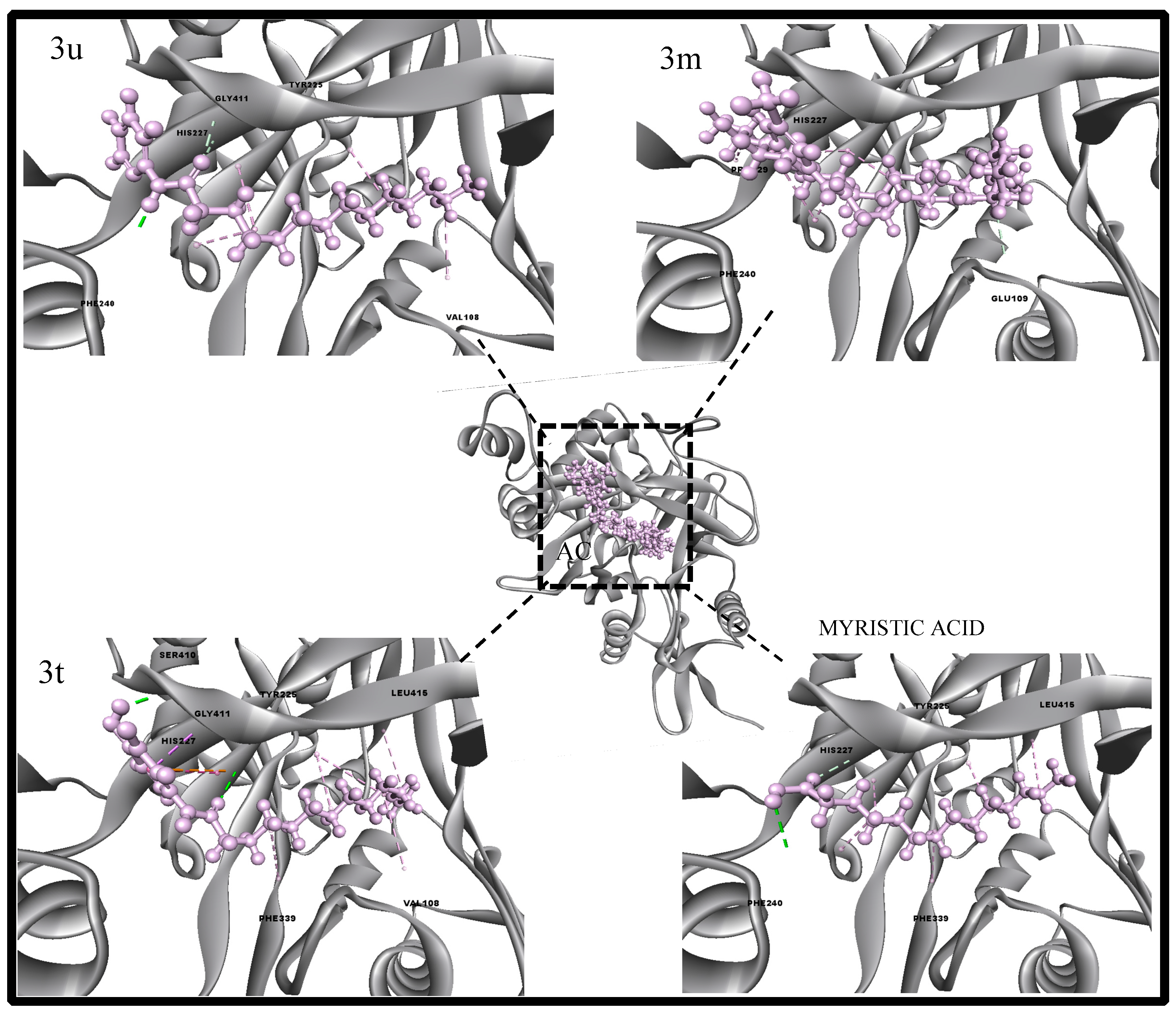
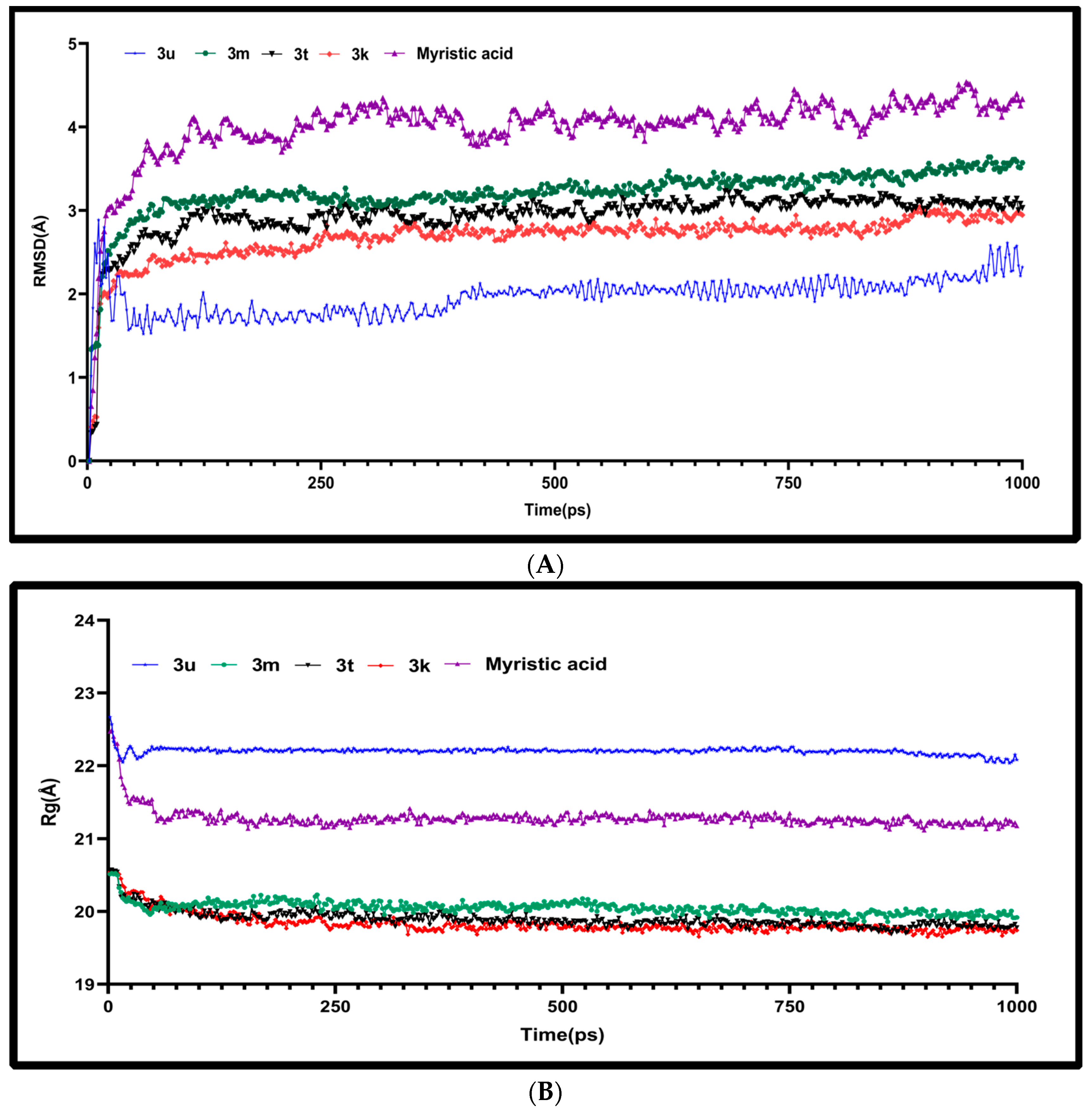
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Characterizations of N-Myristoyltransferase–Ligand Complexes
2.5. Structure Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies
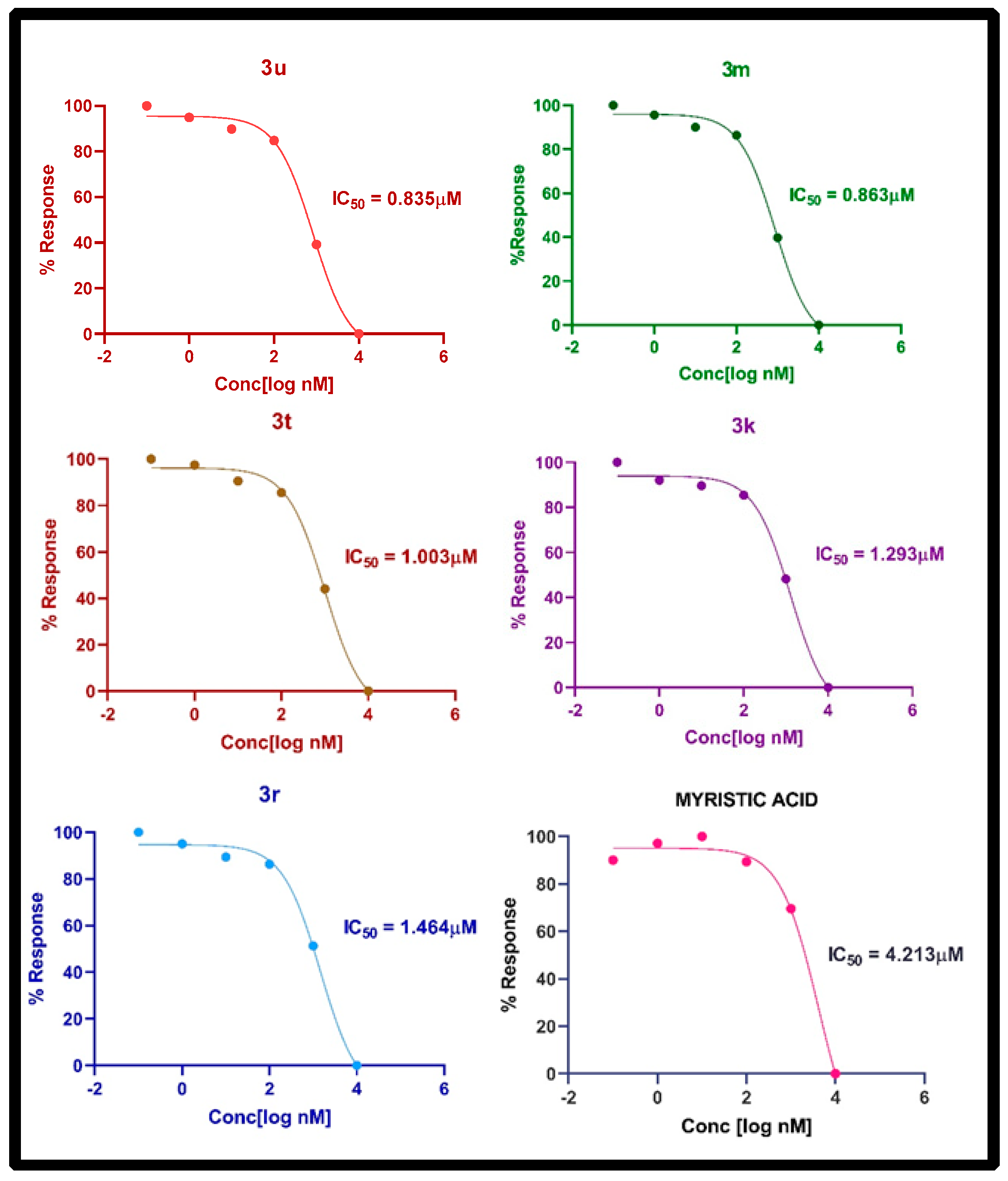
2.6. In Vitro NMT Inhibition Assay
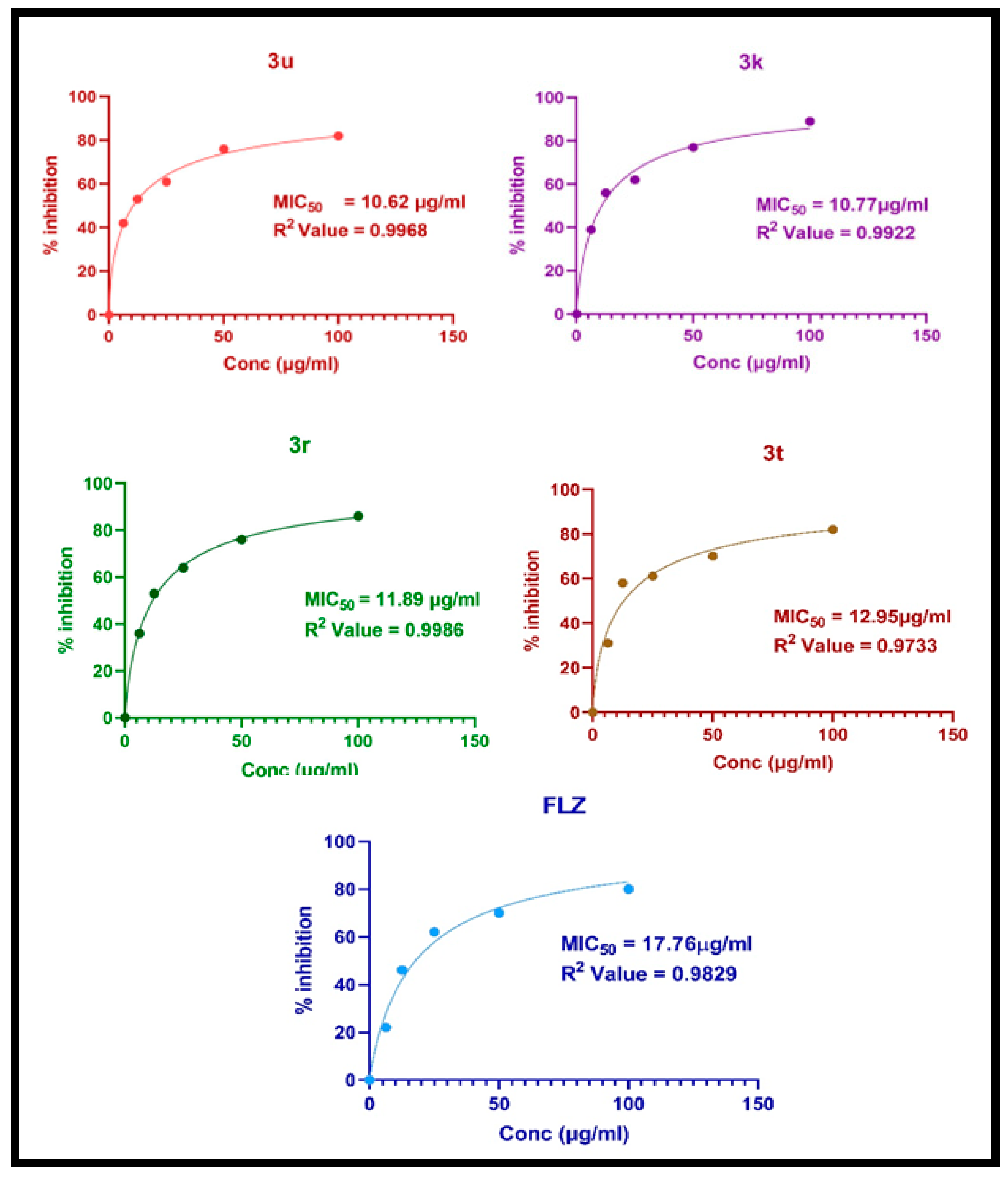
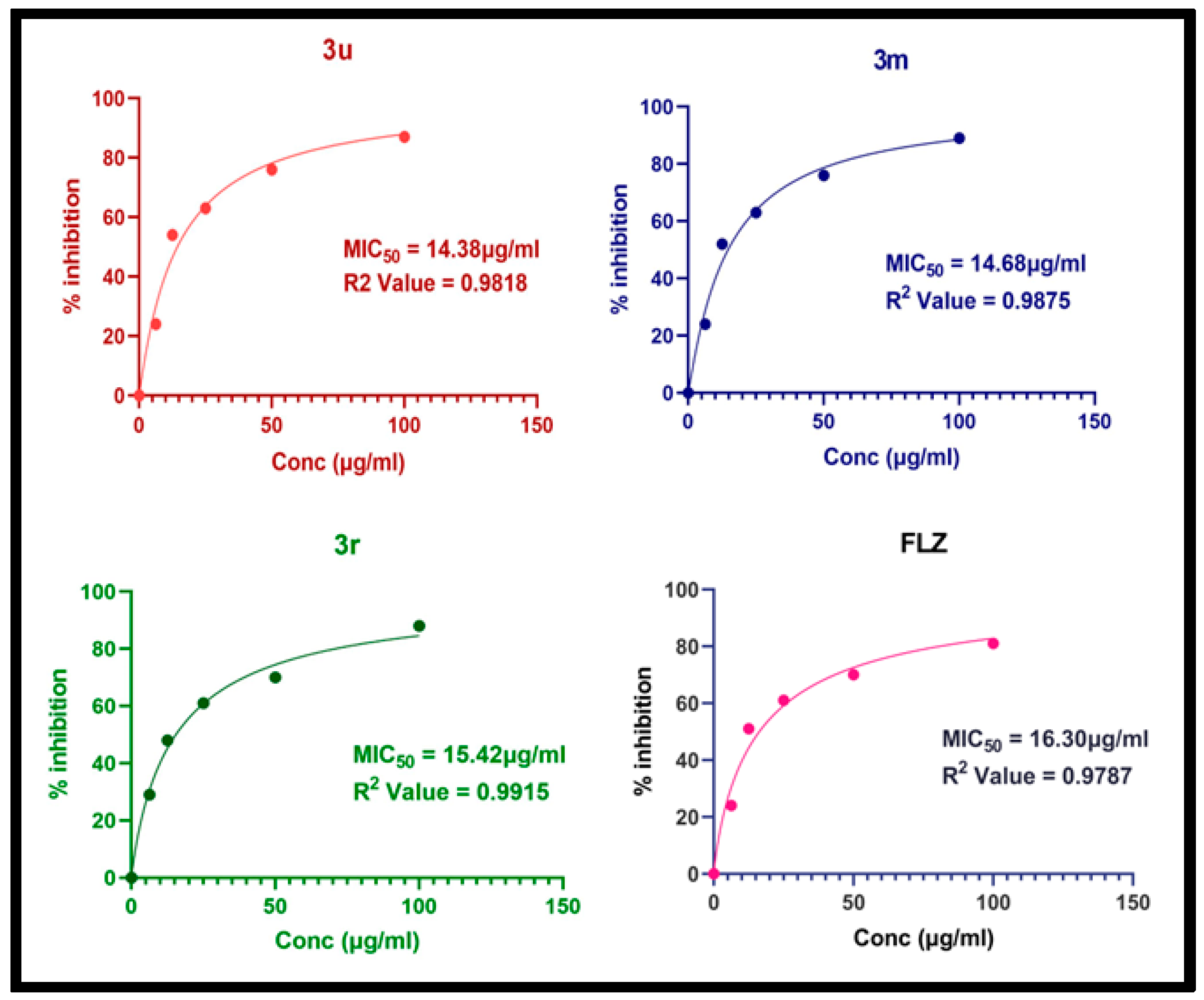
2.7. Antifungal Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico Studies and Spectral Data Analysis
4.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Myristic Acid Derivatives
4.2.1. N-(m-tolyl) tetradecanamide (3k)
4.2.2. N-(4-ethoxyphenyl) tetradecanamide (3l)
4.2.3. N-cyclohexyltetradecanamide: (3m)
4.2.4. 1-morpholinotetradeca-1-one: (3n)
4.2.5. N-methyl-N-phenyltetradecanamide: (3o)
4.2.6. N-phenyltetradecanamide: (3p)
4.2.7. N-ethyl-N-phenyltetradecanamide: (3q)
4.2.8. N-(4-fluorophenyl) tetradecanamide: (3r)
4.2.9. N-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)tetradecanamide: (3s)
4.2.10. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) tetradecanamide: (3t)
4.2.11. N-(pyridine-2-yl) tetradecanamide: (3u)
4.2.12. N-(4-methylthiazol-2-yl) tetradecanamide: (3v)
4.3. Computational Studies
4.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.5. Screening Myristic Acid Derivatives Using Biochemical NMT Assay
4.6. Screening for Antifungal Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Candidiasis. 2016, Update by the Infectious Disease Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Liu, N.; Tu, J.; Li, Z.; Han, G.; Li, J.; Sheng, C. Drug Repurposing of Haloperidol., Discovery of New Benzocyclane Derivatives as Potent Antifungal Agents against Cryptococcosis and Candidiasis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, D.A.; Yang, H.; Aliyu, S.H.; Micallef, C. Human Fungal Pathogen Identification; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Wilson, D.; Drew, R.; Perfect, J. Azole Antifungals: 35 Years of Invasive Fungal Infection Management. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Tu, J.; Ji, C.; Han, G.; Sheng, C. Discovery of Simplified Sampangine Derivatives with Potent Antifungal Activities against Cryptococcal Meningitis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, B.; Freeman, S.K.; Zupec, M.E.; Lu, H.F.; Nagarajan, S.R.; Kishore, N.S.; Lodge, J.K.; Kuneman, D.W.; Vinjamoori, D.V.; Sikorski, J.A.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel imidazole-substituted dipeptide amides as potent and selective inhibitors of Candida albicans Myristoyl CoA:Protein N-Myristoyltransferase and identification of related tripeptide inhibitors with mechanism-based antifungal activity. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 2609–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadas, B.; Freeman, S.K.; Zupec, M.E.; Brown, D.L.; Nagarajan, S.; Sikorski, J.A.; McWherter, C.A.; Getman, D.P.; Gordon, J.I. Design and Synthesis of Potent and Selective Dipeptide Inhibitors of Candida albicans Myristoyl-CoA:Protein N-myristoyltransferase. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1837–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, L.A.; Zheng, G.; De Frees, S.A.; Cassady, J.M.; Geahlen, R.L. Metabolic activation of 2-substituted derivatives of myristic acid to form potent inhibitors of myristoyl CoA: Protein N-myristoyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1990, 29, 10566–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parang, K.; Knaus, E.E.; Wiebe, L.L.; Sardari, S.; Daneshtalab, M.; Csizmadia, F. Synthesis and antifungal activities of myristic acid analogs. Arch. Pharm. 1996, 329, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, H.S.; Puranik, P.; Kulkarni, V.M. QSAR analysis of N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors: Antifungal activity of benzofurans. Med. Chem. Res. 2008, 18, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masubuchi, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Ebiike, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Tsujii, S.; Sogabe, S.; Fujii, T.; Sakata, K.; Shiratori, Y.; Aoki, Y.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel benzofurans as a new class of antifungal agents targeting fungal N-myristoyltransferase. Part 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebiike, H.; Masubuchi, M.; Liu, P.; Kawasaki, K.; Morikami, K.; Sogabe, S.; Hayase, M.; Fujii, T.; Sakata, K.; Shindoh, H.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel benzofurans as a new class of antifungal agents targeting fungal N-myristoyltransferase. Part 2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masubuchi, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Ebiike, H.; Morikami, K.; Hayase, M.; Shindoh, H.; Sogabe, S.; Fujii, T.; Sakata, K.; Shiratori, Y.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel benzofurans as a new class of antifungal agents targeting fungal N-myristoyltransferase. Part 3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara, S.; Naito, H.; Nakazawa, K.; Ishii, F.; Nakamura, M. FTR1335 is a novel synthetic inhibitor of Candida albicans N-myristoyltransferase with fungicidal activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Han, L.; Huang, X. Potential Targets for the Development of New Antifungal Drugs. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, J.A. Myristoylation. Cell. Signal. 1997, 9, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.I.; Duronios, R.J.; Rudnicks, D.A.; Adamss, S.P.; Cokel, G.W. Protein N-myristoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 8647–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnick, D.A.; Getman, D.P.; Mcwherter, C.A.; Rocque, W.J.; Lenon, P.J.; Gordon, J.I. Kinetic and structural evidence for a sequential ordered Bi Bi mechanism of catalysis by Saccharomyces cerevisiae myristoyl-CoA: Protein N-myristoyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9732–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dian, C.; Perez-Dorado, I.; Riviere, F.; Asensio, T.; Legrand, P.; Ritzefeld, M.; Shen, M.; Cota, E.; Meinnel, T.; Tate, E.W.; et al. High-resolution snapshots of human N-myristoyltransferase in action illuminate a mechanism promoting N-terminal Lys and Gly myristoylation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Datzkiw, D.; Varma Shrivastav, S.; Shrivastav, A. In silico identification of microRNAs predicted to regulate N-myristoyltransferase and Methionine Aminopeptidase 2 functions in cancer and infectious diseases. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.; Suri, S.S.; Mohr, R.; Janardhan, K.S.; Sharma, R.K.; Singh, B. Expression and activity of N-myristoyltransferase in lung inflammation of cattle and its role in neutrophil apoptosis. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duronio, R.J.; Knoll, L.J.; Gordon, J.I. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae long chain fatty acyl:CoA synthetase gene (FAA1) and assessment of its role in protein Nmyristoylation. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udenwobele, D.I.; Su, R.C.; Good, S.V.; Ball, T.B.; Varma Shrivastav, S.; Shrivastav, A. Myristoylation: An Important Protein Modification in the Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, I.J.D.S.; Cavalcanti, M.A.T.; de Moura, R.O. Exploring N-myristoyltransferase as a promising drug target against parasitic neglected tropical diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 258, 115550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, J.K.; Johnson, R.L.; Weinberg, R.A.; Gordon, J.I. Comparison of myristoyl-CoA: Protein N-myristoyltransferases from three pathogenic fungi: Cryptococcus neoformans, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Candida albicans. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 2996–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlhinney, R.A.; McGlone, K.; Willis, A.C. Purification and partial sequencing ofmyristoyl-CoA: Protein N-myristoyltransferase from bovine brain. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, S.; Gribskov, M. Predicting N-terminal myristoylation sites in plant proteins. BMC Genom. 2004, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, B.D.; Li, Z.; Villemaine, E.; Poole, C.B.; Chapman, M.S.; Pollastri, M.P.; Wyatt, P.G.; Carlow, C.K. A target repurposing approach identifies N-myristoyltransferase as a new candidate drug target in filarial nematodes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Robinson, D.A.; Raimi, O.G.; Blair, D.E.; Harrison, J.R.; Lockhart, D.E.; Torrie, L.S.; Ruda, G.F.; Wyatt, P.G.; Gilbert, I.H.; et al. N-myristoyltransferase is a cell wall target in Aspergillus fumigatus. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpas-Lopez, V.; Moniz, S.; Thomas, M.; Wall, R.J.; Torrie, L.S.; Zander-Dinse, D.; Tinti, M.; Brand, S.; Stojanovski, L.; Manthri, S.; et al. Pharmacological Validation of NMyristoyltransferaseas a Drug Target in Leishmania donovani. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kiwado, A.; Tanikawa, A.; Kikkawa, Y.; Hosokawa, T.; Otsuka, A.; Luchi, Y.; Kobuchi, H.; Moriya, K. Identification and characterization of protein Nmyristoylation occurring on four human mitochondrial proteins, SAMM50, TOMM40, MIC19, and MIC25. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, R.A.; Gordge, P.C.; Miller, W.R. Expression of enzymes of covalent protein modification during regulated and dysregulated proliferation of mammary epithelial cells: PKA, PKC and NMT. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1999, 39, 175–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Weibin, R.; Jing, L.; Hua, X.; Jingan, W.; Yubao, G.; Jingguo, W. Biological control of phytopathogenic fungi by fatty acids. Mycopathologia 2008, 166, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farazi, T.A.; Waksman, G.; Gordon, J.I. The biology and enzymology of protein N-myristoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39501–39504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, V.; Gupta, A.K. Essential fatty acids as functional components of foods—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.D.J.M.; Franco, J.A.S.; Moreno, E.R.; Cansino, N.D.S.C.; Ortega, J.A.A.; Valencia, J.M.T. Effect on thermoultrasound on the antioxidant compounds and fatty acid profile of blackberry (Rubus fructicosus spp.) juice. Molecules 2016, 21, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, K.; Uchida, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Mizuki, T. Chemical synthesis and cytotoxicity of neo-glycolipids; rare sugar-glycerol-lipid compounds. Heliyon 2018, 4, 00861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, B.; Mourya, V.; Dhake, A. Design, synthesis, antibacterial, and QSAR studies of myristic acid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Merz, K., Jr. Prediction of aqueous solubility of a diverse set of compounds using quantitative structure-property relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.S.; Lu, T.; Knoll, L.J.; Katoh, A.; Rudnick, D.A.; Mehta, P.P.; Devadas, B.; Huhn, M.; Atwood, J.L.; Adams, S.P.; et al. The substrate specificity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae myristoyl-CoA: Protein N-myristoyltransferase. Analysis of myristic acid analogs containing oxygen, sulfur, double bonds, triple bonds, and/or an aromatic residue. J. Chern. 1991, 266, 8835–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.S.; Wood, D.C.; Mehta, P.P.; Wade, A.C.; Lu, T.; Gokel, G.W.; Gordon, J.I. Comparison of the acyl chain specificities of human myristoyl-CoA synthetase and human myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 4889–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Sanders, J.K.M. The nature of. pi.-.pi. Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 5525–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.; Brannigan, J.A.; Thinon, E.; Olaleye, T.O.; Serwa, R.; Lanzarone, S.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Tate, E.W.; Leatherbarrow, R.J. A fluorescence-based assay for N-myristoyltransferase activity. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, E.A.; Redinbo, M.R.; Perfect, J.R.; Poeta, M.D. New potential targets for antifungal development. Emerg. Ther. Target 2000, 4, 265–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.R.; Devadas, B.; Zupec, M.E.; Freeman, S.K.; Brown, D.L.; Lu, H.F.; Mehta, P.P.; Kishore, N.S.; McWherter, C.A.; Getman, D.P.; et al. Conformationally constrained [p-(x-aminoalkyl)phenacetyl]-l-seryl-l-lysyl dipeptide amides as potent peptidomimetic inhibitors of Candida albicans and human myristoyl–CoA:protein N-myristoyl transferase. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 1422–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogabe, S.; Masubuchi, M.; Sakata, K.; Fukami, T.A.; Morikami, K.; Shiratori, Y.; Ebiike, H.; Kawasaki, K.; Aoki, Y.; Shimma, N.; et al. Crystal structures of Candida albicans N-myristoyltransferase with two distinct inhibitors. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 1119–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L., III; Vieth, M. Detailed Analysis of Grid-Based Molecular Docking: A Case Study of CDOCKER—A CHARMm-Based MD Docking Algorithm. J. Comp. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 4th ed.; CLSI Standard M27; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | Solubility | Hepatotoxicity | CYP2D6 | NTP_Rat | Ames Mutagen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | |||||
| 3k | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3l | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3m | 2 | NT | I | NC | NC | NM |
| 3n | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3o | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3p | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3q | 1 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3r | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3s | 1 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3t | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3u | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| 3v | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| Myristic acid | 2 | NT | NI | NC | NC | NM |
| Compound | Alog p | MW | HBA | HBD | Rat Oral Dose | Rat Carcinogenic Potency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD50 (g/kg_body_weight) | TD50 (mg/kg_body_weight/day) | |||||
| 3k | 7.12 | 317.50 | 2 | 1 | 14.98 | 886.91 |
| 3l | 6.96 | 347.53 | 3 | 1 | 8.07 | 887.65 |
| 3m | 6.91 | 309.53 | 2 | 1 | 11.63 | 04.67 |
| 3n | 4.95 | 297.47 | 3 | 0 | 9.63 | 49.60 |
| 3o | 6.84 | 317.50 | 2 | 0 | 2.58 | 205.15 |
| 3p | 6.63 | 303.48 | 2 | 1 | 8.96 | 2761.99 |
| 3q | 7.19 | 331.53 | 2 | 0 | 7.68 | 777.07 |
| 3r | 6.84 | 321.47 | 2 | 1 | 4.90 | 304.41 |
| 3s | 7.57 | 371.48 | 2 | 1 | 6.15 | 289.64 |
| 3t | 6.39 | 319.48 | 3 | 2 | 8.03 | 2336.46 |
| 3u | 6.02 | 304.47 | 3 | 1 | 4.31 | 753.33 |
| 3v | 5.91 | 324.52 | 3 | 1 | 6.04 | 400.96 |
| Myristic acid | 5.48 | 228.371 | 2 | 1 | 5.97 | 233.87 |
| Compound | CDOCKER Interaction Energy |
|---|---|
| 3k | 48.98 |
| 3l | 44.81 |
| 3m | 45.14 |
| 3n | 48.09 |
| 3o | 45.52 |
| 3p | 47.63 |
| 3q | 42.76 |
| 3r | 48.88 |
| 3s | 41.78 |
| 3t | 44.16 |
| 3u | 50.34 |
| 3v | 41.34 |
| Myristic acid | 36.76 |
| Sl. No | Compound Name | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3k | 1.293 |
| 2 | 3l | >1.500 |
| 3 | 3m | 0.863 |
| 4 | 3n | >1.500 |
| 5 | 3o | >1.500 |
| 6 | 3p | >1.500 |
| 7 | 3q | >1.500 |
| 8 | 3r | 1.464 |
| 9 | 3s | >1.500 |
| 10 | 3t | 1.003 |
| 11 | 3u | 0.835 |
| 12 | 3v | >1.500 |
| Myristic acid | - | 4.213 |
 | |||
| Compounds | R | C. albicans | A. niger |
| 3k | 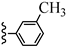 | 10.77 | 59.57 |
| 3l | 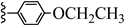 | 21.74 | 75.89 |
| 3m | 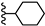 | 17.31 | 14.68 |
| 3n | 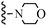 | 27.61 | 31.44 |
| 3o | 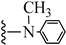 | 17.37 | 94.15 |
| 3p | 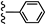 | 15.20 | 24.75 |
| 3q | 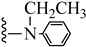 | 28.40 | 28.54 |
| 3r |  | 11.89 | 15.42 |
| 3s | 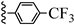 | 38.78 | 34.30 |
| 3t | 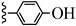 | 12.95 | 17.41 |
| 3u | 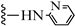 | 10.62 | 14.38 |
| 3v | 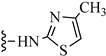 | 32.38 | 22.15 |
| FLZ | - | 17.76 | 16.30 |
| Compound | Chemical Structure | M.Formula | Mol.wt | RF Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3k | 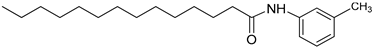 | C21H35NO | 318.27 | 0.59 |
| 3l | 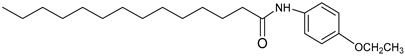 | C22H37NO2 | 348.53 | 0.53 |
| 3m | 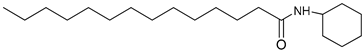 | C20H39NO | 310.36 | 0.44 |
| 3n | 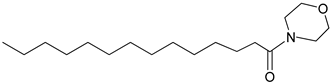 | C18H35NO2 | 298.32 | 0.40 |
| 3o | 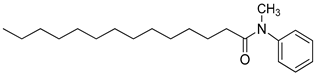 | C21H35NO | 318.51 | 0.42 |
| 3p | 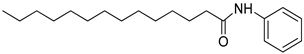 | C20H33NO | 304.31 | 0.41 |
| 3q | 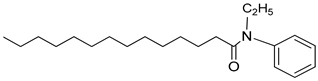 | C22H37NO | 332.34 | 0.51 |
| 3r | 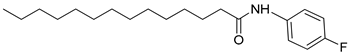 | C20H32FNO | 322.31 | 0.54 |
| 3s | 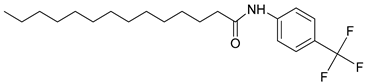 | C21H32F3NO | 370.35 | 0.51 |
| 3t | 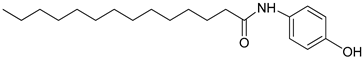 | C20H33NO2 | 320.31 | 0.56 |
| 3u | 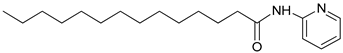 | C19H32N2O | 305.31 | 0.59 |
| 3v | 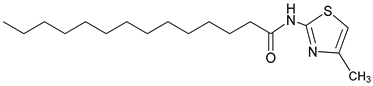 | C18H32N2OS | 325.27 | 0.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javid, S.; Ather, H.; Hani, U.; Siddiqua, A.; Asif Ansari, S.M.; Shanmugarajan, D.; Yogish Kumar, H.; Arivuselvam, R.; Purohit, M.N.; Kumar, B.R.P. Discovery of Novel Myristic Acid Derivatives as N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Analysis, Computational Studies and Antifungal Activity. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071167
Javid S, Ather H, Hani U, Siddiqua A, Asif Ansari SM, Shanmugarajan D, Yogish Kumar H, Arivuselvam R, Purohit MN, Kumar BRP. Discovery of Novel Myristic Acid Derivatives as N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Analysis, Computational Studies and Antifungal Activity. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071167
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavid, Saleem, Hissana Ather, Umme Hani, Ayesha Siddiqua, Shaik Mohammad Asif Ansari, Dhivya Shanmugarajan, Honnavalli Yogish Kumar, Rajaguru Arivuselvam, Madhusudan N. Purohit, and B. R. Prashantha Kumar. 2023. "Discovery of Novel Myristic Acid Derivatives as N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Analysis, Computational Studies and Antifungal Activity" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071167
APA StyleJavid, S., Ather, H., Hani, U., Siddiqua, A., Asif Ansari, S. M., Shanmugarajan, D., Yogish Kumar, H., Arivuselvam, R., Purohit, M. N., & Kumar, B. R. P. (2023). Discovery of Novel Myristic Acid Derivatives as N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Analysis, Computational Studies and Antifungal Activity. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071167





