Antibiotic, Heavy Metal, and Biocide Concentrations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water Body Exceed PNEC Limits: Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Selective Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
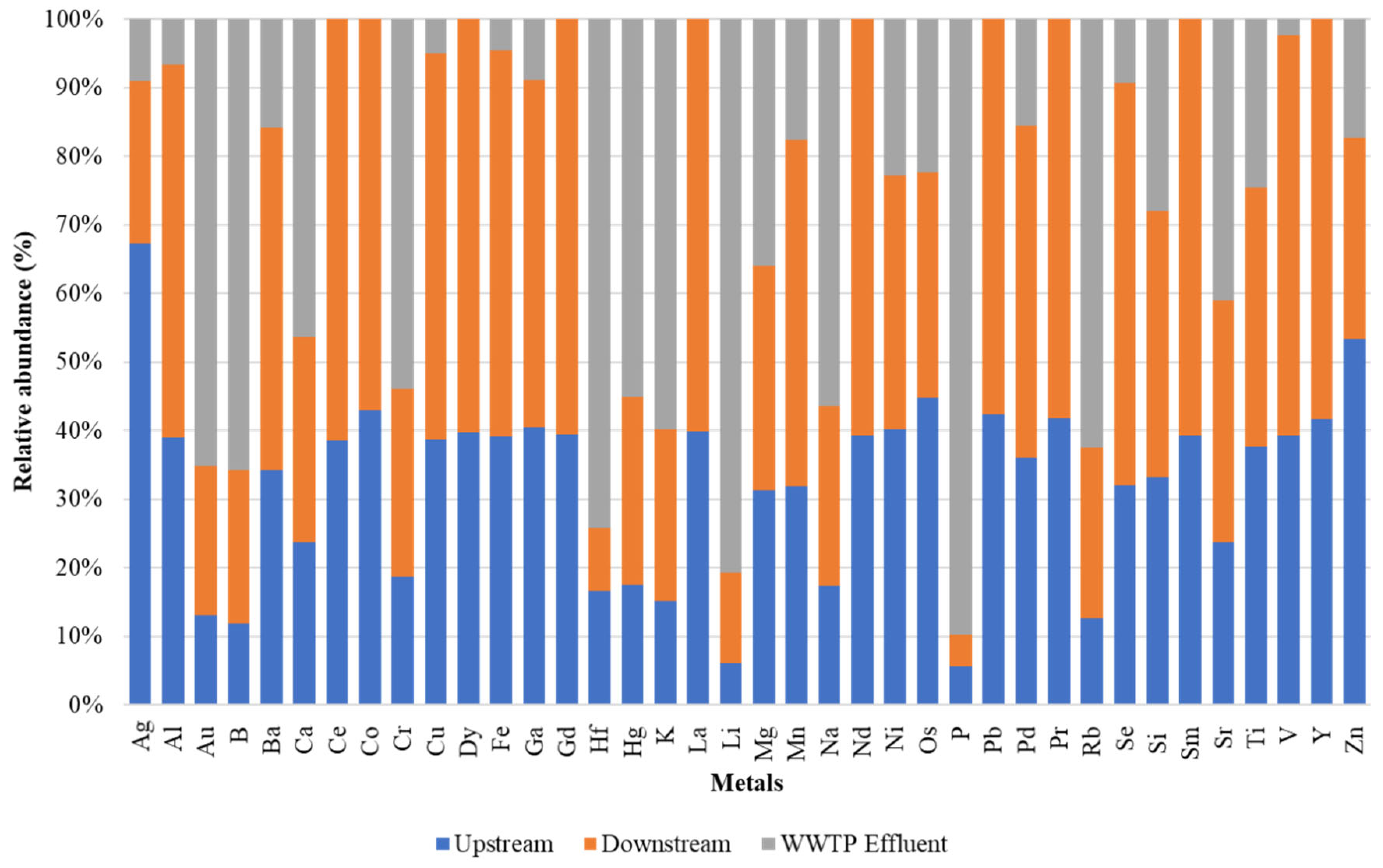
2.1. Distribution of Heavy Metals
2.2. Distribution of Antibiotics
2.3. Distribution of Biocides
3. Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metals
3.2. Antibiotics
3.3. Biocides
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area and Sampling Site
4.2. Sample Collection, Processing, and Analysis
4.3. Metal Analysis
4.3.1. Digestion of Water Samples for Metal Analysis
4.3.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) Analysis of Heavy Metals
4.3.3. Antibiotics and Biocides Analysis
4.3.4. Standard Preparation
4.3.5. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.3.6. Instrumental Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Concentrations of Antibiotics Predicted to Select for Resistant Bacteria: Proposed Limits for Environmental Regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. The Role of Natural Environments in the Evolution of Resistance Traits in Pathogenic Bacteria. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Antibiotics in the Environment. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebele, A.J.; Oluseyi, T.; Drage, D.S.; Harrad, S.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M. Occurrence, Seasonal Variation and Human Exposure to Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Surface Water, Groundwater and Drinking Water in Lagos State, Nigeria. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergie, A.A.; Leng, Y.; Wang, J. Antibiotics and Resistance Genes in Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Ecohealth 2019, 16, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandie, F.J.; Krauss, M.; Beckers, L.M.; Massei, R.; Fillinger, U.; Becker, J.; Liess, M.; Torto, B.; Brack, W. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Organic Micropollutants in Freshwater Systems within the Lake Victoria South Basin, Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S.; Chimuka, L. Analysis, Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in African Water Resources: A Current Status. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matongo, S.; Birungi, G.; Moodley, B.; Ndungu, P. Occurrence of Selected Pharmaceuticals in Water and Sediment of Umgeni River, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10298–10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, P.A.; Takada, H.; Correa, J.A.; El Saadi, K.; Koike, T.; Onwona-Agyeman, S.; Ofosu-Anim, J.; Sabi, E.B.; Wasonga, O.V.; Mghalu, J.M.; et al. Global Occurrence of Anti-Infectives in Contaminated Surface Waters: Impact of Income Inequality between Countries. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanu, D.; Styrishave, B.; Darko, G.; Weisser, J.J.; Abaidoo, R.C. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Water and Lettuce in Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslah, B.; Hapeshi, E.; Jrad, A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Hedhili, A. Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in Wastewater Samples in North-Eastern Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18226–18241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayiga, A.O.; Ipinmoroti, M.O.; Chirenje, T. Environmental Pollution in Africa; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 20, ISBN 1066801698944. [Google Scholar]
- Akele, M.L.; Kelderman, P.; Koning, C.W.; Irvine, K. Trace Metal Distributions in the Sediments of the Little Akaki River, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, C.; Dewaelé, D.; Cazier, F.; Diouf, A.; Ouddane, B. Assessment of Trace Metals Contamination Level, Bioavailability and Toxicity in Sediments from Dakar Coast and Saint Louis Estuary in Senegal, West Africa. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edokpayi, J.; Odiyo, J.; Popoola, O.; Msagati, T. Assessment of Trace Metals Contamination of Surface Water and Sediment: A Case Study of Mvudi River, South Africa. Sustainability 2016, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, M.A.; Adeniji, A.O.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Okoh, O.O. Heavy Metals in Wastewater and Sewage Sludge from Selected Municipal Treatment Plants in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Water 2020, 12, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 98/5/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 February 1998; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijn, J.; Hansen, B.; Johansson, S.; Luotamo, M.; Munn, S.; Musset, C.; Olsen, S.; Olsson, H.; Paya-Perez, A.; Pedersen, F.; et al. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment. Part 1. Part 2; EUR 20418 EN. 2002. JRC23785; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.F.; Ying, G.G.; Lai, H.J.; Chen, F.; Su, H.C.; Liu, Y.S.; Peng, F.Q.; Zhao, J.L. Determination of Biocides in Different Environmental Matrices by Use of Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, H.P. Triclosan: A Widely Used Biocide and Its Link to Antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 202, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; McLaughlin, B.A.; Pal, S.; Aizenman, E. In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Methylisothiazolinone, a Commonly Used Industrial and Household Biocide, Proceeds via a Zinc and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Dependent Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7408–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, L.J.; Liu, S.; Su, H.C.; et al. Evaluation of Triclosan and Triclocarban at River Basin Scale Using Monitoring and Modeling Tools: Implications for Controlling of Urban Domestic Sewage Discharge. Water Res. 2013, 47, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, J.; Peng, F.J.; Lai, H.J.; Pan, C.G. Triclosan as a Surrogate for Household Biocides: An Investigation into Biocides in Aquatic Environments of a Highly Urbanised Region. Water Res. 2014, 58, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuńez, O.; Moyano, E.; Galceran, M.T. Determination of Quaternary Ammonium Biocides by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1058, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaseri, H.; Forbes, P.B.C. A Review of Monitoring Methods for Triclosan and Its Occurrence in Aquatic Environments. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.G.; Fenton, O.; Cormican, M.; Peyton, D.P.; Ordsmith, N.; Kimber, K.; Morrison, L. Antimicrobial Compounds (Triclosan and Triclocarban) in Sewage Sludges, and Their Presence in Runoff Following Land Application. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juksu, K.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Yao, L.; Sarin, C.; Sreesai, S.; Klomjek, P.; Jiang, Y.X.; Ying, G.G. Occurrence, Fate and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Wastewater Treatment Plants and Aquatic Environments in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehutso, R.F.; Daso, A.P.; Okonkwo, J.O. Occurrence and Environmental Levels of Triclosan and Triclocarban in Selected Wastewater Treatment Plants in Gauteng Province, South Africa. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Brownawell, B.J. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds in Urban Estuarine Sediment Environments—A Class of Contaminants in Need of Increased Attention? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7561–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.R.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Chen, Z.F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G. Biocides in the Yangtze River of China: Spatiotemporal Distribution, Mass Load and Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, L.; Yang, Z. Four Typical Personal Care Products in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant in China: Occurrence, Removal Efficiency, Mass Loading and Emission. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Carballo, E.; González-Barreiro, C.; Sitka, A.; Kreuzinger, N.; Scharf, S.; Gans, O. Determination of Selected Quaternary Ammonium Compounds by Liquid Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry. Part II. Application to Sediment and Sludge Samples in Austria. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 146, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMR Industry Alliance List of Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs). AMR Industry Alliance Antibiotic Discharge Targets; AMR Industry Alliance: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- SANS South African National Standard (SANS). Drink. Water SANS 2015, 241, 1–2.
- Chetty, S.; Pillay, L. Assessing the Influence of Human Activities on River Health: A Case for Two South African Rivers with Differing Pollutant Sources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awofolu, O.R.; Mbolekwa, Z.; Mtshemla, V.; Fatoki, O.S. Levels of Trace Metals in Water and Sediment from Tyume River and Its Effects on an Irrigated Farmland. Water SA 2005, 31, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsoalo, M.R.; Godeto, T.W.; Magadzu, T.; Ambushe, A.A. Quantitative Speciation of Arsenic in Water and Sediment Samples from the Mokolo River in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 2761–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.C.T.; Sundarabarathy, T.V.; Sivananthawerl, T.; Kodithuwakku, S.P.; Edirisinghe, U. Arsenic and Cadmium Contamination in Water, Sediments and Fish Is a Consequence of Paddy Cultivation: Evidence of River Pollution in Sri Lanka. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tan, L.; Li, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liu, W. Sublethal Concentrations of Heavy Metals Cu2+ and Zn2+ Can Induce the Emergence of Bacterial Multidrug Resistance. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanauskas, R.; Glenn, T.C.; Jagoe, C.H.; Tuckfield, R.C.; Lindell, A.H.; King, C.J.; McArthur, J.V. Coselection for Microbial Resistance to Metals and Antibiotics in Freshwater Microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gu, A.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Sub-Lethal Concentrations of Heavy Metals Induce Antibiotic Resistance via Mutagenesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y. Bacterial Heavy-Metal and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in a Copper Tailing Dam Area in Northern China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food Animals and Antimicrobials: Impacts on Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; Mcardell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-kassinos, D. Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants as Hotspots for the Release of Antibiotics in the Environment: A Review. Water Res. 2012, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, A.L.; Bruce, I.B.; Aga, D.S. Evaluating the Vulnerability of Surface Waters to Antibiotic Contamination from Varying Wastewater Treatment Plant Discharges. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Mittal, A.K. Occurrences and Fate of Selected Human Antibiotics in Influents and Effluents of Sewage Treatment Plant and Effluent-Receiving River Yamuna in Delhi (India). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5336, Sulfapyridine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/sulfapyridine (accessed on 4 December 2021).
- Marks, S.L. Diarrhea. In Canine and Feline Gastroenterology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 99–108. ISBN 9781416036616. [Google Scholar]
- Ncube, S.; Nuapia, Y.B.; Chimuka, L.; Madikizela, L.M.; Etale, A. Trace Detection and Quantitation of Antibiotics in a South African Stream Receiving Wastewater Effluents and Municipal Dumpsite Leachates. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 733065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekadu, S.; Alemayehu, E.; Dewil, R.; Van der Bruggen, B. Pharmaceuticals in Freshwater Aquatic Environments: A Comparison of the African and European Challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K’oreje, K.O.; Okoth, M.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence and Treatment of Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the African Aquatic Environment: Literature Review and a Look Ahead. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 254, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics South Africa (Stats SA). Statistical Release P0302: Mid-Year Population Estimates 2021 (Embargoed until 19th July 2010 10:00); Statistics South Africa: Pretoria, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Agunbiade, F.O.; Moodley, B. Occurrence and Distribution Pattern of Acidic Pharmaceuticals in Surface Water, Wastewater, and Sediment of the Msunduzi River, Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.; Petrie, B.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wolfaardt, G.M. The Fate of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs), Endocrine Disrupting Contaminants (EDCs), Metabolites and Illicit Drugs in a WWTW and Environmental Waters. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngumba, E.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of Selected Antibiotics and Antiretroviral Drugs in Nairobi River Basin, Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K’oreje, K.O.; Vergeynst, L.; Ombaka, D.; De Wispelaere, P.; Okoth, M.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence Patterns of Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater, Surface Water and Groundwater of Nairobi and Kisumu City, Kenya. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairigo, P.; Ngumba, E.; Sundberg, L.R.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Risk of Antibiotic Resistance Evolution in Selected Kenyan Wastewaters, Surface Waters and Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrani, L.; Mehri, I.; Reyns, T.; Anthonissen, R.; Verschaeve, L.; Khalifa, A.B.H.; Van Loco, J.; Abdenaceur, H.; Mansour, H. Ben UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Antibiotics in Pharmaceutical Effluent in Tunisia: Ecotoxicological Impact and Multi-Resistant Bacteria Dissemination. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCENIHR (Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks). Assessment of the Antibiotic Resistance Effects of Biocides. Environment 2009, 68, 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Javaherdashti, R.; Akvan, F. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC). In Failure Modes, Effects and Causes of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 43–104. ISBN 9780128184486. [Google Scholar]
- Ceng, G.S. Water and Effluents. In Plant Engineer’s Reference Book; Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd.: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ünal, H. Antibiofilm Coatings. In Handbook of Antimicrobial Coatings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 301–319. ISBN 9780128119822. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Seo, M.; Na, M.; Kim, J. Investigation on Combined Inhalation Exposure Scenarios to Biocidal Mixtures: Biocidal and Household Chemical Products in South Korea. Toxics 2021, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Furlong, E.T. Identification of Alkyl Dimethylbenzylammonium Surfactants in Water Samples by Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Ion Trap LC/MS and LC/MS/MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2583–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowska, E.; Polkowska, Z.; Namieśnik, J. A Solid Phase Extraction-Ion Chromatography with Conductivity Detection Procedure for Determining Cationic Surfactants in Surface Water Samples. Talanta 2013, 116, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendonk, T.U.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Kassinos, D.F.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Huovinen, P.; Stefani, S.; Schwartz, T.; et al. Tackling Antibiotic Resistance: The Environmental Framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuzinger, N.; Fuerhacker, M.; Scharf, S.; Uhl, M.; Gans, O.; Grillitsch, B. Methodological Approach towards the Environmental Significance of Uncharacterized Substances—Quaternary Ammonium Compounds as an Example. Desalination 2007, 215, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.A.d.O.; Vianna, M.F.; Nishino, L.K.; Lazarini, P.R. Vestibular Disorders in Bell’s Palsy: A Prospective Study. Rev. Laryngol. Otol. Rhinol. 2015, 136, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS Chemical Registration in South Africa, Hazardous Substances Act, GHS. Available online: https://csra.freyrsolutions.com/chemical-regulatory-services-in-south-africa (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Wong, P.H.P.; von Krosigk, M.; Roscoe, D.L.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Yousefi, M.; Bowie, W.R. Antimicrobial Co-Resistance Patterns of Gram-Negative Bacilli Isolated from Bloodstream Infections: A Longitudinal Epidemiological Study from 2002–2011. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colclough, A.; Corander, J.; Sheppard, S.K.; Bayliss, S.C.; Vos, M. Patterns of Cross-Resistance and Collateral Sensitivity between Clinical Antibiotics and Natural Antimicrobials. Evol. Appl. 2019, 12, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. The Role of the Food Chain in the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR); Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780323417372. [Google Scholar]
- Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants: Microbial Adaptation, Degradation and Ecology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Cay, P.H.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A.; Fleming, G.T.A. Effect of Subinhibitory Concentrations of Benzalkonium Chloride on the Competitiveness of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Grown in Continuous Culture. Microbiology 2010, 156, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemical Agency (ECHA). Guidance on the Biocidal Products Regulation: Volume I: Identity of the Active Substance/Physico-Chemical Properties/Analytical Methodology—Parts A+B+C: Information Requirements, Evaluation and Assessment; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2022; Volume III, ISBN 9789290205029. [Google Scholar]
- Mbanga, J.; Abia, A.L.K.; Amoako, D.G.; Essack, S.Y. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment for Waterborne Pathogens in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Surface Water Body. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). METHOD 200.7—Determination of Elements and Trace Elements in Water and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emmission Spectropemtry; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume EPA/600/4. [Google Scholar]
- Abafe, O.A.; Späth, J.; Fick, J.; Jansson, S.; Buckley, C.; Stark, A.; Pietruschka, B.; Martincigh, B.S. LC-MS/MS Determination of Antiretroviral Drugs in Influents and Effluents from Wastewater Treatment Plants in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ANTIBIOTICS | PNEC (Resistance Selection) # | Mean Environmental Concentrations (µg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | Effluent | Downstream | ||
| Sulfadimidine | NA | 0.95 | 3.92 | 1.01 |
| Sulfamethazine | NA | 0.79 | 1.74 | 0.73 |
| Sulfamonomethoxine | NA | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.25 |
| Sulfamethoxazole * | 16 | 11.63 | 144.41 | 32.33 |
| Sulfapyridine | NA | 0.00 | 5.17 | 0.32 |
| Oxytetracycline * | 0.5 | 18.79 | 18.70 | 18.71 |
| Tetracycline * | 1 | 0.00 | 10.05 | 19.73 |
| Doxycycline * | 2 | 5.75 | 6.68 | 5.60 |
| Lasalocid A | NA | 3.42 | 1.69 | 3.34 |
| Monensin | NA | 0.80 | 1.81 | 1.28 |
| Lincomycin * | 2 | 3.91 | 7.95 | 7.81 |
| Penicillin | NA | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.55 |
| Amoxycillin * | 0.25 | 62.31 | 59.73 | 52.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chukwu, K.B.; Abafe, O.A.; Amoako, D.G.; Essack, S.Y.; Abia, A.L.K. Antibiotic, Heavy Metal, and Biocide Concentrations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water Body Exceed PNEC Limits: Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Selective Pressure. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071166
Chukwu KB, Abafe OA, Amoako DG, Essack SY, Abia ALK. Antibiotic, Heavy Metal, and Biocide Concentrations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water Body Exceed PNEC Limits: Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Selective Pressure. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071166
Chicago/Turabian StyleChukwu, Kelechi B., Ovokeroye A. Abafe, Daniel G. Amoako, Sabiha Y. Essack, and Akebe L. K. Abia. 2023. "Antibiotic, Heavy Metal, and Biocide Concentrations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water Body Exceed PNEC Limits: Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Selective Pressure" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071166
APA StyleChukwu, K. B., Abafe, O. A., Amoako, D. G., Essack, S. Y., & Abia, A. L. K. (2023). Antibiotic, Heavy Metal, and Biocide Concentrations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water Body Exceed PNEC Limits: Potential for Antimicrobial Resistance Selective Pressure. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071166








