Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
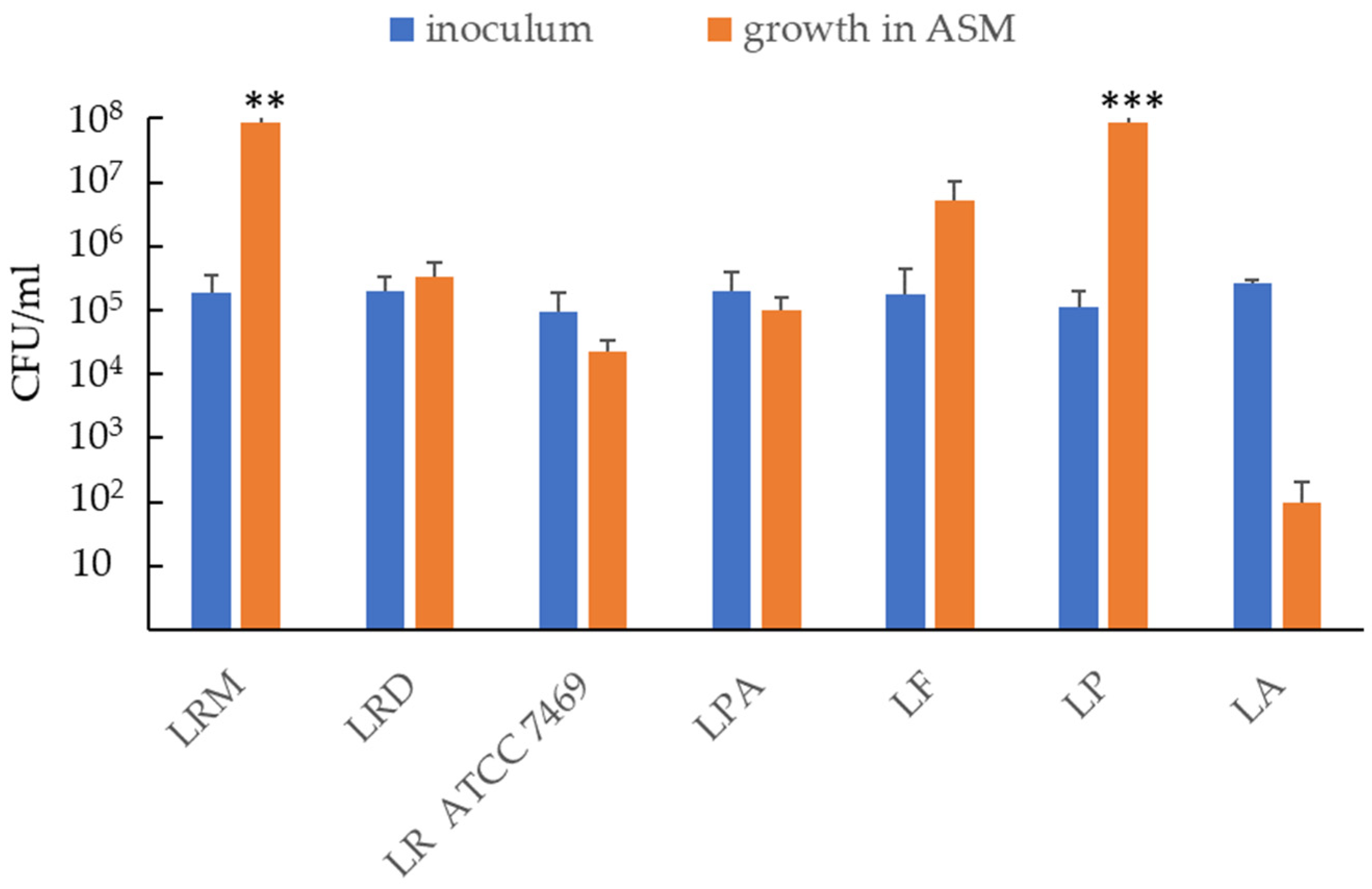
2.1. Ability of Probiotic Strains to Grow and/or Survive in Artificial Sputum Medium (ASM)
2.2. Anti-Bacterial Effect of Lactobacilli on Planktonic P. aeruginosa in ASM
2.3. Coaggregation Ability of LP and LRM vs. P. Aeruginosa
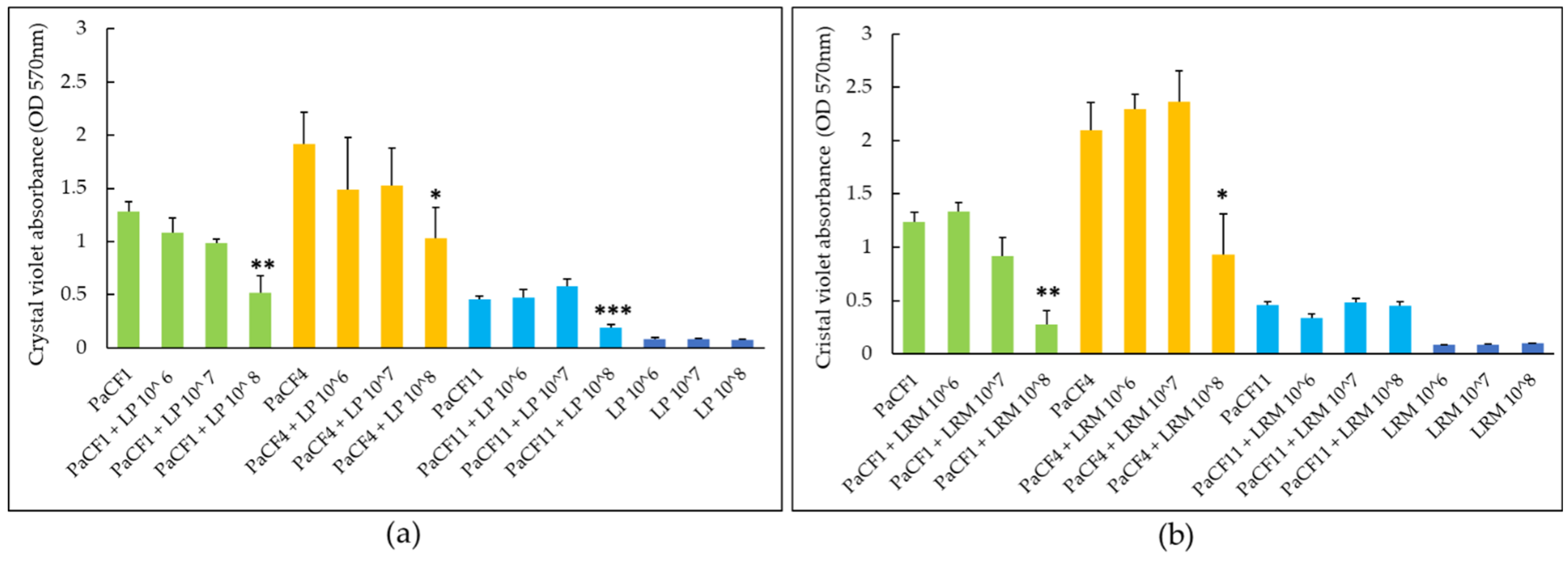
2.4. Effects of Lactobacilli on Biofilm Formation and Pre-Formed Biofilms of P. aeruginosa in ASM
2.5. Confocal Microscopy Analysis of P. aeruginosa Biofilm after Exposure to LP
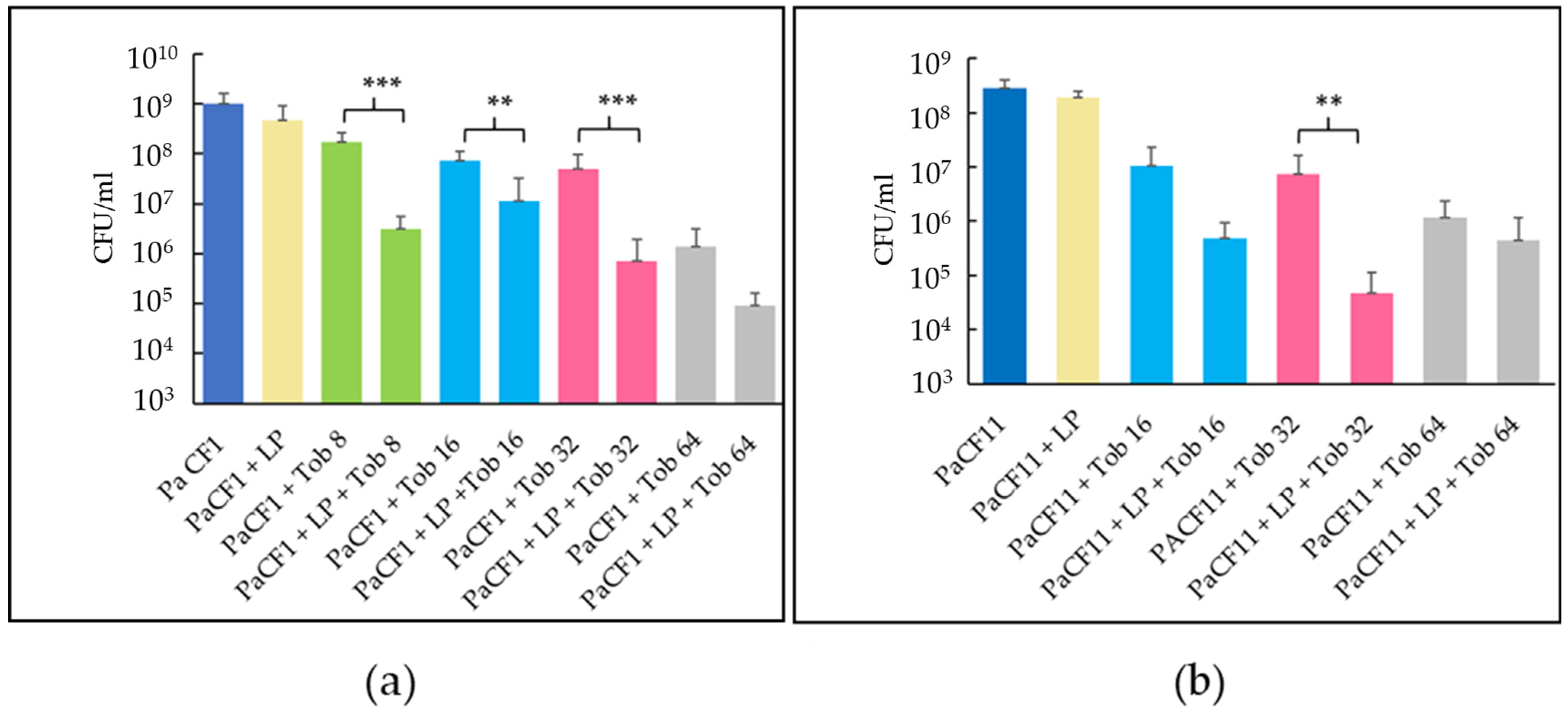
2.6. Activity of Tobramycin against Pre-Formed Biofilms of P. aeruginosa (PaCF1 and PaCF11 strains) Pre-Treated with LP
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
4.3. Preparation of Artificial Sputum Medium (ASM)
4.4. Evaluation of Lactobacilli Growth in ASM and Their Antibacterial Activity
4.5. Coaggregation Assay
4.6. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
4.7. Eradication of Preformed Biofilm Assay
4.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Analysis of P. aeruginosa Biofilm after Exposure to L. plantarum
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turcios, N.L. Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease: An Overview. Respir. Care 2020, 65, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the Natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, D.L.; Haynes, M.R.; Furlan, M.; Schmieder, R.; Lim, Y.W.; Rainey, P.B.; Rohwer, F.; Conrad, D. Spatial distribution of microbial communities in the cystic fibrosis lung. ISME J. 2012, 6, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Whitfield, G.B.; Kitao, T.; Ivey, M.L.; Davis, M.R., Jr.; Grahl, N.; Hogan, D.A.; Rahme, L.G.; Howell, P.L.; O’Toole, G.A.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate Overproduction Promotes Coexistence with Staphylococcus aureus in a Model of Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Infection. mBio 2017, 8, e00186-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, C.R.; Wolter, D.J.; Mishra, M.; Hayden, H.S.; Radey, M.C.; Merrihew, G.; MacCoss, M.J.; Burns, J.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Protein A Mediates Interspecies Interactions at the Cell Surface of Pseudomonas aruginosa. mBio 2016, 7, e00538-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Lin, J. Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infectious Biofilms: Challenges and Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 955286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.; Weldon, S.; Elborn, S.; Downey, D.G.; Taggart, C. The Effect of CFTR Modulators on Airway Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C.S.; Acosta, N.; Surette, M.G.; Parkins, M.D. Exploring the Cystic Fibrosis Lung Microbiome: Making the Most of a Sticky Situation. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, S13–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elborn, J.S.; Blasi, F.; Burgel, P.-R.; Peckham, D. Role of Inhaled Antibiotics in the Era of Highly Effective CFTR Modulators. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2023, 32, 220154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, G.G.; Ronan, N.J.; Mooney, D.; McGettigan, C.; Mullane, D.; NiChroinin, M.; Shanahan, F.; Murphy, D.M.; McCarthy, M.; McCarthy, Y.; et al. Extended-Culture and Culture-Independent Molecular Analysis of the Airway Microbiota in Cystic Fibrosis Following CFTR Modulation with Ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisert, K.B.; Heltshe, S.L.; Pope, C.; Jorth, P.; Wu, X.; Edwards, R.M.; Radey, M.; Accurso, F.J.; Wolter, D.J.; Cooke, G.; et al. Restoring Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Function Reduces Airway Bacteria and Inflammation in People with Cystic Fibrosis and Chronic Lung Infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batoni, G.; Maisetta, G.; Kaya, E.; Esin, S. Lung-Directed Bacteriotherapy in Cystic Fibrosis: Could It Be an Option? Antibiotics 2022, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Pradhan, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Ghosh, K. Current Status of Probiotic and Related Health Benefits. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, E.; Stevens, B.; An, M.; Lam, V.; Ainsworth, M.; Dihle, P.; Stearns, J.; Dombrowski, A.; Rego, D.; Segars, K. Utilizing Probiotics for the Prevention and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 689958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.; Bujanover, Y.; Yahav, Y.; Vilozni, D.; Fireman, E.; Efrati, O. Probiotic Supplementation Affects Pulmonary Exacerbations in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Pilot Study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, E.; Raia, V.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Volpicelli, M.; De Marco, G.; Maiuri, L.; Guarino, A. Effect of Lactobacillus GG Supplementation on Pulmonary Exacerbations in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Pilot Study. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.-A.; Mehdizadeh-Hakkak, A.; Kianifar, H.-R.; Hebrani, P.; Ahanchian, H.; Abbasnejad, E. Effects of Probiotics on Quality of Life in Children with Cystic Fibrosis; a Randomized Controlled Trial. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2013, 23, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Neri, L.D.C.L.; Taminato, M.; da Silva, L.V.R.F. Systematic Review of Probiotics for Cystic Fibrosis Patients: Moving Forward. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangous, M.S.; Alexandre, Y.; Hymery, N.; Gouriou, S.; Arzur, D.; Blay, G.L.; Berre, R.L. Lactobacilli Intra-Tracheal Administration Protects from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection in Mice—A Proof of Concept. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangous, M.-S.; Gosset, P.; Galakhoff, N.; Gouriou, S.; Guilloux, C.-A.; Payan, C.; Vallet, S.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Le Berre, R. Priming with Intranasal Lactobacilli Prevents Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Pneumonia in Mice. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangous, M.-S.; Lazzouni, I.; Alexandre, Y.; Gouriou, S.; Boisramé, S.; Vallet, S.; Le Bihan, J.; Ramel, S.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Le Berre, R. Prevalence and Dynamics of Lactobacillus sp. in the Lower Respiratory Tract of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamalifar, H.; Rahimi, H.; Samadi, N.; Shahverdi, A.; Sharifian, Z.; Hosseini, F.; Eslahi, H.; Fazeli, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Different Lactobacillus species against Multi- Drug Resistant Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2011, 3, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shokri, D.; Khorasgani, M.R.; Mohkam, M.; Fatemi, S.M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Taheri-Kafrani, A. The Inhibition Effect of Lactobacilli against Growth and Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, D.D.; Lünsdorf, H.; Lam, J.S.; Römling, U. Microcolony Formation: A Novel Biofilm Model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the Cystic Fibrosis Lung. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.L.; Aye, L.M.; Whiteley, M. Nutritional Cues Control Pseudomonas aeruginosa Multicellular Behavior in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8079–8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, J.A.; van der Mei, H.C.; van den Heuvel, E.; Busscher, H.J.; Reid, G. Adhesion Forces and Coaggregation between Vaginal Staphylococci and Lactobacilli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, F.J.; Wadsworth, M.P.; Hill, J.E. Evaluation and Optimization of Multiple Fluorophore Analysis of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 90, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory Effects of Probiotics During Pathogenic Infections with Emphasis on Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacterial Origin: Overview of Their Biology and Their Impact against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.D.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G.; Tagg, J.R. Bacteriocins of Gram-Positive Bacteria Having Activity Spectra Extending beyond Closely-Related Species. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.R.; Sardi, J.d.C.O.; Pitangui, N.d.S.; Roque, S.M.; Silva, A.C.B.d.; Rosalen, P.L. Probiotics as an Alternative Antimicrobial Therapy: Current Reality and Future Directions. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siempos, I.I.; Ntaidou, T.K.; Falagas, M.E. Impact of the Administration of Probiotics on the Incidence of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Lu, Z.; Dong, B.R.; Huang, C.Q.; Wu, T. Probiotics for Preventing Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 9, CD006895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Testa, I.; Mariotti Zani, E.; Cunico, D.; Torelli, L.; Grandinetti, R.; Fainardi, V.; Pisi, G.; Principi, N. Probiotics Administration in Cystic Fibrosis: What Is the Evidence? Nutrients 2022, 14, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyanathan, A.; Ramalhete, R.; Blunn, G.; Gibbs, H.; Pumilia, C.A.; Meckmongkol, T.; Lovejoy, J.; Coathup, M.J. Lactobacillus Cell-Free Supernatant as a Novel Bioagent and Biosurfactant against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Prevention and Treatment of Orthopedic Implant Infection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Hassanein, K.M.; Ahmed, A.S.; Gad, G.F.; Amin, M.M.; Hassanein, O.F. Antagonistic Activities of Cell-Free Supernatants of Lactobacilli Against Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, T.C.; Nair, N.U. Engineered Lactobacilli Display Anti-Biofilm and Growth Suppressing Activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abootaleb, M.; Mohammadi Bandari, N.; Arbab Soleimani, N. Interference of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum with Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the Infected Burns in Wistar Rats. J. Burn. Care Res. 2022, 43, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfallah, G.; Gartzen, R.; Möller, M.; Heine, E.; Lütticken, R. A New Approach to Harness Probiotics against Common Bacterial Skin Pathogens: Towards Living Antimicrobials. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Nanda, P.K.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Dhar, P.; Das, A.K. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bacteriocins: Novel Biotechnological Approach for Biopreservation of Meat and Meat Products. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Nieuwboer, M.; van Hemert, S.; Claassen, E.; de Vos, W.M. Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 and Its Host Interaction: A Dozen Years after the Genome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Baek, M.-G.; Chung, M.-J.; Lim, S.; Yi, H. Distribution of Bacteriocin Genes in the Lineages of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricourt, B.V.; Barefoot, S.F.; Testin, R.F.; Hayasaka, S.S. Detection and Activity of Plantaricin F an Antibacterial Substance from Lactobacillus plantarum BF001 Isolated from Processed Channel Catfish. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangler, J.R.; Dean, S.N.; Leary, D.H.; Walper, S.A. Response of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 to the Gram-Negative Pathogen-Associated Quorum Sensing Molecule N-3-Oxododecanoyl Homoserine Lactone. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlková, E.; Rada, V.; Smehilová, M.; Killer, J. Auto-Aggregation and Co-Aggregation Ability in Bifidobacteria and Clostridia. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2008, 53, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.J.; Yau, Y.C.W.; Park, S.; Eisha, S.; McDonald, N.; Parsek, M.R.; Howell, P.L.; Hoffman, L.R.; Nguyen, D.; DiGiandomenico, A.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregation and Psl Expression in Sputum Is Associated with Antibiotic Eradication Failure in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.J.; Jackson, L.; Cw Yau, Y.; Reichhardt, C.; Beaudoin, T.; Uwumarenogie, S.; Guttman, K.M.; Lynne Howell, P.; Parsek, M.R.; Hoffman, L.R.; et al. The Role of Psl in the Failure to Eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Meriluoto, J.; Salminen, S. Adhesion and Aggregation Properties of Probiotic and Pathogen Strains. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekhorst, J.; Helmer, Q.; Kleerebezem, M.; Siezen, R.J. Comparative Analysis of Proteins with a Mucus-Binding Domain Found Exclusively in Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microbiology 2006, 152, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, O.; Butnarasu, C.; Visentin, S.; Reimhult, E. Interplay between Biofilm Microenvironment and Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Chronic Infection. Biofilm 2022, 4, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Bioconversion Using Lactic Acid Bacteria: Ginsenosides, GABA, and Phenolic Compounds. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.; Hill, P.J.; Snarr, B.D.; Alnabelseya, N.; Pestrak, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Jennings, L.K.; Tam, J.; Melnyk, R.A.; Parsek, M.R.; et al. Exopolysaccharide Biosynthetic Glycoside Hydrolases Can Be Utilized to Disrupt and Prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Wood, T.K. Connecting Quorum Sensing, c-Di-GMP, Pel Polysaccharide, and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through Tyrosine Phosphatase TpbA (PA3885). PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, H.; Su, Y.; Cheng, D.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, Q.; Gao, J.; Tang, Y.; Bai, Q. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Honey and Lactobacillus plantarum on Pathogenic Bacteria and Their Promotion of Healing in Infected Wounds. Pathogens 2023, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Duff, A.J.A.; Bell, S.C.; Heijerman, H.G.M.; Munck, A.; Ratjen, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Southern, K.W.; Barben, J.; Flume, P.A.; et al. ECFS Best Practice Guidelines: The 2018 Revision. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, B.E.; Weber, A.; Berger, A.; Ramsey, B.; Smith, A.L. Macromolecular Mechanisms of Sputum Inhibition of Tobramycin Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelman, P.M.; Smith, A.L.; Levy, J.; Weber, A.; Ramsey, B.; Davis, R.L. Aminoglycoside Penetration, Inactivation, and Efficacy in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, W.-C.; Nilsson, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N.; Nielsen, T.E.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Extracellular DNA Shields against Aminoglycosides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, W.W.; Dorrington, S.M.; Slack, M.P.; Walmsley, H.L. Inhibition of Tobramycin Diffusion by Binding to Alginate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, K.M.; Gordon, V.D.; Murakami, K.; Borlee, B.R.; Wozniak, D.J.; Wong, G.C.L.; Parsek, M.R. The Pel Polysaccharide Can Serve a Structural and Protective Role in the Biofilm Matrix of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daboor, S.M.; Rohde, J.R.; Cheng, Z. Disruption of the Extracellular Polymeric Network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Alginate Lyase Enhances Pathogen Eradication by Antibiotics. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germoni, L.A.P.; Bremer, P.J.; Lamont, I.L. The Effect of Alginate Lyase on the Gentamicin Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mucoid Biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10932:2010; Determination of the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antibiotics Applicable to Bifidobacteria and Non-Enterococcal Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB)—Milk and Milk Products. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/46434.html (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Guidance on the Assessment of Bacterial Susceptibility to Antimicrobials of Human and Veterinary Importance. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Specific Probiotic Strains and Their Combinations Counteract Adhesion of Enterobacter Sakazakii to Intestinal Mucus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisetta, G.; Batoni, G.; Caboni, P.; Esin, S.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Zucca, P. Tannin Profile, Antioxidant Properties, and Antimicrobial Activity of Extracts from Two Mediterranean Species of Parasitic Plant Cytinus. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batoni, G.; Catelli, E.; Kaya, E.; Pompilio, A.; Bianchi, M.; Ghelardi, E.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Esin, S.; Maisetta, G. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071158
Batoni G, Catelli E, Kaya E, Pompilio A, Bianchi M, Ghelardi E, Di Bonaventura G, Esin S, Maisetta G. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071158
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatoni, Giovanna, Elisa Catelli, Esingül Kaya, Arianna Pompilio, Marta Bianchi, Emilia Ghelardi, Giovanni Di Bonaventura, Semih Esin, and Giuseppantonio Maisetta. 2023. "Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071158
APA StyleBatoni, G., Catelli, E., Kaya, E., Pompilio, A., Bianchi, M., Ghelardi, E., Di Bonaventura, G., Esin, S., & Maisetta, G. (2023). Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Lactobacilli Strains against Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Conditions Relevant to Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071158










