Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TEO Cytotoxicity on Cell Cultures
2.2. MDR Activity
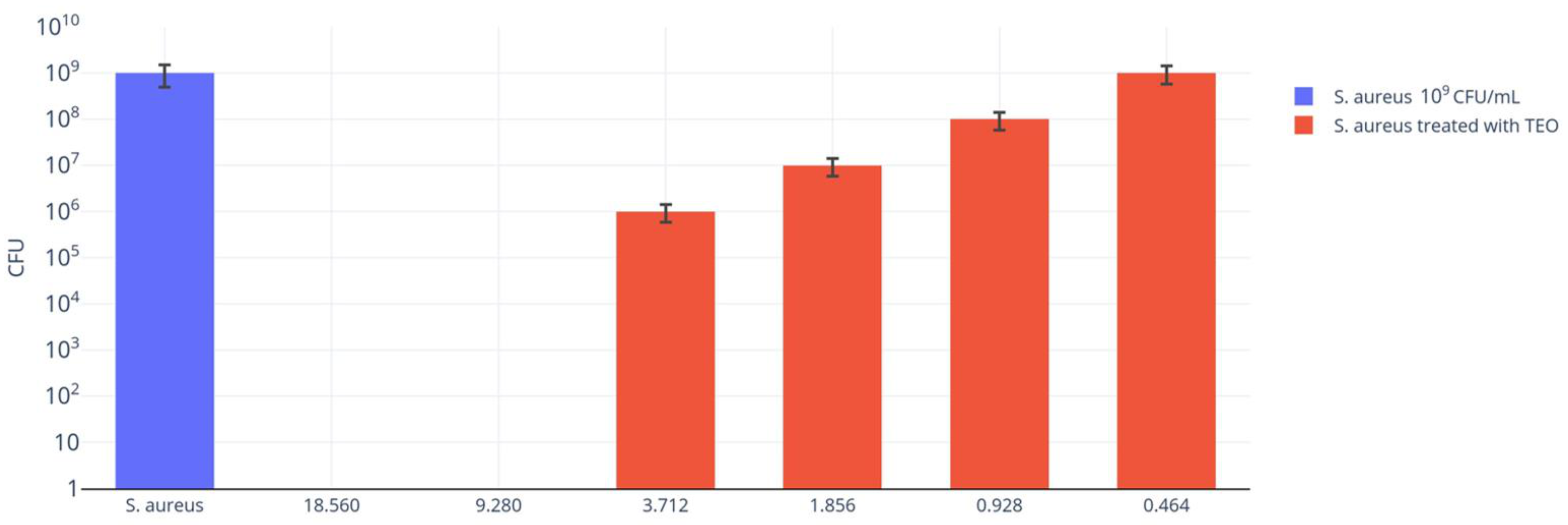
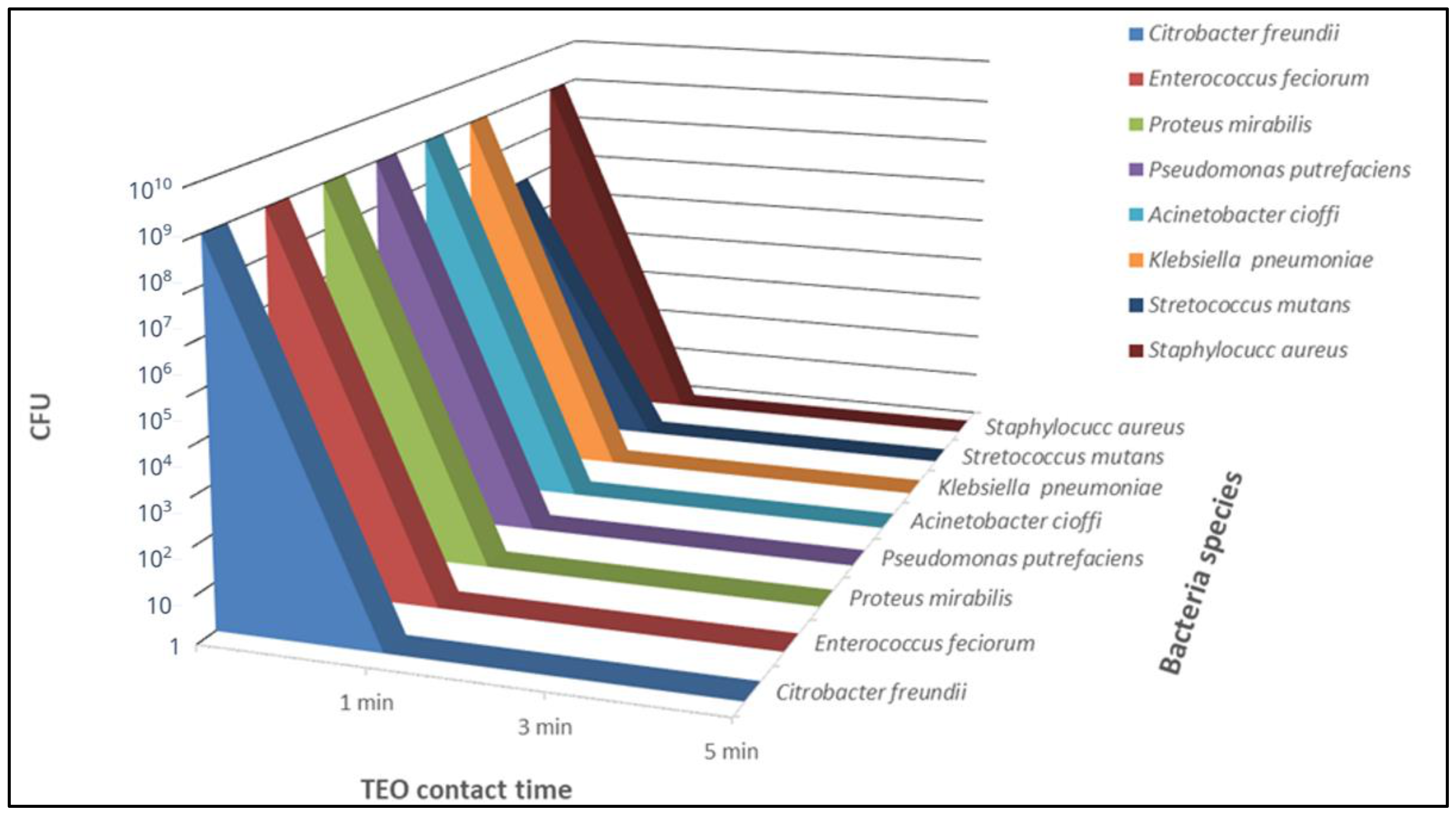
2.3. TEO Antibacterial Activity
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Thymus vulgaris EO
4.2. TEO Cytotoxicity on Cell Cultures
4.3. Bacterial Strains
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
4.5. TEO Antibacterial Activity
4.6. Data Analyses
4.7. TEO Antibacterial Activity in the Presence of Sheep Erythrocytes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMC | Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| ANOVA | One-way Analysis of Variance |
| CL | Cephalexin |
| CLSI | Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute |
| CN | Gentamicin |
| CRO | Ceftriaxone |
| CTX | Cefotaxime |
| DMEM | Dulbecco Minimal Essential Medium |
| DO | Docycycline |
| ENR | Enrofloxacyne |
| EO | Essential Oils |
| EUCAST | European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| GC/MS | Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrophotometry |
| I | Susceptible, Increased Exposure |
| MBC | Minimum Bactericidal Concentration |
| MDBK | Madin Darby Bovine Kidney |
| MDR | Multidrug-Resistant |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MOX | Moxyfloxacin |
| OT | Oxytetracycline |
| PCA | Plate Count Agar |
| R | Resistant |
| RT | Room Temperature |
| S | Sensitive |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SXT | Co-Trimoxazole |
| TEO | Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil |
| TSB | Tryptic Soy Broth |
References
- Couladis, M.; Tzakou, O.; Kujundzic, S.; Sokovic, M.; Mimica-Dukic, N. Chemical Analysis and Antifungal Activity of Thymus Striatus. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2004, 18, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Leone, P.; Solimando, A.G.; Fasano, R.; Malerba, E.; Prete, M.; Corrente, M.; Prati, C.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V. Antibiotics or No Antibiotics, That Is the Question: An Update on Efficient and Effective Use of Antibiotics in Dental Practice. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Latronico, F.; Greco, M.; D’Abramo, M.; Marinaro, M.; Mangini, F.; Corrente, M. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci Carriage in the Oral Cavity: A Study Conducted in Bari (Italy). Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils—Present Status and Future Perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, C.M.; Dutta, D.; Nguyen, A.N.T. Revisiting Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanistic Foundations to Evolutionary Outlook. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ashworth, A.J.; Willett, C.; Cook, K.; Upadhyay, A.; Owens, P.R.; Ricke, S.C.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Moore, P.A., Jr. Review of Antibiotic Resistance, Ecology, Dissemination, and Mitigation in U.S. Broiler Poultry Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarjani, K.M.; Skalicky, M. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus Aureus and Its In-Vitro Potential Inhibition Efficiency. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant Products as Antimicrobial Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Przychodna, M.; Sopata, S.; Bodalska, A.; Fecka, I. Thymol and Thyme Essential Oil—New Insights into Selected Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological Effects of Essential Oils—A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oils’ Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgano, M.; Capozza, P.; Pellegrini, F.; Cordisco, M.; Sposato, A.; Sblano, S.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Fracchiolla, G.; Corrente, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Evaluated In Vitro against Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, R.; Hussain, I.; Mahmood, S.; Akhtar, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oils Extracted from Some Indigenous Spices. Pak. Vet. J. 2013, 33, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Marković, T.; Marković, D.; Giweli, A.; Soković, M. Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antitumor Activity of Thymus serpyllum L., Thymus Algeriensis Boiss. and Reut and Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, E.V.; Valerio, F.; Gannouchi, A.; Trani, A.; Mezzapesa, G. Ecological and Plant Community Implication on Essential Oils Composition in Useful Wild Officinal Species: A Pilot Case Study in Apulia (Italy). Plants 2021, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Nisha, S.A.; Sakthivel, R.; Pandian, S.K. Eugenol (an Essential Oil of Clove) Acts as an Antibacterial Agent against Salmonella Typhi by Disrupting the Cellular Membrane. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, W.T.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Burt, S.A. Synergy between Essential Oil Components and Antibiotics: A Review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.J.; Park, S.M.; Yu, H.; Seo, G.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.A.; Rhee, M.S. Recent Advances in the Application of Antibacterial Complexes Using Essential Oils. Molecules 2020, 25, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinović, D.L.; Dimitrijević, M.V.; Mihajilov-Krstev, T.M.; Marković, M.S.; Ćirić, V.M. The Significance of Minor Components on the Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oil via Chemometrics. LWT 2021, 136, 110305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Lombardini, G.; Rizzo, S.; Scarafile, D.; Modesto, M.; Truzzi, E.; Benvenuti, S.; Elmi, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Fiorentini, L.; et al. Potential Applications of Essential Oils for Environmental Sanitization and Antimicrobial Treatment of Intensive Livestock Infections. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgano, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Fracchiolla, G.; Mrenoshki, D.; Zarea, A.A.K.; Bianco, A.; Del Sambro, L.; Capozzi, L.; Schiavone, A.; Saleh, M.S.; et al. Pilot Study on the Action of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil in Treating the Most Common Bacterial Contaminants and Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Derby in Poultry Litter. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikkema, J.; de Bont, J.A.; Poolman, B. Mechanisms of Membrane Toxicity of Hydrocarbons. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juven, B.J.; Kanner, J.; Schved, F.; Weisslowicz, H. Factors That Interact with the Antibacterial Action of Thyme Essential Oil and Its Active Constituents. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 76, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasqua, R.; Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P.; Ercolini, D.; Mauriello, G. Changes in the Proteome of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Thompson as Stress Adaptation to Sublethal Concentrations of Thymol. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.S.X.; Yiap, B.C.; Ping, H.C.; Lim, S.H.E. Essential Oils, A New Horizon in Combating Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance. Open Microbiol. J. 2014, 8, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norden, C.W.; Wentzel, H.; Keleti, E. Comparison of Techniques for Measurement of in Vitro Antibiotic Synergism. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 140, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, H.C.; Ellner, P.D. The Inhibitory Quotient. Bull. N. Y. Acad. Med. 1983, 59, 430–442. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.-Y.; Chang, W.-N.; Lu, C.-H.; Lin, M.-W.; Cheng, B.-C.; Chien, C.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Chang, H.-W. Clinical Features and in Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Community-Acquired Klebsiella Pneumoniae Meningitis in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimani, J.K.; Huang, S.; Lopatkin, A.J.; You, L. Drug Detoxification Dynamics Explain the Postantibiotic Effect. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.F.; Xu, J.-G.; Liu, J.-X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Q.P. Chemical Constituents, Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of the Essential Oil from Cinnamomum Cassia Bark against Four Food-Related Bacteria. Microbiology 2014, 83, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivey, J.M. The Postantibiotic Effect. Clin. Pharm. 1992, 11, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craig, W.A. The Role of Pharmacodynamics in Effective Treatment of Community-Acquired Pathogens. Adv. Stud. Med. 2002, 2, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Cozzolino, R.; Martignetti, A.; Malorni, L.; De Feo, V.; Cruz, A.G.; d’Acierno, A. Antibacterial Activity of Three Extra Virgin Olive Oils of the Campania Region, Southern Italy, Related to Their Polyphenol Content and Composition. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, H.; Gousia, P.; Economou, V.; Sakkas, V.; Petsios, S.; Papadopoulou, C. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Five Essential Oils on Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Clinical Isolates. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasooli, I.; Rezaei, M.B.; Allameh, A. Ultrastructural Studies on Antimicrobial Efficacy of Thyme Essential Oils on Listeria Monocytogenes. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 10, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faleiro, M.L.; Mendez-Vilas, A. The Mode of Antibacterial Action of Essential Oils. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technological Advances; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2011; pp. 1143–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Romero, J.C.; González-Ríos, H.; Borges, A.; Simões, M. Antibacterial Effects and Mode of Action of Selected Essential Oils Components against Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 795435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Sinniah, U.R. Antimicrobial Properties of Plant Essential Oils against Human Pathogens and Their Mode of Action: An Updated Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 3012462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.; Xu, J. Evaluation of Combined Antibacterial Effects of Eugenol, Cinnamaldehyde, Thymol, and Carvacrol against E. Coli with an Improved Method. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M379–M383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, J.R.; de Jesus Viegas, D.; Martins, A.P.R.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; Soares, C.P.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Jorge, A.O.C.; de Oliveira, L.D. Thymus vulgaris L. Extract Has Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in the Absence of Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2017, 82, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, A.; Reglero, G. Effects of Thyme Extract Oils (from Thymus vulgaris, Thymus Zygis, and Thymus Hyemalis) on Cytokine Production and Gene Expression of OxLDL-Stimulated THP-1-Macrophages. J. Obes. 2012, 2012, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iten, F.; Saller, R.; Abel, G.; Reichling, J. Additive Antimicrobial Effects of the Active Components of the Essential Oil of Thymus vulgaris—Chemotype Carvacrol. Planta Med. 2009, 75, PJ100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schött, G.; Liesegang, S.; Gaunitz, F.; Gleß, A.; Basche, S.; Hannig, C.; Speer, K. The Chemical Composition of the Pharmacologically Active Thymus Species, Its Antibacterial Activity against Streptococcus Mutans and the Antiadherent Effects of T. Vulgaris on the Bacterial Colonization of the in Situ Pellicle. Fitoterapia 2017, 121, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, H.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial Activity of Basil, Oregano, and Thyme Essential Oils. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Ramu, R.; Shirahatti, P.S.; Shivamallu, C.; Amachawadi, R.G. A Systematic Review on Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catella, C.; Camero, M.; Lucente, M.S.; Fracchiolla, G.; Sblano, S.; Tempesta, M.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, C.; Lanave, G. Virucidal and Antiviral Effects of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Feline Coronavirus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cell Growth and Survival. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.R.; Vadhana, P.; Bhardwaj, M.; Kumar, V. Comparative Antimicrobial Activity of Tea Tree Oil (Melaleuca Oil) and Common Topical Antimicrobials against Bacteria Associated with Wound and Topical Infections. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2016, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotic | Bacterial Strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. freundii | E. feciorum | P. mirabilis | P. putrefaciens | A. cioffi | K. pneumonie | |
| AMC | S | I | R | R | I | S |
| AMP | I | R | R | R | R | I |
| CN | S | S | I | I | I | I |
| OT | S | R | R | R | R | S |
| CRO | I | S | R | S | R | S |
| ENR | S | S | I | S | I | S |
| MOX | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| DO | S | I | R | R | I | S |
| CL | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| CTX | S | I | R | S | I | S |
| SXT | S | S | R | S | R | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galgano, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Mrenoshki, D.; Capozza, P.; Omar, A.H.; Salvaggiulo, A.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Tempesta, M.; Pratelli, A.; et al. Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071129
Galgano M, Pellegrini F, Mrenoshki D, Capozza P, Omar AH, Salvaggiulo A, Camero M, Lanave G, Tempesta M, Pratelli A, et al. Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071129
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalgano, Michela, Francesco Pellegrini, Daniela Mrenoshki, Paolo Capozza, Ahmed Hassan Omar, Anna Salvaggiulo, Michele Camero, Gianvito Lanave, Maria Tempesta, Annamaria Pratelli, and et al. 2023. "Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071129
APA StyleGalgano, M., Pellegrini, F., Mrenoshki, D., Capozza, P., Omar, A. H., Salvaggiulo, A., Camero, M., Lanave, G., Tempesta, M., Pratelli, A., & Buonavoglia, A. (2023). Assessing Contact Time and Concentration of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil on Antibacterial Efficacy In Vitro. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071129









