Equine Gram-Negative Oral Microbiota: An Antimicrobial Resistances Watcher?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Information and Bacterial Species Isolated
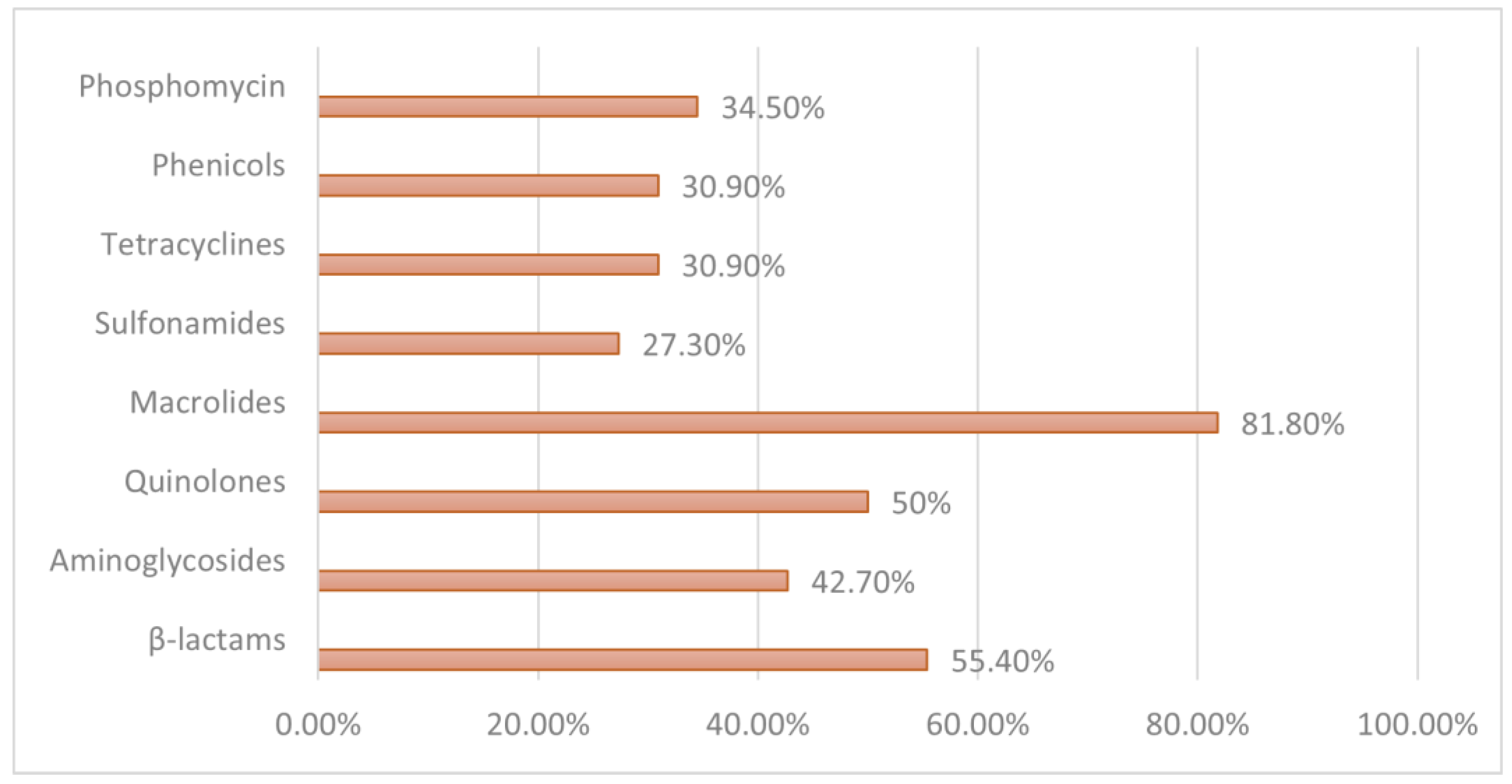
2.2. Antibiotic Resistance Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. Sample Processing
4.4. Species Identification
4.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, R.; Lappin, D.F.; Dixon, P.M.; Buijs, M.J.; Zaura, E.; Crielaard, W.; O’Donnell, L.; Bennett, D.; Brandt, B.W.; Riggio, M.P. The Microbiome Associated with Equine Periodontitis and Oral Health. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chan, Y.; You, M.; Lacap-Bugler, D.C.; Leung, W.K.; Watt, R.M. In-Depth Snapshot of the Equine Subgingival Microbiome. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 94, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, R.; Morris, T. That Horse Bit Me: Zoonotic Infections of Equines to Consider after Exposure through the Bite or the Oral/Nasal Secretions. J. Agromed. 2009, 14, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization and Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- World Organization for Animal Health-OIE and Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/global-initiatives/antimicrobial-resistance/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- One Health Commission. What Is One Health? Available online: https://www.onehealthcommission.org/en/why_one_health/what_is_one_health/ (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Emerging Threat to Public Health Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raidal, S.L. Antimicrobial Stewardship in Equine Practice. Aust. Vet. J. 2019, 97, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönker, N.S.; Fechner, K.; Wahed, A.A. El Horses as a Crucial Part of One Health. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, T.W.; Clegg, P.D.; Williams, N.J.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Horses: Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez–Narváez, S.; Berghaus, L.J.; Morris, E.R.A.; Willingham-Lane, J.M.; Slovis, N.M.; Giguere, S.; Cohen, N.D. A Common Practice of Widespread Antimicrobial Use in Horse Production Promotes Multi-Drug Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, O.M.; Gómez, P.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence, and Genetic Lineages of Staphylococci from Horses Destined for Human Consumption: High Detection of S. Aureus Isolates of Lineage ST1640 and Those Carrying the LukPQ Gene. Animals 2019, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnaiderman-Torban, A.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Dor, Z.; Paitan, Y.; Arielly, H.; Ahmad, W.A.; Kelmer, G.; Fulde, M.; Steinman, A. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Shedding in Farm Horses versus Hospitalized Horses: Prevalence and Risk Factors. Animals 2020, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddox, T.W.; Clegg, P.D.; Diggle, P.J.; Wedley, A.L.; Dawson, S.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Williams, N.J. Cross-Sectional Study of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria in Horses. Part 1: Prevalence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia Coli and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lagarde, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Arsenault, J. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Characterization of Multidrug Resistant and ESBL/AmpC Producing Escherichia Coli in Healthy Horses in Quebec, Canada, in 2015–2016. Animals 2020, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourély, C.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Haenni, M.; Gay, E.; Leblond, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Diseased Horses in France. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcewen, S.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isgren, C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Horses. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauter, A.; Epping, L.; Semmler, T.; Antao, E.-M.; Kannapin, D.; Stoeckle, S.D.; Gehlen, H.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Günther, S.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. The Gut Microbiome of Horses: Current Research on Equine Enteral Microbiota and Future Perspectives. Anim Microbiome 2019, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.K.; Hendrickson, D.A.; Rao, S.; Olea Popelka, F.; Bolte, D. The Bacteria Isolated from the Skin of 20 Horses at a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2010, 30, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraczkowska, K.; Zak-Bochenek, A.; Siwinska, N.; Rypula, K.; Ploneczka-Janeczko, K. Aerobic Commensal Conjunctival Microflora in Healthy Donkeys. Animals 2022, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, D.; Reardon, R.J.M.; McLACHLAN, G.; Glendinning, L.; Dixon, P.M. A Microbiome Analysis of Equine Peripheral Dental Caries Using next Generation Sequencing. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Holyoak, R.; Liu, B.; Li, J. Investigation of Oral Microbiome in Donkeys and the Effect of Dental Care on Oral Microbial Composition. Animals 2020, 10, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.; Bull, M.; Muscatello, G.; Chapman, B.; Coleman, N.V. The Equine Hindgut as a Reservoir of Mobile Genetic Elements and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Meghraoui, A.; Dodémont, M.; Heinrichs, A.; Denis, O.; Nonhoff, C.; Roisin, S. Bacteria from Animals as a Pool of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmawinata, E.; Uemura, R.; Sato, W.; Htun, M.T.; Sueyoshi, M. Multidrug-Resistant Esbl/Ampc-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from Healthy Thoroughbred Racehorses in Japan. Animals 2020, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Rosel, A.C.; Szostak, M.P.; Licka, T.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W.; Spergser, J. Broad-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Klebsiella spp. Isolated from Diseased Horses in Austria. Animals 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Gillis, D.C.; Gurrola-Rodriguez, T.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Murray, S.A.; Ohta, N.; Scott, H.M.; et al. The Occurrence and Characterization of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia Coli Isolated from Clinical Diagnostic Specimens of Equine Origin. Animals 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litterio, M.; Garrahan, J.P. Isolation of Serratia Rubidaea from a Mixed Infection after a Horse Bite. Rev. Argent Microbiol. 2012, 44, 272–274. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, E.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Veterinary Medicine: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, U.; von Lützau, K.; Schlattmann, A.; Rösler, U.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. Zoonotic Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms among Non-Hospitalized Horses from Germany. One Health 2019, 7, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). 2019. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/categorisation-antibiotics-european-union-answer-request-european-commission-updating-scientific_en.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2013).
- Wilson, W.D.; Magdesian, K.G. Antimicrobial Selection for the Equine Practitioner. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Equine Pract. 2021, 37, 461–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, J.d.C.; Saavedra, M.J.; da Silva, G.J.; Cotovio, M. Multidrug-Resistant Serratia Rubidaea Strains in the Oral Microbiota of Healthy Horses. Open Vet. J. 2021, 11, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léon, A.; Castagnet, S.; Maillard, K.; Paillot, R.; Giard, J.C. Evolution of in Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Equine Clinical Isolates in France between 2016 and 2019. Animals 2020, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, E.; Variatza, E.; Balcazar, J.L. The Role of Aquatic Ecosystems as Reservoirs of Antibiotic Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burow, E.; Käsbohrer, A. Risk Factors for Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia Coli in Pigs Receiving Oral Antimicrobial Treatment: A Systematic Review. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, D.E.; Mueller, M.K.; Debra, G.; Siebens, H.C.; Freeman, L.M. The Role of Veterinary Education in Safety Policies for Animal-Assisted Therapy and Activities in Hospitals and Nursing Homes. J. Vet. Med. Educ. 2017, 44, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White-Lewis, S.; Johnson, R.; Ye, S.; Russell, C. An Equine-Assisted Therapy Intervention to Improve Pain, Range of Motion, and Quality of Life in Adults and Older Adults with Arthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2019, 49, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, P.M.C.; de Kraker, M.; Graat, E.A.M.; van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; van Santen, M.G.; de Jong, M.C.M.; van Duijkeren, E.; de Greeff, S.C. Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Humans Living in Municipalities with High and Low Broiler Density. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E256–E259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Understanding the Mechanisms and Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S. Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzer, K.; Wong, N.; Thomas, J.; Talkington, K.; Jungman, E.; Coukell, A. Antimicrobial Drug Use in Food-Producing Animals and Associated Human Health Risks: What, and How Strong, Is the Evidence? BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, J.; Falgenhauer, L.; Domann, E.; Bauerfeind, R.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T. Multiresistant Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from Humans, Companion Animals and Horses in Central Hesse, Germany. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Isolates | n | β-Lactams | Aminoglycosides | Quinolones | Macrolides | Sulfonamides | Tetracyclines | Phenicols | Phosphomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeromonas salmonicida | 3 | 81.3% | 66.7% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 66.7% | 100% | 33.3% |
| Enterobacter cloacae complex | 5 | 51.3% | 80% | 30% | 80% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 0% |
| Escherichia coli | 15 | 38.3% | 51.7% | 20% | 93.3% | 6.7% | 0% | 13.3% | 13.3% |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 3 | 85.4% | 75% | 83.3% | 100% | 66,7% | 66.7% | 66.7% | 66.7% |
| Pantoea agglomerans | 5 | 46.3% | 10% | 75% | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 80% |
| Pantoea spp. | 2 | 84.4% | 50% | 100% | 50% | 50% | 100% | 100% | 50% |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 7 | 67.9% | 32.1% | 64.3% | 85.7% | 14.3% | 14.3% | 28.6% | 57.1% |
| Pseudomonas putida | 2 | 78.1% | 12.5% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Serratia rubidaea | 4 | 62.5% | 43.8% | 75% | 100% | 0% | 50% | 0% | 0% |
| Isolates | n | β-Lactams | Aminoglycosides | Quinolones | Macrolides | Sulfonamides | Tetracyclines | Phenicols | Phosphomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burkholderia gladioli | 1 | 87.5% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 66.7% | 100% | 0% |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 1 | 37.5% | 0% | 50% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Kluyvera intermedia | 1 | 50% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
| Pasteurella pneumotropica | 1 | 31.3% | 0% | 50% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0% |
| Pasteurella testadinis | 1 | 25% | 0% | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Pseudomonas paucimobilis | 1 | 81.3% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Serratia plymuthica | 1 | 56.3% | 50% | 50% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
| Shigella sonnei | 1 | 31.3%% | 25% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0% |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | 1 | 37.5% | 0% | 50% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pimenta, J.; Pinto, A.R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Cotovio, M. Equine Gram-Negative Oral Microbiota: An Antimicrobial Resistances Watcher? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040792
Pimenta J, Pinto AR, Saavedra MJ, Cotovio M. Equine Gram-Negative Oral Microbiota: An Antimicrobial Resistances Watcher? Antibiotics. 2023; 12(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040792
Chicago/Turabian StylePimenta, José, Ana Rita Pinto, Maria José Saavedra, and Mário Cotovio. 2023. "Equine Gram-Negative Oral Microbiota: An Antimicrobial Resistances Watcher?" Antibiotics 12, no. 4: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040792
APA StylePimenta, J., Pinto, A. R., Saavedra, M. J., & Cotovio, M. (2023). Equine Gram-Negative Oral Microbiota: An Antimicrobial Resistances Watcher? Antibiotics, 12(4), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040792






