Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Contribution of a Healthcare Data Warehouse to the Determination of a Toxic Concentration Threshold
Abstract
1. Introduction
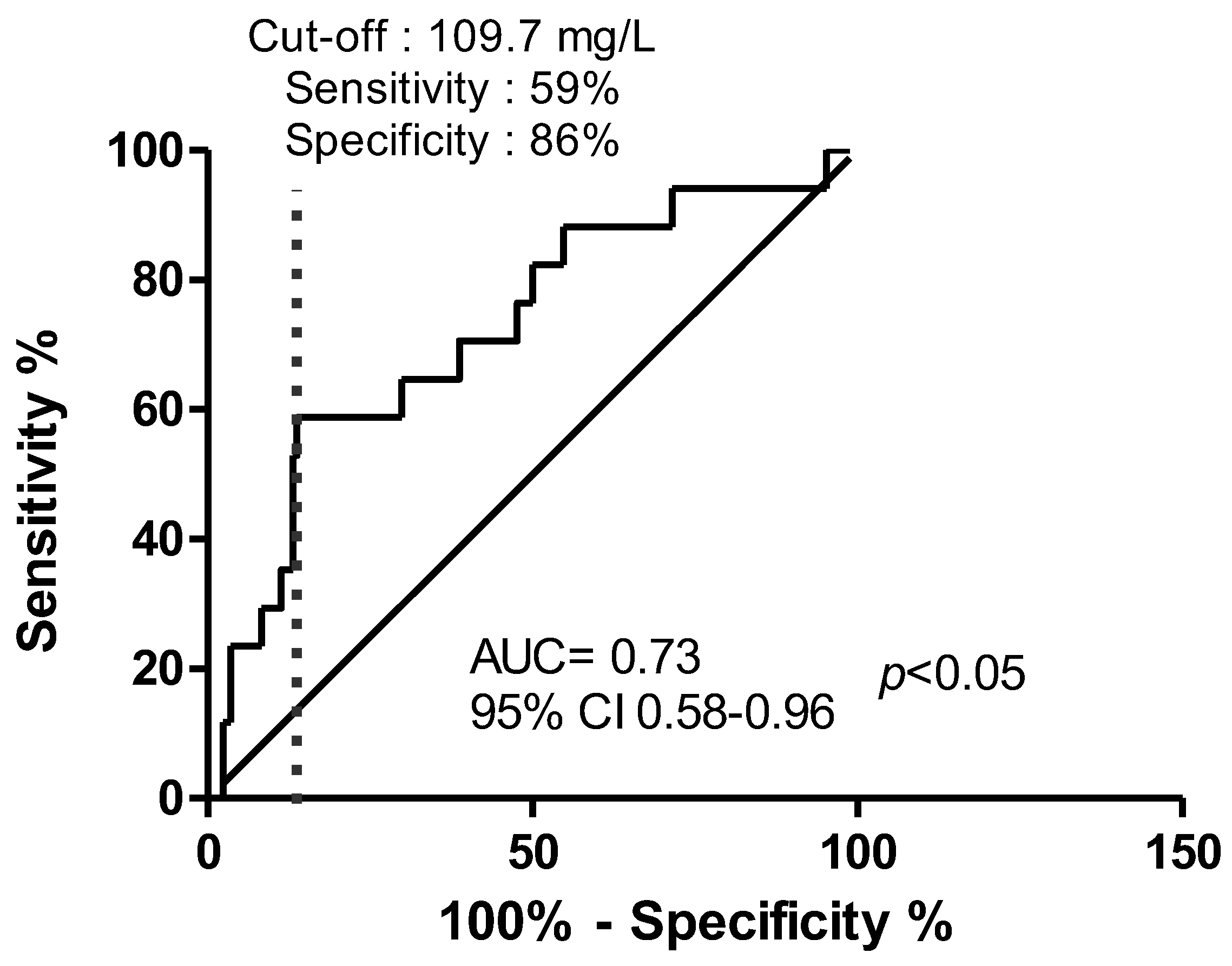
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, A.E.; Johnson, H.C.; Kollros, J.J. Penicillin Convulsions; the Convulsive Effects of Penicillin Applied to the Cerebral Cortex of Monkey and Man. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1945, 81, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roger, C.; Louart, B. Beta-Lactams Toxicity in the Intensive Care Unit: An Underestimated Collateral Damage? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-J. Cefepime-Induced Neurotoxicity. J. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarro, A.; Ammendola, D.; Zappala, M.; Grasso, S.; De Sarro, G.B. Relationship between Structure and Convulsant Properties of Some Beta-Lactam Antibiotics Following Intracerebroventricular Microinjection in Rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atli, O.; Demir-Ozkay, U.; Ilgin, S.; Aydin, T.H.; Akbulut, E.N.; Sener, E. Evidence for Neurotoxicity Associated with Amoxicillin in Juvenile Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhaumou, R.; Benaboud, S.; Bennis, Y.; Dahyot-Fizelier, C.; Dailly, E.; Gandia, P.; Goutelle, S.; Lefeuvre, S.; Mongardon, N.; Roger, C.; et al. Optimization of the Treatment with Beta-Lactam Antibiotics in Critically Ill Patients-Guidelines from the French Society of Pharmacology and Therapeutics (Société Française de Pharmacologie et Thérapeutique-SFPT) and the French Society of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine (Société Française d’Anesthésie et Réanimation-SFAR). Crit. Care 2019, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, S.; Buscher, H.; Marriott, D.; Gentili, S.; Sandaradura, I. Too Much of a Good Thing: A Retrospective Study of β-Lactam Concentration-Toxicity Relationships. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercheval, C.; Sadzot, B.; Maes, N.; Denooz, R.; Damas, P.; Frippiat, F. Continuous Infusion of Cefepime and Neurotoxicity: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwyler, T.; Lenggenhager, L.; Abbas, M.; Ing Lorenzini, K.; Hughes, S.; Huttner, B.; Karmime, A.; Uçkay, I.; von Dach, E.; Lescuyer, P.; et al. Cefepime Plasma Concentrations and Clinical Toxicity: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, E.F.; Webb, A.J.; Pais, G.M.; Rule, A.D.; Jannetto, P.J.; Scheetz, M.H. Setting the Beta-Lactam Therapeutic Range for Critically Ill Patients: Is There a Floor or Even a Ceiling? Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.M.; Hui, A.C.; Szeto, C.C. Neurotoxicity Induced by Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: From Bench to Bedside. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viloria-Alebesque, A.; Povar-Echeverría, M.; Bruscas-Alijarde, M.J.; Gracia-Gutiérrez, A.; Royo-Trallero, L.; Al-Cheikh-Felices, P. Myoclonus Induced by Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid. Epilepsy Behav. Rep. 2020, 14, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.; Frei, C.R. Delirium Associations with Antibiotics: A Pharmacovigilance Study of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Drugs Real. World Outcomes 2021, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgman, T.; Dasta, J.F.; Armstrong, D.K.; Visconti, J.A.; Reilley, T.E. Ampicillin-Associated Seizures. South Med. J. 1984, 77, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Canevini, M.P.; Principi, N. Complications Associated with Antibiotic Administration: Neurological Adverse Events and Interference with Antiepileptic Drugs. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, C.; Stirnemann, J.; Lescuyer, P.; Tonoli, D.; von Dach, E.; Huttner, A. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Outcomes in Severely Ill Patients Receiving Amoxicillin: A Single-Centre Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inácio, V.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, M.X. The Covariate-Adjusted ROC Curve: The Concept and Its Importance, Review of Inferential Methods, and a New Bayesian Estimator. Statist. Sci. 2022, 37, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, M.-C.; Tribut, O.; Tattevin, P.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Michelet, C.; Bentué-Ferrer, D. Simultaneous Determination of 12 Beta-Lactam Antibiotics in Human Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with UV Detection: Application to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4873–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
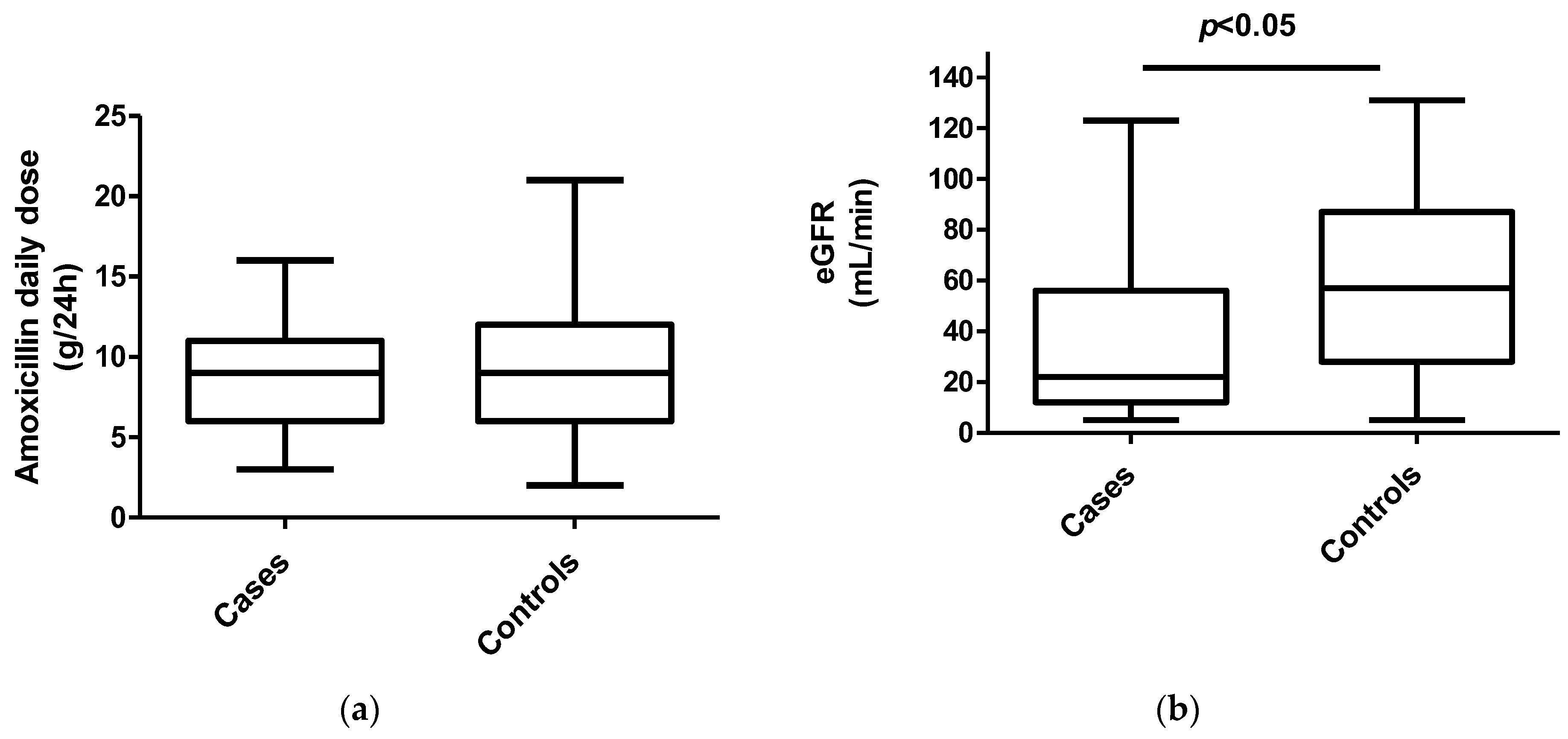


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lalanne, S.; Bouzillé, G.; Tron, C.; Revest, M.; Polard, E.; Bellissant, E.; Verdier, M.-C.; Lemaitre, F. Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Contribution of a Healthcare Data Warehouse to the Determination of a Toxic Concentration Threshold. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040680
Lalanne S, Bouzillé G, Tron C, Revest M, Polard E, Bellissant E, Verdier M-C, Lemaitre F. Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Contribution of a Healthcare Data Warehouse to the Determination of a Toxic Concentration Threshold. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(4):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040680
Chicago/Turabian StyleLalanne, Sébastien, Guillaume Bouzillé, Camille Tron, Matthieu Revest, Elisabeth Polard, Eric Bellissant, Marie-Clémence Verdier, and Florian Lemaitre. 2023. "Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Contribution of a Healthcare Data Warehouse to the Determination of a Toxic Concentration Threshold" Antibiotics 12, no. 4: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040680
APA StyleLalanne, S., Bouzillé, G., Tron, C., Revest, M., Polard, E., Bellissant, E., Verdier, M.-C., & Lemaitre, F. (2023). Amoxicillin-Induced Neurotoxicity: Contribution of a Healthcare Data Warehouse to the Determination of a Toxic Concentration Threshold. Antibiotics, 12(4), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040680





