Sulfonamidoboronic Acids as “Cross-Class” Inhibitors of an Expanded-Spectrum Class C Cephalosporinase, ADC-33, and a Class D Carbapenemase, OXA-24/40: Strategic Compound Design to Combat Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
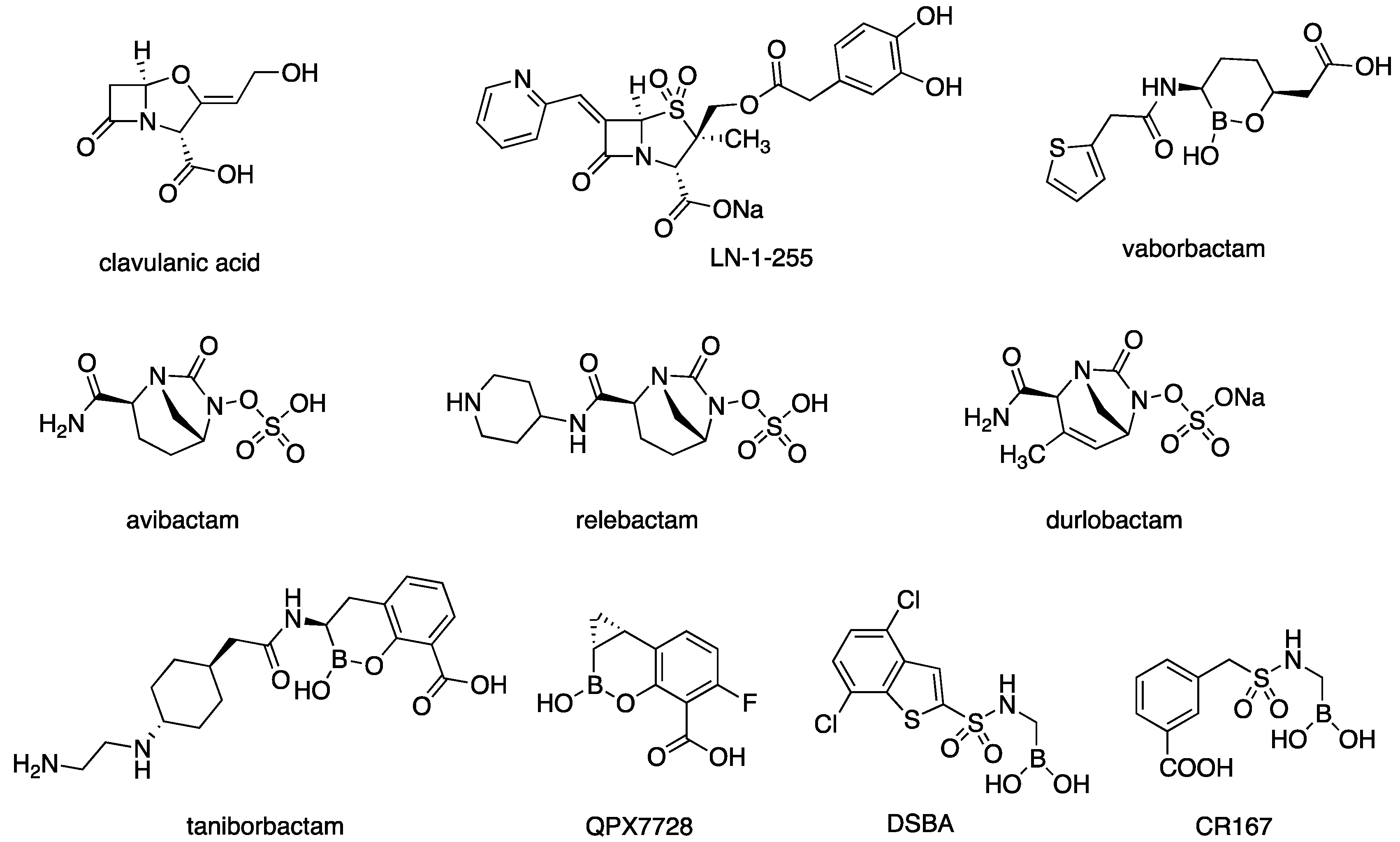
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CR167 as an Inhibitor of Class C and Class D β-Lactamases
- Kinetic assays
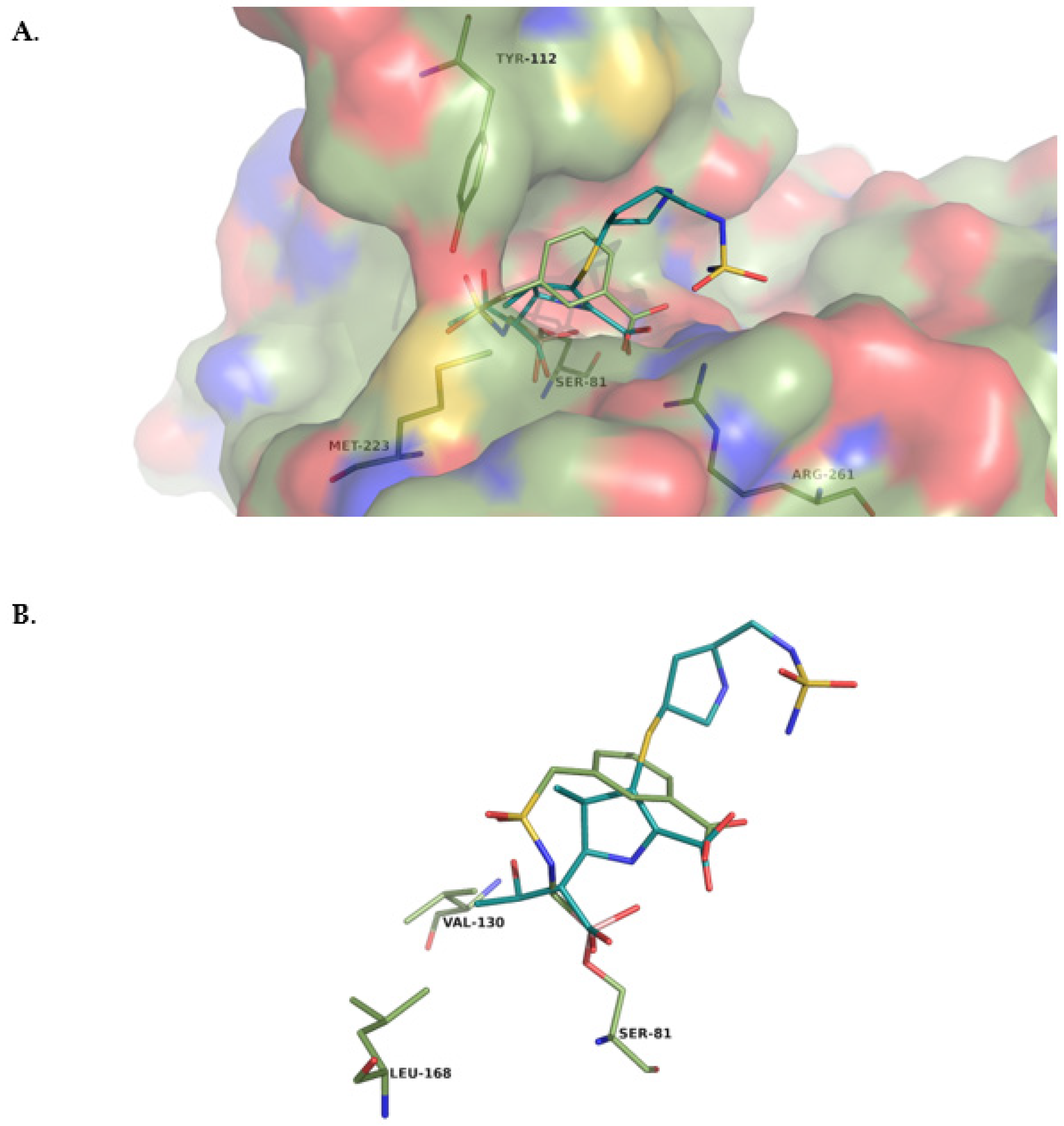
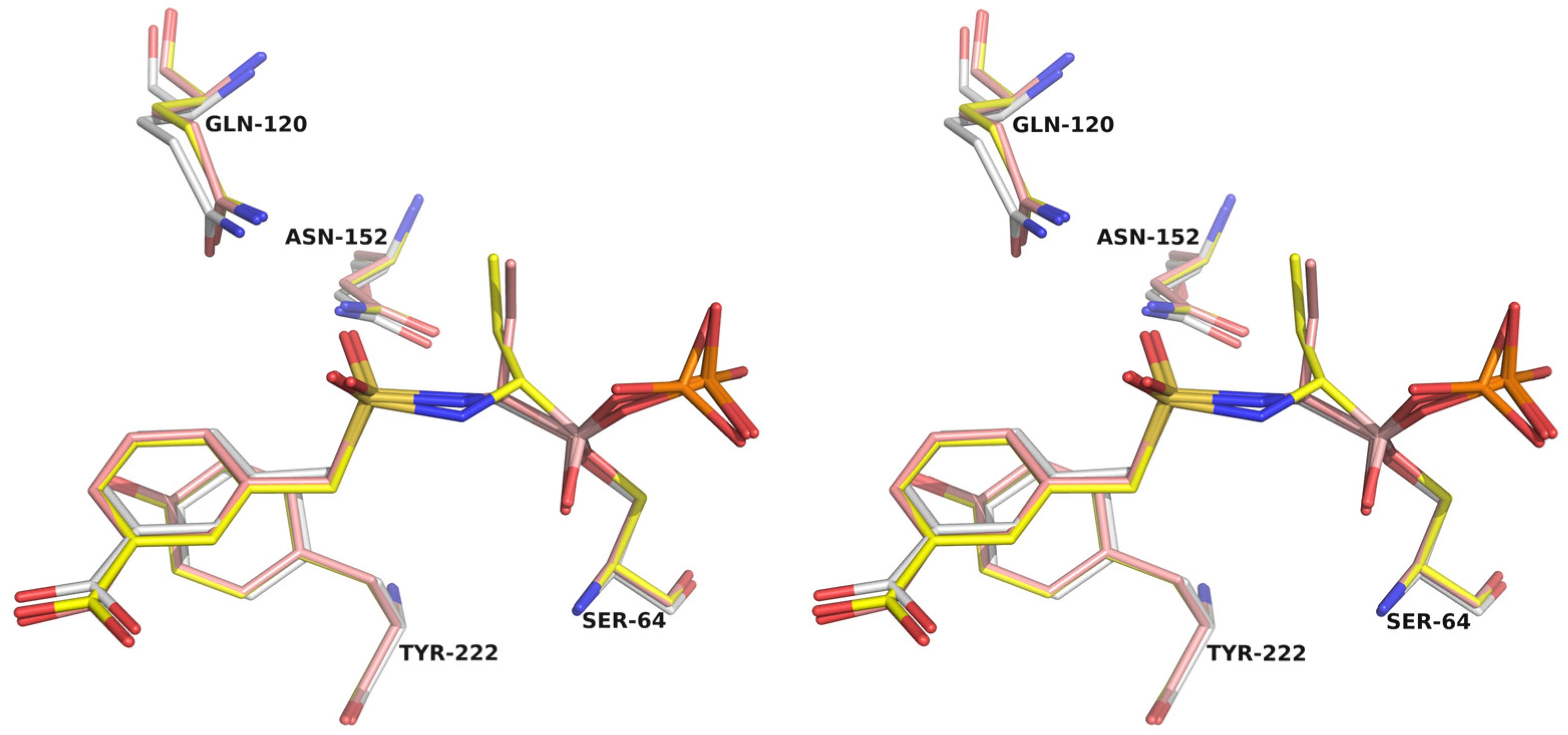
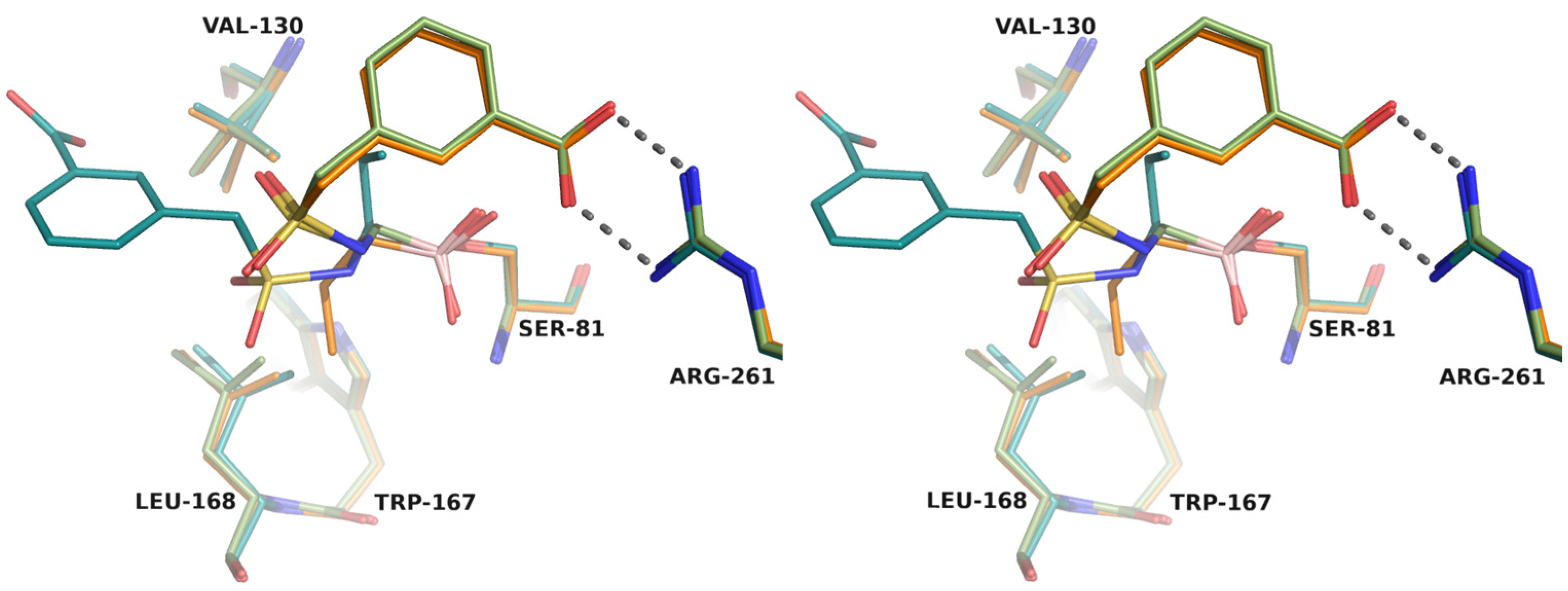
- Crystallographic structures
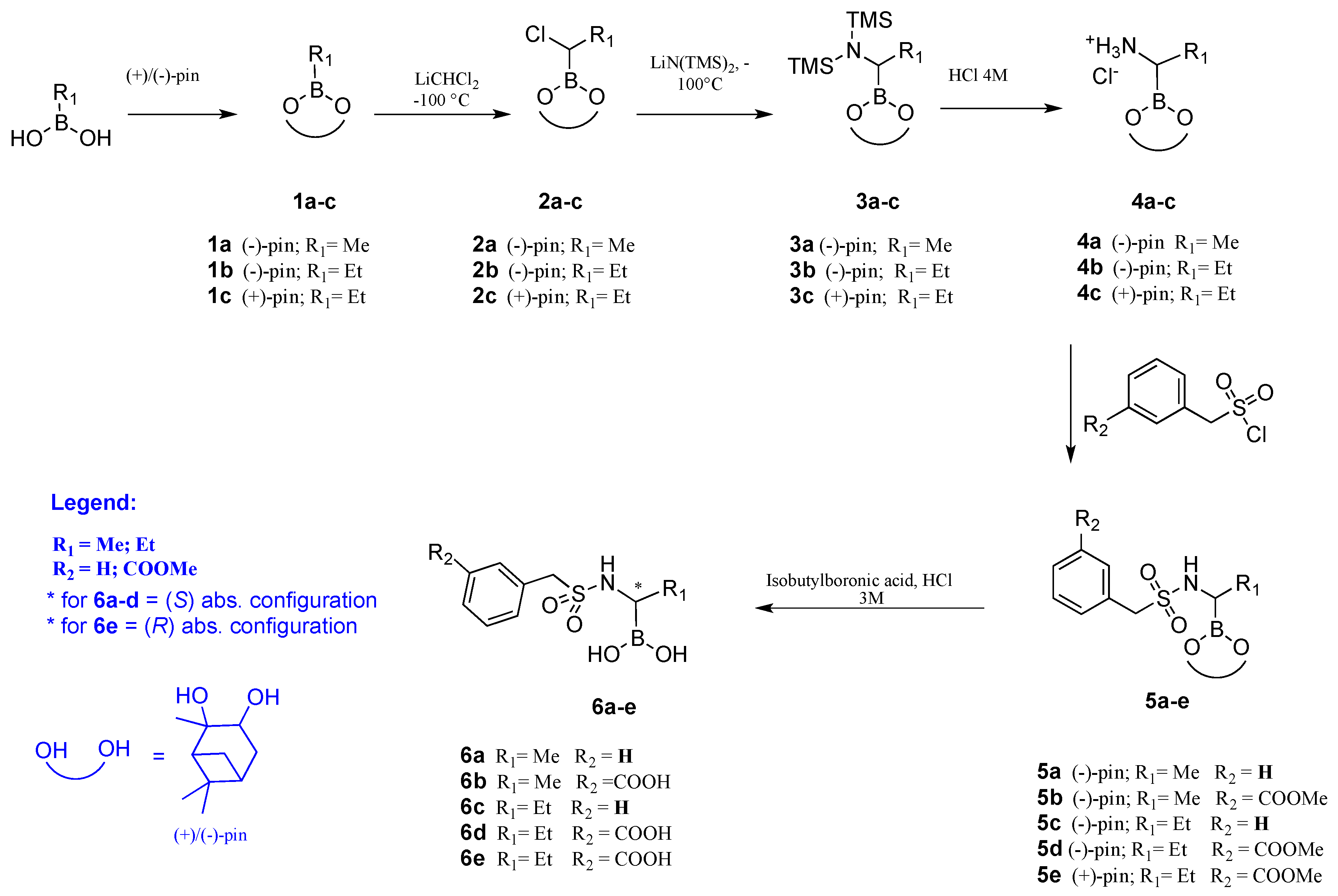
2.2. Chiral Analogues of CR167
- Synthesis
- Inhibition kinetics
- Structural analysis
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Expression, Purification, and Crystallization of ADC-33 and OXA-24/40
4.3. Structure Determination of β-Lactamase/BATSI Complexes
4.4. Determination of Ki Values
4.5. Plasmid Constructs in pBCSK-
4.6. Cloning of blaADC-33 for Expression in A. baumannii
4.7. Cloning the blaOXA-24/-40 for Expression in A. baumannii
4.8. Construction of the blaADC-51 Deletion Mutant of ATCC 17978
4.9. Selection of Clinical Bacterial Isolates
4.10. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Church, N.A.; McKillip, J.L. Antibiotic Resistance Crisis: Challenges and Imperatives. Biologia 2021, 76, 1535–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19: U.S. Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance, Special Report 2022. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/covid19.html (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moubareck, C.A.; Halat, D.H. Insights into Acinetobacter Baumannii: A Review of Microbiological, Virulence, and Resistance Traits in a Threatening Nosocomial Pathogen. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019 AR Threats Report; U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Caselli, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Powers, R.A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bouza, A.A.; Swanson, H.C.; Smolen, K.A.; Fini, F.; Wallar, B.J.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Inhibition of Acinetobacter -Derived Cephalosporinase: Exploring the Carboxylate Recognition Site Using Novel β-Lactamase Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambler, R.P. The Structure of Beta-Lactamases. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujer, A.M.; Hujer, K.M.; Leonard, D.A.; Powers, R.A.; Wallar, B.J.; Mack, A.R.; Taracila, M.A.; Rather, P.N.; Higgins, P.G.; Prati, F.; et al. A Comprehensive and Contemporary “Snapshot” of β-Lactamases in Carbapenem Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Oueslati, S.; Bonnin, R.A.; Dabos, M.L.; Zavala, A.; Dortet, L.; Retailleau, P.; Iorga, B.I. Beta-Lactamase Database (BLDB)—Structure and Function. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Labate, L.; Russo, C.; Vena, A.; Giacobbe, D.R. Therapeutic Options for Difficult-to-Treat Acinetobacter Baumannii Infections: A 2020 Perspective. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujer, K.M.; Hamza, N.S.; Hujer, A.M.; Perez, F.; Helfand, M.S.; Bethel, C.R.; Thomson, J.M.; Anderson, V.E.; Barlow, M.; Rice, L.B.; et al. Identification of a New Allelic Variant of the Acinetobacter Baumannii Cephalosporinase, ADC-7 β-Lactamase: Defining a Unique Family of Class C Enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Karim, A.M.; Lee, C.R.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9654–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.A.; Swanson, H.C.; Taracila, M.A.; Florek, N.W.; Romagnoli, C.; Caselli, E.; Prati, F.; Bonomo, R.A.; Wallar, B.J. Biochemical and Structural Analysis of Inhibitors Targeting the ADC-7 Cephalosporinase of Acinetobacter Baumannii. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 7670–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartal, C.; Rolston, K.V.I.; Nesher, L. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii: Colonization, Infection and Current Treatment Options. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillana, E.; Beceiro, A.; Bou, G.; Romero, A. Crystal Structure of the Carbapenemase OXA-24 Reveals Insights into the Mechanism of Carbapenem Hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5354–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vàzquez-Ucha, J.C.; Maneiro, M.; Martinez-Guitiàn, M.; Buynak, J.; Bethel, C.R.; Bonomo, R.A.; Bou, G.; Poza, M.; González-Bello, C.; Beceiro, A. Activity of the B-Lactamase Inhibitor LN-1-255 against Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D b-Lactamases from Acinetobacter Baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasarte-Monterrubio, C.; Vázquez-Ucha, J.C.; Maneiro, M.; Arca-Suárez, J.; Alonso, I.; Guijarro-Sánchez, P.; Buynak, J.D.; Bou, G.; González-Bello, C.; Beceiro, A. Activity of Imipenem, Meropenem, Cefepime, and Sulbactam in Combination with the β-Lactamase Inhibitor Ln-1-255 against Acinetobacter Spp. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand-Réville, T.F.; Guler, S.; Comita-Prevoir, J.; Chen, B.; Bifulco, N.; Huynh, H.; Lahiri, S.; Shapiro, A.B.; McLeod, S.M.; Carter, N.M.; et al. ETX2514 Is a Broad-Spectrum β-Lactamase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Including Acinetobacter Baumannii. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Bush, K.; Harbarth, S.; Paul, M.; Rex, J.H.; Tacconelli, E.; Thwaites, G.E. Critical Analysis of Antibacterial Agents in Clinical Development. In Nature Reviews Microbiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, S.; Martin, R.; Kindler, A.M.; Paetzel, M.; Gold, M.; Jensen, S.E.; Jones, J.B.; Strynadka, N.C.J. Structure-Based Design Guides the Improved Efficacy of Deacylation Transition State Analogue Inhibitors of TEM-1 β-Lactamase. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 5312–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Shoichet, B.K.; Morandi, S.; Morandi, F.; Focia, P.J.; Prati, F.; Blázquez, J. Nanomolar Inhibitors of AmpC β-Lactamase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Ogawa, A.M.; Painter, R.E.; Park, Y.-W.; Young, K.; DiNinno, F.P. 4,7-Dichloro Benzothien-2-Yl Sulfonylaminomethyl Boronic Acid: First Boronic Acid-Derived Beta-Lactamase Inhibitor with Class A, C, and D Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2622–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, S.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Totrov, M.; Hirst, G.C.; Lomovskaya, O.; Griffith, D.C.; King, P.; Tsivkovski, R.; Sun, D.; Sabet, M.; et al. Discovery of a Cyclic Boronic Acid β-Lactamase Inhibitor (RPX7009) with Utility vs Class A Serine Carbapenemases. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3682–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, D.C.; Zhou, F.; Eyermann, C.J.; Ferguson, A.D.; Prince, D.B.; Breen, J.; Giacobbe, R.A.; Lahiri, S.; Verheijen, J.C. 4,5-Disubstituted 6-Aryloxy-1,3-Dihydrobenzo[c][1,2]Oxaboroles Are Broad-Spectrum Serine β-Lactamase Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajnc, A.; Brem, J.; Hinchliffe, P.; Calvopiña, K.; Panduwawala, T.D.; Lang, P.A.; Kamps, J.J.A.G.; Tyrrell, J.M.; Widlake, E.; Saward, B.G.; et al. Bicyclic Boronate VNRX-5133 Inhibits Metallo- And Serine-β-Lactamases. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8544–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, S.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Lomovskaya, O.; Griffith, D.C.; Rubio-Aparicio, D.; Nelson, K.; Tsivkovski, R.; Sun, D.; Sabet, M.; Tarazi, Z.; et al. Discovery of Cyclic Boronic Acid QPX7728, an Ultrabroad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Serine and Metallo-β-Lactamases. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7491–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.P.; Mitchell, J.M.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A. Exploring the Potential of Boronic Acids as Inhibitors of OXA-24/40 β-Lactamase. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, M.; Spyrakis, F.; Cross, S.; Quotadamo, A.; Farina, D.; Tondi, D.; De Luca, F.; Docquier, J.-D.; Prieto, A.I.; Ibacache, C.; et al. Computational and Biological Profile of Boronic Acids for the Detection of Bacterial Serine- and Metallo-β-Lactamases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidam, O.; Romagnoli, C.; Caselli, E.; Babaoglu, K.; Pohlhaus, D.T.; Karpiak, J.; Bonnet, R.; Shoichet, B.K.; Prati, F. Design, Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Antimicrobial Activity of Sulfonamide Boronic Acids as β-Lactamase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7852–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidam, O.; Romagnoli, C.; Dalmasso, G.; Barelier, S.; Caselli, E.; Bonnet, R.; Shoichet, B.K.; Prati, F. Fragment-Guided Design of Subnanomolar β-Lactamase Inhibitors Active In Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17448–17453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.J.; Taracila, M.A.; Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Bethel, C.R.; Caselli, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Winkler, M.L.; Spellberg, B.; Prati, F.; Bonomoa, R.A. Boronic Acid Transition State Inhibitors Active against KPC and Other Class a β-Lactamases: Structure-Activity Relationships as a Guide to Inhibitor Design. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza, A.A.; Swanson, H.C.; Smolen, K.A.; Vandine, A.L.; Taracila, M.A.; Romagnoli, C.; Caselli, E.; Prati, F.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A.; et al. Structure-Based Analysis of Boronic Acids as Inhibitors of Acinetobacter -Derived Cephalosporinase-7, a Unique Class C β-Lactamase. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.D.; Ortega, C.J.; Renck, N.A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A.; Leonard, D.A. Structures of the Class D Carbapenemase OXA-24 from Acinetobacter Baumannii in Complex with Doripenem. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; June, C.M.; Baggett, V.L.; Lowe, B.C.; Ruble, J.F.; Bonomo, R.A.; Leonard, D.A.; Powers, R.A. Conformational Flexibility in Carbapenem Hydrolysis Drives Substrate Specificity of the Class D Carbapenemase OXA-24/40. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Clasman, J.R.; June, C.M.; Kaitany, K.-C.J.; LaFleur, J.R.; Taracila, M.A.; Klinger, N.V.; Bonomo, R.A.; Wymore, T.; Szarecka, A.; et al. Structural Basis of Activity against Aztreonam and Extended Spectrum Cephalosporins for Two Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamases from Acinetobacter Baumannii. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, D.S.; Sadhu, K.M. Synthesis of 1-amino-2-phenylethane-1-boronic acid derivatives. Organometallics 1984, 3, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, B.N.; Smolen, K.A.; Barlow, S.J.; Caselli, E.; Prati, F.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Wallar, B.J.; Powers, R.A. Structural insights into inhibition of the Acinetobacter derived cephalosporinase ADC-7 by ceftazidime and its boronic acid transition state analog. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G. Xia2: An Expert System for Macromolecular Crystallography Data Reduction. J. Appl. Christallography 2010, 43, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonrhein, C.; Flensburg, C.; Keller, P.; Sharff, A.; Smart, O.; Paciorek, W.; Womack, T.; Bricogne, G. Data Processing and Analysis with the AutoPROC Toolbox. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser Crystallographic Software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and Development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaitany, K.C.J.; Klinger, N.V.; June, C.M.; Ramey, M.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A.; Leonard, D.A. Structures of the Class D Carbapenemases OXA-23 and OXA-146: Mechanistic Basis of Activity against Carbapenems, Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporins, and Aztreonam. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4848–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.E.; Chin, C.Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Rather, P.N. Copy Number of an Integron-Encoded Antibiotic Resistance Locus Regulates a Virulence and Opacity Switch in Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075. mBio 2020, 11, e02338-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, A.T.; Nowicki, E.M.; Boll, J.M.; Knauf, G.A.; Burdis, N.C.; Trent, M.S.; Davies, B.W. Defining gene-phenotype relationships in Acinetobacter baumannii through one-step chromosomal gene inactivation. mBio 2014, 5, e01313-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]



| Compound | Structure | Ki ADC-33 (µM) | Ki OXA-24/40 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR167 |  | 0.057 ± 0.015 | 4.4 ± 0.5 |
| 6a | 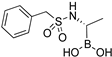 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 630 ± 70 |
| 6b |  | 0.79 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.5 |
| 6c | 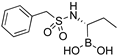 | 193 ± 23 | 9400 ± 2000 |
| 6d | 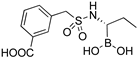 | 22 ± 3 | 320 ± 30 |
| 6e | 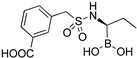 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 1300 ± 100 |
| ADC-33/6d (8CUP) | ADC-33/6e (8CUQ) | OXA-24/40/CR167 (8CUL) | OXA-24/40/6d (8CUM) | OXA-24/40/6e (8CUO) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell constants (Å; °) | a = 43.29; b = 83.82; | a = 43.32; b = 83.94; | a = b = 102.58; | a = b = 102.19; | a = b = 102.18; |
| c = 203.38 | c = 204.46 | c = 86.17 | c = 85.76 | c = 86.43 | |
| α = β = γ = 90 | α = β = γ = 90 | α = β = γ = 90 | α = β = γ = 90 | α = β = γ = 90 | |
| Space group | P 212121 | P 212121 | P 41212 | P 41212 | P 41212 |
| Resolution (Å) a | 43.47–1.54 | 52.91–1.55 | 72.54–2.01 | 55.26–1.49 | 43.98–1.47 |
| (1.57–1.54) | (1.58–1.55) | (2.119–2.015) | (1.52–1.49) | (1.50–1.47) | |
| Unique reflections | 110,715 (5461) | 109,336 (5333) | 26,105 (1305) | 74,330 (3631) | 78,080 (3838) |
| Total observations | 799,219 (39,917) | 736,079 (35,314) | 189,622 (8590) | 597,202 (28,085) | 612,000 (25,015) |
| Rpim (%) (all I +/−) | 5.3 (117.8) | 5.0 (128.7) | 7.3 (52.1) | 4.8 (136.2) | 5.4 (150.2) |
| CC(1/2) | 0.999 (0.336) | 0.999 (0.382) | 0.994 (0.600) | 0.999 (0.396) | 0.999 (0.311) |
| Completeness (%) | 100.00 (100.0) | 100.0 (100.0) | 93.8 (66.8) | 99.9 (98.9) | 100.0 (100.0) |
| <I/σ> | 11.8 (1.0) | 11.6 (1.0) | 7.6 (1.6) | 12.6 (0.8) | 11.6 (0.7) |
| Resolution for refinement (Å) | 43.47–1.54 | 66.24–1.94 | 72.54–2.01 | 51.09–1.49 | 43.98–1.47 |
| No. of protein residues | 718 | 717 | 244 | 244 | 244 |
| No. of waters | 688 | 581 | 123 | 266 | 299 |
| RMSD bond lengths (Å) | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.012 | 0.013 |
| RMSD bond angles (°) | 1.11 | 0.995 | 1.52 | 1.33 | 1.45 |
| R-factor (%) | 18.4 | 18.6 | 21.2 | 18.9 | 18.1 |
| Rfree (%) b | 21.6 | 21.3 | 25.5 | 20.7 | 20.3 |
| Average B factor, protein (Å2) | 25.27 | 27.94 | 39.74 | 24.51 | 22.06 |
| Average B factor, ligand (Å2) | 33.46 | 37.31 | 40.46 | 27.90 | 31.10 |
| Average B factor, waters (Å2) | 35.66 | 37.19 | 46.32 | 36.67 | 35.27 |
| E. coli—MICs in mg/L Broth Microdilution | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC-7 in pBCSK- (DH10B) | ADC-33 in pBCSK- (DH10B) | |||||
| BLI | CAZ | CTX | FEP | CAZ | CTX | FEP |
| None | 64 | 64 | 0.5 | 2048 | 128 | 0.5 |
| CR167 | 4 | 2 | 0.12 | 64 | 2 | NT |
| 6b | 4 | 2 | 0.12 | 64 | 4 | NT |
| A. baumannii ATCC 17978 Native ADC KO—MICs in mg/L Broth Microdilution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC-33 pQF1266 | OXA-24 pWH1266 | ||||||
| BLI | CAZ | CTX | FEP | CAZ | CTX | FEP | IMI |
| None | 128 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 128 |
| CR167 | 32 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 128 |
| 6b | 64 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 128 |
| MICs in mg/L | PR323 | PR328 | PR378 | PR396 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXA-24, OXA-65, ADC-218 | OXA-23, OXA-82, ADC-33 | OXA-24, OXA-65, TEM-1 | OXA-82, ADC-33 | |||||||||
| BLI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | CAZ | CTX | IMI |
| None | 4096 | 2048 | 128 | 2048 | 256 | 128 | 64 | 64 | 256 | 2048 | 512 | 64 |
| CR167 | 4096 | 2048 | 128 | 1024 | 128 | 128 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 1024 | 256 | 64 |
| 6b | 4096 | 2048 | 128 | 2048 | 256 | 128 | 32 | 64 | 256 | 2048 | 512 | 64 |
| PR408 | PR462 | PR474 | ||||||||||
| OXA-24, OXA-71, ADC-212 | OXA-24, OXA-65, ADC-214 | OXA-23, OXA-24, OXA-65, ADC-218 | ||||||||||
| BLI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | CAZ | CTX | IMI | |||
| None | 1024 | 1024 | 128 | 256 | 1024 | 64 | 4096 | 1024 | 128 | |||
| CR167 | 512 | 1024 | 128 | 64 | 256 | 64 | 4096 | 2048 | 128 | |||
| 6b | 512 | 1024 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 64 | 4096 | 2048 | 128 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Introvigne, M.L.; Beardsley, T.J.; Fernando, M.C.; Leonard, D.A.; Wallar, B.J.; Rudin, S.D.; Taracila, M.A.; Rather, P.N.; Colquhoun, J.M.; Song, S.; et al. Sulfonamidoboronic Acids as “Cross-Class” Inhibitors of an Expanded-Spectrum Class C Cephalosporinase, ADC-33, and a Class D Carbapenemase, OXA-24/40: Strategic Compound Design to Combat Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040644
Introvigne ML, Beardsley TJ, Fernando MC, Leonard DA, Wallar BJ, Rudin SD, Taracila MA, Rather PN, Colquhoun JM, Song S, et al. Sulfonamidoboronic Acids as “Cross-Class” Inhibitors of an Expanded-Spectrum Class C Cephalosporinase, ADC-33, and a Class D Carbapenemase, OXA-24/40: Strategic Compound Design to Combat Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(4):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040644
Chicago/Turabian StyleIntrovigne, Maria Luisa, Trevor J. Beardsley, Micah C. Fernando, David A. Leonard, Bradley J. Wallar, Susan D. Rudin, Magdalena A. Taracila, Philip N. Rather, Jennifer M. Colquhoun, Shaina Song, and et al. 2023. "Sulfonamidoboronic Acids as “Cross-Class” Inhibitors of an Expanded-Spectrum Class C Cephalosporinase, ADC-33, and a Class D Carbapenemase, OXA-24/40: Strategic Compound Design to Combat Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii" Antibiotics 12, no. 4: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040644
APA StyleIntrovigne, M. L., Beardsley, T. J., Fernando, M. C., Leonard, D. A., Wallar, B. J., Rudin, S. D., Taracila, M. A., Rather, P. N., Colquhoun, J. M., Song, S., Fini, F., Hujer, K. M., Hujer, A. M., Prati, F., Powers, R. A., Bonomo, R. A., & Caselli, E. (2023). Sulfonamidoboronic Acids as “Cross-Class” Inhibitors of an Expanded-Spectrum Class C Cephalosporinase, ADC-33, and a Class D Carbapenemase, OXA-24/40: Strategic Compound Design to Combat Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics, 12(4), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12040644









