Efficacy of Penicillin–Streptomycin Brands against Staphylococcus aureus: Concordance between Veterinary Clinicians’ Perception and the Realities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2. Farm Antibiotic Utilization Practices
2.3. Knowledge, Perception, and Practices of Veterinarians
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Study Design and Sampling
4.3. Identifying Brands of Penstrep
4.4. Isolation and Identification of S. aureus
4.5. Efficacy Evaluation
4.5.1. Preparation of Antibiotic Discs
4.5.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. WHO|Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson, L.; Miller, M.A. Antibiotic use in food animals: Controlling the human health impact. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McEwen, S.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, S93–S106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, P.D. Public Health Risks: Chemical and Antibiotic Residues-Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 402–413. [Google Scholar]
- Okonko, I.O.; Fajobi, E.A.; Ogunnusi, T.A.; Ogunjobi, A.A.; Obiogbolu, C.U. Antimicrobial chemotherapy and Sustainable Development: The past, The Current Trend, and the future. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2008, 11, 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- De Britto, A.J.; Gracelin, D.H.S.; Kumar, P.B.J.R. Pteris biaurita L.: A potential antibacterial fern against Xanthomonas and Aeromonas bacteria. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 5, 678–680. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, B. Counterfeit drugs and medical devices in developing countries. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2014, 5, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Quality Assurance of Pharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Guidelines and Related Materials, Vol. 2, Good Manufacturing Practices and Inspection, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 409. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Countering the Problem of Falsified and Substandard Drugs; Buckley, G.J., Gostin, L.O., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 376. [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar, G.M.; Breman, J.G.; Newton, P.N.; Herrington, J. Poor-quality antimalarial drugs in southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 488–496. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.; Banerji, J. Counterfeit antimalarial drugs. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 829. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, S.; Evans, D.R.; Bessias, S.; Haynie, D.G.; Yemeke, T.; Laing, S.K.; Herrington, J.E. Prevalence and Estimated Economic Burden of Substandard and Falsified Medicines in Low-and Middle-Income Countries. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e181662. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring System for Substandard and Falsified Medical Products; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 64.
- Casassus, B. Health agency reveals scourge of fake drugs in developing world. Nature 2017, 4, 10. [Google Scholar]
- UN News. Fake Medicines Kill Almost 500,000 Sub-Saharan Africans a Year: UNODC Report|UN News; The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khurelbat, D.; Dorj, G.; Sunderland, B.; Sanjjav, T.; Bayarsaikhan, E.; Damdinjav, D.; Dorj, G.; Jigjidsuren, A.; Lkhagvasuren, O.; Erdenetsetseg, B. A cross-sectional analysis of falsified, counterfeit and substandard medicines in a low-middle income country. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.N.; Green, M.D.; Fernández, F.M. Impact of poor-quality medicines in the ‘developing’ world. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Falagas, M.E. Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T.J.; Endalamaw, D.; Tolossa, Y.; Feyisa, A. Evaluation of rational use of veterinary drugs especially antimicrobials and anthelmintics in Bishoftu, Central Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, T.; Ali, M.; Mitiku, E.; Hailemariam, M. The burden of antimicrobial resistance at tertiary care hospital, southern Ethiopia: A three years’ retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.A. Erratum: Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Ethiopia: Implementation experiences and lessons learned. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 2019, 8, a1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhie, O.A. Antibiotic Use and Resistance Pattern in Ethiopia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 2489063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunna, F.; Bedashu, A.; Beyene, T.; Feyisa, A.D.; Duguma, A. Occurrence of Salmonella and antimicrobial sensitivity test in Abattoir and Dairy farms in Adama town, Oromia, Ethiopia. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 1127. [Google Scholar]
- Beyene, T.; Hayishe, H.; Gizaw, F.; Beyi, A.F.; Abunna, F.; Mammo, B.; Ayana, D.; Waktole, H.; Abdi, R.D. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus in dairy farms, abattoir and humans in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messele, Y.E.; Abdi, R.D.; Tegegne, D.T.; Bora, S.K.; Babura, M.D.; Emeru, B.A.; Werid, G.M. Analysis of milk-derived isolates of E. coli indicating drug resistance in central Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 51, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T.; Kemal, A.; Jibat, T.; Tadese, F.; Ayana, D.; Feyisa, A. Assessment on Chemicals and Drugs Residue in Dairy and Poultry Products in Bishoftu and Modjo, Central Ethiopia. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, S13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Beyene, T.; Assefa, S. Assessment of Rational Veterinary Drugs Use in Livestock at Adama District Veterinary Clinic, Central Ethiopia. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE (World Organization for Animal Health). Guideline 2.1. Laboratory Methodologies for Bacterial Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; OIE Terrestrial Manual: Paris, France, 2012; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Dehaumont, P. OIE International standards on antimicrobial resistance. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, P. Do pharmaceutical sales respond to scientific evidence? J. Econ. Manag. Strateg. 2002, 11, 551–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaika, P. Assessment of commonly available antimicrobial agents. A study from Ilala-Tanzania. Dar Es Salaam Med. Stud. J. 2010, 16, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.W. Combination therapy as a tool to prevent emergence of bacterial resistance. Infection 1999, 27, S24–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K. Fake and Poor-Quality Drugs Plague Developing Countries. Sci. Am. 2001. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/fake-and-poor-quality-dru/ (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Tufa, T.B.; Gurmu, F.; Beyi, A.F.; Hogeveen, H.; Beyene, T.J.; Ayana, D.; Woldemariyam, F.T.; Hailemariam, E.; Gutema, F.D.; Stegeman, J.A. Veterinary medicinal product usage among food animal producers and its health implications in Central Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari-Boatrng, E. Post-Market Quality Surveillance Project: Maternal Healthcare Products (Oxytocin and Ergometrine) on the Ghanaian Market-Report of First Round. 2013; 21. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA). 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/types-applications/abbreviated-new-drug-application-anda (accessed on 17 May 2020).
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkunan, T.; Ashutosh, M.; Sukumar, B.; Chera, J.S.; Ramadas, S.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Ashok Kumar, S.; Rachana, S.; Santhosh Kumar, M.; De, S. Antibiotic resistance: A cross-sectional study on knowledge, attitude, and practices among veterinarians of Haryana state in India Thulasiraman. Vet. World 2019, 12, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, S.; Pereira, A.; Alves, A.; da Silva, P.G.V.; Dos Santos, C.; Davis, S.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Yan, J.; Francis, J.R.; Jong, J.B.D.C.; et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of government animal health workers on antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance in Timor-Leste. Front. Vet.Sci. 2022, 9, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, X.; Lim, R.H.M.; Rymer, C.; Ray, P. Fijian Veterinarian and Para-Veterinarians’ Behavior, Attitude and Knowledge Toward Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Qualitative Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 898737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishoftu-Wikipedia. Wikipedia. 2020. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bishoftu (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- The Free Encyclopedia, Location of Sebeta. Wikipedia. 2020. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sebeta (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Central Statistical Agency (CSA). The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Agricultural Sample Survey 2017/2018 [2010 E.C]: Report on Livestock and Livestock Characteristics (Private Peasant Holdings); Statistical Bulletin 587; Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, P.N.; Lee, S.J.; Goodman, C.; Fernández, F.M.; Yeung, S.; Phanouvong, S.; Kaur, H.; Amin, A.A.; Whitty, C.J.M.; Kokwaro, G.O.; et al. Guidelines for Field Surveys of the Quality of Medicines: A Proposal. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Notice to applicants: A guideline on summary of product characteristics. In Module 1.3 Summary of Product Characteristics; Revision 2; European Commission: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Markey, B.; Leonard, F.; Archambault, M.; Cullinae, A.; Maguire, D. Clinical Veterinary Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Mosby Ltd.: St Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vineetha, N.; Vignesh, R.; Sridhar, D. Preparation, Standardization of Antibiotic Discs and Study of Resistance Pattern for First-Line Antibiotics in Isolates from Clinical Samples. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2015, 1, 624–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2016, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, J.E. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Methods and Interpretation of Results. In Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine, 5th ed.; Giguere, S., Prescott, J.F., Dowling, P.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 25th informational supplement. In CLSI Document M100-S25, 25th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2015; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufa, T.B.; Guta, A.; Tufa, T.B.; Nigussie, D.; Regassa, F.; Beyi, A.F. Efficacy of different brands of penicillin-streptomycin against Staphylococcus aureus: The clinicians’ myths and the realities (Preprints). Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar]
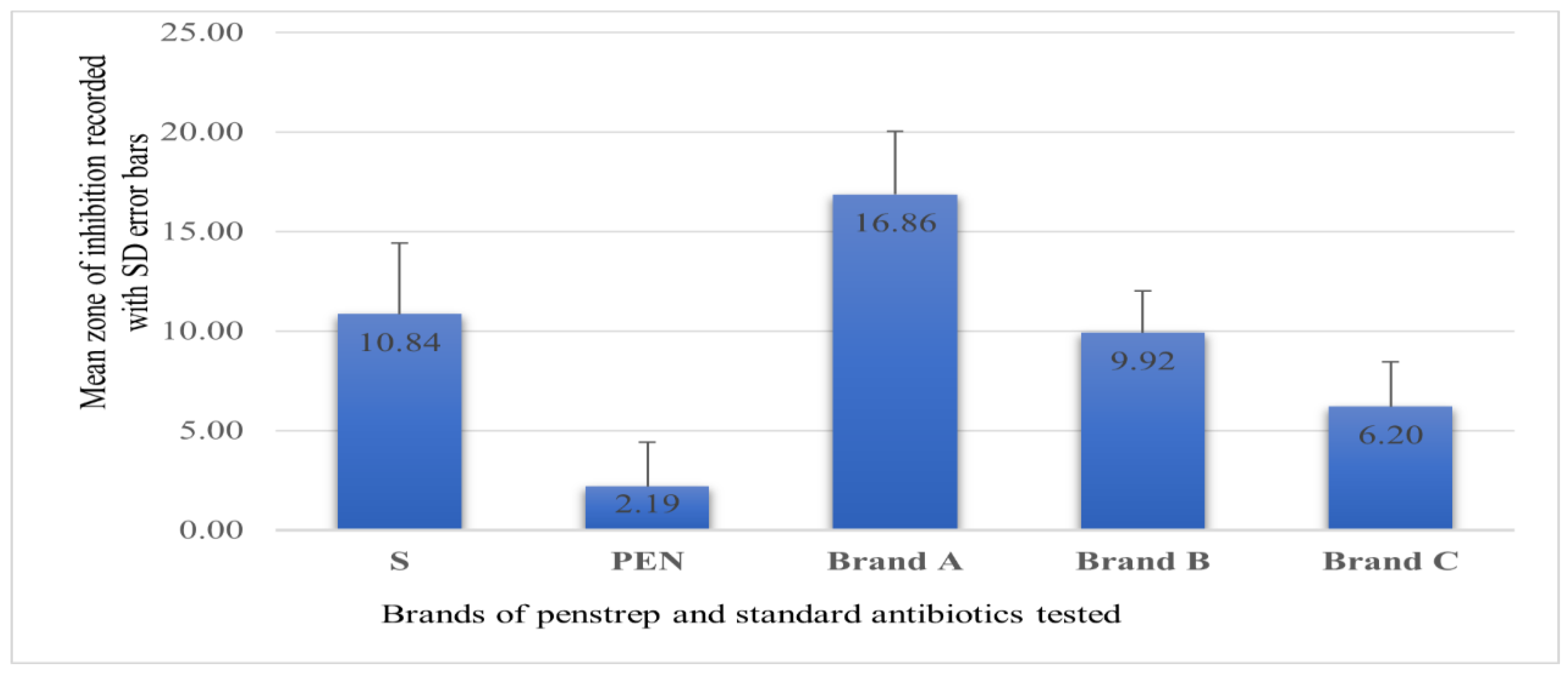
| Drugs Tested | Susceptibility of the Isolates | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant n (%) | IR n (%) | Susceptible n (%) | |
| Penicillin (P) | 43 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Streptomycin (S) | 27 (63) | 9 (21) | 7 (16) |
| Brand A compared to (P) * | 43 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Brand A compared to (S) # | 4 (9) | 4 (9) | 35 (81) |
| Brand B compared to (P) * | 43 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Brand B compared to (S) # | 33 (77) | 10 (23) | 0 (0.0) |
| Brand C compared to (P) * | 43 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Brand C compared to (S) # | 42 (98) | 1 (2) | 0 (0.0) |
| Question | Participants’ Agreement/Total Participants (%) |
|---|---|
| Perception of veterinary antibiotics quality and brand prescribing | |
| Agree that some antibiotics on the market are of poor quality | 30/30 (100) |
| Penstrep imported from a Western country (e.g., the UK) is perceived as of better quality than those from Eastern countries (e.g., China) | 30/30 (100) |
| Generic antibiotics are perceived as of equivalent quality compared to branded antibiotics | 21/30 (70) |
| Generic antibiotics are perceived as substandard drugs | 9/30 (30) |
| Prescribe antibiotics by international nonproprietary name | 14/30 (80) |
| Prescribe antibiotics by brand name | 20/30 (67) |
| Prescribe brands of penstrep | 26/30 (87) |
| Variation in clinical improvements among brands of penstrep | 30/30 (100) |
| Which brands of penstrep showed better clinical improvements? | |
| Pen&Strep (Norbrook) | 30/30 (100) |
| Which brands of penstrep are mostly prescribed? | |
| Pen&Strep (Norbrook) | 30/30 (100) a |
| Penstrep (Chengdu Quiankun) | 16/30 (53) b |
| Pro&Strep (Hebei Yuanzheng) | 8/30 (27) c |
| Knowledge of antibiotics and their use | |
| Penstrep indicated for both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections | 30/30 (100) |
| Oxytetracycline indicated for gastro-intestinal and respiratory bacterial infections | 30/30 (100) |
| Sulfa drugs indicated for diarrheic cases | 30/30 (100) |
| Antibiotics indicated for prophylactic use for severe viral cases | 30/30 (100) |
| Antibiotic prescribing practices | |
| Perception of antibiotic overuse in the dairy farms | 16/30 (53) |
| Perception of antibiotic overuse in the veterinary clinics | 26/30 (87) |
| Brand Name | Concentration (mg/mL) | Country of Origin | Average Price per Bottle of 100 mL in ETB (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | S (250 mg/mL) P (200 mg/mL) | UK | 500 (9.615) |
| Brand B | S (200 mg/mL) | China | 380 (7.307) |
| P (200 mg/mL) | |||
| Brand C | S (200 mg/mL) | China | 350 (6.730) |
| P (200 mg/mL) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tufa, T.B.; Guta, A.; Tufa, T.B.; Nigussie, D.; Beyi, A.F.; Gutema, F.D.; Regassa, F. Efficacy of Penicillin–Streptomycin Brands against Staphylococcus aureus: Concordance between Veterinary Clinicians’ Perception and the Realities. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030570
Tufa TB, Guta A, Tufa TB, Nigussie D, Beyi AF, Gutema FD, Regassa F. Efficacy of Penicillin–Streptomycin Brands against Staphylococcus aureus: Concordance between Veterinary Clinicians’ Perception and the Realities. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030570
Chicago/Turabian StyleTufa, Takele Beyene, Asegid Guta, Tafese B. Tufa, Dereje Nigussie, Ashenafi Feyisa Beyi, Fanta D. Gutema, and Fikru Regassa. 2023. "Efficacy of Penicillin–Streptomycin Brands against Staphylococcus aureus: Concordance between Veterinary Clinicians’ Perception and the Realities" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030570
APA StyleTufa, T. B., Guta, A., Tufa, T. B., Nigussie, D., Beyi, A. F., Gutema, F. D., & Regassa, F. (2023). Efficacy of Penicillin–Streptomycin Brands against Staphylococcus aureus: Concordance between Veterinary Clinicians’ Perception and the Realities. Antibiotics, 12(3), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030570






