Methacrylate Cationic Nanoparticles Activity against Different Gram-Positive Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
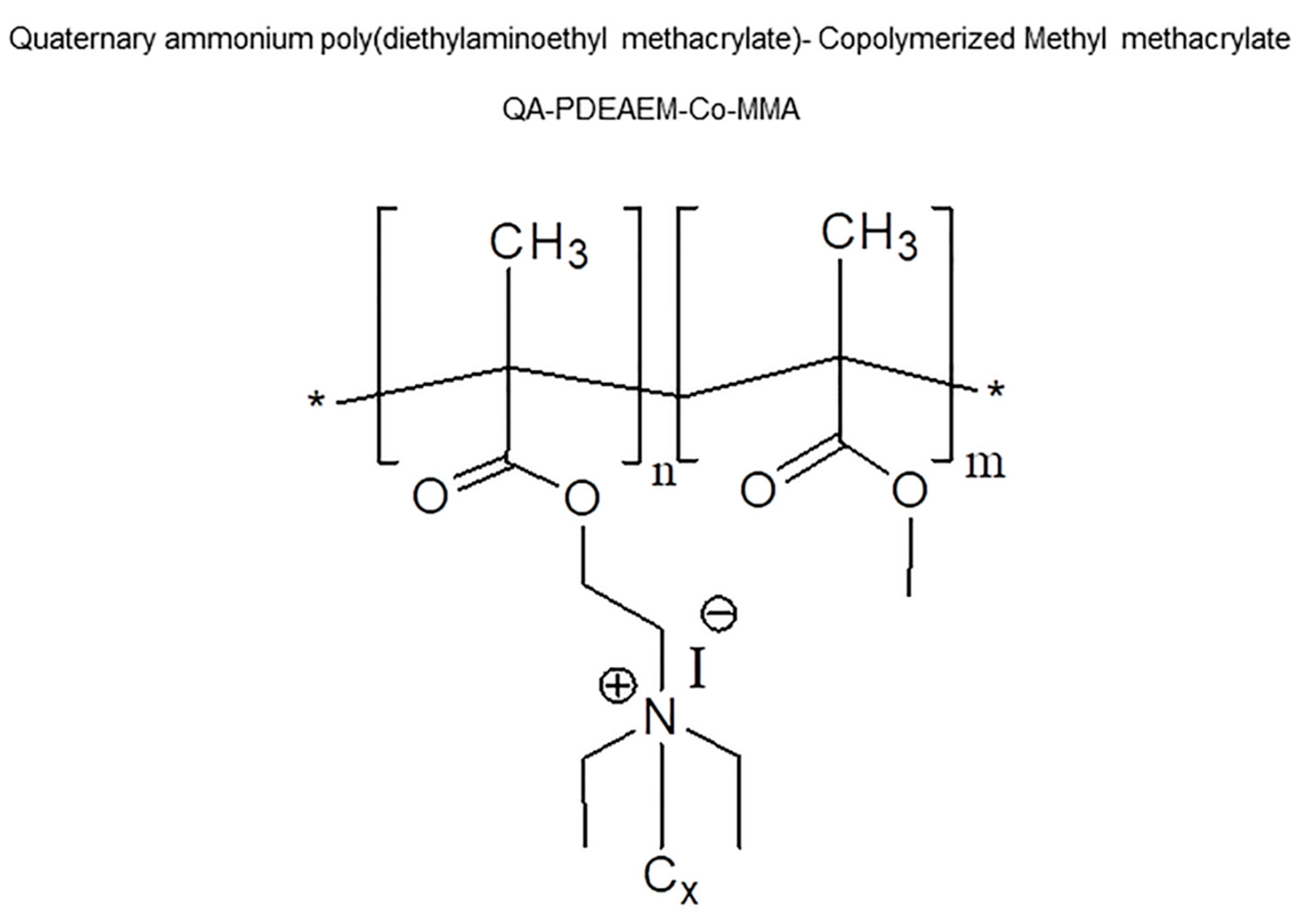
2.1. Origin and Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.2. Cell Cultures
2.3. Toxicity Studies
2.4. Microbiological Study Using Clinical Strains
3. Results
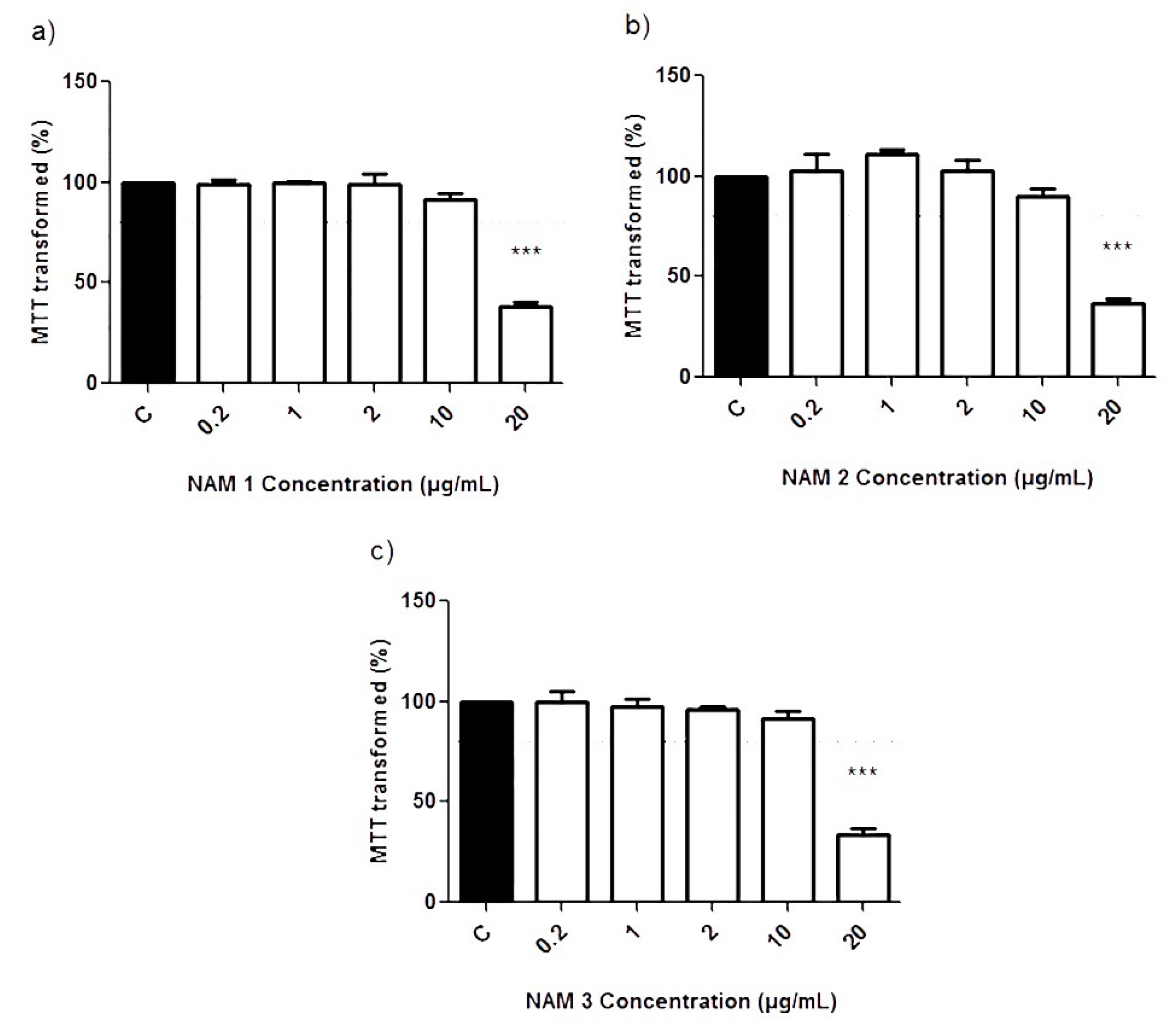
3.1. Cell Viability Study by MTT Assays
3.2. Effects of NPs on the Gram-Positive Clinical Bacterial Strains
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, G.L.; Conn, L.A.; Pinner, R.W. Trends in infectious disease mortality in the United States during the 20th century. JAMA 1999, 281, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, I.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Craig, J.; Laxminarayan, R. Global geographic trends in antimicrobial resistance: The role of international travel. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. ECDC/EMEA Joint Technical Report: The Bacterial Challenge: Time to React; European Medicine Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Calvo, J. Development of antibiotic resistance: Causes, consequences and their importance for public health. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28 (Suppl. S4), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, A.L.; Madero, C.M.; Moyano, C.A.; Herreras, M.A.; Parralo, R.B.; Álvarez, S.S.; Vázquez, R.C.; Teixeira, C.J. National Plan against Antibiotic Resistance 2019–2020; Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS): Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antibacterial Agents in Clinical and Preclinical Development: An Overview and Analysis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Contera, S.; Bernardino de la Serna, J.; Tetley, T.D. Biotechnology, nanotechnology and medicine. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2020, 4, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Martínez, F.C.; Carrión, B.; Ceña, V. The use of nanoparticles for gene therapy in the nervous system. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 31, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, G.D.; Rumbles, G. Excitons in nanoscale systems. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Langer, R.; Jia, X. Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyth, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Domb, A.; Khan, W.; Hazan, R. Alternative antimicrobial approach: Nano-antimicrobial materials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 246012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y. Application of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against a cancer promoter cyanobacterium, microcystis aeruginosa. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6773–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.; Guerra, R.; Lara, V.; Guzmán, A. Gold nanoparticles as efficient antimicrobial agents for Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Habib, S.S.; Memic, A. Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokulakrishnan, R.; Ravikumar, S.; Raj, J.A. In Vitro Antibacterial Potential of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles against Antibiotic Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2012, 2, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panacek, A.; Kvitek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Pizurova, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevecna, T.; Zboril, R. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.-Y.; Byeon, J.H.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, J. Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 373, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano- and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Mir, A.; Mallik, D.; Sinha, A.; Nayar, S.; Webster, T.J. Bactericidal effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Ashagrie, M.; Ali, O.; Ramachandran, B. Chapter 17. Overview of Antimicrobial Resistance and Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Approach to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance; Abraham, J., Domb, K., Reddy, K., Shady, F., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X. Antimicrobial cationic polymers: From structural design to functional control. Polym. J. 2017, 50, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, L.-A.B.; Ryan, S.M.; Mantovani, G.; Syrett, J.A.; Haddleton, D.M.; Brayden, D.J. Antibacterial effects of poly(2-(dimethylamino ethyl)methacrylate) against selected gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Biomacromolecules 2009, 11, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouras, T.; Koufakis, E.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Vamvakaki, M. A facile route towards PDMAEMA homopolymer amphiphiles. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3777–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Aviv, O.; Laout, N.; Ratner, S.; Beyth, N.; Domb, A.J. Quaternary ammonium poly(diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) possessing antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufakis, E.; Manouras, T.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Vamvakaki, M. Film Properties and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Quaternized PDMAEMA Brushes: Short vs Long Alkyl Chain Length. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3482–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.; Farah, S.; Tranque, P.; Ocaña, A.V.; Nam-Cha, S.H.; Beyth, N.; Gómez-Roldán, C.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Domb, A.J.; Pérez-Martínez, F.C.; et al. Antimicrobial evaluation of quaternary ammonium polyethyleneimine nanoparticles against clinical isolates of pathogenic bacteria. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí, P.; Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Domínguez-Jurado, E.; Sánchez-López, C.M.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Ocaña, A.V.; Castro-Osma, J.A.; Esteban, J.; Marcilla, A.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; et al. A novel bis(pyrazolyl)methane compound as a potential agent against Gram-positive bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.E.; Hatfield, K.M.; Wolford, H.; Samore, M.H.; Scott, R.D.; Reddy, S.C.; Olubajo, B.; Paul, P.; Jernigan, A.J.; Baggs, J. National Estimates of Healthcare Costs Associated with Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infections Among Hospitalized Patients in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, S17–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Moreno-Morales, J.; Ballesté-Delpierre, C. Current landscape in the discovery of novel antibacterial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles/halloysite nanotubes/graphene nanocomposites with sandwich-like structure. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chung, B.L.; Ma, M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Fayad, Z.A.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Mass production and size control of lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles through controlled microvortices. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3587–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizentsov, A.N.; Kvan, O.V.; Miroshnikova, E.P.; Gavrish, I.A.; Serdaeva, V.A.; Bykov, A.V. Assessment of biotoxicity of Cu nanoparticles with respect to probiotic strains of microorganisms and representatives of the normal flora of the intestine of broiler chickens. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15765–15773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanone, S.; Rogerieux, F.; Geys, J.; Dupont, A.; Maillot-Marechal, E.; Boczkowski, J.; Lacroix, G.; Hoet, P. Comparative toxicity of 24 manufactured nanoparticles in human alveolar epithelial and macrophage cell lines. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesler, M.; Aengenheister, L.; Ellinger, B.; Drexel, R.; Straskraba, S.; Jost, C.; Wagner, S.; Meier, F.; von Briesen, H.; Büchel, C.; et al. Multi-endpoint toxicological assessment of polystyrene nano- and microparticles in different biological models in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 61, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gentile, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Nie, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Safety of Nanoparticles in Medicine. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, A. Historical overview of nanotechnology and nanotoxicology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 926, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebremedhin, B.; Layer, F.; Konig, W.; Konig, B. Genetic classification and distinguishing of Staphylococcus species based on different partial gap, 16S rRNA, hsp60, rpoB, sodA, and tuf gene sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyart, C.; Quesne, G.; Boumaila, C.; Trieu-Cuot, P. Rapid and accurate specieslevel identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci by using the sodA gene as a target. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4296–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloos, W.E.; Schleifer, K.H. Genus IV Staphylococcus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Sneath, P.H.A., Mair, N.S., Sharpe, M.E., Holt, J.G., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 1013–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Kloos, W.E.; George, C.G. Identification of Staphylococcus species and subspecies with the MicroScan Pos ID and Rapid Pos ID panel systems. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.Y.; Su, S.C.; Reynolds, R.P.; Bay, S.J.; Av-Gay, Y.; Dovichi, N.J.; Chow, A.W. Species identification and phylogenetic relationships based on partial HSP60 gene sequences within the genus Staphylococcus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 3, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Satoh, I.; Kikuchi, N. Phylogenetic relationships of 38 taxa of the genus Staphylococcus based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 2, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, R.P.; Muthukrishnan, G.; Castoe, T.A.; Tafur, S.; Cole, A.M.; Parkinson, C.L. Phylogenetic relationships among Staphylococcus species and refinement of cluster groups based on multilocus data. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Martin, V.; Loux, V.; Dahyot, S.; Lebeurre, J.; Guffroy, A.; Martin, M.; Velay, A.; Keller, D.; Riegel, P.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Seven Strains of Staphylococcus lugdunensis Allows Identification of Mobile Genetic Elements. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Cramton, S.E.; Götz, F.; Peschel, A. Key role of teichoic acid net charge in Staphylococcus aureus colonization of artificial surfaces. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3423–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatan, A.B.; Patsula, V.; Dydowiczová, A.; Gunár, K.; Velychkivska, N.; Hromádková, J.; Petrovský, E.; Horák, D. Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.-W.; An, Y.-J. Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus aureus. Sci. Total. Environ. 2011, 409, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, K.; Moore, H.; Tandon, A.; Gupta, S.; Khanna, R.; Mohan, R.R. Nanotechnology and adeno-associated virus-based decorin gene therapy ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 307, F777–F782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.; Sanchez, M.; Elasri, M.O.; Lowe, A.B. Antimicrobial Activity of Statistical Polymethacrylic Sulfopropylbetaines against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Lee, M.C.; Lin, Z.I.; Lee, C.A.; Tung, Y.C.; Lou, C.W.; Chen, N.-T.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Lin, J.-H. Intensifying the Antimicrobial Activity of Poly [2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl Methacrylate]/Polylactide Composites by Tailoring Their Chemical and Physical Structures. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Wu, D.; Fu, R. Preparation of antibacterial poly(methyl methacrylate) by solution blending with water-insoluble antibacterial agent poly[(tert-butylamino) ethyl methacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, S.; Chen, F.; Fan, P.; Zhong, M.; Tan, J.; Yang, J. Salt-responsive “killing and release” antibacterial surfaces of mixed polymer brushes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8938–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, M.; Gumbart, J.C.; Roux, B.; Jensen, G.J. Architecture and assembly of the Gram-positive cell wall. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, I.M.; Sharma, B.; Labhasetwar, V. Nanoparticles: Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 811, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-Martínez, N.; Salas Orozco, M.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.-A.; Torres Méndez, F.; Ruiz, F. Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance to Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Fromm, K.M.; Ashkarran, A.A.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; de Larramendi, I.R.; Rojo, T.; Serpooshan, V.; Parak, W.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D. Cationic antimicrobial polymers and their assemblies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9906–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, M.; Ni, P. Facile approach for dna encapsulation in functional polyion complex for triggered intracellular gene delivery: Design, synthesis, and mechanism. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5199–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keely, S.; Ryan, S.M.; Haddleton, D.M.; Limer, A.; Mantovani, G.; Murphy, E.P.; Colgan, S.P.; Brayden, D.J. Dexamethasone-pDMAEMA polymeric conjugates reduce inflammatory biomarkers in human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, N.; Zhang, D. Poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) modification of activated carbon for copper ions removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumo, A.; Bombalski, L.; Lin, Q.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Schneider, J.W.; Tilton, R.D. High capacity, charge-selective protein uptake by polyelectrolyte brushes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4448–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, S.; Pagnoulle, C.; Galleni, M.; Compère, P.; Jérôme, R.; Detrembleur, C. Polyolefin matrixes with permanent antibacterial activity: Preparation, antibacterial activity, and action mode of the active species. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Lee, K.-M.; Liu, Z.-X.; Lai, R.-Y.; Chen, C.-K.; Chen, W.-C.; Hsu, J.-F. Antimicrobial Activity of Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers Filled with Poly [2-(tert-butylaminoethyl) Methacrylate]-Grafted Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Polymers 2020, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Antimicrobialaction, Synthesis, Medical Applications, and Toxicity Effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pornpattananangkul, D.; Hu, C.-M.; Huang, C.-M. Development of nanoparticles for antimicrobial drug delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CliftPeter, M.J.D.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Nanotoxicology: A perspective and discussion of whether or not in vitro testing is a valid alternative. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowack, B.; Bucheli, T.D. Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, A.D.; Aitken, R.J.; Butz, T.; Colvin, V.; Donaldson, K.; Oberdörster, G.; Philbert, M.A.; Ryan, J.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; et al. Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 2006, 444, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.; Prabhakaran, M.; Low, S.; Choon, A.; Zhang, Y.; Deepika, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanotechnology for Nanomedicine and Delivery of Drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2184–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Saxena, N.; Dwivedi, P.D. Emerging Trends of Nanoparticles Application in Food Technology: Safety Paradigms. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Maynard, A.; Donaldson, K.; Castranova, V.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Ausman, K.; Carter, J.; Karn, B.; Kreyling, W.; Lai, D.; et al. Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: Elements of a screening strategy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2005, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Lüderwald, S.; McKee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, G.; Merinero, M.; Pérez-Aranda, M.; Pérez-Soriano, E.M.; Ortiz, T.; Villamor, E.; Begines, B.; Alcudia, A. Environmental Impact of Nanoparticles’ Application as an Emerging Technology: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaiya, R.; Saravanan, M.; Priya, A.R.; Shankar, K.R.; Selvam, M.; Ovais, M.; Balajee, R.; Barabadi, H. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Streptomyces atrovirens and their potential anticancer activity against human breast cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassin, J.-M.; Lenoir, S.; Riga, J.; Jérôme, R.; Detrembleur, C. Grafting of Poly [2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate] onto polypropylene by reactive blending and antibacterial activity of the copolymer. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nanoparticle | S. aureus | S. epidermidis | S. lugdunensis | E. faecalis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAM1 (µg/mL) | 128 | 32 | 0.5 | 32 |
| NAM2 (µg/mL) | 128 | 64 | 1 | 32 |
| NAM3 (µg/mL) | 128 | 64 | 32 | 32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam-Cha, S.H.; Ocaña, A.V.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Domb, A.J.; Ruiz-Grao, M.C.; Cebada-Sánchez, S.; López-Gónzalez, Á.; Molina-Alarcón, M.; Pérez-Martínez, J.; et al. Methacrylate Cationic Nanoparticles Activity against Different Gram-Positive Bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030533
Nam-Cha SH, Ocaña AV, Pérez-Tanoira R, Aguilera-Correa JJ, Domb AJ, Ruiz-Grao MC, Cebada-Sánchez S, López-Gónzalez Á, Molina-Alarcón M, Pérez-Martínez J, et al. Methacrylate Cationic Nanoparticles Activity against Different Gram-Positive Bacteria. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030533
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam-Cha, Syong H., Ana V. Ocaña, Ramón Pérez-Tanoira, John J. Aguilera-Correa, Abraham J. Domb, Marta C. Ruiz-Grao, Sandra Cebada-Sánchez, Ángel López-Gónzalez, Milagros Molina-Alarcón, Juan Pérez-Martínez, and et al. 2023. "Methacrylate Cationic Nanoparticles Activity against Different Gram-Positive Bacteria" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030533
APA StyleNam-Cha, S. H., Ocaña, A. V., Pérez-Tanoira, R., Aguilera-Correa, J. J., Domb, A. J., Ruiz-Grao, M. C., Cebada-Sánchez, S., López-Gónzalez, Á., Molina-Alarcón, M., Pérez-Martínez, J., & Pérez-Martínez, F. C. (2023). Methacrylate Cationic Nanoparticles Activity against Different Gram-Positive Bacteria. Antibiotics, 12(3), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030533









