Abstract
Acinetobacter baumannii is recognized as a clinically significant pathogen causing a wide spectrum of nosocomial infections. Colistin was considered a last-resort antibiotic for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. Since the reintroduction of colistin, a number of mechanisms of colistin resistance in A. baumannii have been reported, including complete loss of LPS by inactivation of the biosynthetic pathway, modifications of target LPS driven by the addition of phosphoethanolamine (PEtN) moieties to lipid A mediated by the chromosomal pmrCAB operon and eptA gene-encoded enzymes or plasmid-encoded mcr genes and efflux of colistin from the cell. In addition to resistance to colistin, widespread heteroresistance is another feature of A. baumannii that leads to colistin treatment failure. This review aims to present a critical assessment of relevant published (>50 experimental papers) up-to-date knowledge on the molecular mechanisms of colistin resistance in A. baumannii with a detailed review of implicated mutations and the global distribution of colistin-resistant strains.
Keywords:
Acinetobacter baumannii; colistin resistance; lpx; pmr; mcr; LPS; lipid A; phosphoethanolamine transferase; epidemiology 1. Introduction
Colistin (polymyxin E) is a nonribosomally synthesized polycationic peptide that belongs to the class of polymyxin antibiotics, of which only two are used clinically: polymyxin B and colistin [1]. Colistin was introduced into clinical practice in the 1950s, but its use in human medicine was mainly limited to the treatment of pulmonary infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative pathogens in patients with cystic fibrosis due to nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity [2,3]. However, the widespread use of colistin in animal feed production has been maintained in developing countries and poses a major public health risk [4]. The rise of MDR, extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pan drug-resistant (PDR) strains of Gram-negative bacteria has sparked interest in the revival of antibiotics, such as colistin, which can be used as a last resort [5,6,7].
Colistin is a mixture of the cyclic decapeptide colistin A and B with a fatty acid chain (6-methyl-octanoic acid in colistin A or 6-methyl-heptanoic acid in colistin B) linked by an alpha-amide bond. The amphiphilic surfaces of colistin, which allow detergent-like activity on bacterial membranes, are formed by the N-terminal fatty acyl chain, D-Leu-Leu (hydrophobic), and three cationic amino acids (hydrophilic) [8,9]. Two forms, colistin sulfate for oral administration and colistimethate sodium for parenteral formulations, are currently commercially available.
Colistin is positively charged, therefore, it interacts electrostatically with the negatively charged phosphate groups of lipid A, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) component of Gram-negative bacilli outer membrane [10]. After the initial interaction, colistin displaces the divalent calcium and magnesium cations that affect the three-dimensional structure of LPS. In the next step, colistin inserts its hydrophobic terminal acyl fatty chain, leading to disruption and permeabilization of the outer membrane. When permeabilization occurs, colistin penetrates the outer membrane and alters the integrity of the phospholipid bilayer of the inner membrane, causing intracellular material to leak out and leading to cell death [11] (Figure 1A). Therefore, colistin is considered a bactericidal antibiotic.
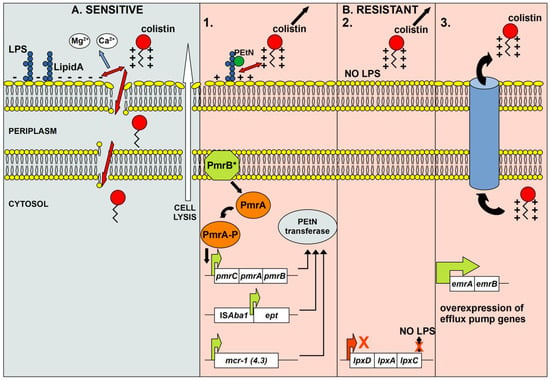
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the mode of action of colistin in susceptible cells (A) and the molecular mechanisms of resistance to colistin in resistant cells (B). A—Colistin causes lysis of susceptible cells due to induced disruption of the outer and inner membranes. Initial interactions between the positively charged moiety of colistin and the negatively charged phosphate groups of lipid A of LPS lead to the displacement of calcium and magnesium cations affecting the LPS structure. In the next step, the hydrophobic acyl fatty chain of colistin penetrates the outer membrane leading to its permeabilization. As a result of permeabilization, colistin penetrates the inner membrane and alters it integrity, leading to leakage of intracellular material and cell death. B—Resistance to colistin arises through several common mechanisms. 1. As a result of PEtN moiety addition to lipid A (mutations and overexpression of pmrCAB, eptA, or presence of plasmid-mediated mcr genes), the overall charge of the outer membrane changes so that colistin can no longer interact with lipid A of LPS. 2. Inactivation of the LPS biosynthetic pathway results in the absence of LPS, the target molecule for colistin. 3. Overexpression of specific efflux pumps leads to efficient extrusion of colistin, resulting in resistance.
This review aims to provide a comprehensive insight into the clinical significance of A. baumannii, the molecular mechanisms of colistin resistance, and the epidemiology of colistin-resistant strains, as well as an overview of recent advances in the field.
2. Clinical Significance of Acinetobacter baumannii
A. baumannii is recognized as a clinically significant pathogen causing a wide spectrum of nosocomial infections, especially in vulnerable patient groups [12]. These groups include intensive care unit (ICU) patients, patients with prolonged hospitalization in long-term care facilities, patients undergoing surgeries, central vascular catheterization, tracheostomy, and enteral hemorrhage, and low birth weight neonates [13,14,15,16,17]. The literature data on nosocomial A. baumannii infections are mainly based on reports of outbreaks [18]. These outbreaks are usually due to contamination from common sources or cross-infection, and frequent serial or overlapping outbreaks could be observed once A. baumannii was introduced into a clinical setting with a single strain dominating each outbreak [19,20,21]. Community-acquired A. baumannii infections are less common (mainly pneumonia and bacteremia) and have a more severe course than nosocomial infections and are generally considered fulminant. These infections occur mainly in elderly male patients in association with alcoholism, diabetes renal disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [22,23,24]. Mortality rates associated with A. baumannii infections vary considerably depending on concomitant diseases, length of hospital stay, demographic characteristics, and antibiotic susceptibility of the strains causing the infection, generally ranging from 12 to 50% [19,25,26,27,28]. Of particular importance is the difficulty in distinguishing A. baumannii colonization from infection. The recognized risk factors for infection were age, total number of hospitalized wards, absolute neutrophil count, and C-reactive protein (CRP) [29].
Bacteria of the genus Acinetobacter are considered ubiquitous microorganisms, obtained from various environments, including soil, rivers, and wastewaters. Although A. baumannii reservoirs have been reported in the environment outside hospitals [30], the natural habitats of clinically relevant strains remain unclear [31].
A. baumannii possesses extraordinary plasticity that allows it to adapt to a variety of living conditions, enabling its success as a nosocomial pathogen [32]. The ability of A. baumannii to adapt to the challenges of the hospital environment is considered to be the major factor in its pathogenicity. In addition, the strain-dependent differential regulation of virulence genes, the large number of transcriptional regulators compared to other Acinetobacter species, and the synergy of multiple genes encoding virulence factors are thought to contribute to the virulence potential of A. baumannii [32,33,34].
A burning issue in the biology of A. baumannii is the global spread of MDR strains. The increase in MDR strains is driven by both intrinsic and acquired antibiotic resistance mechanisms. Strains of A. baumannii are capable of upregulating intrinsic mechanisms of antibiotic resistance, which, in conjunction with the acquisition of new resistance genes through horizontal gene transfer, contributes to the spread and diversity of the A. baumannii resistome. A variety of intrinsic resistance mechanisms of A. baumannii, such as beta-lactamases, multiple drug efflux pumps, changes in membrane-associated proteins, ribosomal methylation, and enzymes that recognize multiple antimicrobials as substrates, have been described previously [35].
In addition to intrinsic resistance, gene flow and horizontal transfer have been shown to be another important driver of antibiotic resistance genes in A. baumannii [36]. These processes resulted in observable, significant variation in the resistome within different lineages, and antibiotic resistance was shaped by phylogeny, resulting in what has been termed an open resistome [36].
A. baumannii is considered intrinsically resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins [37]. The resistance of A. baumannii to beta-lactams is significant because penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams are the first-line therapeutics for the treatment of infections caused by A. baumannii. Inherent in all A. baumannii are chromosomally encoded cephalosporinases (formerly blaAmpC, now referred to Acinetobacter-derived cephalosporinase, ADC). Insertion of ISAba1 or ISAba125 sequences upstream of genes encoding ADC cephalosporinase induces its overexpression by providing stronger promoters [38,39,40]. The ADC enzymes may confer extended-spectrum resistance to beta-lactams [41,42,43]. In addition, covalent modification (dephosphorylation) of ADC enzymes could alter their substrate specificity and lead to imipenem resistance [44]. Several other beta-lactamases, such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) (including TEM, SHV, CTX-M, PER, VEB, and GES), metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs) (including IMP, VIM, GIM, and NDM), and oxacillinases (OXAs) (including OXA-23-like, OXA-24-like, OXA-51-like, and OXA-58-like) are commonly found in A. baumanni clinical isolates [45,46]. Resistance to beta-lactams could result from changes in the permeability of the cell to the antibiotic, usually due to changes in outer membrane proteins such as CarO, OmpA, and Omp33-36 porins [47,48,49,50]. It has been found that overexpression of the AdeABC efflux pump synergistically with the aforementioned beta-lactamases in A. baumannii leads to carbapenem and cephalosporin resistance [51,52].
Colistin is considered one of the last therapeutic options for the treatment of MDR A. baumannii infections and is used as rescue therapy for severe infections. Colistin resistance poses a greater risk of excess patient mortality [53,54]. The published data show that the prevalence of colistin resistance is higher in Southeast Asia and Eastern Mediterranean countries than in other regions of the world, with an overall value of 11.2% (Germany 0.2%, United Kingdom 2.3%, India 8.2%, China 11.8%, and Lebanon 17.5%) [55].
3. Molecular Mechanisms of Colistin Resistance in A. baumannii
Colistin, as a positively charged peptide, exerts its antibacterial effect via electrostatic interactions with negatively charged lipid A, a component of LPS [56]. Accordingly, two main mechanisms of colistin resistance have been described in A. baumannii: the complete loss or modifications of the target LPS, leading to abolishing or reducing its negative charge [57]. The complete loss of LPS results from inactivation of the first three genes of the lipid A biosynthetic pathway (lpxA, lpxC, and lpxD genes) [58], whereas the modification of LPS occurs through the addition of phosphoethanolamine (PEtN) moieties to lipid A by the pmrCAB operon-encoded enzymes [59]. Although 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose (L-Ara4N) modification of LPS has been described as a more common and effective colistin resistance mechanism compared to PEtN LPS modification in diverse Gram-negative pathogens (Salmonella enterica, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), it was absent in A. baumannii [57]. In addition to chromosome-mediated mechanisms, plasmid-mediated colistin resistance encoded by mcr genes has been recognized as a major driver of rapid dissemination by horizontal gene transfer among pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria, including A. baumannii [60] (Figure 1B).
3.1. Loss of LPS Structure
The first observation that LPS deficiency causes colistin resistance in A. baumannii was made by Moffat and coauthors [58]. Laboratory-induced colistin-resistant A. baumannii derivatives contained mutations in one of the first three lipid A biosynthetic genes (lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) (Figure 1B). Although, these mutations ranged from single nucleotide mutations to large deletions (up to 445 nucleotides), they all resulted in complete loss of LPS. Moreover, disruption of the lpxD gene by insertion of an IS element similar to the ISX03 element (IS4 family) was described in a colistin-resistant clinical isolate [58]. Shortly thereafter, the same team found that ISAba11 inactivated the lpxC and lpxA genes in colistin-resistant derivatives of A. baumannii ATCC19606 [61]. In subsequent studies, the insertion of ISAba1 or ISAba11 within the lpxC gene was described as a common event in colistin-resistant A. baumannii. As the disruption of the lpxC gene occurred in the same region (321–420 nt) in different isolates, it was suggested that this region might represent a hot spot for the integration of ISs [61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68]. Colistin resistance in A. baumannii has also been associated with various nucleotide substitutions, deletions, and insertions in all three lipid A biosynthetic genes (lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) that cause frameshifts or result in truncated proteins that impair lipid A biosynthesis. While the described mutational events in the lpxA gene are not site-specific, non-synonymous mutations in the lpxC (P30L or S, N287D) and lpxD (E117K) genes were previously found to be present in colistin-resistant isolates from different origins [58,69,70,71,72,73,74]. Although the amino acid substitutions N287D (lpxC) and E117K (lpxD) were detected in both colistin-susceptible and colistin-resistant isolates, it is possible that these alterations in combination with a mutation in the pmrCAB operon have a synergistic effect leading to colistin resistance [69,70,71,72,73,74]. In addition, the downregulation of lpxACD expression has been observed in some colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates, leading to decreased LPS production [68,73,74,75,76].
At the time when LPS deficiency was described as the mechanism causing colistin resistance in A. baumannii, this discovery was surprising because LPS biosynthesis was thought to be essential for the viability of Gram-negative bacteria [77]. So far, survival without LPS has been described only in a few species, such as Neisseria meningitidis, Moraxella catarrhalis, and two Acinetobacter species (A. baumannii and A. nosocomialis) [78,79,80]. Although this mechanism ensures a high level of colistin resistance [58,61,65], the frequency of mutations in the lpxACD is lower compared to changes in the pmrCAB operon in colistin-resistant A. baumannii clinical isolates [66,81,82]. The proposed explanation for the lower prevalence of LPS-deficient colistin-resistant mutants in clinical settings could be the significant negative impact of LPS loss on fitness and virulence, as well as the susceptibility of these isolates to various antibiotics and disinfectants. This was supported by the findings that the lpx mutants grew more slowly compared to the parental wild-type strains in vitro [64,66,68,81,83], while in vitro and in vivo competition tests showed significant fitness costs of colistin resistance [81]. Determination of the pathogenicity of the lpx mutants also revealed lower cytotoxicity (A549 human alveolar epithelial cells) and attenuated virulence of these strains in the animal models (Caenorhabditis elegans, Galleria mellonella, and mouse) compared to wild-type or even pmrB mutants [63,66,81]. As expected, the absence of LPS on the cell surface resulted in weak stimulation of neutrophils and, consequently, lower production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines [66,83]. Nevertheless, the lpx mutants were more prone to killing mediated by neutrophils compared to the wild type since they were more susceptible to neutrophil-secreted lysozyme [83]. Moreover, reduced virulence of LPS-deficient A. baumannii in the host could also be explained by reduced biofilm formation, surface motility, as well as poor growth under iron limitation [66,83]. Finally, another disadvantage of LPS loss for the bacterial cell is evident in the increased susceptibility to various clinically used antibiotics, especially antibiotics used in the therapy of A. baumannii infections (ceftazidime, imipenem, meropenem, tigecycline, ciprofloxacin, amikacin, and rifampin), and various disinfectants (phenol-based disinfectants, quaternary ammonium disinfectants, sodium dodecyl sulfate, benzalkonium, chlorhexidine, deoxycholate, and ethanol) [58,63,64,65,66,68,83].
3.2. PEtN Modification of LPS Structure
3.2.1. PmrCAB and EptA
The modification of LPS is a commonly described mechanism for acquired colistin resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. In A. baumannii, PetN is added to the 4′-phosphate or 1-phosphate group of lipid A, reducing the negative charge of this LPS component and the binding affinity of colistin [57] (Figure 1B). This type of colistin resistance is predominantly mediated by mutations in genes encoding the PmrAB two-component system, resulting in the overexpression of the phosphoethanolamine transferase PmrC [84] (Figure 1B). The most common and diverse amino acid changes associated with colistin resistance in A. baumannii were detected in the PmrB protein (Table 1). Since Adams et al. [59] observed that mutations in the pmrB gene can cause high colistin resistance (MIC greater than 128 µg/mL) in laboratory-induced A. baumannii derivatives, numerous studies have described the presence of altered PmrB proteins in colistin-resistant clinical isolates or in vitro-derived derivatives of A. baumannii (Table 1). Although these nonsynonymous mutations were detected in all domains of PmrB, the greatest number were located in the histidine kinase A (HisKA) domain (predominantly at positions 226, 227, 232, 233, 235, and 263) (Table 1), which is responsible for autophosphorylation and the transfer of the phosphoryl group to the PmrA response regulator [85]. Accordingly, pmrB mutations could lead to the constitutive activation of PmrA, resulting in increased expression of the pmrCAB and resistance to colistin [59]. In addition, previous studies reported frequent amino acid substitutions of PmrB at position 170 (P to Y, L, Q, or S) (Table 1) and 315 (G to D, S, or V) in colistin-resistant isolates [68,70,76,84,86]. Although Oikonomou and coauthors [69] described the PmrB mutations (A138T, A226V, and A444V) repeated in colistin-resistant A. baumannii [70,72,73,74,76,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91] as not responsible for colistin resistance, the involvement of A138T and A226V in this phenomenon should not be excluded. Indeed, the amino acid change at position 226 (A to V) in PmrB alone or in combination with A138T enabled high colistin resistance (64 or 128 and 256, respectively) in the tested isolates [84,88]. The amino acid substitutions within the receiver domain (REC) of the PmrA response regulator have also been described in A. baumannii as resistant to colistin (E8D, D10N, M12I, K, or V, I13M, or S, A14V, I18T, L20F, G54E, A80V, D82G, P102H, or R, F105L) [59,68,69,72,84,86,89,90,92,93,94,95,96,97,98]. Some of the PmrA mutations alone (G54E) or in combination with mutations in other genes (P102R) can confer significantly high colistin resistance to A. baumannii (>256 µg/mL or 512 µg/mL) [97,98]. To date, little data are available on the relationship between PmrC amino acid changes and colistin resistance. A comparison of PmrC amino acid sequences between colistin-susceptible and colistin-resistant isolates revealed rare changes and mostly at different positions [65,69,72,73,74,75,76,84,89,95,97]. In the study conducted by Nurtop and coauthors [72], the two most commonly described mutations in the pmrC gene (resulting in I42V and L150F) were found to be associated with an increased expression of the pmrA and pmrC genes and, consequently, colistin resistance. The PmrC substitution R109H, detected in colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates in two previous studies [69,72], was associated with colistin resistance along with a mutation in the pmrA gene [69]. In addition, it was observed that the PmrC alteration R125P in combination with changes within the PmrB protein had a synergistic effect on colistin resistance in A. baumannii [97]. In summary, mutations in the pmrCAB locus are recognized as gain-of-function mutations because they lead to PmrC overexpression and PEtN modification of lipid A, which, in turn, results in colistin resistance [84,99]. In addition to increased expression of PmrC as a mechanism of colistin resistance in A. baumannii [65,72,73,75,76,84,85,88,92,97,98,100], the upregulation of the pmrA and pmrB genes was found in some colistin-resistant isolates [59,71,96,101,102], but to a much lesser extent [68,72,73,75,76,84,92,98]. Although this observation is to be expected as these genes are part of the same operon as the pmrC gene (pmrCAB), there are cases where no correlation was found between PmrAB and PmrC overexpression [72,73,76]. In addition, Lesho and coauthors [92] noted the overexpression of another pmrC homolog (eptA, ethanolamine phosphotransferase A) in some colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates. Detailed analysis revealed that the gene encoding for EptA was detected only in isolates belonging to the international clone 2 (IC2), was found in ≥3 copies in a single isolate, and was distant from the pmrCAB operon in A. baumannii genomes [88,90,92]. Although the presence of the eptA gene in the bacterial genome alone does not confer resistance to colistin, the integration of ISAba1 upstream of the eptA gene could lead to increased expression of this enzyme [88] (Figure 1B). In contrast, Gerson et al. [100] found the presence of ISAba1 upstream of the eptA gene in colistin-susceptible and colistin-resistant counterparts, but only in isolates with mutations in the eptA gene (R127L) and ISAba1 (A→T in position 1091) was overexpression of EptA detected. Interestingly, a previous study showed that disruption of the gene encoding the global regulator H-NS by ISAba125 causes high colistin resistance in A. baumannii through increased expression of the eptA gene in this mutant strain [103].

Table 1.
Overview of PmrB sensor kinase mutations in colistin-resistant A. baumannii.
A negative correlation was found between PmrAB-related colistin resistance and the fitness and virulence of A. baumannii in the host. The colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates showed lower fitness in vitro and in vivo and reduced virulence potential in animal models of infection compared to their colistin-susceptible parental strains [62,92,93,104,105,106,107,108]. This could be explained by the downregulation of metabolic and antioxidant proteins, virulent porins OmpA and CarO, and the system responsible for biofilm formation in colistin-resistant A. baumannii [107,109,110]. In addition, some studies reported a correlation between colistin resistance and decreased biofilm formation ability [108,110]. In contrast to the initially reported negative correlation, additional studies showed unchanged fitness [63,64,68,100,111,112] and pathogenicity of colistin-resistant A. baumannii [63,81,100,111]. Interestingly, two studies described the emergence of colistin resistance in A. baumannii isolated from patients exposed to colistin therapy and the subsequent disappearance of this resistance after the discontinuation of colistin [111,113]. Durante-Mangoni and coauthors [111] observed that colistin-resistant pmrB-mutated isolates were comparable to wild type in in vitro and in vivo assays, whereas Snitkin et al. [113] hypothesized that resistant isolates were outcompeted by colistin-susceptible isolates due to lower in vivo fitness costs. In addition, a comparison of five longitudinal colistin-resistant A. baumannii isolates from the same patient indicated an increase in growth rate as well as virulence in the mouse lung infection model during colistin therapy [114]. Jones and coauthors [114] explained this phenomenon by more pronounced resistance to ROS in late colistin-resistant isolates. Overall, these data suggest that no clear conclusion can be made about the correlation of colistin resistance due to pmrAB mutations and biological costs in A. baumannii. Although some pmrAB mutations responsible for colistin resistance initially appeared to be maladaptive to bacterial cells, prolonged exposure to the selective agent (colistin) may have allowed the emergence of compensatory changes at different regulatory levels and remedied a deficit in fitness and virulence [63,104,113,114]. In addition, in this type of research, the genetic background should be taken into account as the results obtained from different isolates containing the same PmrB alteration P233S were different [107,108,111,112]. The studies comparing the behavior of the pmrAB mutants with lpxACD mutants have undoubtedly confirmed that the LPS modification causes lower fitness and virulence costs than LPS deficiency [63,64,81]. Most studies that examined colistin-resistant A. baumannii showed that PmrAB alterations had no significant impact on the antibiotic resistance profile of these isolates [64,68,69,84,92,112]. Consistent with the above observations, a systematic review concluded that LPS modification mediated by the pmrAB mutations is the major in vivo mechanism of colistin resistance [82].
3.2.2. Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance
Since the first report of the phosphoethanolamine transferase-encoding mcr gene (mcr-1) in E. coli in China [119], the presence of this gene and its variants has been demonstrated in many Gram-negative bacteria distributed worldwide [60]. To date, ten different mcr gene families (mcr-1 to mcr-10) with more than 100 variants have been described in bacteria isolated from animals, food, humans, and the environment [60,120]. In A. baumannii, the mcr-1 and mcr-4.3 variants are most commonly detected (Figure 1B). The mcr-1 has been reported in clinical isolates from Asia (Pakistan, Iraq, and China) and Africa (Egypt) at sporadic frequency (n = 1–3) with the exception of samples collected from hospitals in Iraq (up to 89) [121,122,123,124,125,126]. The earliest mcr-4.3-positive isolate of A. baumannii was recovered from the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with meningitis in Brazil in 2008 [127], which preceded the mcr discovery by Lui and coauthors [119]. Subsequently, mcr-4.3 was detected in pig feces from a slaughterhouse in China [128] and in isolates from the Czech Republic [129,130]. The studies from the Czech Republic suggest that food imports from Latin America (frozen turkey livers from Brazil) and Asia (frog legs from Vietnam) may represent the primary route of transmission of mcr-carrying A. baumannii to Europe and thus to European hospitals [129,130]. As some studies showed that the recombinant expression of mcr-4.3 in E. coli did not alter colistin MIC [131,132], while another study indicated that the heterologous expression of mcr-4.3 could ensure colistin resistance through LPS modification in A. baumannii [127], it is not possible to draw a firm conclusion about its role in colistin resistance. Moreover, a comparative analysis revealed that the mcr-4.3-harbouring plasmids in A. baumannii share a common origin for this structure. It was found that these plasmids are untypable and cannot be transferred to other bacteria by conjugation or transformation [128,129,130]. Although mcr-1 and mcr-4.3 are predominant, other mcr variants have also been described in clinical and environmental samples of A. baumannii, as in a study from Iraq where the mcr-2 and mcr-3 genes were found. A large number of these isolates carry a single mcr gene or a combination of different mcr families (mcr-1, mcr-2, and mcr-3) [122]. Finally, it is important to highlight that most of the mcr-carrying A. baumannii isolates are MDR [121,122,124,125,126,127], and there are few antibiotic-susceptible isolates [128,129].
3.3. Other Mechanisms of Colistin Resistance
In addition to the aforementioned mechanisms of colistin resistance in A. baumannii, expulsion of the antibiotic by efflux pump systems is another mechanism of importance (Figure 1B). Lin and coauthors [133] demonstrated the contribution of the EmrAB efflux system to colistin resistance in A. baumannii using the ΔemrB mutant (Figure 1B). In addition, the upregulation of genes encoding protein components of efflux pumps (adeI, adeC, emrB, mexB, and macAB) was shown in colistin-resistant strains [67]. In addition, an amino acid substitution (N104M) in the gene encoding the toluene tolerance efflux pump (ttg2C) was found to be associated with high-level colistin resistance [70]. Further evidence for the role of efflux pumps in colistin resistance is the suppression of resistance in the presence of the efflux pump inhibitor (EPI), cyanide-3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) [134].
Another mechanism of colistin resistance in A. baumannii is associated with certain non-Lpx (lipo) proteins involved in the composition and maintenance of the outer membrane (OM) (lpsB, lptD, vacJ, pldA, and A1S_0807) [99,135]. The study conducted by Hood et al. [136] indicated that the loss of LpsB, a glycosyltransferase responsible for LPS core synthesis, leads to increased susceptibility to colistin and cationic host defense peptides, highlighting the role of this protein in A. baumannii virulence. Along with changes in the pmr and lpx genes, single mutations in the lpsB gene (H181Y and *241K) of colistin-resistant A. baumannii have been reported [108,137]. In addition, the final translocation of LPS from the cytosol to OM could be disturbed by mutations in the lptD gene, which has resulted in moderate polymyxin B resistance [138]. Colistin resistance of certain A. baumannii isolates analyzed by Nhu and coauthors [70] was attributed, in whole or in part, to amino acid substitutions of the OM lipoprotein VacJ (R166N and Q249T) and the phospholipase PldA (T200T). As VacJ, part of the ABC transporter system, and PldA are recognized as factors responsible for maintaining lipid asymmetry in OM, the proposed mechanism of this type of colistin resistance is OM disorganization due to vacJ and pldA mutations [70]. In addition, it has been observed that impaired lipid metabolism caused by a reduction in biotin synthesis could provide protection to A. baumannii during colistin exposure [136]. Recent studies using modern technologies (whole genome sequencing, RNA sequencing, and transposon-directed insertion site sequencing) have identified numerous genes (Ab09_2943, ACICU_02910, ACICU_RS15345, A1S_1983, A1S_2024/ACICU_01043, A1S_2027, A1S_2230/ACICU_02436, A1S_2443, A1S_2928, A1S_3026, aroP_3, baeR, benP, betI_2, cho1, cobS, cobV, cysH, dcm, dnmT1, dtyMK, eno, filD, garK, glxK, hepA, iclR, lpsO, mdh, miaA, mlaC, mlaD, mlaF, mutY, mpsT, pgaB, pheS, pssA, pstS, ptk, rsfS, shlB_1, sseA, tmk, tst udg, ureC, and zndP) whose sequence or expression in colistin-resistant A. baumannii was altered compared to colistin-susceptible strains [64,67,70,75,76,97,98,139]. The degree of association of these candidate genes with colistin resistance in A. baumannii should be confirmed experimentally in future studies.
3.4. Colistin Heteroresistance and Dependence
Antibiotic heteroresistance is defined as the presence of a resistant subpopulation within a population susceptible to a given antibiotic [140]. Since the first report of colistin heteroresistance in clinical isolates of A. baumannii from Australia [141], this phenomenon has been described in many studies with prevalence ranging from 1.84 to 100% [142,143,144]. Hawley and coauthors [142] found a higher rate of heteroresistance in isolates from patients treated with colistin, suggesting that previous colistin therapy may be a risk factor for the induction of heteroresistance. Data indicating resistance stability within the surviving subpopulation after cultivation under non-selective conditions were conflicting in different studies, suggesting a possible species-specific dependence [140,141,142,145]. Interestingly, Hong et al. [140] observed isolates that exhibited a heteroresistance phenotype only at low antibiotic concentrations alongside the typical colistin-heteroresistant isolates that emerged at exposure to high colistin concentrations. The previously described mechanisms of colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii are the same as those of colistin resistance (LpxACD, PmrCAB, and efflux pumps) [73,140,143,145,146]. Amino acid changes in LpxC (S186R) and LpxD (N148K and T289I) were associated with partial loss of LPS in heteroresistant strains [143], while another study showed upregulation of the pmrCAB operon in combination with mutations in the pmrA and pmrB genes in resistant subpopulations of A. baumannii [146]. The overexpression of efflux pumps and the synergistic effect of EPIs and colistin against the resistant subpopulation of heteroresistant A. baumannii clearly demonstrated the involvement of efflux pumps in this phenotype [143,145]. Of particular concern is the fact that conventional susceptibility testing identifies heteroresistant isolates as susceptible to colistin, resulting in colistin treatment failure [143]. As population analysis profiling (PAP) is recognized as the gold standard for detecting heteroresistance, the introduction of the mini-PAP method with colistin at >2 mg/L into clinical practice has been recommended [147]. Moreover, the prevalence of heteroresistant isolates clearly exceeds the occurrence of colistin-resistant A. baumannii [148]. Moreover, under selection pressure, a resistant subpopulation of heteroresistant populations could become predominant and lead to a resistant cell population [145]. Accordingly, isolates identified as colistin-heteroresistant have been proposed for colistin-based combination therapy instead of colistin monotherapy [144]. Although the phenomenon of colistin heteroresistance has been studied mainly in A. baumannii of nosocomial origin, it has also been detected in samples from hospital wastewaters [73,149].
Another phenomenon observed in some colistin-susceptible A. baumannii isolates exposed to colistin is colistin dependence. After exposure to colistin, a colistin-dependent subpopulation of cells becomes dependent on this antibiotic for optimal growth [150]. Previous findings have suggested the colistin-dependent phenotype as a survival response to colistin pressure and an intermediate stage between colistin susceptibility or heteroresistance and even extreme resistance to colistin [65,150].
4. Epidemiology of Colistin-Resistant A. baumannii
Data providing information on the epidemiology of colistin-resistant A. baumannii are generally shown by MLST categorization (Oxford and Pasteur) of these isolates [151,152]. According to the less discriminating Pasteur scheme, colistin-resistant A. baumannii sequence type (ST) 2 isolates are found to be most prevalent ST associated with colistin resistance in A. baumannii and occur in all continents for which data are available (Europe, Asia, Africa, and North and South America) [73,74,75,76,86,88,89,90,91,97,107,153,154,155] (Figure 2). In addition, ST1 was detected in Europe and Africa [90,95,97,154,156], whereas other Pasteur STs occurred exclusively in specific continents (Europe—ST195, ST345, ST490, ST492, ST537, ST632, ST636, ST745, ST1421, and ST1816; Asia—ST1303; Africa—ST158 and ST570; North America—ST46 and ST94; South America—ST15, ST25, ST79, and ST730) [74,76,86,88,89,92,97,116,128,129,130,157] (Figure 2). In addition, ST1 has been transmitted both nosocomially [90,97], and by animals in Europe [95].
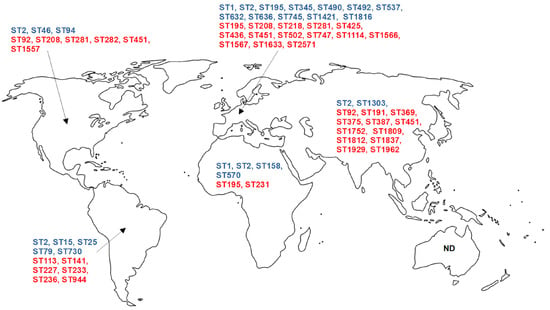
Figure 2.
Global distribution of colistin-resistant A. baumannii STs according to published studies. Data for North America include the United States of America and Canada, while data for South America include data for the rest of the American continent. Pasteur MLST scheme—blue letters, Oxford MLST scheme—red letters. ND—no data available.
MLST typing according to the Oxford scheme revealed that some STs of A. baumannii resistant to colistin are distributed across different continents: ST92 (Asia and North America) [101,158], ST195 (Europe and Africa) [76,154], ST208 [76,86,90,97] and ST281 [75,86,97] (Europe and North America), and ST451 (Europe, Asia, and North America) [86,90,97,139,158] (Figure 2). Interestingly, ST208 has been suggested to be identical to ST92, with the typing result depending on the sequencing performed (high-throughput or Sanger, respectively) [86]. This suggests a significant dissemination of colistin-resistant A. baumannii in Europe, Asia, and North America. In Europe, the following STs have been reported in more than one study: ST208 [76,90,97]; ST281 [75,97]; ST425 [76,90,97]; and ST436, ST451, and ST1567 [90,97]. However, in North America and South America, only a single ST, ST451 [86,158] and ST233 [96,157] were detected, respectively. Additionally, some STs were detected only in single studies (ST113, ST141, ST191, ST218, ST227, ST231, ST233, ST236, ST282, ST369, ST375, ST387, ST502, ST747, ST944, ST1114, ST1557, ST1566, ST1633, ST1752, ST1809, ST1812, ST1837, ST1929, ST1962, and ST2571) [76,86,96,97,102,117,127,128,129,139,154,157,158,159,160] (Figure 2).
The literature search revealed a lack of data on the epidemiology of colistin-resistant A. baumannii STs in Australia and Oceania, pointing out the need for additional primary research to fill the existing knowledge gap.
5. Conclusions
A. baumannii has become a significant nosocomial pathogen because of its adaptability to healthcare settings, virulence characteristics, and ability to acquire antibiotic resistance. The increasing prevalence of MDR strains enhanced the use of colistin as rescue therapy, leading to the rise in colistin-resistance strains worldwide. The diversity of the colistin resistome in A. baumannii encompassing multiple mechanisms, including dissemination through horizontal gene transfer, requires thorough investigations that will provide comprehensive knowledge of this emerging pathogen and provide insights into the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance that will direct novel areas of research. Given the increasing prevalence of colistin-resistant strains, a reassessment of current therapeutic approaches, including alternatives to traditional antibiotics therapies, is strongly recommended. Promising results have been shown in vitro for cefiderocol (a molecule with an innovative mode of action), intravenous fosfomycin (in combination with cefiderocol), and combination therapy with sulbactam–durlobactam [161,162,163].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.N. and B.J.; writing—original draft preparation, K.N. and B.J; writing—review and editing, K.N. and B.J.; visualization, B.J.; supervision, B.J.; funding acquisition, K.N. and B.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant Nos. 451-03-68/2022-14/200042 and 451-03-47/2023-01/200178).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cassir, N.; Rolain, J.M.; Brouqui, P. A new strategy to fight antimicrobial resistance: The revival of old antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, S.P.; Pond, M.N.; Watson, A.; Etherington, C.; Robey, H.L.; Goldman, M.H. Intravenous colistin sulphomethate in acute respiratory exacerbations in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 1997, 52, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.; Prasad, A.; Collyer, L.; Carr, S.; Lynn, I.B.; Wallis, C. Bronchoconstriction following nebulised colistin in cystic fibrosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 84, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Brunel, J.M.; Dubus, J.C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Rolain, J.M. Colistin: An update on the antibiotic of the 21st century. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannot, K.; Bolard, A.; Plesiat, P. Resistance to polymyxins in Gram-negative organisms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.; Rivard, K. Polymyxin resistance in Gram-negative pathogens. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.G.; Zhong, L.L.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.B. Colistin and its role in the Era of antibiotic resistance: An extended review (2000–2019). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Demain, A.L. The peptide antibiotics of Bacillus: Chemistry, biogenesis, and possible functions. Bacteriol. Rev. 1977, 41, 449–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, D.R.; Rosenthal, K.S.; Swanson, P.E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1977, 46, 723–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deris, Z.Z.; Akter, J.; Sivanesan, S.; Roberts, K.D.; Thompson, P.E.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J.; Velkov, T. A secondary mode of action of polymyxins against Gram-negative bacteria involves the inhibition of NADH-quinone oxidoreductase activity. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkov, T.; Thompson, P.E.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Structure-activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1898–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, F.C.; Dexter, C.; Kostoulias, X.; Uddin, M.I.; Peleg, A.Y. The mechanisms of disease caused by Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.E.; Richet, H. The epidemiology and control of Acinetobacter baumannii in health care facilities. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Arheart, K.; Nordmann, P.; Boulanger, A.E.; Cleary, T.; Alvarez, R.; Pizano, L.; Namias, N.; Kett, D.H.; Poirel, L. Eighteen years of experience with Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care hospital. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub Moubareck, C.; Hammoudi Halat, D. Insights into Acinetobacter baumannii: A Review of Microbiological, Virulence, and Resistance Traits in a Threatening Nosocomial Pathogen. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risser, C.; Pottecher, J.; Launoy, A.; Ursenbach, A.; Belotti, L.; Boyer, P.; Willemain, R.; Lavigne, T.; Deboscker, S. Management of a Major Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Outbreak in a French Intensive Care Unit While Maintaining Its Capacity Unaltered. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.C.; Chau, P.H.; So, S.Y.C.; Lam, G.K.M.; Chan, V.W.M.; Yuen, L.L.H.; Au Yeung, C.H.Y.; Chen, J.H.K.; Ho, P.L.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Control of Healthcare-Associated Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by Enhancement of Infection Control Measures. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, M.V.; Hartstein, A.I. Acinetobacter outbreaks, 1977–2000. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Cevallos, M.A.; Castro-Jaimes, S.; Castillo-Ramírez, S.; Velázquez-Acosta, C.; Martínez-Oliva, D.; Pérez-Oseguera, A.; Rivera-Buendía, F.; Volkow-Fernández, P. High mortality in an outbreak of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection introduced to an oncological hospital by a patient transferred from a general hospital. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Wu, J.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Quyen, T.L.T.; Liao, W.C.; Li, S.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Pan, Y.J. An Outbreak of tet(X6)-Carrying Tigecycline-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates with a New Capsular Type at a Hospital in Taiwan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.M.; Cho, H.W.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, J.S.; Jung, J.; Song, K.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Park, K.U. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Investigating a Health Care-Associated Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.N.; Lu, C.H.; Huang, C.R.; Chuang, Y.C. Community-acquired Acinetobacter meningitis in adults. Infection 2000, 28, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Karveli, E.A.; Kelesidis, I.; Kelesidis, T. Community acquired Acinetobacter infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 26, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Rafailidis, P.I. Attributable mortality of Acinetobacter baumannii: No longer a controversial issue. Crit. Care 2007, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xiang, D.; Liu, Q.; Xing, X. Prognosis of patients with Acinetobacter baumannii infection in the intensive care unit: A retrospective analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.V.; Shah, J.S.; Revathi, G.; Siika, W.; Shah, R. Acinetobacter infections: A retrospective study to determine inhospital mortality rate and clinical factors associated with mortality. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2019, 1, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.J.; Cho, E.B.; Bae, M.; Lee, S.C.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.N.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; et al. Clinical and Microbiological Analysis of Risk Factors for Mortality in Patients With Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremia. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appaneal, H.J.; Lopes, V.V.; LaPlante, K.L.; Caffrey, A.R. Treatment, Clinical Outcomes, and Predictors of Mortality among a National Cohort of Admitted Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0197521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.Y.; Zhou, J.X.; Li, X.; Wu, W.B.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.T. Differentiation between Acinetobacter baumannii colonization and infection and the clinical outcome prediction by infection in lower respiratory tract. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5401–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Qiao, L. The Acinetobacter baumannii group: A systemic review. World J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 4, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenovic, J.; Durn, G.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Kovacic, A. Occurrence of an environmental Acinetobacter baumannii strain similar to a clinical isolate in paleosol from Croatia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperi, F.; Antunes, L.C.; Blom, J.; Villa, L.; Iacono, M.; Visca, P.; Carattoli, A. The genomics of Acinetobacter baumannii: Insights into genome plasticity, antimicrobial resistance and pathogenicity. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; de Breij, A.; Adams, M.D.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Mocali, S.; Galardini, M.; Nibbering, P.H.; Earl, A.M.; Ward, D.V.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. The success of Acinetobacter species; genetic, metabolic and virulence attributes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, N.C.; Campos, T.L.; Rezende, A.M.; Docena, C.; Mendes-Marques, C.L.; de Sá Cavalcanti, F.L.; Wallau, G.L.; Rocha, I.V.; Cavalcanti, C.L.B.; Veras, D.L.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains From Brazil Reveals Polyclonal Dissemination and Selective Exchange of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated With Resistance Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, I.; Vasileiou, E.; Pana, Z.D.; Tragiannidis, A. Acinetobacter baumannii Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms. Pathogens 2021, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-González, I.L.; Mateo-Estrada, V.; Castillo-Ramirez, S. The promiscuous and highly mobile resistome of Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héritier, C.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Cephalosporinase over-expression resulting from insertion of ISAba1 in Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.S.; Amyes, S.G.B. Role of ISAba1 and ISAba125 in governing the expression of bla ADC in clinically relevant Acinetobacter baumannii strains resistant to cephalosporins. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidian, M.; Hall, R.M. ISAba1 targets a specific position upstream of the intrinsic ampC gene of Acinetobacter baumannii leading to cephalosporin resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2682–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.B.; Adams-Haduch, J.M.; Taracila, M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Wang, H.N.; Doi, Y. Extended-spectrum AmpC cephalosporinase in Acinetobacter baumannii: ADC-56 confers resistance to cefepime. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4922–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.C.; Lee, Y.T.; Lauderdale, T.L.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Chuang, M.F.; Chen, C.P.; Su, S.C.; Lee, K.R.; Chen, T.L. Contribution of Acinetobacter-derived cephalosporinase-30 to sulbactam resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingti, B.; Upadhyay, S.; Hazarika, M.; Khyriem, A.B.; Paul, D.; Bhattacharya, P.; Joshi, S.R.; Bora, D.; Dhar, D.; Bhattacharjee, A. Distribution of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii with blaADC-30 and induction of ADC-30 in response to beta-lactam antibiotics. Res. Microbiol. 2020, 171, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.H.; Yang, J.T.; Chern, J.; Chen, T.L.; Wu, W.L.; Liao, J.H.; Tsai, S.F.; Liang, S.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Wu, S.H. Comparative phosphoproteomics reveals the role of AmpC β-lactamase phosphorylation in the clinical imipenem-resistant strain Acinetobacter baumannii SK17. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2016, 15, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, R.A. β-Lactamases: A focus on current challenges. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a025239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Kooguchi, K.; Moriyama, K. Molecular diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, and antimicrobial resistance. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, M.D.M.; Beceiro, A.; Pérez, A.; Velasco, D.; Moure, R.; Villanueva, R.; Martínez-Beltrán, J.; Bou, G. Cloning and functional analysis of the gene encoding the 33- to 36-kilodalton outer membrane protein associated with carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 5172–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussi, M.A.; Limansky, A.S.; Relling, V.; Ravasi, P.; Arakaki, A.; Actis, L.A.; Viale, A.M. Horizontal gene transfer and assortative recombination within the Acinetobacter baumannii clinical population provide genetic diversity at the single carO gene, encoding a major outer membrane protein channel. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4736–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novovic, K.; Mihajlovic, S.; Vasiljevic, Z.; Filipic, B.; Begovic, J.; Jovcic, B. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from Serbia: Revision of CarO classification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novović, K.; Mihajlović, S.; Dinić, M.; Malešević, M.; Miljković, M.; Kojić, M.; Jovčić, B. Acinetobacter spp. porin Omp33-36: Classification and transcriptional response to carbapenems and host cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, L.; Xu, G.; Xia, T. Differential susceptibility to carbapenems due to the AdeABC efflux pump among nosocomial outbreak isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in a Chinese hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkey, J.; Ascher, D.B.; Judd, L.M.; Wick, R.R.; Kostoulias, X.; Cleland, H.; Spelman, D.W.; Padiglione, A.; Peleg, A.Y.; Holt, K.E. Evolution of carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii during a prolonged infection. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzarlis, K.; Makris, D.; Zakynthinos, E. Risk factors for the first episode of Acinetobacter baumannii resistant to colistin infection and outcome in critically ill patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanakos, G.; Andrianopoulos, I.; Papathanasiou, A.; Priavali, E.; Koulenti, D.; Koulouras, V. Colistin resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia: A serious threat for critically ill patients. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pormohammad, A.; Mehdinejadiani, K.; Gholizadeh, P.; Nasiri, M.J.; Mohtavinejad, N.; Dadashi, M.; Karimaei, S.; Safari, H.; Azimi, T. Global prevalence of colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausell, A.; Garcia-Subirats, M.; Pujol, M.; Busquets, M.A.; Rabanal, F.; Cajal, Y. Gram-negative outer and inner membrane models: Insertion of cyclic cationic lipopeptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.; Hale, J.D.; Vinogradov, E.; Seemann, T.; Henry, R.; Crane, B.; St Michael, F.; Cox, A.D.; et al. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Nickel, G.C.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Lavender, H.; Murthy, A.R.; Jacobs, M.R.; Bonomo, R.A. Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntayaporn, P.; Thirapanmethee, K.; Chomnawang, M.T. An update of mobile colistin resistance in non-fermentative gram-negative bacilli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 882236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Adler, B.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J.; Boyce, J.D. Insertion sequence IS Aba11 is involved in colistin resistance and loss of lipopolysaccharide in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3022–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.P.; Ong, R.T.; Hon, P.Y.; Hawkey, J.; Holt, K.E.; Koh, T.H.; Leong, M.L.N.; Teo, J.Q.M.; Tan, T.Y.; Ng, M.M.L.; et al. Multiple genetic mutations associated with polymyxin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7899–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, M.E.; Bock, L.J.; Bonney, L.C.; Sutton, J.M. Retention of virulence following adaptation to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii reflects the mechanism of resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hua, X. The effect of colistin resistance-associated mutations on the fitness of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chung, E.S.; Ko, K.S. Transition of colistin dependence into colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Ledesma, M.; García-Quintanilla, M.; Martín-Peña, R.; Pulido, M.R.; Pachón, J.; McConnell, M.J. Phenotypic changes associated with Colistin resistance due to Lipopolysaccharide loss in Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2018, 9, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinett, C.J.; Cain, A.K.; Hawkey, J.; Do Hoang, N.T.; Khanh, N.N.T.; Thanh, D.P.; Dordel, J.; Campbell, J.I.; Lan, N.P.H.; Mayho, M.; et al. Clinical and laboratory-induced colistin-resistance mechanisms in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoshida, G.; Yamada, N.; Nakamura, T.; Yamaguchi, D.; Kai, D.; Yamashita, M.; Hayashi, C.; Kanda, N.; Sakaguchi, M.; Morimoto, H.; et al. Preferential Selection of Low-Frequency, Lipopolysaccharide-Modified, Colistin-Resistant Mutants with a Combination of Antimicrobials in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01928-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, O.; Sarrou, S.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Georgiadou, S.; Mantzarlis, K.; Zakynthinos, E.; Dalekos, G.N.; Petinaki, E. Rapid dissemination of colistin and carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Central Greece: Mechanisms of resistance, molecular identification and epidemiological data. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, N.T.K.; Riordan, D.W.; Nhu, T.D.H.; Thanh, D.P.; Thwaites, G.; Lan, N.P.H.; Wren, B.W.; Baker, S.; Stabler, R.A. The induction and identification of novel Colistin resistance mutations in Acinetobacter baumannii and their implications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Aurosree, B.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Balada-Llasat, J.M.; Pancholi, V.; Pancholi, P. The role of LpxA/C/D and pmrA/B gene systems in colistin-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Lab. Med. 2017, 1, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurtop, E.; Bilman, F.B.; Menekse, S.; Azap, O.K.; Gönen, M.; Ergonul, O.; Can, F. Promoters of colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovcic, B.; Novovic, K.; Dekic, S.; Hrenovic, J. Colistin resistance in environmental isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ušjak, D.; Novović, K.; Filipić, B.; Kojić, M.; Filipović, N.; Stevanović, M.M.; Milenković, M.T. In vitro colistin susceptibility of pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii is restored in the presence of selenium nanoparticles. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, V.; Stracquadanio, S.; Lo Verde, F.; Gabriele, G.; Mezzatesta, M.L.; Caio, C.; Pigola, G.; Ferro, A.; Stefani, S. Colistin resistant A. baumannii: Genomic and transcriptomic traits acquired under colistin therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabic, J.; Novovic, K.; Kekic, D.; Trudic, A.; Opavski, N.; Dimkic, I.; Gajic, I. Comparative genomics and molecular epidemiology of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 21, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Meredith, T.C.; Kahne, D. On the essentiality of lipopolysaccharide to Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, L.; den Hartog, R.; den Boer, A.; Zomer, B.; Roholl, P.; van der Ley, P. Meningitis bacterium is viable without endotoxin. Nature 1998, 392, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Hong, W.; Choudhury, B.P.; Carlson, R.W.; Gu, X.X. Moraxella catarrhalis bacterium without endotoxin, a potential vaccine candidate. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Farrés, X.; Ferrer-Navarro, M.; Callarisa, A.E.; Martí, S.; Espinal, P.; Gupta, S.; Rolain, J.M.; Giralt, E.; Vila, J. Loss of LPS is involved in the virulence and resistance to colistin of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter nosocomialis mutants selected in vitro. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Moreno, A.; Fernández, N.; Vallejo, J.A.; Aranda, J.; Adler, B.; Harper, M.; Boyce, J.D.; Bou, G. Biological cost of different mechanisms of colistin resistance and their impact on virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakonstantis, S. A systematic review of implications, mechanisms, and stability of in vivo emergent resistance to colistin and tigecycline in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Chemother. 2020, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoshida, G.; Akaji, T.; Takemoto, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kai, D.; Hibino, T.; Yamaguchi, D.; Kikuchi-Ueda, T.; Nishida, S.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Deficient Acinetobacter baumannii Due to Colistin Resistance Is Killed by Neutrophil-Produced Lysozyme. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, L.A.; Herrera, C.M.; Fernandez, L.; Hankins, J.V.; Trent, M.S.; Hancock, R.E. The pmrCAB operon mediates polymyxin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 and clinical isolates through phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeili, M.; Kafshdouz, M.; Feizabadi, M.M. Molecular mechanisms of colistin resistance among pandrug-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii with high case-fatality rate in intensive care unit patients. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, M.M.; Li, B.; Pacey, M.P.; Mettus, R.T.; McElheny, C.L.; Marshall, C.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Cooper, V.S.; Doi, Y. Phylogenomics of colistin-susceptible and resistant XDR Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2952–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroidi, A.; Likousi, S.; Palla, E.; Katsiari, M.; Roussou, Z.; Maguina, A.; Platsouka, E.D. Molecular identification of tigecycline-and colistin-resistant carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii from a Greek hospital from 2011 to 2013. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebosc, V.; Gartenmann, S.; Tötzl, M.; Lucchini, V.; Schellhorn, B.; Pieren, M.; Lociuro, S.; Gitzinger, M.; Tigges, M.; Bumann, D.; et al. Dissecting colistin resistance mechanisms in extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. mBio 2019, 10, e01083-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, N.S.; Gamal, D.; Mohamed, S.H.; Wasfy, R.M.; Soliman, M.S.; El-Kholy, A.A.; Higgins, P.G. Molecular characterization of Carbapenem/Colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Egypt by whole-genome sequencing. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Pelegrin, A.C.; Perrot, N.; Mirande, C.; Blanc, B.; Legakis, N.; Goossens, H.; Rossolini, G.M.; van Belkum, A. Abundance of colistin-resistant, OXA-23-and ArmA-producing Acinetobacter baumannii belonging to international clone 2 in Greece. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadtapong, N.; Chaturongakul, S.; Soodvilai, S.; Dubbs, P. Colistin and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Aci46 in Thailand: Genome analysis and antibiotic resistance profiling. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesho, E.; Yoon, E.J.; McGann, P.; Snesrud, E.; Kwak, Y.; Milillo, M.; Onmus-Leone, F.; Preston, L., St.; Clair, K.; Nikolich, M.; et al. Emergence of colistin-resistance in extremely drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii containing a novel pmrCAB operon during colistin therapy of wound infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rojas, R.; McConnell, M.J.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Pachón, J. Colistin resistance in a clinical Acinetobacter baumannii strain appearing after colistin treatment: Effect on virulence and bacterial fitness. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4587–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolain, J.M.; Diene, S.M.; Kempf, M.; Gimenez, G.; Robert, C.; Raoult, D. Real-time sequencing to decipher the molecular mechanism of resistance of a clinical pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolate from Marseille, France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misic, D.; Asanin, J.; Spergser, J.; Szostak, M.; Loncaric, I. OXA-72-mediated carbapenem resistance in sequence type 1 multidrug (Colistin)-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii associated with urinary tract infection in a dog from Serbia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00219-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, G.C.; Stabler, R.A.; Neves, P.; Neto, L.V.P.; Martins, R.C.R.; Rizek, C.; Rossi, F.; Levin, A.S.; Costa, S.F. Genetic and virulence characterization of colistin-resistant and colistin-sensitive A. baumannii clinical isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, S.; Lucassen, K.; Wille, J.; Nodari, C.S.; Stefanik, D.; Nowak, J.; Wille, T.; Betts, J.W.; Roca, I.; Vila, J.; et al. Diversity of amino acid substitutions in PmrCAB associated with colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, D. New mutations involved in colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Msphere 2020, 5, e00895-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, W.G.; Alves, M.C.; Cruz, W.S.; Paiva, M.C. Chromosomally encoded and plasmid-mediated polymyxins resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: A huge public health threat. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, S.; Betts, J.W.; Lucaßen, K.; Nodari, C.S.; Wille, J.; Josten, M.; Göttig, S.; Nowak, J.; Stefanik, D.; Roca, I.; et al. Investigation of novel pmrB and eptA mutations in isogenic Acinetobacter baumannii isolates associated with colistin resistance and increased virulence in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01586-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.K.; Choi, J.Y.; Shin, D.; Ko, K.S. Correlation between overexpression and amino acid substitution of the PmrAB locus and colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnood, S.; Savari, M.; Abbasi Montazeri, E.; Farajzadeh Sheikh, A. Survey on genetic diversity, biofilm formation, and detection of colistin resistance genes in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveson Lucas, D.; Crane, B.; Wright, A.; Han, M.L.; Moffatt, J.; Bulach, D.; Gladman, S.L.; Powell, D.; Aranda, J.; Seemann, T.; et al. Emergence of high-level colistin resistance in an Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate mediated by inactivation of the global regulator H-NS. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02442-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rojas, R.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; McConnell, M.J.; Docobo-Peréz, F.; Smani, Y.; Fernández-Reyes, M.; Rivas, L.; Pachón, J. Impaired virulence and in vivo fitness of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolain, J.M.; Roch, A.; Castanier, M.; Papazian, L.; Raoult, D. Acinetobacter baumannii resistant to colistin with impaired virulence: A case report from France. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1146–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hraiech, S.; Roch, A.; Lepidi, H.; Atieh, T.; Audoly, G.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D.; Brunel, J.M.; Papazian, L.; Brégeon, F. Impaired virulence and fitness of a colistin-resistant clinical isolate of Acinetobacter baumannii in a rat model of pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5120–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaras, S.; Poulou, A.; Dafopoulou, K.; Chabane, Y.N.; Kristo, I.; Makris, D.; Hardouin, J.; Cosette, P.; Tsakris, A.; Dé, E. Growth retardation, reduced invasiveness, and impaired colistin-mediated cell death associated with colistin resistance development in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafopoulou, K.; Xavier, B.B.; Hotterbeekx, A.; Janssens, L.; Lammens, C.; Dé, E.; Goossens, H.; Tsakris, A.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Pournaras, S. Colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains with deficient biofilm formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Wong, S.; Spelman, D.; Franklin, C. Antibiograms of multidrug-resistant clinical Acinetobacter baumannii: Promising therapeutic options for treatment of infection with colistin-resistant strains. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Reyes, M.; Rodríguez-Falcón, M.; Chiva, C.; Pachón, J.; Andreu, D.; Rivas, L. The cost of resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii: A proteomic perspective. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1632–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Del Franco, M.; Andini, R.; Bernardo, M.; Giannouli, M.; Zarrilli, R. Emergence of colistin resistance without loss of fitness and virulence after prolonged colistin administration in a patient with extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahdouh, E.; Gómez-Gil, R.; Sanz, S.; González-Zorn, B.; Daoud, Z.; Mingorance, J.; Suárez, M. A novel mutation in pmrB mediates colistin resistance during therapy of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snitkin, E.S.; Zelazny, A.M.; Gupta, J.; Palmore, T.N.; Murray, P.R.; Segre, J.A. NISC Comparative Sequencing Program Genomic insights into the fate of colistin resistance and Acinetobacter baumannii during patient treatment. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Singh, S.S.; Alamneh, Y.; Casella, L.G.; Ernst, R.K.; Lesho, E.P.; Waterman, P.E.; Zurawski, D.V. In vivo fitness adaptations of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates to oxidative stress. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00598-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Llobet, E.; Aranda, J.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Hornsey, M.; Dhanji, H.; Chart, H.; Bou, G.; Livermore, D.M.; et al. Phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A in colistin-resistant variants of Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by the pmrAB two-component regulatory system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3370–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, V.; Conzemius, R.; Varda-Brkić, D.; Bogdan, M.; Grisold, A.; Gyssens, I.C.; Bedenić, B.; Barišić, I. Epidemiology of colistin-resistant, carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter baumannii in Croatia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bae, I.K.; Lee, H.; Jeong, S.H.; Yong, D.; Lee, K. In vivo emergence of colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates of sequence type 357 during colistin treatment. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Kil, M.C.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Ko, K.S. Characterisation of successive Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a deceased haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patient. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.H.; AL-Kadmy, I.; Taha, B.M.; Hussein, J.D. Mobilized colistin resistance (mcr) genes from 1 to 10: A comprehensive review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, F.; Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, H.; Sarwar, T.; Bilal, H.; Rehman, T.U. Plasmid-mediated mcr-1 gene in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: First report from Pakistan. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20190237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Al-Saryi, N.; Aziz, S.N.; Besinis, A.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence of genes involved in colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: First report from Iraq. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Li, C.; Duan, R.; Qin, S.; Liang, J.; Xiao, M.; Lv, D.; Jing, H.; Wang, X. Retrospective Screening and Analysis of mcr-1 and blaNDM in Gram-Negative Bacteria in China, 2010–2019. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.M. Emergence of mcr- and fosA3-mediated colistin and fosfomycin resistance among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Iraq. Meta Gene 2020, 25, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabban, M.; Fahim, N.A.E.; Montasser, K.; El Magd, N.M.A. Resistance to colistin mediated by mcr-1 among multidrug resistant Gram negative pathogens at a tertiary care hospital, Egypt. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, H.; Younas, S.; Qamar, M.U.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosalif, K.O.A.; Alameen, A.A.M.; Elamir, M.Y.M.; Ahmad, N.; Hamam, S.S.M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of extensively drug-resistant mcr encoded colistin-resistant bacterial strains co-expressing multifarious β-lactamases. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Sorenson, N.; Snesrud, E.; Xavier, D.E.; Cacci, L.C.; Iavarone, A.T.; McGann, P.; Riley, L.W.; Moreira, B.M. A novel plasmid-encoded mcr-4.3 gene in a colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Shen, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhong, L.; Liang, Y.; Liao, K.; Xia, Y.; Tian, G.B.; et al. Identification of a novel plasmid carrying mcr-4.3 in an Acinetobacter baumannii strain in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00133-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, I.; Medvecky, M.; Gelbicova, T.; Jakubu, V.; Hrabak, J.; Zemlickova, H.; Karpiskova, R.; Dolejska, M. Complete nucleotide sequences of mcr-4.3-carrying plasmids in Acinetobacter baumannii sequence type 345 of human and food origin from the Czech Republic, the first case in Europe. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01166-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalová, A.; Gelbíčová, T.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Litrup, E.; Karpíšková, R. Characterisation of colistin-resistant Enterobacterales and Acinetobacter strains carrying mcr genes from Asian aquaculture products. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, J.W.; Kalisvar, M.; Venkatachalam, I.; Ng, O.T.; Lin, R.T.; Octavia, S. mcr-3 and mcr-4 variants in carbapenemase-producing clinical Enterobacteriaceae do not confer phenotypic polymyxin resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01562-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyman, Y.; Reuter, S.; Whitelaw, A.C.; Stein, L.; Maloba, M.R.B.; Newton-Foot, M. Characterisation of mcr-4.3 in a colistin-resistant Acinetobacter nosocomialis clinical isolate from Cape Town, South Africa. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lan, C.Y. Contribution of EmrAB efflux pumps to colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Effects of efflux pump inhibitors on colistin resistance in multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3215–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailing, Z.; Jieling, Z.; Honglang, L. Mechanism of Colistin Resistance to Acinetobacter Baumannii and its Progress-A Review Article. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2020, 29, 22183–22188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, M.I.; Becker, K.W.; Roux, C.M.; Dunman, P.M.; Skaar, E.P. Genetic determinants of intrinsic colistin tolerance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, S.S.; Suhaili, Z.; Ismail, S.; Rahman, N.I.A.; Othman, N.; Abdullah, F.H.; Jusoh, Z.; Yeo, C.C.; Thong, K.L. Prevalence and genetic characterization of carbapenem- and polymyxin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from a tertiary hospital in Terengganu, Malaysia. Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2014, 2014, 953417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkovic, J.; Richie, D.L.; Six, D.A.; Rath, C.M.; Sawyer, W.S.; Hu, Q.; Dean, C.R. Characterization of an Acinetobacter baumannii lptD deletion strain: Permeability defects and response to inhibition of lipopolysaccharide and fatty acid biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, C.; Chung, H.S.; Lee, M. Whole-genome sequencing for the characterization of resistance mechanisms and epidemiology of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.K.; Kim, H.; Ko, K.S. Two types of colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rayner, C.R.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Spelman, D.; Tan, K.E.; Liolios, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.S.; Murray, C.K.; Jorgensen, J.H. Colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter and its association with previous colistin therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Deciphering colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Wenzhou, China. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Saridakis, I. Colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter spp.: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and discussion of the mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, D.; Antunes, J.; Simões, A.; Perdigão, J.; Couto, I.; McCusker, M.; Martins, M.; Portugal, I.; Pacheco, T.; Batista, J.; et al. Contribution of efflux to colistin heteroresistance in a multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charretier, Y.; Diene, S.M.; Baud, D.; Chatellier, S.; Santiago-Allexant, E.; van Belkum, A.; Guigon, G.; Schrenzel, J. Colistin heteroresistance and involvement of the PmrAB regulatory system in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00788-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.; Owen, R.J.; Poudyal, A.; Bell, J.M.; Turnidge, J.D.; Heidi, H.Y.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Colistin hetero-resistance in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from the Western Pacific region in the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme. J. Infect. 2009, 58, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chai, D.; Wang, R.; Liang, B.; Bai, N. Colistin resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii: Clinical reports, mechanisms and antimicrobial strategies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Music, M.S.; Hrenovic, J.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Hunjak, B.; Skoric, D.; Ivankovic, T. Emission of extensively-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from hospital settings to the natural environment. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, H.; Hameir, A.; Temkin, E.; Keren-Paz, A.; Schwartz, D.; Schechner, V.; Carmeli, Y. Colistin Dependency among Colistin-Heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartual, S.G.; Seifert, H.; Hippler, C.; Luzon, M.A.D.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4382–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Nemec, A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Brisse, S. The population structure of Acinetobacter baumannii: Expanding multiresistant clones from an ancestral susceptible genetic pool. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Voulgari, E.; Barchitta, M.; Quattrocchi, A.; Bellocchi, P.; Poulou, A.; Santangelo, C.; Castiglione, G.; Giaquinta, L.; Romeo, M.A.; et al. Spread of a carbapenem-and colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 clonal strain causing outbreaks in two Sicilian hospitals. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Singh-Moodley, A.; Ismail, H.; Thomas, T.; Chibabhai, V.; Nana, T.; Lowman, W.; Ismail, A.; Chan, W.Y.; Perovic, O. Molecular characterisation of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from bloodstream infections in a tertiary-level hospital in South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogbou, N.D.; Ramashia, M.; Nkawane, G.M.; Allam, M.; Obi, C.L.; Musyoki, A.M. Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strain Isolated at a Tertiary Health Facility in Pretoria, South Africa. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, Y.; Whitelaw, A.C.; Reuter, S.; Dramowski, A.; Maloba, M.R.B.; Newton-Foot, M. Clonal expansion of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in Cape Town, South Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodari, C.S.; Cayô, R.; Streling, A.P.; Lei, F.; Wille, J.; Almeida, M.S.; De Paula, A.I.; Pignatari, A.C.C.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G.; et al. Genomic analysis of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates belonging to major endemic clones in South America. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 584603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Hittle, L.E.; O’Hara, J.A.; Rivera, J.I.; Syed, A.; Shields, R.K.; Pasculle, A.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Doi, Y. Colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Beyond carbapenem resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Casallas, J.C.; Robayo-Amortegui, H.; Corredor-Rozo, Z.; Carrasco-Márquez, A.M.; Escobar-Perez, J. Bacteremia by colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolate: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahraman, M.R.K.; Hosseini-Nave, H.; Azizi, O.; Shakibaie, M.R.; Mollaie, H.R.; Shakibaie, S. Molecular characterization of lpxACD and pmrA/B two-component regulatory system in the colistin resistance Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Gene Rep. 2020, 21, 100952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracquadanio, S.; Bonomo, C.; Marino, A.; Bongiorno, D.; Privitera, G.F.; Bivona, D.A.; Mirabile, A.; Bonacci, P.G.; Stefani, S. Acinetobacter baumannii and Cefiderocol, between Cidality and Adaptability. Microbiol Spectr. 2022, 10, e0234722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Stracquadanio, S.; Campanella, E.; Munafò, A.; Gussio, M.; Ceccarelli, M.; Bernardini, R.; Nunnari, G.; Cacopardo, B. Intravenous Fosfomycin: A Potential Good Partner for Cefiderocol. Clinical Experience and Considerations. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlowsky, J.A.; Hackel, M.A.; McLeod, S.M.; Miller, A.A. In Vitro Activity of Sulbactam-Durlobactam against Global Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus Complex Collected from 2016 to 2021. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0078122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).