Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressing for Advanced Management of Infected Wound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Integrating Antibacterial Nanomaterials into Wound Dressings for Infection Control
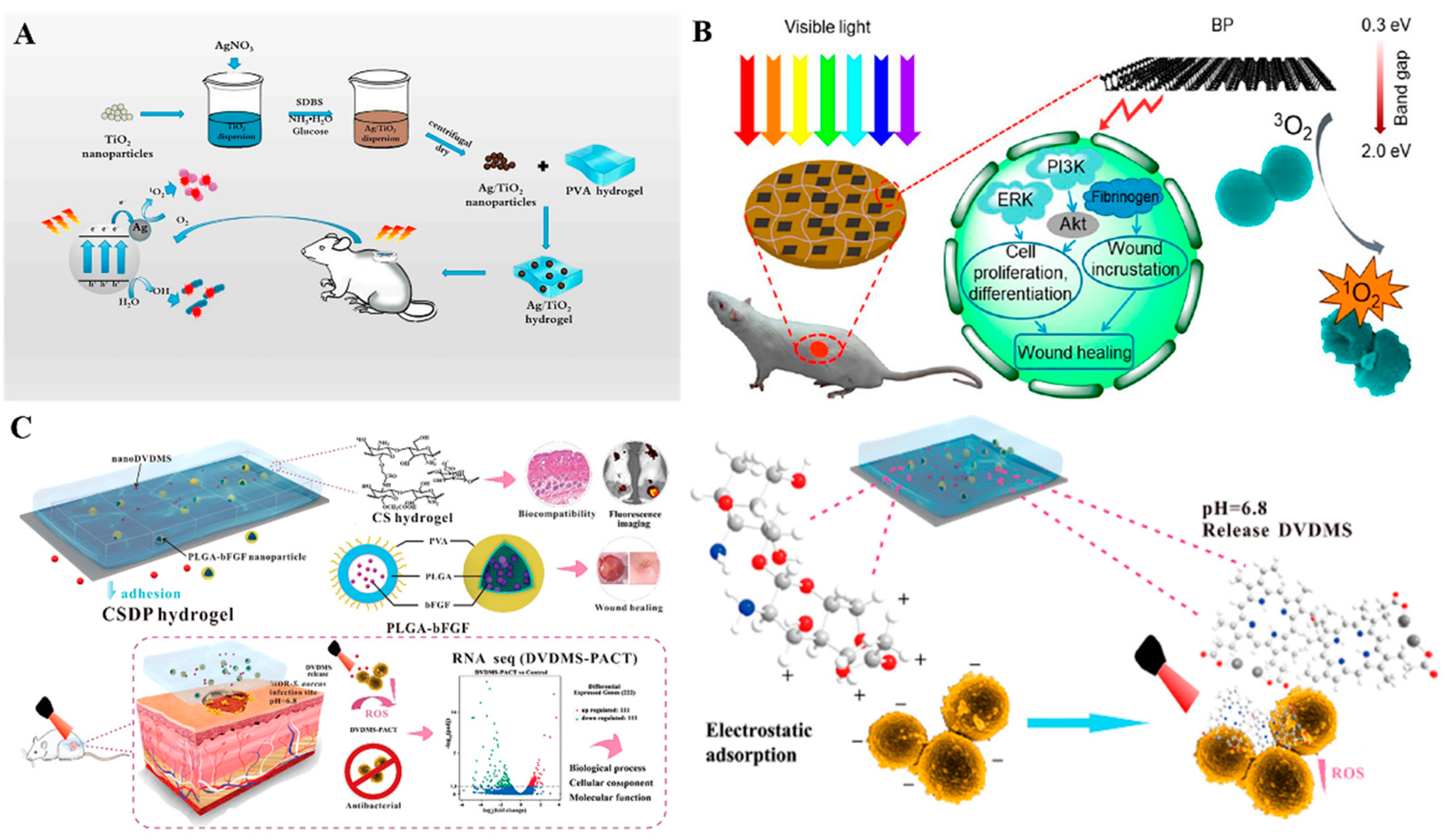
2.1. Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Intrinsic Antibacterial Treatment Agents
2.2. Nanomaterials as Passive Carriers of Antibacterial Agents for Antibacterial Treatment
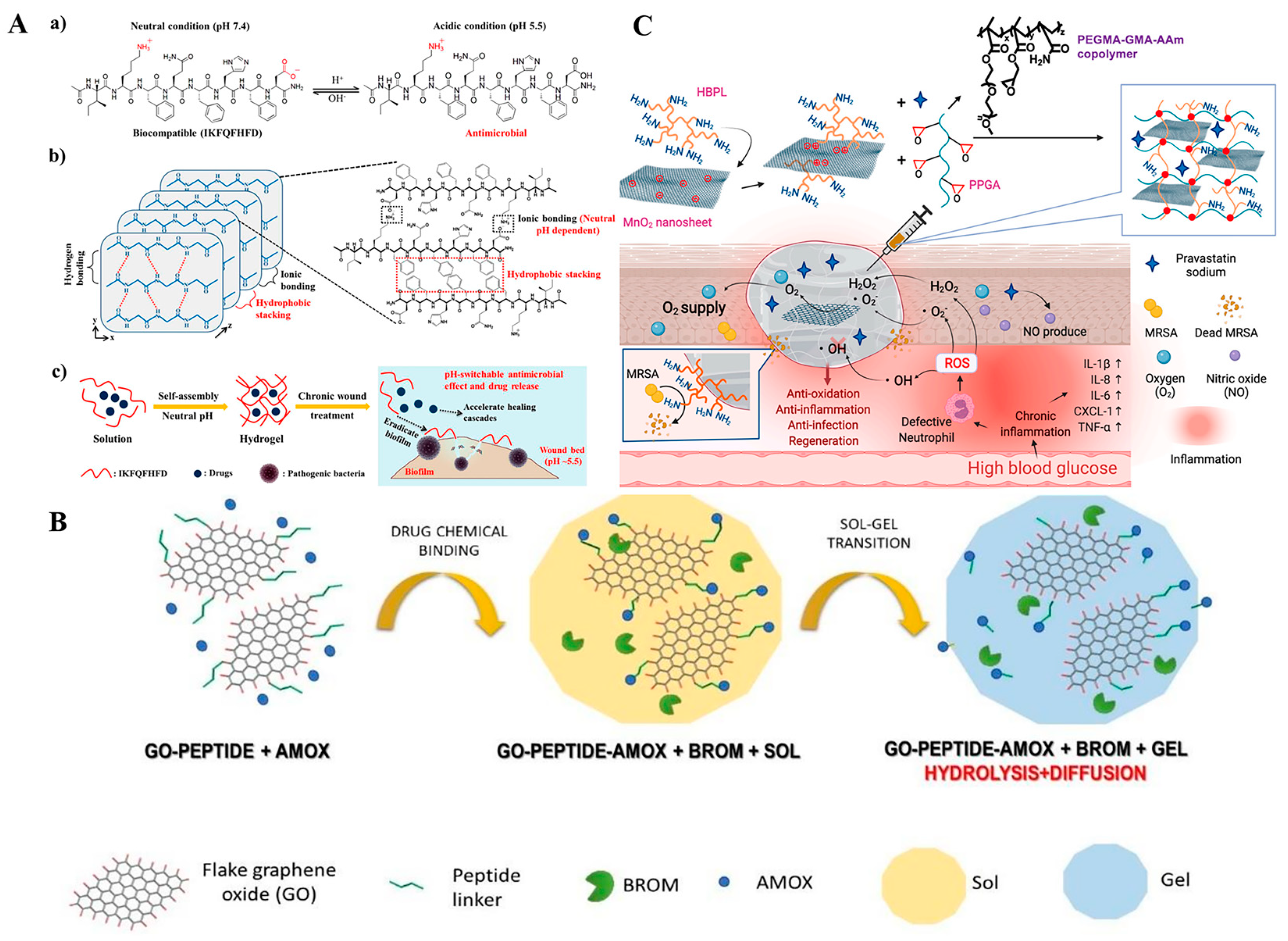
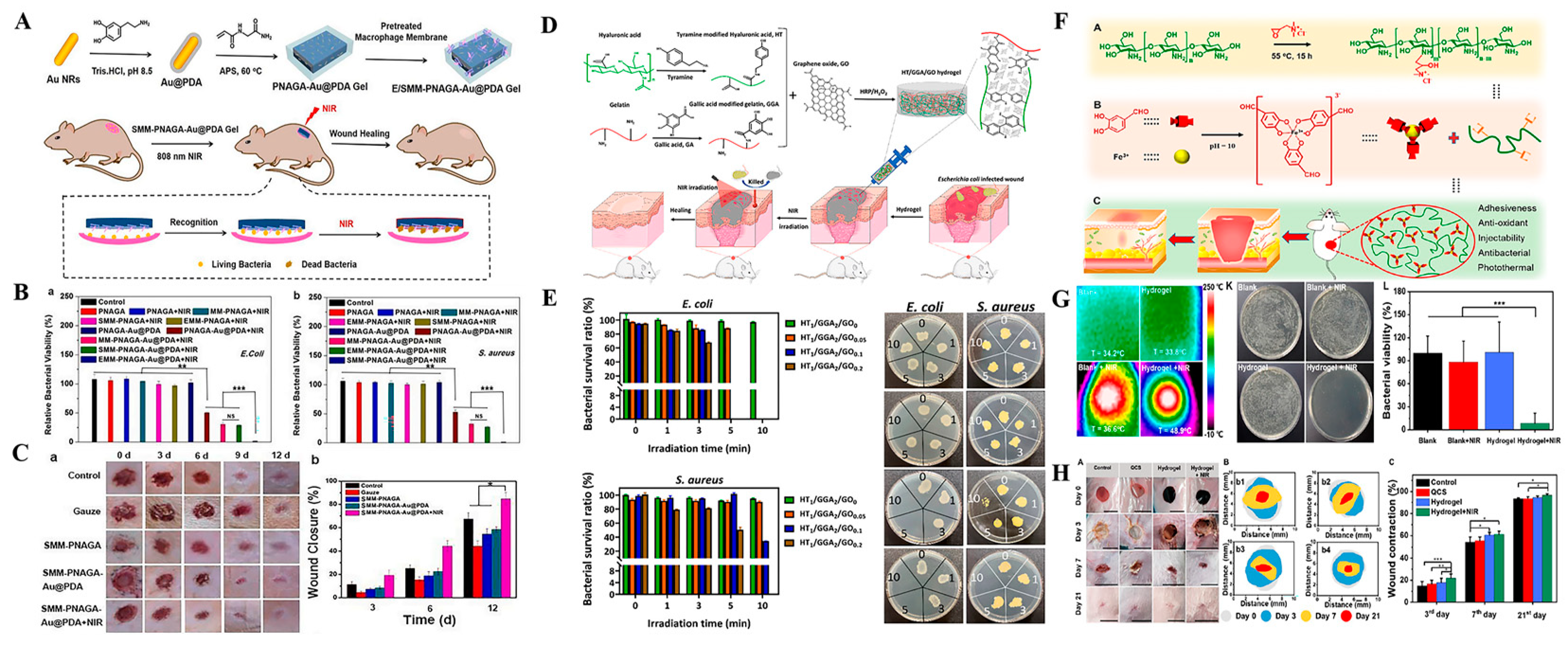
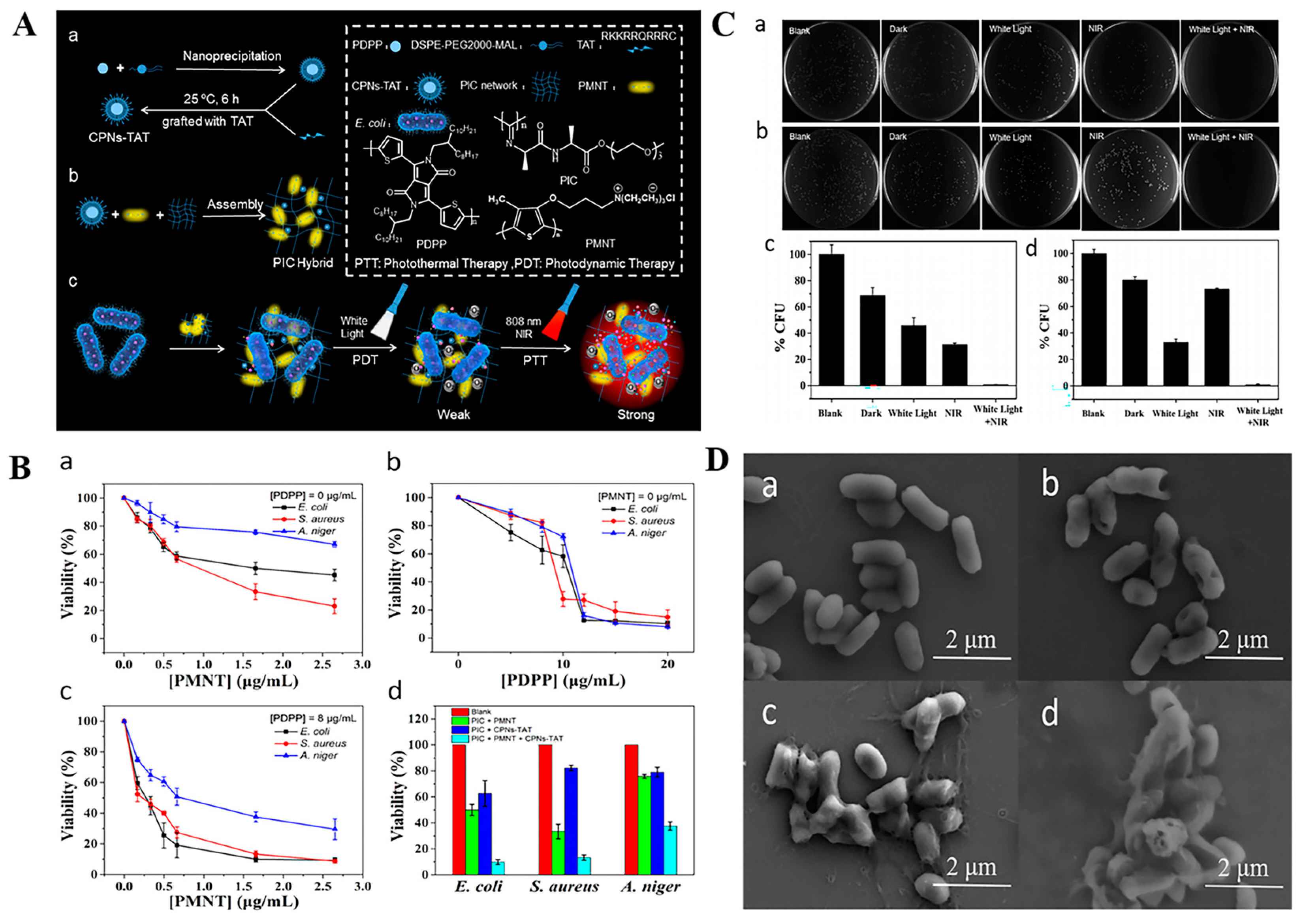
2.3. Stimuli-Responsive Nanomaterials Carriers of Antibacterial Agents for Antibacterial Treatment
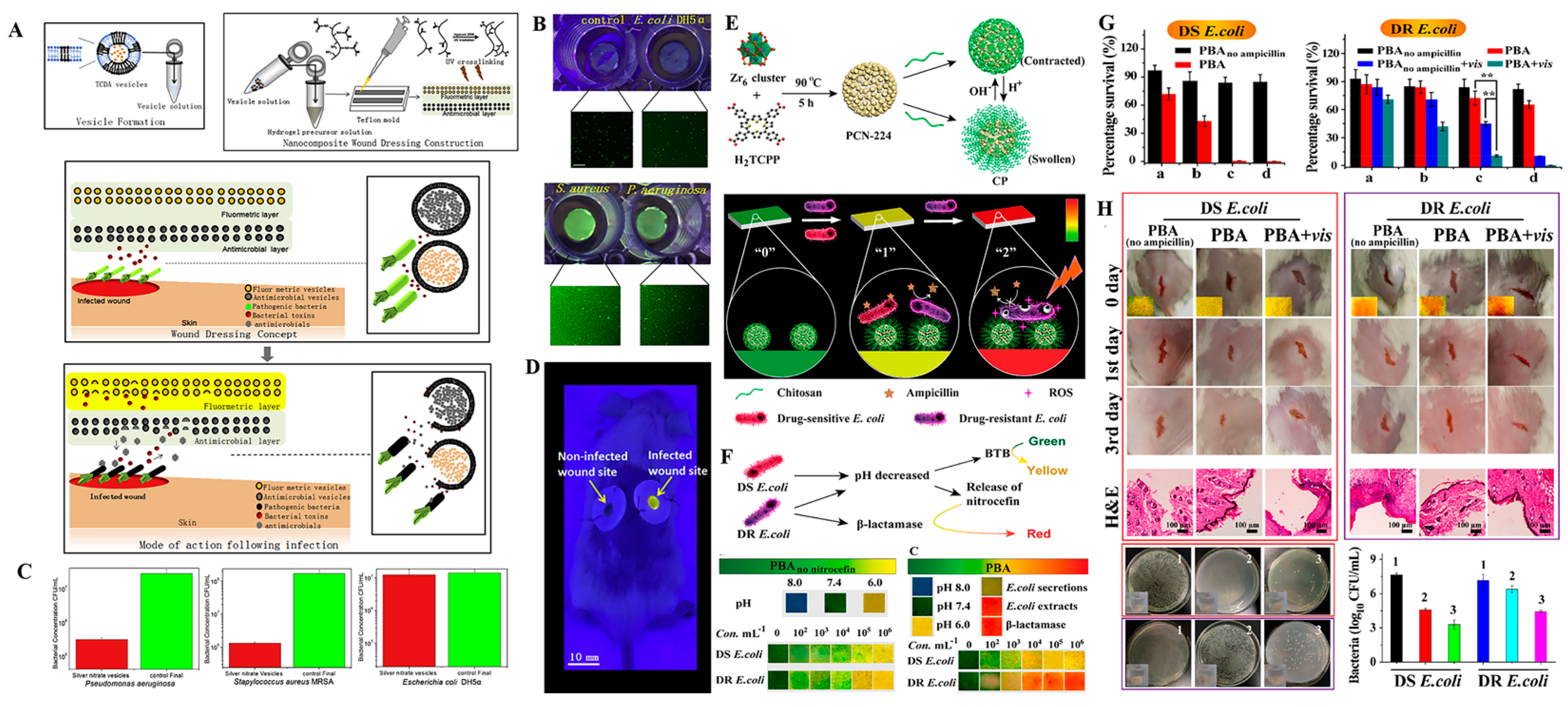
3. Intelligent Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressings for Infection Detection and Treatment
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, C.K.; Gordillo, G.M.; Roy, S.; Kirsner, R.; Lambert, L.; Hunt, T.K.; Gottrup, F.; Gurtner, G.C.; Longaker, M.T. Human skin wounds: A major and snowballing threat to public health and the economy. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markova, A.; Mostow, E.N. US skin disease assessment: Ulcer and wound care. Dermatol. Clin. 2012, 30, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Repair Regen. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, H.; Khodaei, M.; Alizadeh, Z.; Banitalebi-Dehkordi, M. Cationic, anionic and neutral polysaccharides for skin tissue engineering and wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 298–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Acute and impaired wound healing: Pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 2: Role of growth factors in normal and pathological wound healing: Therapeutic potential and methods of delivery. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2012, 25, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2011, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cefalu, J.E.; Barrier, K.M.; Davis, A.H. Wound infections in critical care. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 29, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.; Li, C.; Cui, Z.; Liang, Y. Rapid bacteria trapping and killing of metal-organic frameworks strengthened photo-responsive hydrogel for rapid tissue repair of bacterial infected wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, S.F.; Caruso, G.I.; Pasquale, R.D.; Sortino, M.A.; Merlo, S. The treatment of impaired wound healing in diabetes: Looking among old drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Armstrong, D.G.; Lipsky, B.A. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 293, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, G.E. Epidemiology of foot ulcers and amputations in the diabetic foot. Diabet. Foot Ankle 2001, 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Selection of appropriate wound dressing for various wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obagi, Z.; Damiani, G.; Grada, A.; Falanga, V. Principles of wound dressings: A review. Surg. Technol. Int. 2019, 35, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, A. Wound assessment and dressing selection: An overview. Br. J. Nurs. 2021, 30, S12–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Emanuel, C.; Cutting, K.F.; Williams, D.W. Microbiology of the skin and the role of biofilms in infection. Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.D.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, O.; Brancaccio, M.; Mennitti, C.; Laneri, S.; Lombardo, B.; De Biasi, M.G.; De Gregorio, E.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Salvatore, P.; et al. Human defensins: A novel approach in the fight against skin colonizing Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Song, Q.; Li, P.; Huang, W. Rejuvenated photodynamic therapy for bacterial infections. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, M. Gold-silver nanoshells promote wound healing from drug-resistant bacteria infection and enable monitoring via surface-enhanced raman scattering imaging. Biomaterials 2020, 234, 119763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A.M. Nanomaterials for wound healing and infection control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethi, S.K.; Das, S.; Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S. Recent advances in inorganic nanomaterials for wound-healing applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2652–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parani, M.; Lokhande, G.; Singh, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. Engineered nanomaterials for infection control and healing acute and chronic wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10049–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Xu, C.; Akakuru, O.U.; Ma, X.; Zheng, J. Nanoparticle-based wound dressing: Recent progress in the detection and therapy of bacterial infections. Bioconj. Chem. 2020, 31, 1708–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Hska, C.; Xs, B.; Jhlc, D.; Hwkcd, E.; Xf, B.; Kwla, F. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 209–239. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, A.; He, J.; Bochani, S.; Nosrati, V.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Guo, B. Multifunctional photoactive hydrogels for wound healing acceleration. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18895–18930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, X.; Zheng, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, L. Nanomaterials applied in wound healing: Mechanisms, limitations and perspectives. J. Control. Release 2021, 337, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Loo, S. Intelligent Nanoparticle-based dressings for bacterial wound infections. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Qi, X.; Shi, G.; Zhang, M.; Haick, H. Wound dressing: From nanomaterials to diagnostic dressings and healing evaluations. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1708–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, A.E.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanomaterials for wound dressings: An up-to-date overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Chen, N.; Dash, B.C.; Hsia, H.C.; Berthiaume, F. Self-assembled nanomaterials for chronic skin wound healing. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 10, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.; Lou, D.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Wu, Z. Smart flexible electronics integrated wound dressing for real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment of infected wounds. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.; Shafiee, A. Wound healing: From passive to smart dressings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, F.; Deng, L. Gold nanomaterials as a promising integrated tool for diagnosis and treatment of pathogenic infections—A review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 744–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haam, S. Application of nanomaterials as an advanced strategy for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of viral diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar]
- Makabenta, J.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.H.; Schmidt-Malan, S.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, M.; Qi, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, J.; Yuan, X.; Sun, D. Nanoparticle-based strategies and approaches for the treatment of chronic wounds. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2018, 8, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Su, L.; van der Mei, H.C.; Jutte, P.C.; Ren, Y.; Busscher, H.J. Nanotechnology-based antimicrobials and delivery systems for biofilm-infection control. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Calabrese, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P.; Conoci, S. Metal-based nanoparticles: Antibacterial mechanisms and biomedical application. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.; Dille, J.; Godet, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdusel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoanta, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Reddy, Y.A.K.; Reddy, P.S. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size by pH variation. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Castanon, G.A.; Nino-Martinez, N.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Martinez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.; Wood, F.; Fowler, B. A silver coated dressing reduces the incidence of early burn wound cellulitis and associated costs of inpatient treatment: Comparative patient care audits. Burns 2005, 31, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniak, A. Effect of silver nanoparticles on human primary keratinocytes. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadia, M.; Adibhesamib, M. The effect of silver nanoparticles on wounds contaminated with pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice: An experimental study. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 661–669. [Google Scholar]
- Pangli, H.; Vatanpour, S.; Hortamani, S.; Jalili, R.; Ghahary, A. Incorporation of silver nanoparticles in hydrogel matrices for controlling wound infection. J. Burn. Care Res. 2020, 42, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z. Silver nanoparticle/bacterial cellulose gel membranes for antibacterial wound dressing: Investigation in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Nisi, R.; Stoppa, M.; Licciulli, A. Silver-functionalized bacterial cellulose as antibacterial membrane for wound-healing applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, E.I.; Udekwu, K.I.; Noel, C.W.; Gagnon, L.B.P.; Taylor, P.K.; Vulesevic, B.; Simpson, M.J.; Gkotzis, S.; Islam, M.M.; Lee, C.J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of composite collagen-silver nanoparticle hydrogels as tissue engineering scaffolds. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18789–18798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Masoud, M.S.; Ali, I.; Asghar, R.; Andleeb, A.; Hasan, A. Silver nanoparticle impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel enhances wound healing in diabetes induced rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Fan, C.; Yang, Y.; Lee, B.H.; Wei, K. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural-embedded poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hybrid hydrogels accelerate wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, M. in reduction of silver nanoparticles in the lignin based hydrogel for enhanced antibacterial application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Du, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Encapsulation of AgNPs within zwitterionic hydrogels for highly efficient and antifouling catalysis in biological environments. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rafael, S.; Ivanova, K.; Stefanov, I.; Puiggalí, J.; Tzanov, T. Nanoparticle-driven self-assembling injectable hydrogels provide a multi-factorial approach for chronic wound treatment. Acta Biomater. 2021, 134, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Buyana, B.; Feketshane, Z.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Electrospun nanofibers/nanofibrous scaffolds loaded with silver nanoparticles as effective antibacterial wound dressing materials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lun, X.; Sheng, H.; Yan, A. Effects of wound dressing based on the combination of silver@curcumin nanoparticles and electrospun chitosan nanofibers on wound healing. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4328–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, S.S.I.; Katas, H.; Azmi, F.; Busra, M.F.M. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm biosynthesised silver and gold nanoparticles for medical applications: Mechanism of action, toxicity and current status. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehravani, B.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Zille, A. Gold nanoparticles synthesis and antimicrobial effect on fibrous materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobed, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Seidi, F. Anti-bacterial activity of gold nanocomposites as a new nanomaterial weapon to combat photogenic agents: Recent advances and challenges. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34688–34698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Ren, J. AuNPs-PCL nanocomposite accelerated abdominal wound healing through photothermal effect and improving cell adhesion. J. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 29, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomi, P.; Ganesan, R.; Poorani, G.P.; Jegatheeswaran, S.; Saravanan, M. Phyto-engineered gold nanoparticles (aunps) with potential antibacterial, antioxidant, and wound healing activities under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 15, 7553–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.A.; Chen, H.M.; Yao, Y.D.; Hung, C.F.; Liang, Y.J. Topical treatment with anti-oxidants and Au nanoparticles promote healing of diabetic wound through receptor for advance glycation end-products. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapalli, P.K.; Labala, S.; Chawla, S.; Janupally, R.; Venuganti, V. Polymer-gold nanoparticle composite films for topical application: Evaluation of physical properties and antibacterial activity. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.N.; Hikmat, S.; Ghith, D.A.; Hajeer, M.; Khalil, E.A. Gold nanoparticles loaded into polymeric hydrogel for wound healing in rats: Effect of nanoparticles’ shape and surface modification. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Menon, S.; Kumar, S.V.; Rajeshkumar, S. Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chem. Biol. Intereact. 2018, 286, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, Z.; Tahira, S.; Naqvi, Q.; Rasul, S.; Muhammad, S.A. Antibacterial activity and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by microalgae. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alavi, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Synthesis and modification of bio-derived antibacterial Ag and ZnO nanoparticles by plants, fungi, and bacteria. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuja, A.; Raguvaran, R.; Kumar, B.; Kalia, A.; Tripathi, B.N. Accelerated healing of full thickness excised skin wound in rabbits using single application of alginate/acacia based nanocomposites of ZnO nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Ali, I.; Asghar, R.; Noorunnisa Khanam, P.; Augustine, R.; Hasan, A. Novel electrospun chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zinc oxide nanofibrous mats with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Thangavelu, K.; Karanikolos, G.N. Bimetallic nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Sharma, A.S.; Ahmad, W.; Zareef, M.; Chen, Q. Noble metals based bimetallic and trimetallic nanoparticles: Controlled synthesis, antimicrobial and anticancer applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 454–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Mehata, A.K.; Priya, V.; Malik, A.K.; Setia, A.; Suseela, M.N.L.; Vikas; Gokul, P.; Samridhi; Singh, S.K.; et al. Bimetallic Au-Ag nanoparticles: Advanced nanotechnology for tackling antimicrobial resistance. Molecules 2022, 27, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fei, L.; Zhou, G.; Yu, K.; Lan, G. Silver inlaid with gold nanoparticle/chitosan wound dressing enhances antibacterial activity and porosity, and promotes wound healing. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Behera, S.K.; Paul, P.; Das, B.; Suar, M.; Jayabalan, R.; Fawcett, D.; Poinern, G.E.J.; Tripathy, S.K.; Mishra, A. Biogenic Au@ZnO core-shell nanocomposites kill Staphylococcus aureus without provoking nuclear damage and cytotoxicity in mouse fibroblasts cells under hyperglycemic condition with enhanced wound healing proficiency. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, M.A.M.; Zangabad, P.S.; Basri, S.M.M.; Zangabad, K.S.; Ghamarypour, A.; Aref, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: Preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 123, 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.; Bavya, M.C.; Rohan, K.V.; Srivastava, R. A therapeutic polyelectrolyte-vitamin C nanoparticulate system in polyvinyl alcohol-alginate hydrogel: An approach to treat skin and soft tissue infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehterami, A.; Salehi, M.; Farzamfar, S.; Vaez, A.; Samadian, H.; Sahrapeyma, N.; Mirzaii, M.; Ghorbani, S.; Goodarzi, A. In vitro and in vivo study of PCL/COLL wound dressing loaded with insulin-chitosan nanoparticles on cutaneous wound healing in rats model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, S.; Asgarpour, K.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Hashemipour, M.; Ebrahimi, M.S.; Fathizadeh, H.; Khorshidi, A.; Khan, H.; Marzhoseyni, Z.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; et al. Chitosan-based nanoparticles against bacterial infections. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchera, A.; Buttini, F.; Bettini, R. Micro/nanosystems and biomaterials for controlled delivery of antimicrobial and anti-biofilm agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 981–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, L.S.; Shapouri, R.; Dezfulian, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Ardestani, M.S. Exotoxin A-PLGA nanoconjugate vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: Protectivity in murine model. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, A.; Pedram, P.; Makvandi, P.; Malinconico, M.; D’Ayala, G.G. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, M.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Goodarzi, A.; Ababzadeh, S.; Sagharjoghi Farahani, M.; Mohandesnezhad, S.; Bahrami, N.; Nabipour, I.; Ai, J. Encapsulation of curcumin loaded chitosan nanoparticle within poly (ε-caprolactone) and gelatin fiber mat for wound healing and layered dermal reconstitution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Vandermeulen, G.; Preat, V. PLGA based drug delivery systems: Promising carriers for wound healing activity. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Her, C.H.; Comune, M.; Moia, C.; Lopes, A.; Porporato, P.E.; Vanacker, J.; Lam, M.C.; Steinstraesser, L.; Sonveaux, P.; et al. PLGA nanoparticles loaded with host defense peptide LL37 promote wound healing. J. Control. Release 2014, 194, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplantier, A.J.; Hoek, M.V. The human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide ll-37 as a potential treatment for polymicrobial infected wounds. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Lee, J.; Naeem, M.; Hlaing, S.P.; Kim, J.; Jung, Y.; Lee, B.L.; Yoo, J.W. PEI/NONOates-doped PLGA nanoparticles for eradicating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in diabetic wounds via binding to the biofilm matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109741. [Google Scholar]
- Hlaing, S.P.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Hasan, N.; Cao, J.; Naeem, M.; Lee, E.H.; Shin, J.H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, B.L.; et al. S-Nitrosoglutathione loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles for prolonged nitric oxide release and enhanced healing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus -infected wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Cao, J.; Lee, J.; Hlaing, S.P.; Oshi, M.A.; Naeem, M.; Ki, M.H.; Lee, B.L.; Jung, Y.; Yoo, J.W. Bacteria-targeted clindamycin loaded polymeric nanoparticles: Effect of surface charge on nanoparticle adhesion to mrsa, antibacterial activity, and wound healing. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fukushima, K.; Venkataraman, S.; Hedrick, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y. Supramolecular nanofibers self-assembled from cationic small molecules derived from repurposed poly(ethylene teraphthalate) for antibiotic delivery. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Wang, W.; Dong, A. Combating drug-resistant bacterial infection using biodegradable nanoparticles assembled from comb-like polycarbonates grafted with amphiphilic polyquaternium. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Singh, B.; Maharjan, S.; Jang, Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, C.S. Local delivery of ctgf sirna with poly(sorbitol-co-pei) reduces scar contraction in cutaneous wound healing. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 14, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, J.; Cheng, Y. A nanocomposite hydrogel with potent and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15163–15173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Dai, L.; Li, C. A lignocellulose-based nanocomposite hydrogel with pH-sensitive and potent antibacterial activity for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriboni, A.B.; Couto, V.M.; de Morais Ribeiro, L.N.; Freires, I.A.; Groppo, F.C.; de Paula, E.; Franz-Montan, M.; Cogo-Muller, K. Fusogenic liposomes increase the antimicrobial activity of vancomycin against staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, N.; Jones, M. Encapsulation of vancomycin and gentamicin within cationic liposomes for inhibition of growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Drug Target. 1996, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.; Martins, M.; Martins, A.; Fonseca, N.A.; Moreira, J.N.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanofiber meshes with liposomes immobilized releasing gentamicin. Acta Biomater. 2015, 18, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina, Z.; Šegvić Klarić, M.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Lovrić, J.; Vanić, Ž. Azithromycin-loaded liposomes for enhanced topical treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus aureus (MRSA) infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, A.-M.; Caruntu, C.; Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Matei, C.; Constantin, M.M.; Constantin, T.V.; Calina, D.; Ciubotaru, D.A.; Badarau, I.A.; et al. Applications of nanosized-lipid-based drug delivery systems in wound care. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rkt, A.; Klk, B.; Mos, A. Encapsulation of collagen mimetic peptide-tethered vancomycin liposomes in collagen-based scaffolds for infection control in wounds. Acta Biomater. 2020, 103, 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Moghassemi, S.; Hadjizadeh, A. Nano-niosomes as nanoscale drug delivery systems: An illustrated review. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, R.; Nematollahi, M.H.; Pols, T.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Pardakhty, A.; Asadikaram, G.; Poolman, B. Niosomes, an alternative for liposomal delivery. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Elbanna, T.E.; Sonbol, F.I.; Gamaleldin, N.M.; El Maghraby, G.M. Optimization of niosomes for enhanced antibacterial activity and reduced bacterial resistance: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.; Boroujeni; Barzi, S.M.; Zafari, M.; Chiani, M.; Chehrazi, M.; Nosrati, H.; Shams Nosrati, M.S.; Nayyeri, S.; Khodaei, M.; et al. Electrosprayed cefazolin-loaded niosomes onto electrospun chitosan nanofibrous membrane for wound healing applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajkowska-Konik, A.; Szekalska, M.; Winnicka, K. Nanostructured lipid carriers: A potential use for skin drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (sln & nlc): Present state of development & industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Souza, M.L.; Dos Santos, W.M.; de Sousa, A.L.M.D.; de Albuquerque Wanderley Sales, V.; Nóbrega, F.P.; de Oliveira, M.V.G.; Rolim-Neto, P.J. lipid nanoparticles as a skin wound healing drug delivery system: Discoveries and advances. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4536–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglad, E.H.; Fatima, F.; Mohammed, M.A.; Devanathad, V.; Aldawsa, M.F. Development of topical antibacterial gel loaded with cefadroxil solid lipid nanoparticles: In vivo wound healing activity and epithelialization study. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 16, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumakia, M.D.; Ho, E.A. Nanoparticles encapsulated with LL37 and serpin A1 promotes wound healing and synergistically enhances antibacterial activity. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Alihosseini, F.; Rezayat Sorkhabadi, S.M.; Arbabi Bidgoli, S.; Mousavi, S.E.; Haghighat, S.; Afshar Nasab, A.; Kianvash, N. Nanotechnology in wound healing; semisolid dosage forms containing curcumin-ampicillin solid lipid nanoparticles, in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo characteristics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Orue, I.; Gainza, G.; Girbau, C.; Alonso, R.; Hernandez, R.M. LL37 Loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A new strategy for the topical treatment of chronic wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mg, A.; Mrf, B.; Hh, C. Encapsulation of peppermint essential oil in nanostructured lipid carriers: In-vitro antibacterial activity and accelerative effect on infected wound healing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 564, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.K.; Surekha, D.B.; Tripathi, M.; Anjum, M.M.; Singh, S. Anti-biofilm potential of silver sulfadiazine loaded nanoparticle formulations: A study on the role of DNase-I in microbial biofilm and wound healing activity. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3916–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashapov, R.; Ibragimova, A.; Pavlov, R.; Gabdrakhmanov, D.; Sinyashin, O. Nanocarriers for biomedicine: From lipid formulations to inorganic and hybrid nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulin-Sarfraz, T.; Kalantzopoulos, G.N.; Pettersen, M.K.; Asli, A.W.; Tho, I.; Axelsson, L.; Sarfraz, J. Inorganic nanocarriers for encapsulation of natural antimicrobial compounds for potential food packaging application: A comparative study. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.R.; Ali, S.; Ateeq, M.; Perveen, S.; Ahmed, S.; Bertino, M.F.; Ali, M. Morphological analysis of the antimicrobial action of silver and gold nanoparticles stabilized with ceftriaxone on Escherichia coli using atomic force microscopy. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5633–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, C.; Lan, M.; Guo, Q.; Xia, J. Antibacterial photodynamic gold nanoparticles for skin infection. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3124–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.Y.; Rafi, Z.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Shoaib, A.; Ahmad, I.; Asiri, M.; Zaman, G.S.; Wahab, S.; Saeed, M.; Khan, S. A comparative antibacterial, antioxidant, and antineoplastic potential of Rauwolfia serpentina (L.) leaf extract with its biologically synthesized gold nanoparticles (R-AuNPs). Plants 2021, 10, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lv, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Ren, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Fan, K.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Mussel-inspired nanozyme catalyzed conductive and self-setting hydrogel for adhesive and antibacterial bioelectronics. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refat, M.S.; Elsabawy, K.M.; Alhadhrami, A.; Almalki, A.; El-Sayed, M.Y.; Hassan, R.F. Development of medical drugs: Synthesis and in vitro bio-evaluations of nanomedicinal zinc-penicillins polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound skin dressing by new chemical technology. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 255, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Recent developments on MOF-based platforms for antibacterial therapy. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, K.; Han, I.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.N. Novel metal-organic framework-based photocrosslinked hydrogel system for efficient antibacterial applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20234–20242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework/enzyme hybrid nanocatalyst as a benign and self-activated cascade reagent for in vivo wound healing. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5222–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, F.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X. Glucose-responsive biomimetic nanoreactor in bacterial cellulose hydrogel for antibacterial and hemostatic therapies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Rahim, A.; Muhammad, N.; Rahman, S.U.; Azhar, U.; Sultana, K.; Sharif, F.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Rehman, F. Controllable delivery from gentamicin loaded polycaprolactone/grafted silica nanoparticles composite mats. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, M.; Bao, F.; Xing, M.; Wang, E.; Xu, Q.; Huan, Z.; Guo, F.; Chang, J. Multifunctional Zn doped hollow mesoporous silica/polycaprolactone electrospun membranes with enhanced hair follicle regeneration and antibacterial activity for wound healing. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6315–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduraimova, A.; Molkenova, A.; Duisembekova, A.; Mulikova, T.; Kanayeva, D.; Atabaev, T.S. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)-loaded SiO2-Ag mesoporous nanocomposite as an efficient antibacterial agent. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Ge, W.; Yin, J.; Yang, D.; Dong, X. Mesoporous silica supported silver-Bismuth nanoparticles as photothermal agents for skin infection synergistic antibacterial therapy. Small 2020, 16, e2000436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, S.; Lepry, W.C.; Nazhat, S.N. Bioactive glasses in wound healing: Hope or hype? J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6167–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Sol-gel processing of bioactive glass nanoparticles: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Jiang, G. Microneedles integrated with ZnO quantum dots capped mesoporous bioactive glasses for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, G.; Song, G.; Liu, T.; Cao, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, W. Incorporation of ZnO/bioactive glass nanoparticles into alginate/chitosan composite hydrogels for wound closure. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5042–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Q.; Zenji, T.; Maçon, A.L.B.; Norris, E.; Poologasundarampillai, G.; Obata, A.; Jones, J.R.; Kasuga, T. Silver-doped calcium silicate sol-gel glasses with a cotton-wool-like structure for wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Shah, H.; Nawaz, A.; Xie, W.; Akram, M.Z. Antibacterial carbon-based nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1804838. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, M.; Jabari, E.; Jabbari, E. Functionalized carbon-based nanomaterials and quantum dots with antibacterial activity: A review. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patarroyo, J.L.; Cifuentes, J.; Muoz, L.N.; Cruz, J.C.; Reyes, L.H. Novel antibacterial hydrogels based on gelatin/polyvinyl-alcohol and graphene oxide/silver nanoconjugates: Formulation, characterization, and preliminary biocompatibility evaluation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopezmachado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A. Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: An overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zheng, X.T.; Zhao, S.; Su, X.; Loh, X.J. Stimuli-activable metal-bearing nanomaterials and precise on-demand antibacterial strategies. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19840–19872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Shao, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, X. Recent advances in pH-responsive nanomaterials for anti-infective therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10700–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Tan, P.; Fu, S.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Gu, Z.; Luo, K. Preparation and application of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 206–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhu, W.; Pei, D. Hydrogel containing minocycline and zinc oxide-loaded serum albumin nanopartical for periodontitis application: Preparation, characterization and evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Li, J. pH-Responsive polymeric nanocarriers for efficient killing of cariogenic bacteria in biofilms. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloom-Jalali, A.; Shariatinia, Z.; Tamai, I.A.; Pakzad, S.R.; Malakootikhah, J. Fabrication of chitosan-polyethylene glycol nanocomposite films containing ZIF-8 nanoparticles for application as wound dressing materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.Q. pH-switchable antimicrobial nanofiber networks of hydrogel eradicate biofilm and rescue stalled healing in chronic wound. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11686–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Giovannini, G.; Zhang, S.; Altenried, S.; Zuber, F.; Chen, Q.; Boesel, L.F.; Ren, Q. pH-responsive silica nanoparticles for the treatment of skin wound infections. Acta Biomater. 2022, 145, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Dhasmana, N.; Dubey, N.; Kumar, N.; Gangwal, A.; Gupta, M.; Singh, Y. Bacterial virulence factors: Secreted for survival. Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Y. Fabrication of enzyme-responsive composite coating for the design of antibacterial surface. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Han, H. Endogenous stimulus-powered antibiotic release from nanoreactors for a combination therapy of bacterial infections. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, T. Bacteria-targeting nanoparticles with microenvironment-responsive antibiotic release to eliminate intracellular staphylococcus aureus and associated infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14299–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; Permana, A.D.; Rodgers, A.M.; Donnelly, R.F.; Rehman, A.U. Enhancement in site-specific delivery of carvacrol against methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus induced skin infections using enzyme responsive nanoparticles: A proof of concept study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusek, A.; Kijak, E. Drug carriers based on graphene oxide and hydrogel: Opportunities and challenges in infection control tested by amoxicillin release. Materials 2021, 14, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Xu, H. Recent progress in the biological applications of reactive oxygen species-responsive polymers. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, B. ROS-responsive drug delivery systems. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderburgh, J.P.; Kwakwa, K.A.; Werfel, T.A.; Merkel, A.R.; Rhoades, J.A. Systemic delivery of a Gli inhibitor via polymeric nanocarriers inhibits tumor-induced bone disease. J. Control. Release 2019, 311, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.G.; Jiao, W.Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, D. Phenylboronic acid-conjugated chitosan nanoparticles for high loading and efficient delivery of curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 256, 117497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Chen, S. Reactive oxygen species-sensitive thioketal-linked mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug carrier for effective antibacterial activity. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Feng, W.; Pu, W.; Zhang, D. Targeted delivery of antibiotics to the infected pulmonary tissues using ROS-responsive nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Lu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Deng, L.; Cao, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Ding, J.; et al. Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by an anti-bacterial and nano-enzyme-containing hydrogel with inflammation-suppressing, ROS-scavenging, oxygen and nitric oxide-generating properties. Biomaterials 2022, 286, 121597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Yan, L.X.; Chen, L.J.; Zhao, X.; Yan, X.P. Responsive nanoplatform for persistent luminescence “turn-on” imaging and “on-demand” synergistic therapy of bacterial infection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnarain, N.; Osman, N.; Fasiku, V.O.; Makhathini, S.; Salih, M.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Govender, T. Intrinsicstimuli-responsivenanocarriers for smart drug delivery of antibacterial agents-Anin-depthreview of the last two decades. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, L.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J. Stimuli-responsive nanoplatforms for antibacterial applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, R. Remote light-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug delivery: Advances and perspectives. Small 2019, 15, 1903060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chan, H.F.; Shi, B.; Li, M.; Leong, K.W. Light: A magical tool for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscari, G.; Pitarresi, G.; Fiorica, C.; Schillaci, D.; Catania, V.; Palumbo, F.S.; Giammona, G. Near-infrared light-responsive and antibacterial injectable hydrogels with antioxidant activity based on a dopamine-functionalized Gellan Gum for wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Song, H.; Yu, C. Antibiotic-free antibacterial strategies enabled by nanomaterials: Progress and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, C.A.S.; Correa, D.S.; Zucolotto, V. Polycaprolactone nanofiber mats decorated with photoresponsive nanogels and silver nanoparticles: Slow release for antibacterial control. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 107, 110334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Tao, X.; Xie, Y.; Xia, W. Light-triggered nitric oxide release photosensitizer to combat bacterial biofilm infections. Chemistry 2021, 27, 5453–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, J.; Gan, G.; Shen, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, G. Red light-triggered intracellular carbon monoxide release enables selective eradication of MRSA infection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13513–13520. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Li, A.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.J. Silica coated gold-silver nanocages as photothermal antibacterial agents for combined anti-infective therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17177–17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Karmacharya, M.; Joshi, S.R.; Gulenko, O.; Park, J.; Kim, G.-H.; Cho, Y.-K. Photoactive antiviral face mask with self-sterilization and reusability. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Shi, K.; Han, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zha, R.; Qu, Y. Ultrasmall CuS@BSA nanoparticles with mild photothermal conversion synergistically induce MSCs-differentiated fibroblast and improve skin regeneration. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Xue, J.; Wu, J.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Defective black nano-titania thermogels for cutaneous tumor-induced therapy and healing. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiu, W.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Huang, L.; et al. Mussel-inspired multifunctional hydrogel dressing with hemostasis, hypoglycemic, photothermal antibacterial properties on diabetic wounds. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 4796–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, C.; Han, S.; Ruan, J.; Wang, Y. Photothermal-assisted antibacterial application of graphene oxide-Ag nanocomposites against clinically isolated multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 192019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Bicontinuous, high-strength, and multifunctional chemical-cross-linked mxene/superaligned carbon nanotube film. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19293–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z. Polydopamine antibacterial materials. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1618–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.S.; Koo, J.; Park, W.H. Multifunctional and thermoresponsive methylcellulose composite hydrogels with photothermal effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorcroft, S.C.T.; Roach, L.; Jayne, D.G.; Ong, Z.Y.; Evans, S.D. Nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel for the light-activated release and photothermal enhancement of antimicrobial peptides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24544–24554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Bacteria activated-macrophage membrane-coated tough nanocomposite hydrogel with targeted photothermal antibacterial ability for infected wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 420, 127638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Guo, S.; Chang, R.; He, Y.; Yao, M.; Guan, F. Functionalized injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel with antioxidative and photothermal antibacterial activity for infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yu, Z.; Chen, S.; Fei, L.; Sha, Q.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Z.; Xu, C. Facile and eco-friendly fabrication of polysaccharides-based nanocomposite hydrogel for photothermal treatment of wound infection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, X. An injectable photothermally active antibacterial composite hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel for promoting the wound healing process through photobiomodulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4567–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, R.; Guo, B. Dual-dynamic-bond cross-linked antibacterial adhesive hydrogel sealants with on-demand removability for post-wound-closure and infected wound healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7078–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Chi, M.; Sun, X.; Xie, X.; Xu, H. Novel nanomaterial-based antibacterial photodynamic therapies to combat oral bacterial biofilms and infectious diseases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6937–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Photo-inspired antibacterial activity and wound healing acceleration by hydrogel embedded with Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO nanostructures. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9010–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yin, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Huo, Y.; Li, H. Synergistic Ag/TiO2-N photocatalytic system and its enhanced antibacterial activity towards Acinetobacter baumannii. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.N.; Singh, M.; Weerathunge, P.; Bian, P.; Zheng, R.; Dekiwadia, C.; Ahmed, T.; Walia, S.; Gaspera, E.D.; Singh, S. Visible light-triggered ros-mediated antibacterial activity of peroxidase-mimic CuO nanorods. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, S. Metal organic framework-based antibacterial agents and their underlying mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7138–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Long, Z.; Dong, R.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X. Titanium incorporation into ZrPorphyrinic metal-organic frameworks with enhanced antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Small 2020, 16, 1906240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Peng, Q. Graphene-based nanomaterials: The promising active agents for antibiotics-independent antibacterial applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, P.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXene-chitosan composites and their biomedical potentials. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wu, S. Repeatable photodynamic therapy with triggered signaling pathways of fibroblast cell proliferation and differentiation to promote bacteria-accompanied wound healing. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, A.; Chi, R.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) hydrogel incorporated with Ag/TiO2 for rapid sterilization by photoinspired radical oxygen species and promotion of wound healing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Jia, M.; Liu, S.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, P. Smart hydrogel-based DVDMS/bFGF nanohybrids for antibacterial phototherapy with multiple damaging sites and accelerated wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10156–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ramasamy, M.; Dong, K.Y. Antibacterial activity of ordered gold nanorod arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Local photothermal/photodynamic synergistic therapy by disrupting bacterial membrane to accelerate reactive oxygen species permeation and protein leakage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17902–17914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, D.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. Photosensitizer synergistic effects: D–A–D structured organic molecule with enhanced fluorescence and singlet oxygen quantum yield for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Rapid sterilization and accelerated wound healing using Zn2+ and graphene oxide modified G-C3N4 under dual light irradiation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. A bifunctional hydrogel incorporated with CuS@MoS2 microspheres for disinfection and improved wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 382, 122849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Yuan, H.; Bao, X.; Ma, G.; Xing, C. Synergistic photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial therapy based on conjugated polymer nanoparticles doped hydrogel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4436–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J. Hydrogel combined with phototherapy in wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2200494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Sun, T.; Su, W.; Jing, X.; Ye, B.; Su, Y.; Zeng, L.; Qu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Bioinspired multifunctional black phosphorus hydrogel with antibacterial and antioxidant properties: A stepwise countermeasure for diabetic skin wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gan, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, D.; Qiu, X. Fabrication of a lignin-copper sulfide-incorporated pva hydrogel with near-infrared-activated photothermal/photodynamic/peroxidase-like performance for combating bacteria and biofilms. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Mao, C.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Jing, D.; Yang, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Rapid and superior bacteria killing of carbon quantum dots/zno decorated injectable folic acid-conjugated pda hydrogel through dual-light triggered ros and membrane permeability. Small 2019, 15, 1900322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission nanoparticles for single near-infrared light-triggered photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial therapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7961–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargaville, T.R.; Farrugia, B.L.; Broadbent, J.A.; Pace, S.; Upton, Z.; Voelcker, N.H. Sensors and imaging for wound healing: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Mclister, A. Wound diagnostics and diagnostic dressings. In Smart Bandage Technologies: Design and Application; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 145–193. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshandeh, H.; Kashaf, S.S.; Aghabaglou, F.; Ghanavati, I.O.; Tamayol, A. Smart Bandages: The Future of Wound Care. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, D.; Haick, H. Multifunctional dressing for wound diagnosis and rehabilitation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; He, B.; Gao, B. Intelligent patches for wound management: In situ sensing and treatment. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4687–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, D.E.; Pamuku, A.; Karakaplan, M.B.; Kocaoglu, O.; Rosenholm, J.M. Recent advances in the use of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the diagnosis of bacterial infections. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6575–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduraiveeran, G.; Sasidharan, M.; Ganesan, V. Electrochemical sensor and biosensor platforms based on advanced nanomaterials for biological and biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, D.; Qian, Z.; Hou, S.; Li, L.; Jenkins, A.T.A.; Fan, Y. Bacteria-responsive intelligent wound dressing: Simultaneous In situ detection and inhibition of bacterial infection for accelerated wound healing. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.L.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.L.; Li, Q.Y.; Liao, D.K.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, H.B. Development of an intelligent photosensitive antibacterial wound dressing: Simultaneous detection and treatment of bacterial infection for accelerated wound healing. ChemNanoMat 2020, 6, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Pang, Q.; Yuan, P.; Luo, Y.; Ma, L. Smart wound dressing for infection monitoring and NIR-triggered antibacterial treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Niu, J.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Colorimetric band-aids for point-of-care sensing and treating bacterial infection. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, K.; Hou, R.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressing for Advanced Management of Infected Wound. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020351
Pang Q, Jiang Z, Wu K, Hou R, Zhu Y. Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressing for Advanced Management of Infected Wound. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020351
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Qian, Zilian Jiang, Kaihao Wu, Ruixia Hou, and Yabin Zhu. 2023. "Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressing for Advanced Management of Infected Wound" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020351
APA StylePang, Q., Jiang, Z., Wu, K., Hou, R., & Zhu, Y. (2023). Nanomaterials-Based Wound Dressing for Advanced Management of Infected Wound. Antibiotics, 12(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020351





