Novel Sulfonylurea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry of the Compounds
2.2. The In Vitro Antimicrobial Activities and Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR)
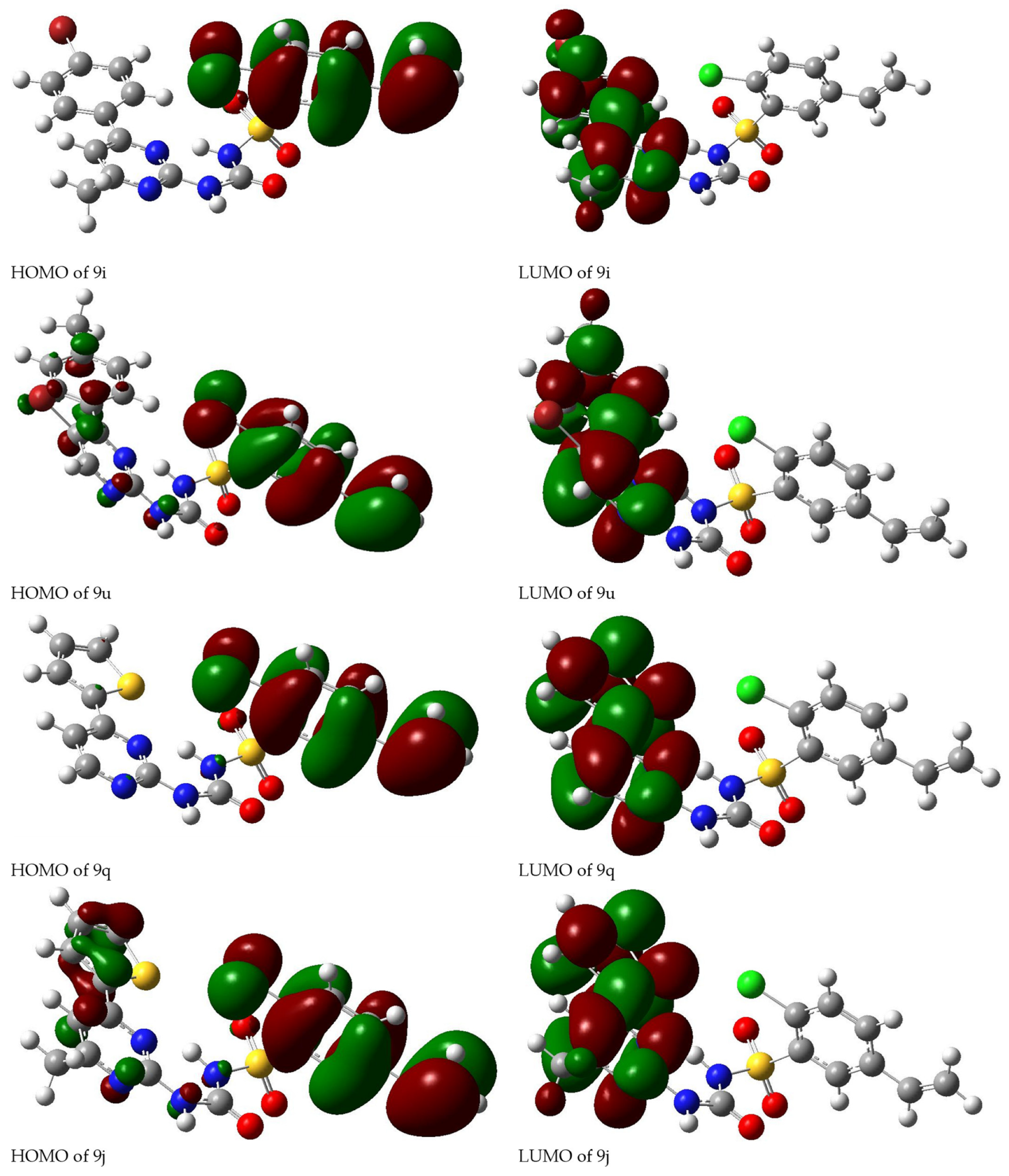
2.3. Quantum Calculation Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Regents and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis of Intermediates 2–5
3.2.1. Synthesis of Intermediates 2 [32]
3.2.2. Synthesis of Intermediates 3 [33]
3.2.3. Synthesis of Intermediates 4a–i and 4m–p [34]
3.2.4. Synthesis of Intermediates 4j–l [35]
3.2.5. Synthesis of Intermediates 5a–d
3.2.6. Synthesis of Intermediates 4q and 6a–c [36]
3.2.7. Synthesis of Intermediates 4r–u
3.3. Synthesis of Target Compounds 9a–u [37]
3.4. Bacterial Strains and In Vitro Antibacterial Susceptibility and MIC Determination
3.5. Human Pathogen Fungus and In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility and MIC Determination
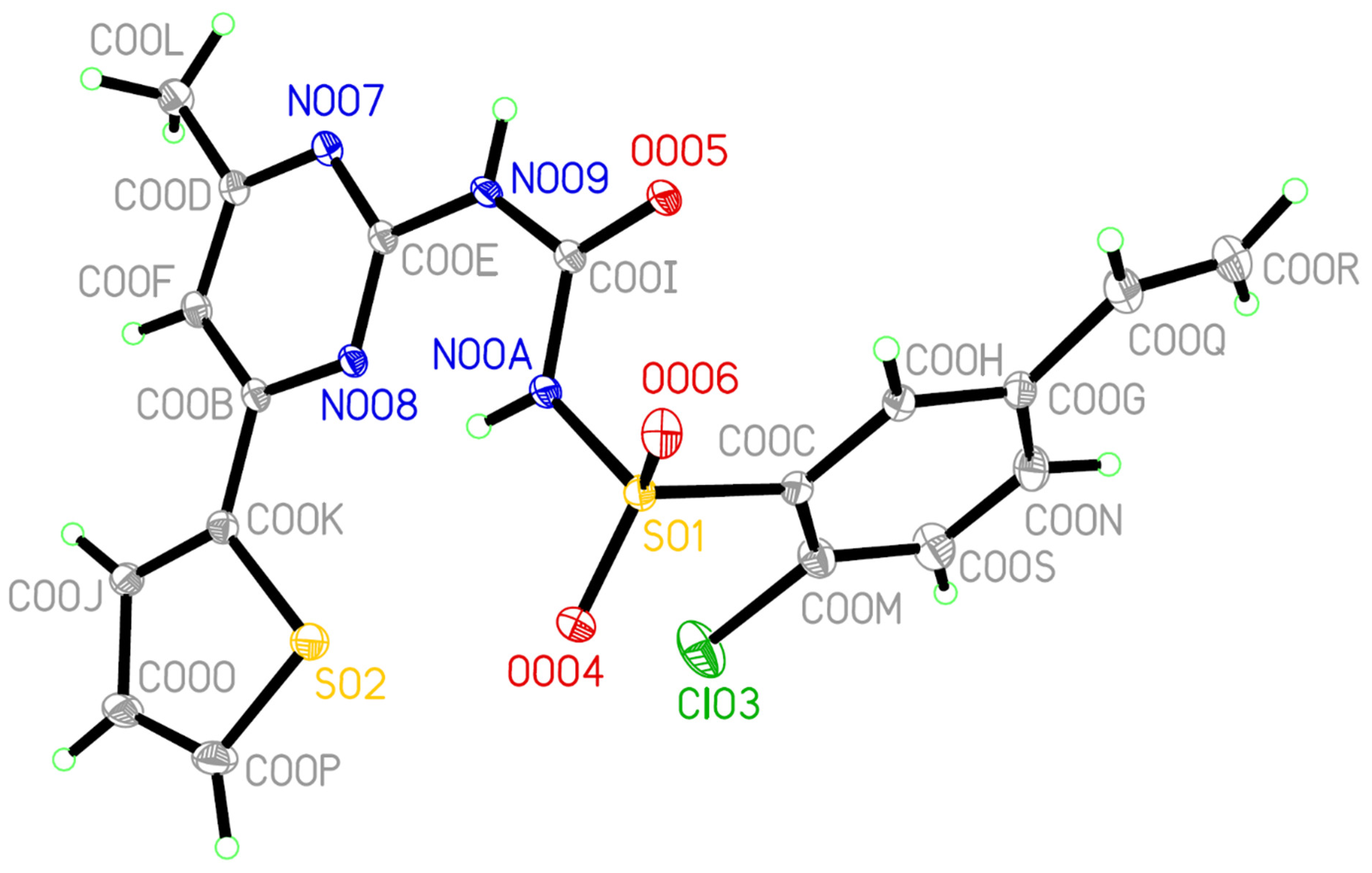
3.6. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction
3.7. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: Pathogenesis and regulatory mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus: Molecular characterization, evolution, and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubes, G. The bacteria fight back. Science 2008, 321, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisuknimit, V.; Yuan, Q.; Schaefer, K.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. Peptidoglycan cross-linking preferences of Staphylococcus aureus penicillin binding proteins have implications for treating MRSA Infections. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9791–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eed, E.M.; Ghonaim, M.M.; Hussein, Y.M.; Al-Shehri, S.S.; Khalifa, A.S. Molecular characterisation of Panton-Valentine leucocidin-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones isolated from the main hospitals in Taif, KSA. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazee, B.W.; Charlebois, J.; Lynn, E.D.; Lambert, L.; Lowery, D.; Perdreau-Remington, F. High prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in emergency department skin and soft tissue infections. Ann. Emer. Med. 2005, 45, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. 1,2,3-Triazole-containing hybrids with potential antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollef, M.H. Limitations of vancomycin in the management of resistant staphylococcal infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45 (Suppl. S3), S191–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howden, B.P.; Davies, J.K.; Johnson, P.D.R.; Stinear, T.P.; Grayson, M.L. Reduced vancomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus, including vancomycin-intermediate and heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate strains: Resistance mechanisms, laboratory detection, and clinical implications. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 99–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hal van, S.J.; Lodise, T.P.; Paterson, D.L. The clinical significance of vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration in Staphylococcus aureus infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttley, A.H.; Collins, C.H.; Naidoo, J.; George, R.C. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet 1988, 1, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahdouh, E.; Díaz-Pollán, B.; Falces-Romero, I.; Mingorance, J.; Gómez-Gil, R. Characterization of an osteomyelitis case caused by dalbavancin, ceftaroline, and vancomycin non-susceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 2029–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcguinness, W.A.; Malachowa, N.; Deleo, F.R. Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.; Yang, S.; Rao, X. Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A review of case updating and clinical features. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 21, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRossa, R.A.; Schloss, J.V. The sulfonylurea herbicide sulfometuron methyl is an extremely potent and selective inhibitor of acetolactate synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 8753–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, G.; Baraldi, B.; Tiraboschi, L.; Caputo, G. New oral hypoglycemic agent: K 4024 or glipizide. Clinical trial. Clin. Ter. 1972, 63, 438–452. [Google Scholar]
- Schweinburg, F.B.; Yetwin, I.J. Sulfamethazine: In vitro Action on enteric pathogens as compared with sulfadiazine and sulfamerazine. J. Bacteriol. 1945, 49, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.J.; Ren, T.; Gao, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Q.; Yao, Z.; Song, G.Q.; Ruan, W.B.; Niu, C.W.; Song, F.H.; et al. Chemical preparation, biological evaluation and 3D-QSAR of ethoxysulfuron derivatives as novel antifungal agents targeting acetohydroxyacid synthase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.T.; Cui, C.J.; Chow, E.W.; Pue, N.; Lonhienne, T.; Wang, J.G.; Fraser, J.A.; Guddat, L.W. Sulfonylureas have antifungal activity and are potent inhibitors of Candida albicans acetohydroxyacid synthase. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.D.; Chua, S.M.H.; Low, Y.S.; Lee, Y.T.; Agnew-Francis, K.; Wang, J.G.; Nouwens, A.; Lonhienne, T.; Williams, C.M.; Fraser, J.A.; et al. Commercial AHAS-inhibiting herbicides are promising drug leads for the treatment of human fungal pathogenic infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9649–E9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.M.; Wang, D. Synthesis and evaluation of novel monosubstituted sulfonylurea derivatives as antituberculosis agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 50, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Cheng, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Design, synthesis and SAR study of novel sulfonylureas containing an alkenyl moiety. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 8356–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Mi, P.; Yu, Z.; Wei, W.; Gao, L.; Ren, J.; Li, Z.; Dai, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 5–substituted sulfonylureas as novel antifungal agents targeting acetohydroxyacid synthase. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1260, 132756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, E.J.; Meyer, E.; Rudolph, J.; Davisson, V.J.; Stubbe, J. N5-Carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide: Evidence for a new intermediate and two new enzymatic activities in the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Wolf, N.M.; Zhu, T.; Johnson, M.E.; Deng, J.; Cook, J.L.; Fung, L.W.M. Identification of Bacillus anthracis PurE inhibitors with antimicrobial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.S.; Song, F.H.; Wang, W.M.; Dai, H.Q.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, J.G. Synthesis and evaluation of isatin-β-thiosemicarbazones as novel agents against antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive bacterial species. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Yu, W.; Min, L.J.; Wedge, D.E.; Tan, C.X.; Weng, J.Q.; Wu, H.K.; Cantrell, C.L.; Bajsa-Hirschel, J.; Hua, X.W.; et al. Synthesis and pesticidal activities of new quinoxalines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.J.; Zhou, K.X.; Yang, H.; Song, G.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Fu, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Xiong, L.X.; et al. Chemical synthesis, crystal structure, versatile evaluation of their biological activities and molecular simulations of novel pyrithiobac derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Li, H.R.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yang, W.T.; Yao, Z.; Wu, R.J.; Niu, C.W.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.G. Discovery of ortho-alkoxy substituted novel sulfonylurea compounds that display strong herbicidal activity against monocotyledon grasses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8415–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.S.; Niu, C.W.; Li, Y.H.; Song, F.H.; Wang, J.G. Chemical synthesis, biological activities, and molecular simulations of novel sulfonylurea compounds bearing ortho-alkoxy substitutions. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Yu, Z.; Niu, C.; Ban, S.; Yang, G. Development of a general quantum-chemical descriptor for steric effects: Density functional theory based QSAR study of herbicidal sulfonylurea analogues. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guo, P.; Yang, W.; Li., M.; Jiang, C.; Sun, W.; Loh, T.P.; Jiang, Y. Stereoselective synthesis of trifluoromethyl-substituted 2H-furan-amines from enaminones. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Saito, K.; Suto, S.; Aihara, H.; Sugawara, A.; Tamura, S.; Kawano, T. Synthesis of 5-aryl-3(2 H)-furanones using intramolecular cyclization of sulfonium salts. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13834–13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djung, J.F.; Mears, R.J.; Montalbetti, C.A.G.N.; Coulter, T.S.; Golebiowski, A.; Carr, A.N.; Barker, O.; Greis, K.D.; Zhou, S.; Dolan, E.; et al. The synthesis and evaluation of indolylureas as PKCα inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallesham, B.; Subramanya, H.; Natarajan, M. Trisubstituted Heterocyclic Derivatives as RORγ Modulators. International Patent Application No. PCT/IB2014/058957; PCT Patent WO 2014125426A1. 14 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, B.; Allen, F.L.; Robert, G.; Saul, J.F.; Liu, Y.; Kern, M.A.; George, P.D.; Kurt, W.K.; Zhao, S.H. Aryl Pyrimidine Derivatives. U.S. Patent 5952331A, 14 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Hua, X.W.; Wei, W.; Gu, Y.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, M.G.; Xie, Y.T.; Zhou, S.; Meng, X.D.; et al. Research on controllable degradation of novel sulfonylurea herbicides in acidic and alkaline soils. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2017, 65, 7661–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.L.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.S.; Ren, B.; Li, Z.M.; Dai, H.Q.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, J.G. Synthesis and evaluation of novel sulfenamides as novel anti Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R.; Bian, J.; Zheng, C.; Sun, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, N.; An, R.; et al. High-throughput synergy screening identifies microbial metabolites as combination agents for the treatment of fungal infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4606–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 3rd ed.; Approved standard M27-A3; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]


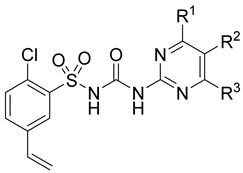 | ||||||||
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | MRSA (Chaoyang Clinical Isolates) | S. aureus (ATCC 6538) | VRE-309 | B. subtilis (ATCC 6633) | C. albicans SC 5314 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9a | H | H | Ph | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | >100 |
| 9b | H | H | 4-OMe-Ph | 6.25 | 6.25 | 25 | 6.25 | >100 |
| 9c | H | H | 4-F-Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9d | H | H | 4-Br-Ph | 25 | 50 | 25 | 25 | >100 |
| 9e | H | H | 4-Cl-Ph | 12.5 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | >100 |
| 9f | H | H | 4-NO2-Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9g | Me | H | Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9h | Me | H | 4-OMe-Ph | 100 | 50 | 100 | 100 | >100 |
| 9i | Me | H | 4-Br-Ph | 0.78 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 1.56 | >100 |
| 9j | Me | H | 2-thienyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9k | OMe | H | Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9l | OMe | H | 4-Br-Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9m | OMe | H | 2-thienyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9n | Cl | H | Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9o | H | H | 2-furanyl | 25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 25 | >100 |
| 9p | OMe | H | 4-OMe-Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9q | H | H | 2-thienyl | 0.78 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 0.78 | >100 |
| 9r | H | H | 4-Me-Ph | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | >100 |
| 9s | H | Br | 2-furanyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9t | H | Br | 2-thienyl | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | >100 |
| 9u | H | Br | 4-Me-Ph | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| chlorsulfuron | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| metsulfuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| ethametsulfuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| chlorimuron ethyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| tribenuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| sulfometuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| thifensulfuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| pyrazosulfuron ethyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| bensulfuron methyl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| ethoxysulfuron | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | ND | |||
| fluconazole | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1.56 | |||
| vancomycin | 1.00 | 1.00 | >16 | 0.5-1.00 | ND | |||
| methicillin | >200 | 3.13 | ND | ND | ND | |||
| Compound | 309-4 | 6281 | 309-8 | 6-42 | 8-21 | 309-3 | 309-1 | 309-7 | 8-24 | 309-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9i | 0.78 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 1.56 |
| 9q | 0.78 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 1.56 |
| 9b | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| 9e | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| Vancomycin | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Methicilin | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, F.-F.; Shang, M.-H.; Wei, W.; Yu, Z.-W.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, Z.-M.; Wang, Z.-W.; Wang, J.-G.; Dai, H.-Q. Novel Sulfonylurea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Study. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020323
Meng F-F, Shang M-H, Wei W, Yu Z-W, Liu J-L, Li Z-M, Wang Z-W, Wang J-G, Dai H-Q. Novel Sulfonylurea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Study. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020323
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Fan-Fei, Ming-Hao Shang, Wei Wei, Zhen-Wu Yu, Jun-Lian Liu, Zheng-Ming Li, Zhong-Wen Wang, Jian-Guo Wang, and Huan-Qin Dai. 2023. "Novel Sulfonylurea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Study" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020323
APA StyleMeng, F.-F., Shang, M.-H., Wei, W., Yu, Z.-W., Liu, J.-L., Li, Z.-M., Wang, Z.-W., Wang, J.-G., & Dai, H.-Q. (2023). Novel Sulfonylurea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Chemical Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Study. Antibiotics, 12(2), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020323






