Evaluating the Use of Neonatal Colonization Screening for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy of Sepsis and Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Patients and Setting
2.3. Hygienic Management
2.4. Microbiological Diagnostics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
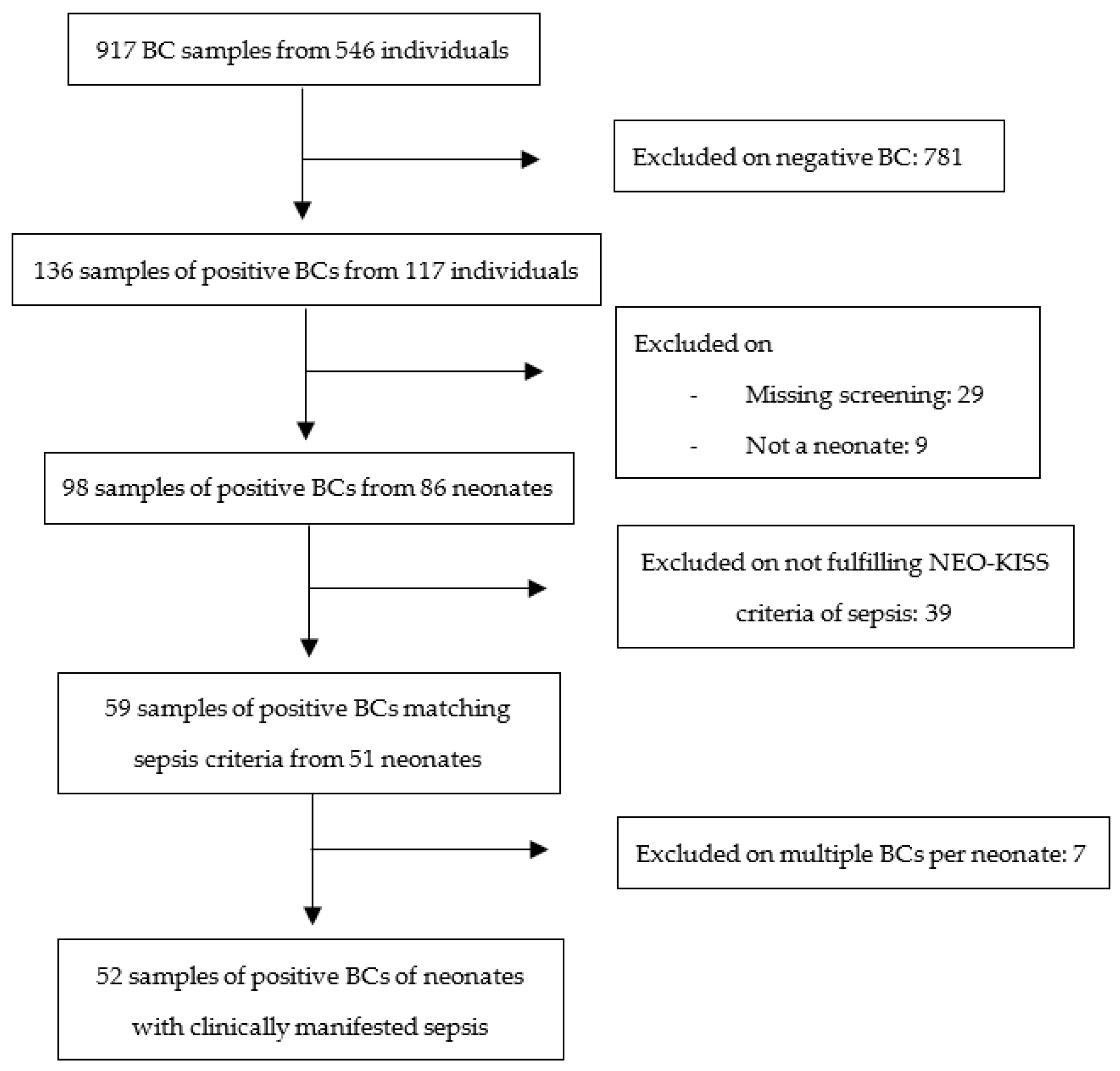
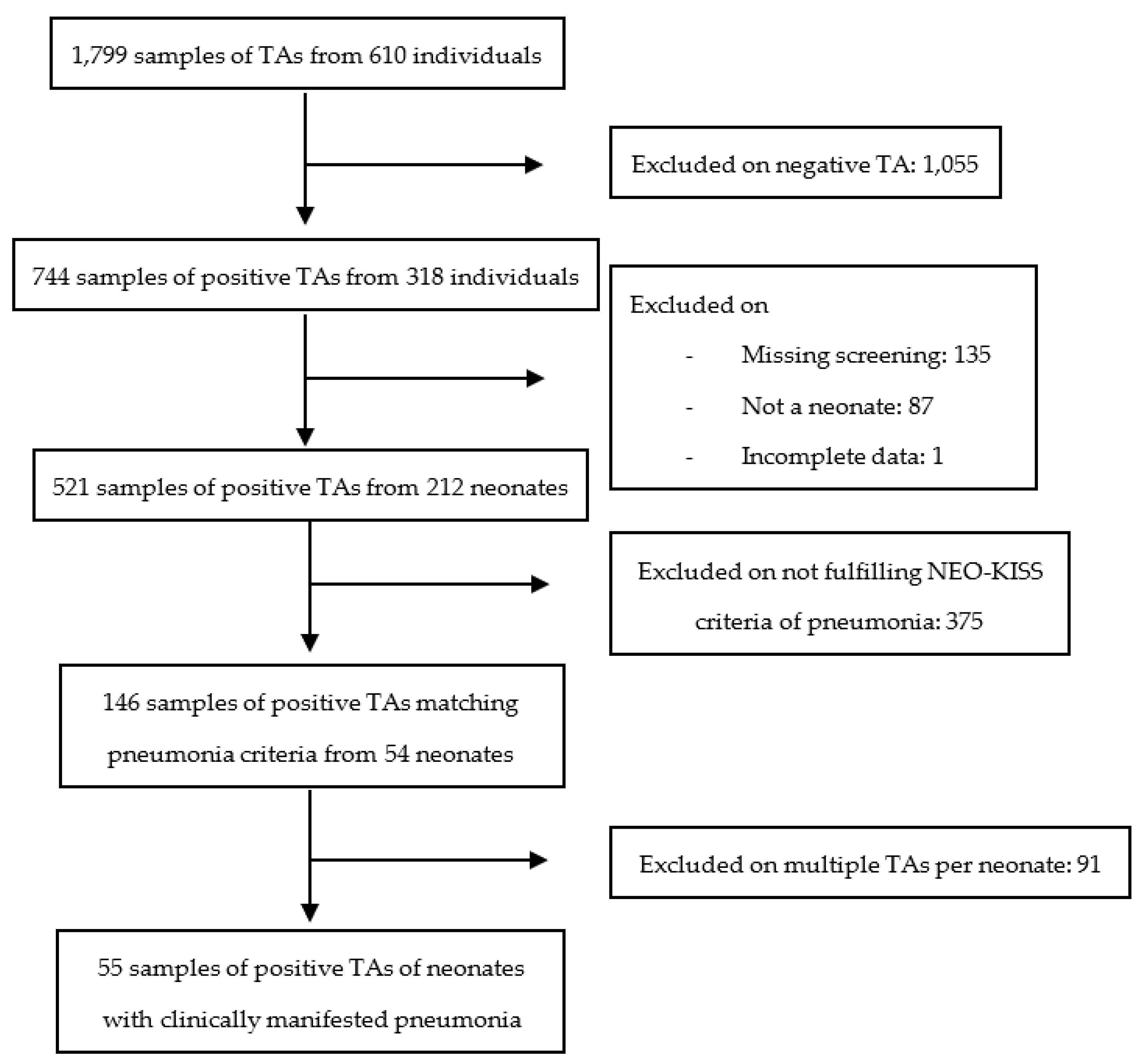
3.1. Study Selection and Description
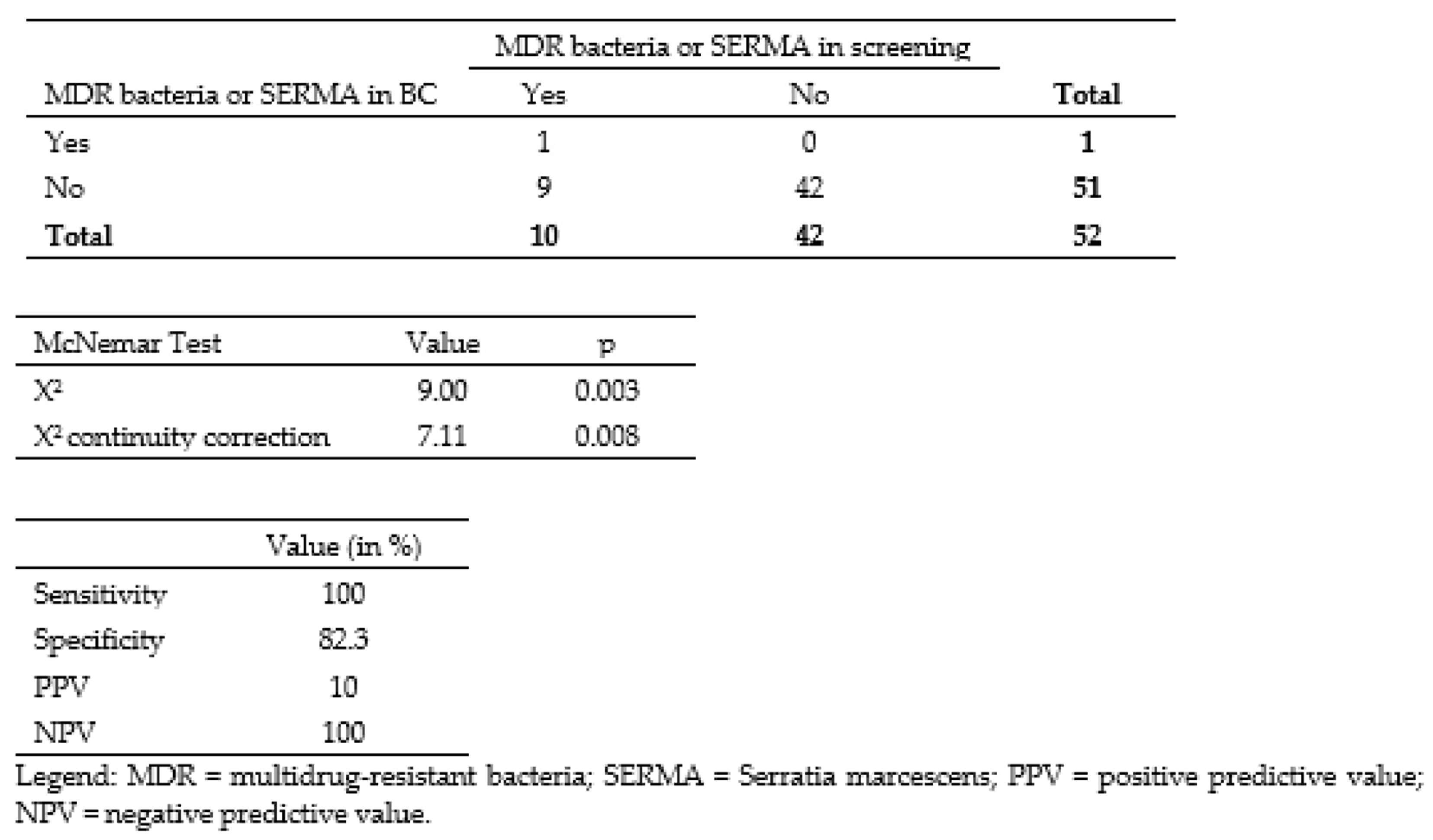
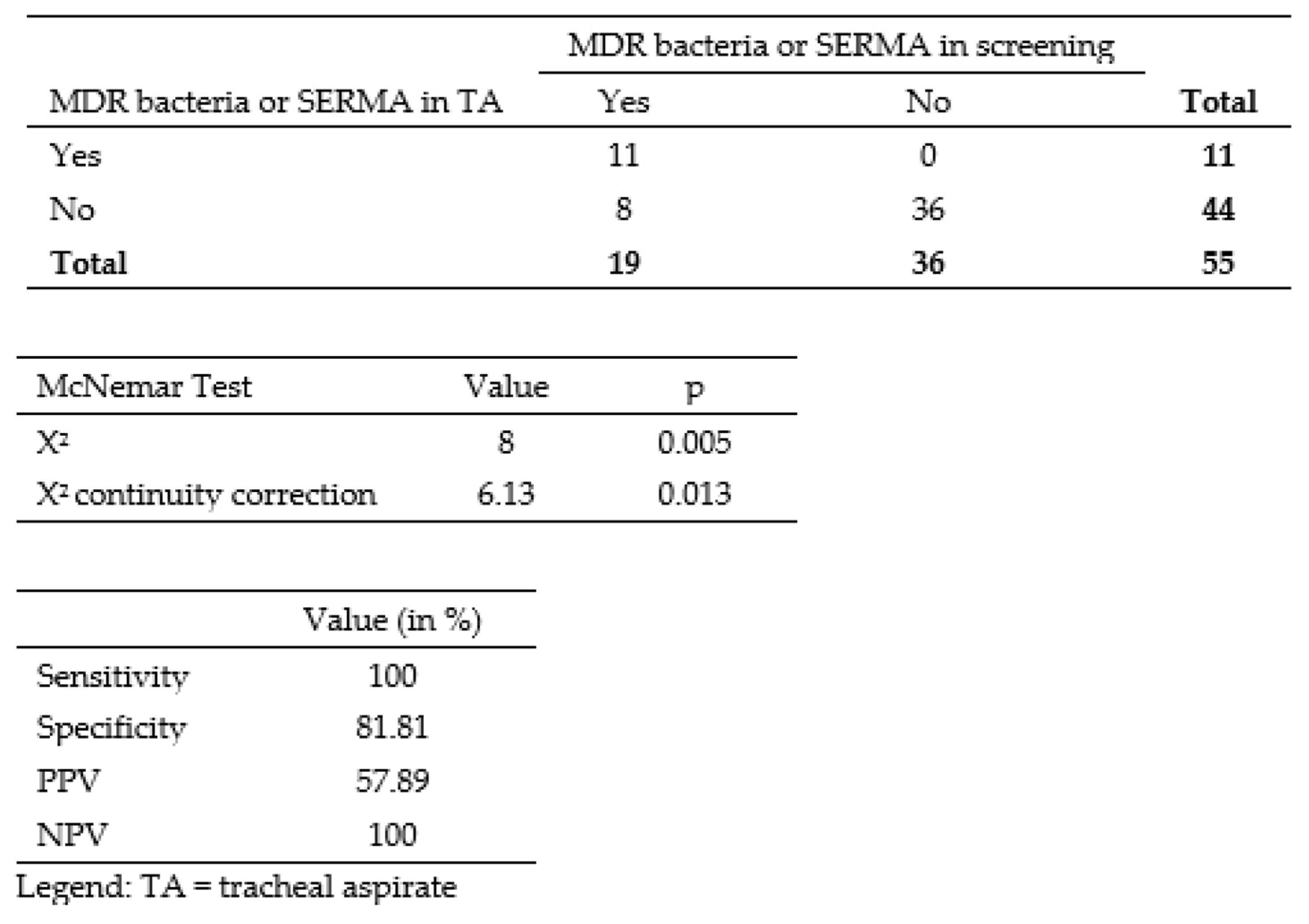
3.2. Correlation between Colonizing and Infecting Bacteria
3.3. Infectious Agents of Sepsis and Pneumonia
3.4. Identification of Risk Factors for Acquiring MDR and SERMA for Patients with Pneumonia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldmann, D.A.; Durbin, W.A.; Freeman, J. Nosocomial infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 144, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, K.; Mylonas, I.; Schulze, A. Infektionserkrankungen der Schwangeren und des Neugeborenen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-540-78324-4. [Google Scholar]
- Auriti, C.; Maccallini, A.; Di Liso, G.; Di Ciommo, V.; Ronchetti, M.P.; Orzalesi, M. Risk factors for nosocomial infections in a neonatal intensive-care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2003, 53, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, R.F.; Obladen, M. Neugeborenenintensivmedizin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-662-53575-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mammina, C.; Di Carlo, P.; Cipolla, D.; Giuffrè, M.; Casuccio, A.; Di Gaetano, V.; Plano, M.R.A.; D’Angelo, E.; Titone, L.; Corsello, G. Surveillance of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli in a neonatal intensive care unit: Prominent role of cross transmission. Am. J. Infect. Control 2007, 35, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarro, M.J.; Gallagher, P.G. Antibiotic-resistant organisms in the neonatal intensive care unit. Semin. Perinatol. 2007, 31, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Koch-Institut. Mitteilung der Kommission für Krankenhaushygiene und Infektionsprävention: Ergänzende Empfehlung (2011) zur „Prävention nosokomialer Infektionen bei neonatologischen Intensivpflegepatienten mit einem Geburtsgewicht unter 1.500 g“ (2007). Epidemiol. Bull. 2012, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, N.; Wallace, C.M.; Kieffer, P.; Schroeder, P.; Schootman, M.; Hamvas, A. Improving survival of vulnerable infants increases neonatal intensive care unit nosocomial infection rate. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Koch-Institut. Mitteilung der Kommission für Krankenhaushygiene und Infek tions prävention (KRINKO): Praktische Umsetzung sowie krankenhaushygienische und infektionspräventive Konsequenzen des mikrobiellen Kolonisationsscreenings bei intensivmedizinisch behandelten Früh- und Neugeborenen. Epidemiol. Bull. 2013, 42, 421–436. [Google Scholar]
- Folgori, L.; Tersigni, C.; Hsia, Y.; Kortsalioudaki, C.; Heath, P.; Sharland, M.; Bielicki, J. The relationship between Gram-negative colonization and bloodstream infections in neonates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.; Haller, S.; Eckmanns, T.; Harder, T. Routine screening for colonization by Gram-negative bacteria in neonates at intensive care units for the prediction of sepsis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Tenenbaum, T. Surveillance of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens in high-risk neonates—Does it make a difference? Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.J.; Green, N.; Clock, S.A.; Paul, D.A.; Perlman, J.M.; Zaoutis, T.; Ferng, Y.-H.; Alba, L.; Jia, H.; Larson, E.L.; et al. Gram-Negative Bacilli in Infants Hospitalized in The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2017, 6, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Saiman, L.; Zhou, J.; Della-Latta, P.; Jia, H.; Graham, P.L. Concordance of Gastrointestinal Tract Colonization and Subsequent Bloodstream Infections With Gram-negative Bacilli in Very Low Birth Weight Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härtel, C.; Hartz, A.; Bahr, L.; Gille, C.; Gortner, L.; Simon, A.; Orlikowsky, T.; Müller, A.; Körner, T.; Henneke, P.; et al. Media Stories on NICU Outbreaks Lead to an Increased Prescription Rate of Third-Line Antibiotics in the Community of Neonatal Care. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeh, I.; Kidszun, A.; Welk, A.; Schwanz, T.; Jansen, B.; Mildenberger, E. Evaluation of microbiological screening in a neonatal intensive care unit to optimize empiric antibiotic use. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 101, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, A.; Falkiner, F.R. Serratia marcescens. J. Med. Microbiol. 1997, 46, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nationales Referenzzentrum (NRZ) für Surveillance von Nosokomialen Infektionen am Institut für Hygiene und Umweltmedizin Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin. Protokoll Surveillance von Nosokomialen Infektionen, Multiresistenten Erregern und Antibiotika-Anwendungen bei Frühgeborenen mit Einem Geburtsgewicht unter 1.500g 2020. [Online]. Available online: https://www.nrz-hygiene.de/files/Protokolle/NEO%20Protokolle/NEOKISS_Protokoll_Jun_2020.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Zemlin, M.; Berger, A.; Franz, A.; Gille, C.; Härtel, C.; Küster, H.; Müller, A.; Pohlandt, F.; Simon, A.; Merz, W. Bakterielle Infektionen bei Neugeborenen. Arb. Der Wiss. Med. Fachgesellschaften E. V. 2021, 223, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, R.; Worlitzsch, D.; Schmidt, F.; Kulka, R.; Kekulé, A.S.; Körholz, D. Colonization and infection due to multi-resistant bacteria in neonates: A single center analysis. Klin. Padiatr. 2014, 226, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, C.; Pirr, S.; Ziesing, S.; Ebadi, E.; Hansen, G.; Bohnhorst, B.; Bange, F.-C. Prospective surveillance of bacterial colonization and primary sepsis: Findings of a tertiary neonatal intensive and intermediate care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 102, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Chu, S.-M.; Hsu, J.-F.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-C. Risk factors and outcomes for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteremia in the NICU. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e322–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenglet, A.; Schuurmans, J.; Ariti, C.; Borgundvaag, E.; Charles, K.; Badjo, C.; Clezy, K.; Evens, E.; Senat-Delva, R.; Berthet, M.; et al. Rectal screening displays high negative predictive value for bloodstream infection with (ESBL-producing) Gram-negative bacteria in neonates with suspected sepsis in a low-resource setting neonatal care unit. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtel, C.; Faust, K.; Fortmann, I.; Humberg, A.; Pagel, J.; Haug, C.; Kühl, R.; Bohnhorst, B.; Pirr, S.; Viemann, D.; et al. Sepsis related mortality of extremely low gestational age newborns after the introduction of colonization screening for multi-drug resistant organisms. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-C.; Liao, C.-C.; Chu, S.-M.; Lai, M.-Y.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Hsu, J.-F.; Tsai, M.-H. Impacts of Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens and Inappropriate Initial Antibiotic Therapy on the Outcomes of Neonates with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragosa, H.; Marçal, M.; Gonçalves, E.; Martins, F.; Lopo-Tuna, M. Multi-drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in a Portuguese neonatal intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Patel, K.M.; Léger, M.-M.; Short, B.; Sprague, B.M.; Kalu, N.; Campos, J.M. Risk of resistant infections with Enterobacteriaceae in hospitalized neonates. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakanthi, N.; Bahl, D.; Kaur, N.; Maria, A.; Dubey, N.K. Frequency and characteristics of infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing organisms in neonates: A prospective cohort study. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 756209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Protonotariou, E.; Boutsikou, T.; Makrakis, E.; Sarandakou, A.; Creatsas, G. The influence of the mode of delivery on circulating cytokine concentrations in the perinatal period. Early Hum. Dev. 2005, 81, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutayisire, E.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Tao, F. The mode of delivery affects the diversity and colonization pattern of the gut microbiota during the first year of infants’ life: A systematic review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.M.; Iensue, T.N.A.N.; Pereira, K.O.; de Souza, N.A.A.; Silva, C.M.; Salvador, M.S.D.A.; Rodrigues, R.; Capobiango, J.D.; Pelisson, M.; Vespero, E.C.; et al. Colonization by multidrug-resistant microorganisms of hospitalized newborns and their mothers in the neonatal unit context. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocevar, S.N.; Edwards, J.R.; Horan, T.C.; Morrell, G.C.; Iwamoto, M.; Lessa, F.C. Device-associated infections among neonatal intensive care unit patients: Incidence and associated pathogens reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network, 2006–2008. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Xian-Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Peng-Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Xue, J.; Ling-Huang, Y.; Li-Li, Y.; Fu-Qiu, J. Epidemiology of pathogens and drug resistance of ventilator-associated pneumonia in Chinese neonatal intensive care units: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernada, M.; Brugada, M.; Golombek, S.; Vento, M. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in neonatal patients: An update. Neonatology 2014, 105, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.C.; Kefala, K.; Simpson, A.J.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Everingham, K.; Kerslake, D.; Raby, S.; Laurenson, I.F.; Swann, D.G.; Walsh, T.S. Evaluation of the effect of diagnostic methodology on the reported incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Thorax 2009, 64, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species | Blood Culture | Tracheal Aspirate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||
| Acinetobacter sp. | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Citrobacter sp. | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 1 | 1.92 | 3 | 5.45 |
| Escherichia coli | 3 | 5.77 | 5 | 9.09 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 3 | 5.77 | 8 | 14.55 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5.45 |
| Serratia marcescens | 1 | 1.92 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Serratia liquefaciens | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5.45 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||
| Saprophytic germs | 0 | 0 | 11 | 20.00 |
| CoNS | 34 | 65.38 | 14 | 25.45 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 2 | 3.85 | 3 | 5.45 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 3 | 5.77 | 3 | 5.45 |
| Enterococcus spp. | 4 | 7.69 | 8 | 14.55 |
| Bacillus cereus | 1 | 1.92 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR | ||||
| 2MRGN NeoPäd | 0 | 0 | 7 | 12.73 |
| 3MRGN | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.64 |
| VRE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MRSA | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Other | 1 | 1.92 | 1 | 1.82 |
| Total | 53 | 77 | ||
| Patient Group | n | MDR Bacteria or SERMA | Χ2 | p | Fisher’s Exact Test | CC | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Gestational age at birth | 55 | 19 | - | - | 0.501 | 0.173 | - | - | - |
| Full-term (≥37 + 0) | 18 | 5 | |||||||
| Middle to late preterm (32 + 0 to 36 + 6) | 12 | 6 | |||||||
| Early preterm (<32 + 0) | 25 | 8 | |||||||
| Adjusted gestational age | 55 | 19 | - | - | 0.296 | 0.209 | - | - | - |
| Full-term (≥37 + 0) | 25 | 10 | |||||||
| Middle to late preterm (32 + 0 to 36 + 6) | 14 | 6 | |||||||
| Early preterm (< 32 + 0) | 16 | 3 | |||||||
| Type of pneumonia | 55 | 19 | 4.10 | 0.043 * | - | 0.264 | 4.80 | 0.955 | 24.2 |
| EOP ≤ 7 days (ref.) | 15 | 2 | |||||||
| LOP > 7 days | 40 | 17 | |||||||
| Delivery mode | 52 | 19 | 4.90 | 0.027 * | - | 0.293 | 0.181 | 0.0357 | 0.917 |
| Cesarean (ref.) | 37 | 17 | |||||||
| Vaginal | 15 | 2 | |||||||
| Sex | 55 | 19 | 0.02 | 0.992 | - | 0.0014 | 1.01 | 0.330 | 3.06 |
| Male | 29 | 10 | |||||||
| Female | 26 | 9 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bär, A.; Schmitt-Grohé, S.; Held, J.; Lubig, J.; Hanslik, G.; Fahlbusch, F.B.; Reutter, H.; Woelfle, J.; van der Donk, A.; Schleier, M.; et al. Evaluating the Use of Neonatal Colonization Screening for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy of Sepsis and Pneumonia. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020189
Bär A, Schmitt-Grohé S, Held J, Lubig J, Hanslik G, Fahlbusch FB, Reutter H, Woelfle J, van der Donk A, Schleier M, et al. Evaluating the Use of Neonatal Colonization Screening for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy of Sepsis and Pneumonia. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleBär, Alisa, Sabina Schmitt-Grohé, Jürgen Held, Julia Lubig, Gregor Hanslik, Fabian B. Fahlbusch, Heiko Reutter, Joachim Woelfle, Adriana van der Donk, Maria Schleier, and et al. 2023. "Evaluating the Use of Neonatal Colonization Screening for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy of Sepsis and Pneumonia" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020189
APA StyleBär, A., Schmitt-Grohé, S., Held, J., Lubig, J., Hanslik, G., Fahlbusch, F. B., Reutter, H., Woelfle, J., van der Donk, A., Schleier, M., Hepp, T., & Morhart, P. (2023). Evaluating the Use of Neonatal Colonization Screening for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy of Sepsis and Pneumonia. Antibiotics, 12(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020189








