Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
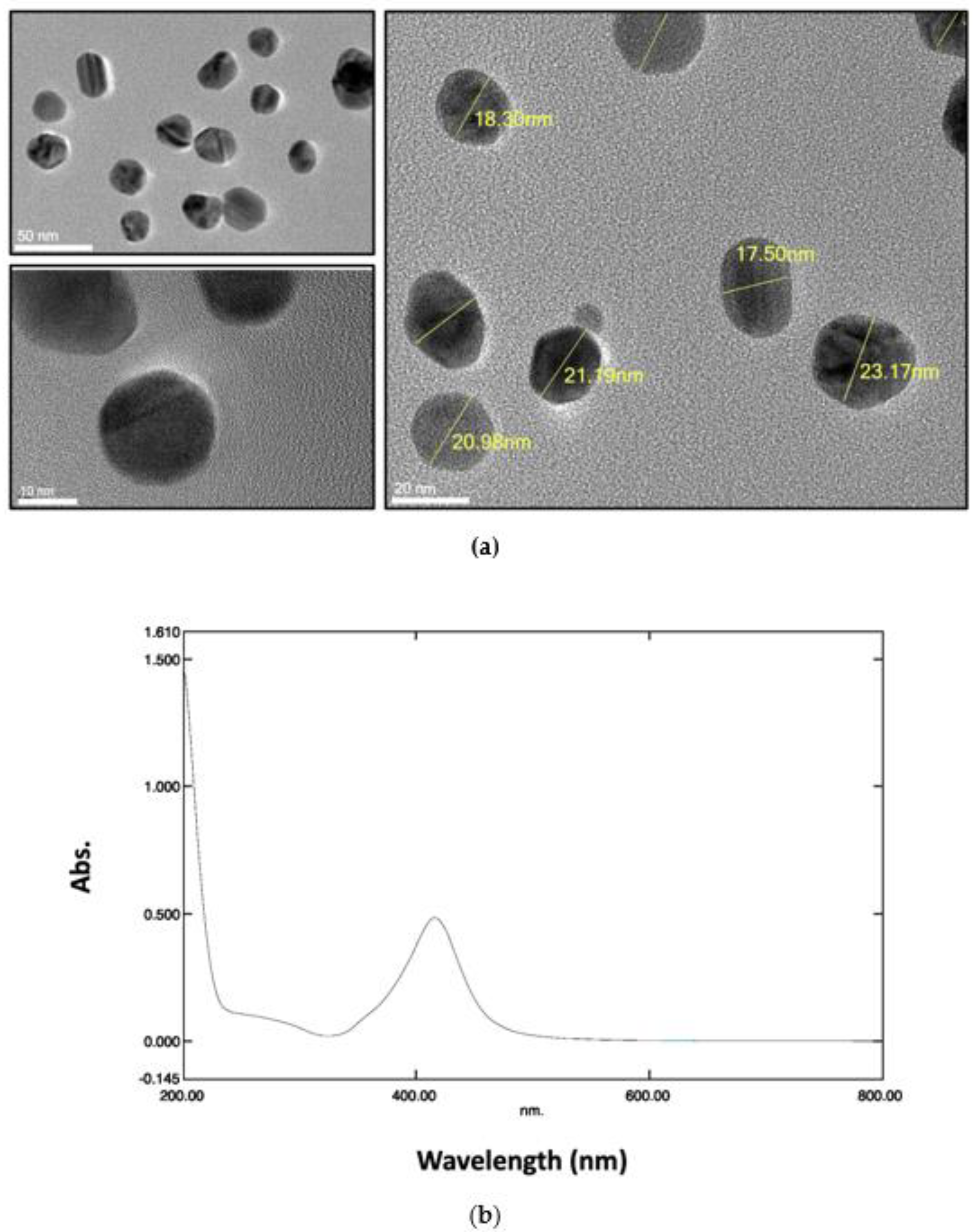
2.1. Characterization of AgNPs
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of AgNPs and Other Antimicrobial agents
2.3. Synergy between AgNPs and Tested Antimicrobials
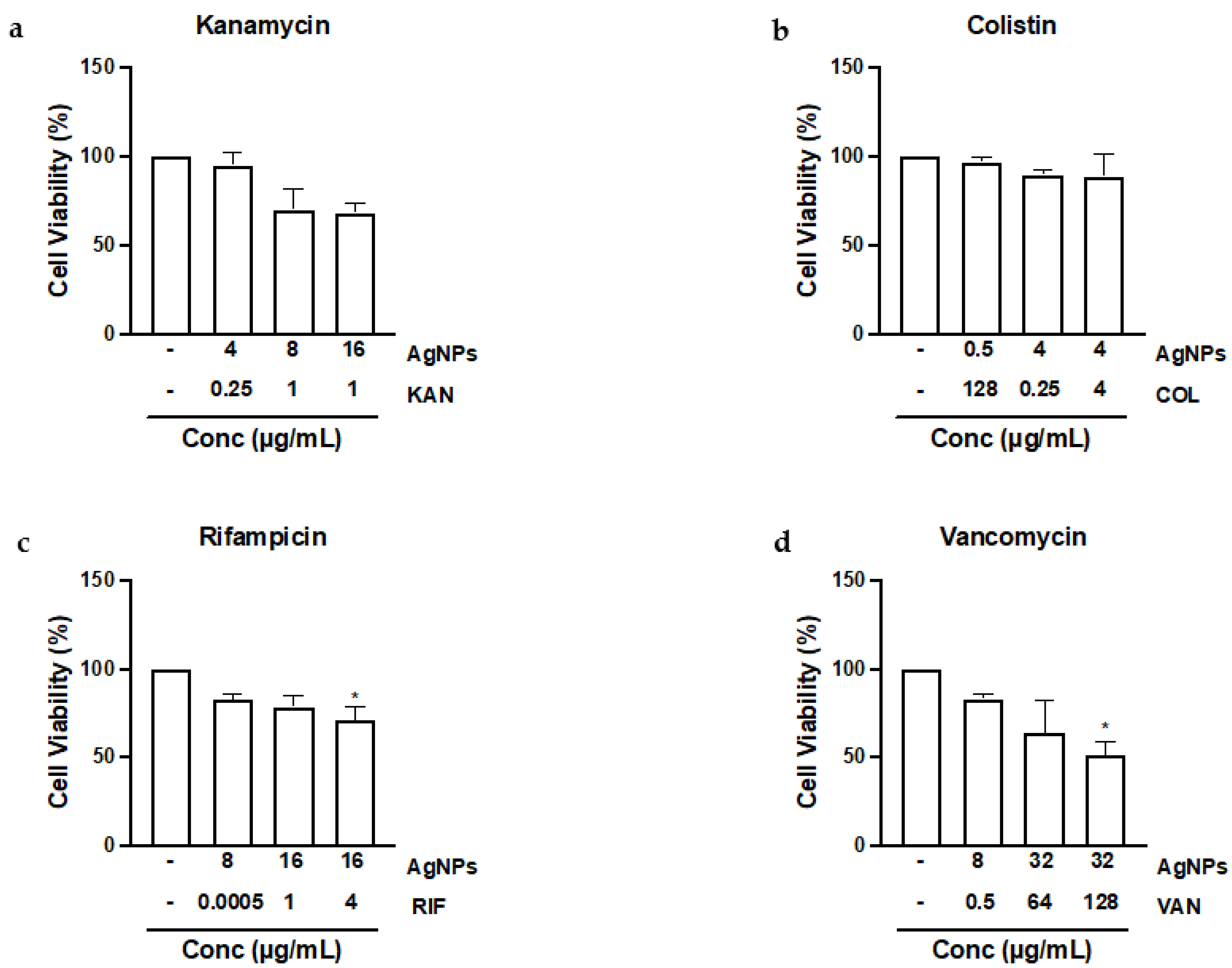
2.4. Cytotoxicity of AgNP-Based Combinations with Synergy in Mammalian Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization of AgNPs
3.3. Bacterial Strains
3.4. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of AgNPs and Other Antimicrobial agents
3.5. Synergistic Effect of AgNP-Based Combination with Other Antimicrobial agents
3.6. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of AgNP-Based Synergistic Combination with Other Antimicrobial Agents
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panda, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Nayak, P.S.; Arakha, M.; Jha, S. Screening of metal-resistant coal mine bacteria for biofabrication of elemental silver nanoparticle. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.B.; Hussain, M.A.; Nye, R.; Mehta, V.; Mamun, K.T.; Hossain, N. A Review on Antibiotic Resistance: Alarm Bells are Ringing. Cureus 2017, 9, e1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, K.; Slay, B.; Knackstedt, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Antimicrobial Activity of Metal and Metal-Oxide Based Nanoparticles. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.L.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Manaia, E.B.; Junior, J.A.O.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Rebezov, M.B.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. A Mini Review of Antibacterial Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 641481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashajyothi, C.; Harish, K.H.; Dubey, N.; Chandrakanth, R.K. Antibiofilm activity of biogenic copper and zinc oxide nanoparticles-antimicrobials collegiate against multiple drug resistant bacteria: A nanoscale approach. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D.; Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria “A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.C.; Haberbeck, L.U.; Riella, H.G.; Ribeiro, D.H.B.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by solochemical process. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Who Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 444–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadini, H. Antimicrobial resistance in Saudi Arabia: A review for immediate action and solution. Int. J. Med. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 4, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowawi, H.M. Antimicrobial resistance in Saudi Arabia: An urgent call for an immediate action. Saudi Med. J. 2016, 37, 16139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, T.U.; Alrodayyan, M.; Albladi, M.; Aldrees, M.; Siddique, M.I.; Aljohani, S.; Balkhy, H.H. Clonal diversity and genetic profiling of antibiotic resistance among multidrug/carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkofide, H.; Alhammad, A.M.; Alruwaili, A.; Aldemerdash, A.; Almangour, T.A.; Alsuwayegh, A.; Almoqbel, D.; Albati, A.; Alsaud, A.; Enani, M. Multidrug-resistant and extensively drugresistant enterobacteriaceae: Prevalence, treatments, and outcomes—A retrospective cohort study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4653–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabdullatif, M.; Alrehaili, J. Three years of evaluation to determine reduction of antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria by the saudi national action plan. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A.; Giacobbe, D.R. Treatment of Infections Due to MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kant, V.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, M. Synthesis, characterization and concentration dependant antibacterial potentials of nickel oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli 2020. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2020, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskos, I.; Souli, M.; Galani, I.; Giamarellou, H. Colistin: Still a lifesaver for the 21st century? Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M. Synergistic activities of colistin combined with other antimicrobial agents against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, R.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Engineered nanoparticles and organic matter: A review of the state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalawi, F.; Hussein, M.Z.; Fakurazi, S.; Masarudin, M.J. Engineered nanomaterials: The challenges and opportunities for nanomedicines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssekatawa, K.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Kato, C.D.; Ejobi, F.; Tweyongyere, R.; Lubwama, M.; Kirabira, J.B.; Wampande, E.M. Nanotechnological solutions for controlling transmission and emergence of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, future prospects, and challenges: A systematic review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, R.; Barbosa, A.A.T.; Dolabela, S.S.; Jain, S. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Alternative Methods to Control Them: An Overview. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 890–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Rahman, A.U.; Tajuddin; Husen, A. Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Activity Against Microbes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escárcega-González, C.E.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Vazquez-Rodríguez, A.; Montelongo-Peralta, L.Z.; Treviño-Gonzalez, M.T.; Castro, E.D.B.; Saucedo-Salazar, E.M.; Morales, R.C.; Soto, D.R.; González, F.T.; et al. In vivo antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles produced via a green chemistry synthesis using acacia rigidula as a reducing and capping agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Lim, D.W.; Choi, J. Assessment of size-dependent antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 763807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Smékalová, M.; Večeřová, R.; Bogdanová, K.; Röderová, M.; Kolář, M.; Kilianová, M.; Hradilová, Š.; Froning, J.P.; Havrdová, M.; et al. Silver nanoparticles strongly enhance and restore bactericidal activity of inactive antibiotics against multiresistant Enterobacteriaceae. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.L.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, I.C.; Huang, Y.J. Trojan-horse mechanism in the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles verified by direct intra- and extracellular silver speciation analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzammil, S.; Hayat, S.; Fakhar-E-Alam, M.; Aslam, B.; Siddique, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Saqalein, M.; Atif, M.; Sarwar, A.; Khurshid, A.; et al. Nanoantibiotics: Future nanotechnologies to combat antibiotic resistance. Front. Biosci.-Elit. 2018, 10, 352–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, P.; Singh, M.; Mudila, H. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial therapeutics: Current perspectives and future challenges. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Singh, R.K.; Tyagi, P.K.; Gore, D. Assessment of Toxicity and Safety Profiles of Nanoparticles. Lett. Appl. Nanobiosci. 2020, 10, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.A.; Mourad, M.I.; Alsewy, F.Z.; El Moez Azzam, N.F.A. Combination of silver nanoparticles with ineffective antibiotics against extended spectrum beta-lactamases producing isolates at Alexandria Main University Hospital, Egypt. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaran, S.; Zarif, B.R. Synergistic Effect of Silver Nanoparticles with Neomycin or Gentamicin Antibiotics on Mastitis-Causing Staphylococcus aureus. Open J. Ecol. 2016, 6, 67043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.A.; el Maghraby, G.M.; Sonbol, F.I.; Allam, N.G.; Ateya, P.S.; Ali, S.S. Enhanced Efficacy of Some Antibiotics in Presence of Silver Nanoparticles Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Recovered From Burn Wound Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Zhai, Y.; Xue, J.; Song, H.; Yang, F.; Xu, P.; et al. Synergetic Effect of Rifampin Loaded Mussel-Inspired Silver Nanoparticles for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Strain of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; McShan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sinha, S.S.; Arslan, Z.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanistic Study of the Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Combined Silver Nanoparticles and Common Antibiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, K.A.A.; Mohamed, A.M.A. Bactericidal and antibiotic synergistic effect of nanosilver against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.A.; al Othman, M.R.; Mohammed, A.E. Bio fabrication of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial and cytotoxic abilities using lichens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélteky, P.; Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Szerencsés, B.; Tóth, I.Y.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M.; Kónya, Z. Silver nanoparticles: Aggregation behavior in biorelevant conditions and its impact on biological activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 18965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rónavári, A.; Bélteky, P.; Boka, E.; Zakupszky, D.; Igaz, N.; Szerencsés, B.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kónya, Z.; Kiricsi, M. Polyvinyl-pyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles—The colloidal, chemical and biological consequences of steric stabilization under biorelevant conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M100-S24; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014.
- European Committee on Antimicrobial. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 10.0. 2020. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- CLSI M100-ED29; 2019 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 29th Edition. CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- Guzman, M.; Dille, J.; Godet, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, A.; Ganesh, M.; Jayaprakash, J.; Jang, H.T. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cassia tora leaf extract and its antioxidant and antibacterial activities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.H.; Aslam, B.; Imran, M.; Ashraf, A.; Nadeem, H.; Hayat, S.; Khurshid, M.; Afzal, M.; Malik, I.R.; Shahzad, M.; et al. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Biofilm Formation and EPS Production of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, R.S.; Ali, M.A.; Goda, D.A.; Khalil, M.I.; Redhwan, A. Cytotoxic effect of green silver nanoparticles against ampicillin-resistantKlebsiella pneumoniae. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21136–21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, V.; Devineau, S.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Bhargava, A.; Panwar, J.; Srikumar, S.; Fanning, S. Silver Nanoparticles Induce a Triclosan-Like Antibacterial Action Mechanism in Multi-Drug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanesan, S.; Alsalhi, M.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the flower extract of abelmoschus esculentus for cytotoxicity and antimicrobial studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3343–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Shafiq, A.; Khan, H.M.; Husain, F.M.; Khan, R.A.; Alenazi, B.; Alsalme, A.; Ahmad, I. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Murraya koenigii (L.) against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2019, 2019, 4649506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Feng, J. The intrinsic resistance of bacteria. Yi chuan 2016, 38, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Bera, T.; Roy, A.; Singh, G.; Ramachandrarao, P.; Dash, D. Characterization of enhanced antibacterial effects of novel silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, S.; Prasad, S.; Gambhir, I.S. Nanotechnology in Medicine and Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2008, 3, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Chung, E.; Johnston, I.; Ren, G.; Cheong, Y.K. Exploitation of antimicrobial nanoparticles and their applications in biomedical engineering. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, P.; Thangapandiyan, S.; Immanuel, G. CMC stabilized nano silver synthesis, characterization and its antibacterial and synergistic effect with broad spectrum antibiotics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5-100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Deng, K.K.; Kim, N.J.; Ross, L.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Hu, Z. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, M.P.; Das, J. Fabrication of porous chitosan/silver nanocomposite film and its bactericidal efficacy against multi-drug resistant (MDR) clinical isolates. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 6, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.L. Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.H. Antibacterial activity and synergistic antibacterial potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against foodborne pathogenic bacteria along with its anticandidal and antioxidant effects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, D.; Golinska, P.; Wypij, M.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. A new report of Nocardiopsis valliformis strain OT1 from alkaline Lonar crater of India and its use in synthesis of silver nanoparticles with special reference to evaluation of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 205, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vazquez-Muñoz, R.; Meza-Villezcas, A.; Fournier, P.G.J.; Soria-Castro, E.; Juarez-Moreno, K.; Gallego-Hernández, A.L.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Huerta-Saquero, A. Enhancement of antibiotics antimicrobial activity due to the silver nanoparticles impact on the cell membrane. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panácek, A.; Smékalová, M.; Kilianová, M.; Prucek, R.; Bogdanová, K.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Havrdová, M.; Płaza, G.A.; Chojniak, J.; et al. Strong and nonspecific synergistic antibacterial efficiency of antibiotics combined with silver nanoparticles at very low concentrations showing no cytotoxic effect. Molecules 2016, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, J.M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Alobaidi, A.S.; Nauman, K.; Alahmedi, S.; Almazyed, A.O.; Almosallam, M.A.; Al Jurayyan, A.N. A synergic action of colistin, imipenem, and silver nanoparticles against pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwarh, R.; Gogoi, B.; Philip, R.; Laskar, M.A.; Karak, N. Biomimetic preparation of polymer-supported free radical scavenging, cytocompatible and antimicrobial ‘green’ silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Citrus sinensis peel. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.; Ruan, L.; Yin, Y.; Yang, T.; Ge, M.; Cheng, X. Effects of silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics on the resistant bacteria Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Pandey, R.; Barman, I.; Prasad, R. Leveraging the attributes of mucor hiemalis-derived silver nanoparticles for a synergistic broad-spectrum antimicrobial platform. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, K.; Grudniak, A.M.; Krawczyk, K.; Wróbel, I.; Wolska, K.I. Modulation of antibiotic resistance and induction of a stress response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by silver nanoparticles. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebimieowei, E.; Ibemologi, A. Antibiotics: Classification and mechanisms of action with emphasis on molecular perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2016, 4, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore, D.; Chaudhari, A.; Barlow, B.; Barlow, B.; Harper, T.; Vig, K.; Miller, M.; Singh, S.; Nelson, E.; Pillai, S. Evaluation of E. Coli inhibition by plain and polymer-coated silver nanoparticles. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2018, 60, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyoti, K.; Baunthiyal, M.; Singh, A. Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Kumar, R. Enhanced bactericidal efficacy of polymer stabilized silver nanoparticles in conjugation with different classes of antibiotics. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidaillac, C.; Benichou, L.; Duval, R.E. In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4856–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yin, F.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Zhu, H.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X. Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-1 Mediates Cell Permeability and Resistance to Hydrophobic Antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.E. Structure, biochemistry and mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1989, 8, 7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Rajasekar, S.; Selvakumar, P.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Mohan, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.B.; Rajamohan, G. KpnEF, a new member of the Klebsiella pneumoniae cell envelope stress response regulon, is an SMR-type efflux pump involved in broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4449–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Labby, K.J. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics: Overview and perspectives. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, P.; Singh, M.; Mudila, H. Oligodynamic Effect of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipe, D.S.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Love, R.M.; Hamlet, S.M. Silver Nanoparticles at Biocompatible Dosage Synergistically Increases Bacterial Susceptibility to Antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Carrizales, M.; Velasco, K.I.; Castillo, C.; Flores, A.; Magaña, M.; Martinez-Castanon, G.A.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F. In vitro synergism of silver nanoparticles with antibiotics as an alternative treatment in multiresistant uropathogens. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kora, A.J.; Rastogi, L. Enhancement of antibacterial activity of capped silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics, on model gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2013, 2013, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gubala, V.; Johnston, L.J.; Liu, Z.; Krug, H.; Moore, C.J.; Ober, C.K.; Schwenk, M.; Vert, M. Engineered nanomaterials and human health: Part 1. Preparation, functionalization and characterization (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 1283–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.A.; Seckler, M.M.; Ingle, A.P.; Gupta, I.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Silver nanoparticles: Therapeutical uses, toxicity, and safety issues. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, T.; Strigun, A.; Verlohner, A.; Huener, H.A.; Peter, E.; Herold, M.; Bordag, N.; Mellert, W.; Walk, T.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Prediction of liver toxicity and mode of action using metabolomics in vitro in HepG2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazar, E.; Ai, J.; Biazar, E.; Jafarpour, M.; Montazeri, M.; Majdi, A.; Aminifard, S.; Zafari, M.; Akbari, H.R.; Rad, H.G. Nanotoxicology and nanoparticle safety in biomedical designs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shama, U.H.; El-Gendy, H.; Mousa, W.S.; Hamouda, R.A.; Yousuf, W.E.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdeen, E.E. Synergistic and antagonistic effects of metal nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some reference strains of pathogenic microorganisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CLSI DOCUMENTE M07-A10; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard-Tenth Edition. CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015; Volume 35.
- Rabadia, A.; Kamat, S.D.; Kamat, D.V. Study of synergistic action of cefotaxime and Terminalia chebula on Acinetobacter baumannii using checkerboard Assay. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 830–832. [Google Scholar]
- Hep G2 [HEPG2]—HB-8065|ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/products/hb-8065 (accessed on 30 August 2022).
| ENMs | Medium | Hydrodynamic size (nm) | Zeta potential (mV) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | Water | 54 ± 1 | −2.7 ± 0.9 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| DMEM | 153 ± 16 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | |
| CAMHB | 48 ± 3 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.29 ± 0.01 |
| Gram-Negative Bacteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | MIC μg/mL | ||||||
| AgNPs | AMP | KAN | VAN | CIP | COL | RIF | |
| E. coli (ATCC 25922) | 64 | 2 | 2 | 256 | 0.015 | 2 | 4 |
| K. pneumoniae (ATCC 13883) | 128 | >256 | 1 | >256 | 0.25 | ND | 16 |
| P. aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) | 16 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >0.25 | 0.5 | 16 |
| A. baumannii (ATCC BAA-747) | 32 | 16 | 4 | >256 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | |||||||
| S. aureus (ATCC 29213) | 256 | 0.5 | 4 | 1 | >0.25 | >256 | >0.25 |
| S. saprophyticus (ATCC 49453) | 256 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.25 | 64 | >0.25 |
| S. sciuri (ATCC 29061) | 256 | 2 | 8 | 0.5 | 0.25 | ND | <0.25 |
| S. epidermidis (ATCC 12228) | 256 | ND | ND | 2 | 0.25 | >256 | <0.25 |
| AMR strains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | MIC μg/mL | ||||||
| AgNPs | AMP | KAN | VAN | CIP | COL | RIF | |
| K. pneumoniae Strain I | 64 | 4096 | 4 | 1024 | 4 | 1 | 16 |
| K. pneumoniae (ESBL) Strain II | 64 | 4096 | 4 | 2048 | 1 | 64 | 16 |
| K. pneumoniae (ESBL) Strain III | 128 | 0.5 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 256 | 0.002 |
| CLSI breakpoints (μg/mL) | NR | ≥32 | ≥64 | NR | ≥1 | ≥4 | NR |
| Combination | MIC of AgNPs Alone | MIC of AgNPs in Combination | MIC of AM Alone | MIC of AM in Combination | ΣFIC | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-type (E. coli) strain | ||||||
| AMP + AgNPs | 64 | 32 | 4 | 2 | 1 | Indifference |
| KAN + AgNPs | 64 | 4 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.1 | Synergism |
| COL + AgNPs | 128 | 4 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.1 | Synergism |
| CIP + AgNPs | 128 | 32 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.7 | Indifference |
| RIF + AgNPs | 128 | 16 | 8 | 1 | 0.2 | Synergism |
| VAN + AgNPs | 128 | 32 | 512 | 128 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| K. pneumoniaeStrain I | ||||||
| AMP + AgNPs | 64 | 16 | 4096 | 2048 | 0.7 | Indifference |
| KAN + AgNPs | 64 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | Synergism |
| COL + AgNPs | 32 | 8 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| CIP + AgNPs | 128 | 64 | 4 | 0.065 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| RIF + AgNPs | 64 | 16 | 16 | 4 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| VAN + AgNPs | 64 | 8 | 1024 | 512 | 0.6 | Indifference |
| K. pneumoniae(ESBL) Strain II | ||||||
| AMP + AgNPs | 64 | 16 | 4096 | 2048 | 0.7 | Indifference |
| KAN + AgNPs | 64 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | Synergism |
| COL + AgNPs | 64 | 4 | 64 | 4 | 0.1 | Synergism |
| CIP + AgNPs | 64 | 32 | 4 | 1 | 0.75 | Indifference |
| RIF + AgNPs | 64 | 16 | 16 | 4 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| VAN + AgNPs | 64 | 32 | 1024 | 64 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| K. pneumoniae(ESBL) Strain III | ||||||
| AMP + AgNPs | 128 | 64 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 0.75 | Indifference |
| KAN + AgNPs | 128 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | Synergism |
| COL + AgNPs | 128 | 0.5 | 256 | 128 | 0.5 | Synergism |
| CIP + AgNPs | 128 | 16 | 32 | 16 | 0.625 | Indifference |
| RIF + AgNPs | 128 | 8 | 0.002 | 0.0005 | 0.3 | Synergism |
| VAN + AgNPs | 128 | 8 | 8 | 0.5 | 0.1 | Synergism |
| Organism | Resistant Phenotypes |
|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae Strain I | Ampicillin, cephalosporin, ciprofloxacin, vancomycin |
| K. pneumoniae (ESBL) Strain II | Ampicillin, cephalosporin, ciprofloxacin, colistin, vancomycin |
| K. pneumoniae (ESBL) Strain III | Cephalosporin, ciprofloxacin, ertapenem, tobramycin, Trimethoprim/ Sulfamethoxazole, colistin, vancomycin |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alotaibi, A.M.; Alsaleh, N.B.; Aljasham, A.T.; Tawfik, E.A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Assiri, M.A.; Alkholief, M.; Almutairi, M.M. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091219
Alotaibi AM, Alsaleh NB, Aljasham AT, Tawfik EA, Almutairi MM, Assiri MA, Alkholief M, Almutairi MM. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(9):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091219
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlotaibi, Areej M., Nasser B. Alsaleh, Alanoud T. Aljasham, Essam A. Tawfik, Mohammed M. Almutairi, Mohammed A. Assiri, Musaed Alkholief, and Mashal M. Almutairi. 2022. "Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates" Antibiotics 11, no. 9: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091219
APA StyleAlotaibi, A. M., Alsaleh, N. B., Aljasham, A. T., Tawfik, E. A., Almutairi, M. M., Assiri, M. A., Alkholief, M., & Almutairi, M. M. (2022). Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics, 11(9), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091219






