Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.2. Synergy between ZnO-NPs and Meropenem
2.3. Antibiofilm Activity of ZnO-NPs
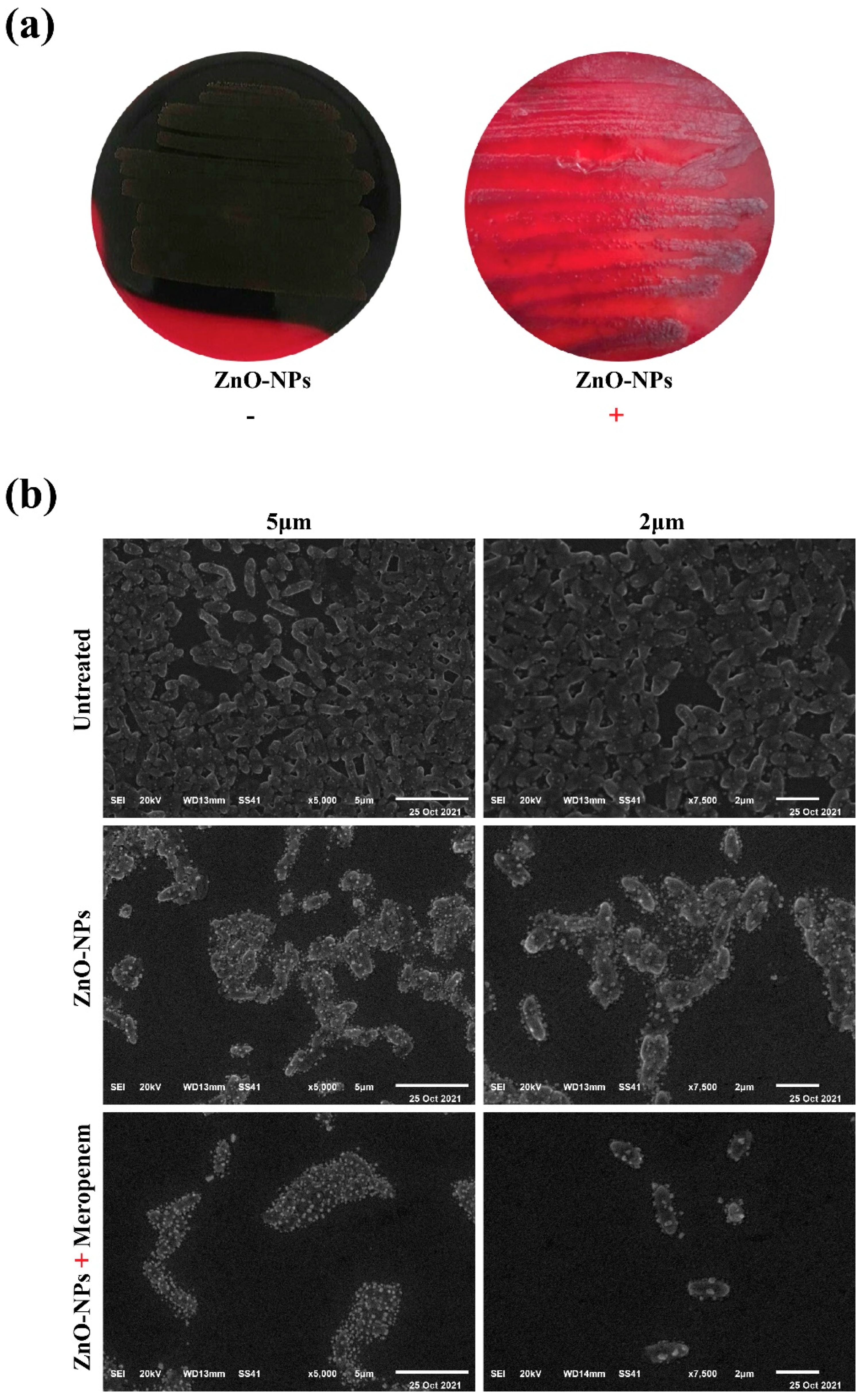
2.4. Macroscopical and Microscopical Examination of Biofilm Disruption
2.5. Expression of Biofilm Genes
2.6. Effect of ZnO-NPs and Meropenem on the Area % of Corneal Opacity as a Measure of Corneal Lesions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Biofilm Assay Method
4.4. Preparation of Antimicrobial Agents (Meropenem and ZnO-NPs)
4.5. Detection of the Antibiofilm Activity of ZnO-NPs
4.6. Determination of MICs of Meropenem and ZnO-NPs (Microdilution Method)
4.7. Evaluation of Synergistic Antibacterial Activity (Checkerboard Microdilution Assay)
4.8. Congo Red Agar Assay (CRA)
4.9. SEM
4.10. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction RT-PCR
4.11. Animal Study
4.11.1. Induction of Keratitis
4.11.2. Experimental Design
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maurice, N.M.; Bedi, B.; Sadikot, R.T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: Host response and clinical implications in lung infections. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development; Infection Control Africa Network: Cape Town, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.N.; Khan, A.U. Breaking the spell: Combating multidrug resistant ‘superbugs’. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Bjarnsholt, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in cystic fibrosis. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Kronfl, A.A.; Wu, Y. Type VI secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with biofilm formation but not environmental adaptation. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyanarayanan, T.; Periasamy, S.; Lin, M.H.; Ishihama, Y.; Swarup, S. Flagellin FliC phosphorylation affects type 2 protease secretion and biofilm dispersal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Nikokar, I.; Ghasemi, Y.; Ebrahimpour, M.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Araghian, A.; Faezi, S.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Rajabi, A. Antibiotic resistance pattern and distribution of pslA gene among biofilm producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from waste water of a burn center. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e23669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.J.; Jackson, L.; Yau, Y.C.W.; Reichhardt, C.; Beaudoin, T.; Uwumarenogie, S.; Guttman, K.M.; Lynne Howell, P.; Parsek, M.R.; Hoffman, L.R.; et al. The role of Psl in the failure to eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in children with cystic fibrosis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, B.L.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Manaia, E.B.; Junior, J.A.O.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, H.C.; Labthavikul, P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, L.R.; Wagstaff, A.J.; Brogden, R.N.; Bryson, H.M. Meropenem. Drugs 1995, 50, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragasam, A.K.; Raghanivedha, M.; Anandan, S.; Veeraraghavan, B. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with discrepant carbapenem susceptibility profile. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Perumal, E. Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: A promise for the future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.L.; Han, P.; Guo, L.C.; Cao, Y.Q.; Li, A.D.; Kong, J.Z.; Zhai, H.F.; Wu, D. The antibacterial activity of Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, L.S.; Nisha, M.M.; Joice, M.; Shilpa, P.N. Antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhluf, S.; Dror, R.; Nitzan, Y.; Abramovich, Y.; Jelinek, R.; Gedanken, A. Microwave-assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline MgO and its use as a bacteriocide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Harrison, A.; Sabbani, S.; Munson Jr, R.S.; Dutta, P.K.; Waldman, W.J. Silver nanoparticles embedded in zeolite membranes: Release of silver ions and mechanism of antibacterial action. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1833. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Wong, M.T.; Chan, C.M.N.; Yu, L.H.; Phillips, D.L.; Ma, A.P.Y.; et al. Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of MgO: Non-ROS mediated toxicity of MgO nanoparticles towards Escherichia coli. Small 2014, 10, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Halim, M.S.; Askoura, M.; Mansour, B.; Yahya, G.; El-Ganiny, A.M. In vitro activity of celastrol in combination with thymol against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. J. Antibiot. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masák, J.; Čejková, A.; Schreiberová, O.; Řezanka, T. Pseudomonas biofilms: Possibilities of their control. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nanomicro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A.; Tiwari, M. Mechanism of anti-bacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticle against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Jalal, M.; AlYahya, S.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Khan, H.M. Effect of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadwa, A.O.; Alkoblan, D.K.; Mateen, A.; Albarag, A.M. Synergistic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and various antibiotics combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinically isolated bacterial strains. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, E.O. In vitro activity of carvacrol in combination with meropenem against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gizawy, S.A.; Nouh, A.; Saber, S.; Kira, A.Y. Deferoxamine-loaded transfersomes accelerates healing of pressure ulcers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, B.K.; Gaur, A.H. The use and abuse of antibiotics and the development of antibiotic resistance. In Hot Topics in Infection and Immunity in Children VI; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, J.A.; Brody, S.L.; Kollef, M.H. The epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs 2007, 67, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venubabu Thati, A.; Roy, S.; Prasad, M.A.; Shivannavar, C.; Gaddad, S. Nanostructured zinc oxide enhances the activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biosci. Technol. 2010, 1, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, S.Z.H.; Kiran, U.; Ali, M.I.; Jamal, A.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, N. Combined efficacy of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles and different antibiotics against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdiyev, A.M.; Kon, K.V.; Abamor, E.S.; Bagirova, M.; Rafailovich, M. Coping with antibiotic resistance: Combining nanoparticles with antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 1035–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, A.J.; Kwon, Y.J. “Nanoantibiotics”: A new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Ruan, L.; Yin, Y.; Yang, T.; Ge, M.; Cheng, X. Effects of silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics on the resistant bacteria Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3789–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; McShan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sinha, S.S.; Arslan, Z.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanistic Study of the Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Combined Silver Nanoparticles and Common Antibiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8840–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J. Synergism testing: Broth microdilution checkerboard and broth macrodilution method. In Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook; Gracia, L.S., Ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 16, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Endimiani, A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenems: Past, present, and future. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen,, A. Properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their activity against microbes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuni-Badiger, P.P.; Patil, P.M.; Badiger, M.V.; Patel, P.R.; Thorat-Gadgil, B.S.; Pandit, A.; Bohara, R.A. Biofilm formation to inhibition: Role of zinc oxide-based nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, M.; Bangera, M.G.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Parsek, M.R.; Teitzel, G.M.; Lory, S.; Greenberg, E.P. Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nature 2001, 413, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, S.E.; Shaker, G.H.; Mosallam, F.M.; Abbas, H.A. Knocking down Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by oral hypoglycemic metformin nano emulsion. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Saqr, A.A.; Alalaiwe, A.; Abbas, H.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Goda, R.M. Tackling virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the Natural Furanone Sotolon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Elshawadfy, A.M.; Amin, G.; Askora, A. Characterization of R-pyocin activity against Gram-positive pathogens for the first time with special focus on Staphylococcus aureus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, R.; Yahya, G.; Abdo, W.S.; El-Tanbouly, G.S.; Johar, D.; Abdel-Halim, M.S.; Eissa, H.; Magheru, C.; Saber, S.; Cavalu, S. Emerging Approach for the Application of Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract Ointment in the Superficial Burn Care. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, A.M.; Yahya, G.; Mansour, B.; El-Sokkary, M.M.; Alshaman, R.; Alattar, A.; El-Ganiny, A.M. The Link between occurrence of class I integron and acquired aminoglycoside resistance in clinical MRSA isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2011, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Clinical and Laboratory standards Institute: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2021; 352p. [Google Scholar]
- Azeredo, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Briandet, R.; Cerca, N.; Coenye, T.; Costa, A.R.; Desvaux, M.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Hébraud, M.; Jaglic, Z.; et al. Critical review on biofilm methods. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 313–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Telbany, M.; El-Didamony, G.; Askora, A.; Ariny, E.; Abdallah, D.; Connerton, I.F.; El-Shibiny, A. Bacteriophages to control multi-drug resistant Enterococcus faecalis infection of dental root canals. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, G.; Hashem, M.N.; Pijuan, J.; Seleem, N.M.; Mosbah, R.; Hess, S.; Abdelmoaty, A.A.; Almeer, R.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Alshaman, H.S.; et al. Profiling the physiological pitfalls of anti-hepatitis C direct-acting agents in budding yeast. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 2199–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.L.D.C.; Alves, L.R.; Jacomé, P.R.L.D.A.; Bezerra Neto, J.P.; Maciel, M.A.V.; Morais, M.M.C.D. Biofilm production by clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and structural changes in LasR protein of isolates non biofilm-producing. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.C.; Ma, P.; Zhong, W.; Liu, J.S. Statistical assessment of the global regulatory role of histone acetylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T.; Spilker, T.; Van Schoor, A.; LiPuma, J.J.; Vandamme, P. Recovery of Burkholderia cenocepacia strain PHDC from cystic fibrosis patients in Europe. Thorax 2004, 59, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ghadaksaz, A.; Fooladi, A.A.I.; Hosseini, H.M.; Amin, M. The prevalence of some Pseudomonas virulence genes related to biofilm formation and alginate production among clinical isolates. J. Appl. Biomed. 2015, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Khalil, R.M.; Abdo, W.S.; Nassif, D.; El-Ahwany, E. Olmesartan ameliorates chemically-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulating NFκB and Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling crosstalk. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 364, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Teiama, M.; Ismail, A.; Ebada, A.; Saber, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cubosomal nanoparticles as an ocular delivery system for fluconazole in treatment of keratomycosis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, G.; Ebada, A.; Khalaf, E.M.; Mansour, B.; Nouh, N.A.; Mosbah, R.A.; Saber, S.; Moustafa, M.; Negm, S.; El-Sokkary, M.M.; et al. Soil-associated Bacillus species: A reservoir of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic activity against human pathogens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, R.; Rabia, I.; El-Ahwany, E.; Saber, S.; Gamal, R.; Nagy, F.; Mahmoud, O.; Hamad, R.S.; Barakat, W. Blockade of PGE2, PGD2 receptors confers protection against prepatent Schistosomiasis mansoni in mice. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



| Tested Strains | Antibiotics and Diameter of Inhibition | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imipenem (10 µg) | Meropenem (10 µg) | Levofloxacin (5 µg) | Ceftazidime (30 µg) | Gentamycin (10 µg) | Amikacin (30 µg) | Aztreonam (30 µg) | Piperacillin (100 µg) | Cefepime (30 µg) | Norfloxacin (10 µg) | |||||||||||
| R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | |
| ≤15 | ≥19 | ≤15 | ≥19 | ≤13 | ≥17 | ≤14 | ≥18 | ≤12 | ≥15 | ≤14 | ≥17 | ≤15 | ≥22 | ≤14 | ≥21 | ≤14 | ≥18 | ≤12 | ≥17 | |
| PS20 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | ||||||||||
| PS21 | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS22 | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS23 | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS24 | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | S | ||||||||||
| PS25 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | ||||||||||
| PS26 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | ||||||||||
| PS27 | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | S | R | ||||||||||
| PS28 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS29 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS30 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS32 | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | S | ||||||||||
| PS33 | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | ||||||||||
| Pp6 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | ||||||||||
| Pp7 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | ||||||||||
| Pp8 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | ||||||||||
| Pp10 | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| Pp12 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | ||||||||||
| Pp13 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS35 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PS34 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PU17 | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PC38 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| PU15 | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||||||
| R % | 91.6 | 100 | 96 | 96 | 96 | 91.6 | 83 | 96 | 79 | 75 | ||||||||||
| Antibacterial Agents | MIC (mg/mL) | FIC | FICI | Interpretation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alone | Combination | ||||
| ZnO-NPs | 0.0640 ± 0.00462 | 0.0080 ± 0.00231 | 0.125 | 0.132 | Synergy |
| Meropenem | 0.5120 ± 0.01848 | 0.0040 ± 0.00058 | 0.007 | ||
| Target Gene | Primer Sequences | Reverse Transcription | Primary Denaturation | Amplification (40 Cycles) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary Denaturation | Annealing (Optics On) | Extension | |||||
| 16S-rRNA | GACGGGTGAGTAATGCCTA | 50 °C 30 min | 94 °C 15 min | 94 °C 15 s | 60 °C 30 s | 72 °C 30 s | [57] |
| CACTGGTGTTCCTTCCTATA | |||||||
| lasR | AAGTGGAAAATTGGAGTGGAG | [58] | |||||
| GTAGTTGCCGACGACGATGAAG | |||||||
| pslA | TCCCTACCTCAGCAGCAAGC | [32] | |||||
| TGTTGTAGCCGTAGCGTTTCTG | |||||||
| fliC | TGAACGTGGCTACCAAGAACG | [40] | |||||
| TCTGCAGTTGCTTCACTTCGC | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Telbany, M.; Mohamed, A.A.; Yahya, G.; Abdelghafar, A.; Abdel-Halim, M.S.; Saber, S.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Abdelrahman, F.; Fathey, H.A.; et al. Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101374
El-Telbany M, Mohamed AA, Yahya G, Abdelghafar A, Abdel-Halim MS, Saber S, Alfaleh MA, Mohamed AH, Abdelrahman F, Fathey HA, et al. Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101374
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Telbany, Mohamed, Alzhraa Ali Mohamed, Galal Yahya, Aliaa Abdelghafar, Mahmoud Saad Abdel-Halim, Sameh Saber, Mohamed A. Alfaleh, Asmaa H. Mohamed, Fatma Abdelrahman, Hoda A. Fathey, and et al. 2022. "Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101374
APA StyleEl-Telbany, M., Mohamed, A. A., Yahya, G., Abdelghafar, A., Abdel-Halim, M. S., Saber, S., Alfaleh, M. A., Mohamed, A. H., Abdelrahman, F., Fathey, H. A., Ali, G. H., & Abdel-Haleem, M. (2022). Combination of Meropenem and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles; Antimicrobial Synergism, Exaggerated Antibiofilm Activity, and Efficient Therapeutic Strategy against Bacterial Keratitis. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101374








