A Promising Antifungal and Antiamoebic Effect of Silver Nanorings, a Novel Type of AgNP
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
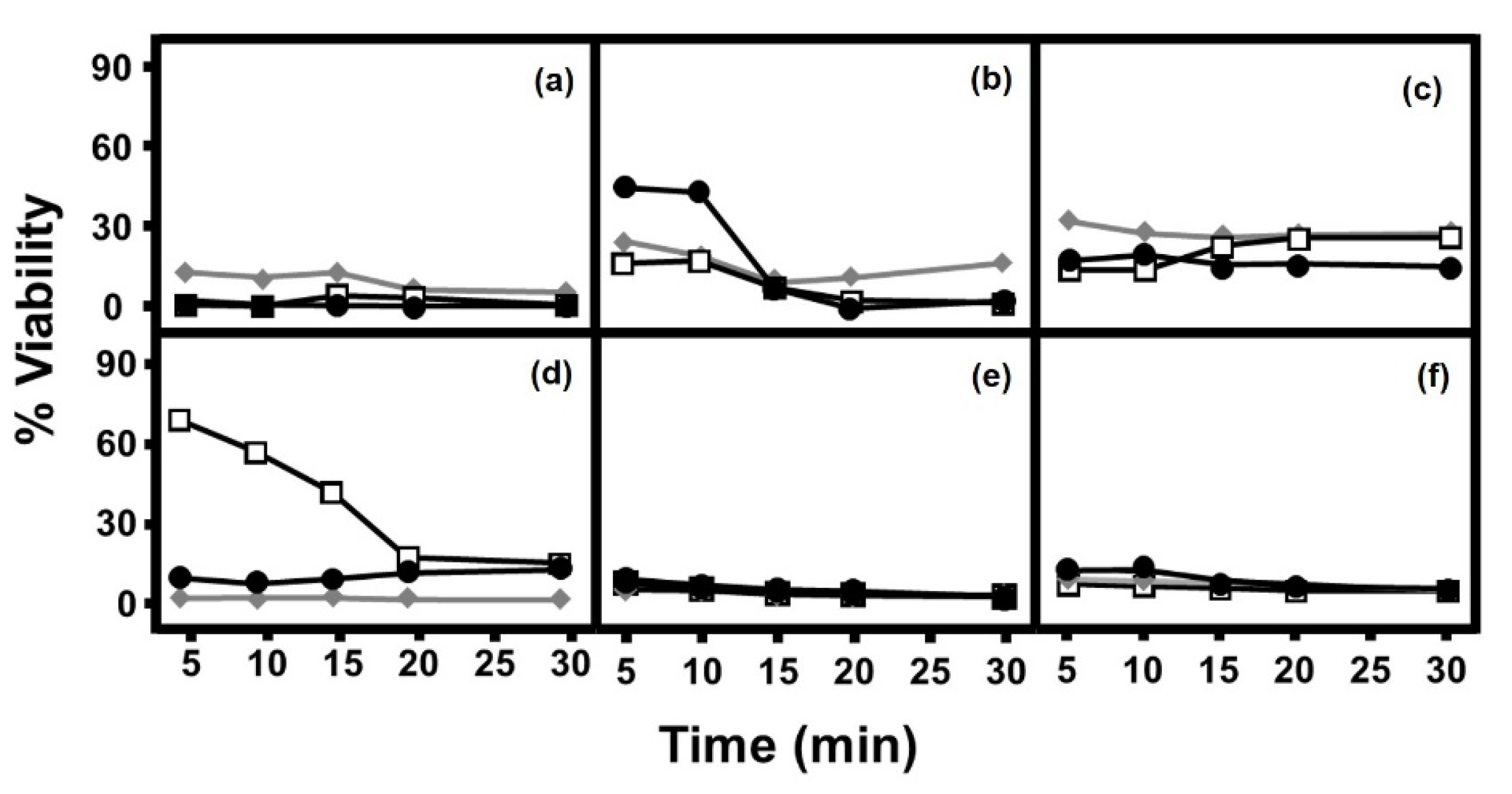
2.1. Antifungal Effect of AgNPs Depends on Their Structure and the Species with Which They Interact
2.2. Fungal Growth Is Influenced by the Presence of AgNPs and by Their Morphology
2.3. Culture Medium Conditioned by the Presence of AgNPs Shows an Antifungal Effect, although the Effect Is Not Dependent on the Release of Ag Ions
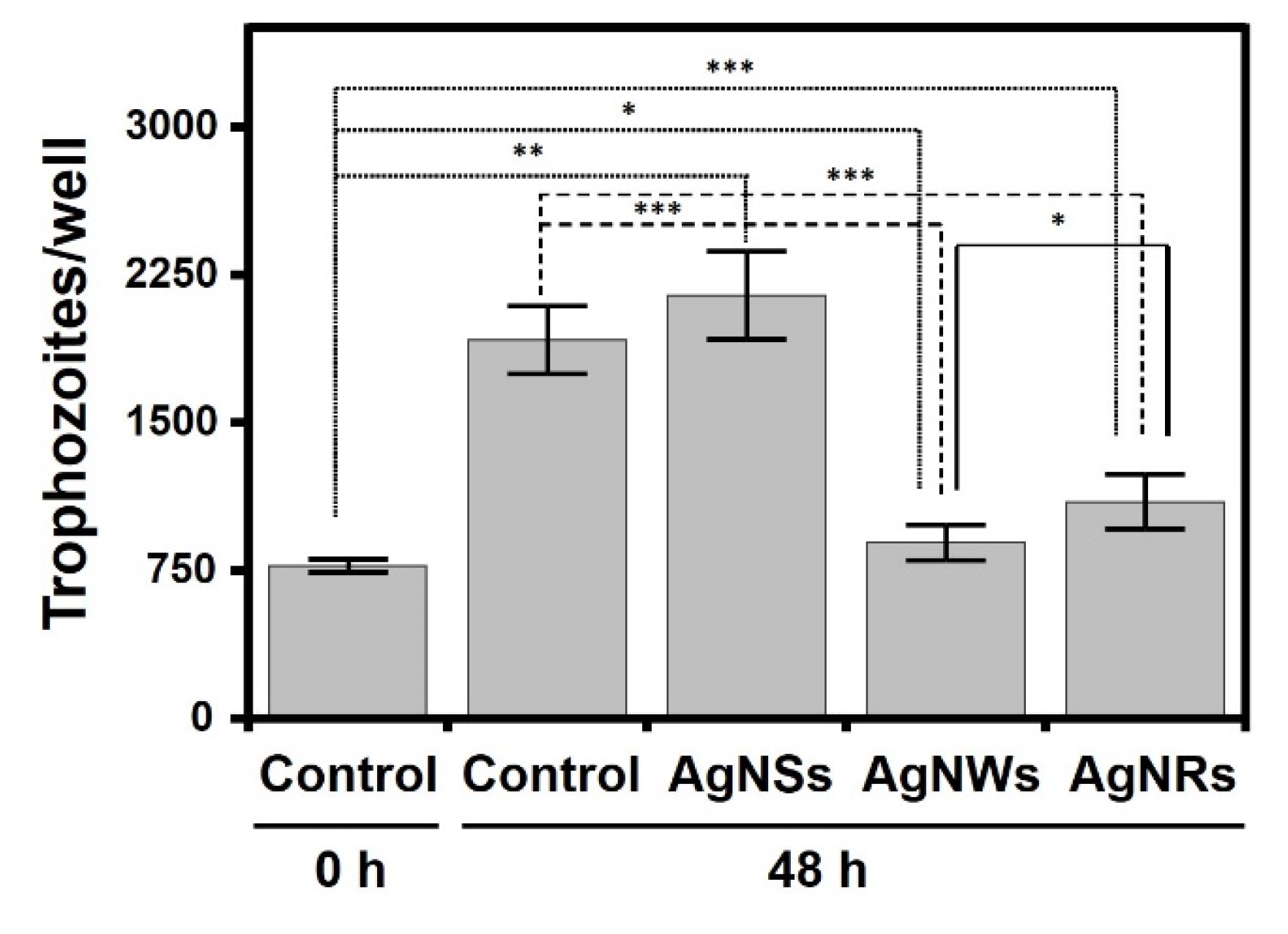
2.4. AgNWs and AgNRs Reduce the Proliferation of Acanthamoeba castellanii Trohozoites
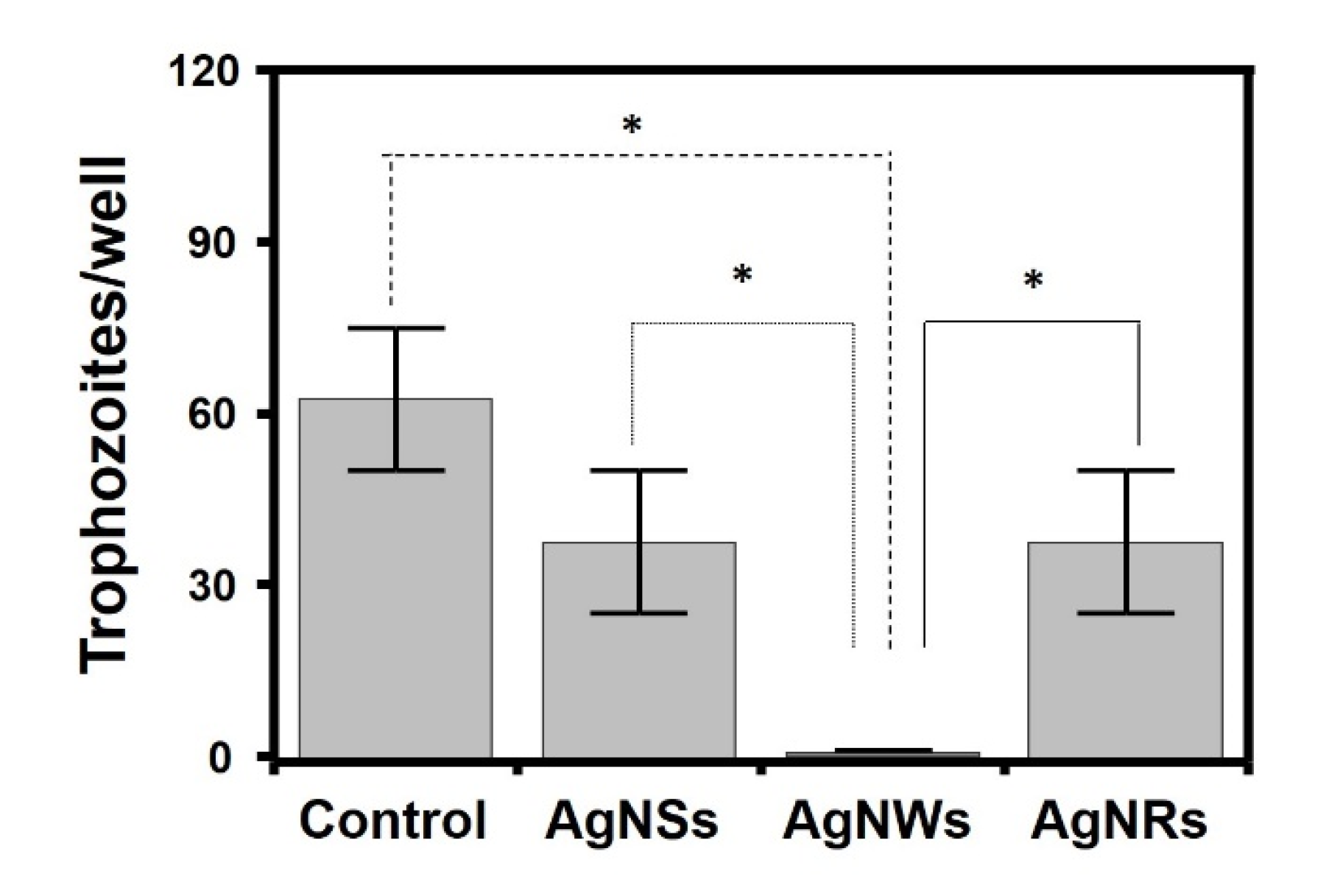
2.5. AgNWs Inhibits Germination of A. castellanii Cysts
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Fungal Species, Amoeba and Culture Conditions
4.2. Synthesis of AgNPs
4.3. Effect of AgNPs on Cell Viability in Fungal Cultures
4.4. Effect of AgNPs on Cell Growth in Fungal Cultures
4.5. Determination of the Concentration of Silver Ions Released by AgNPs
4.6. Study of the Toxic Effect of Media Conditioned by AgNPs
4.7. Effect of AgNPs on Cell Viability in Trophozoites and Cyst Form of A. castellanii
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules. 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Das, S.S.; Khatoon, A.; Ansari, T.H.; Afzal, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles: A mechanistic review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naganthran, A.; Verasoundarapandian, G.; Khalid, F.E.; Masarudin, M.J.; Zulkharnain, A.; Nawawi, N.M.; Karim, M.; Che Abdullah, C.A.; Ahmad, S.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Biomedical Application of Silver Nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Krishnan, S.; Hii, Y.S.; Pan, S.; Chan, Y.S.; Acquah, C.; Danquah, M.K.; Rodrigues, J. Synthesis approach-dependent antiviral properties of silver nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.B.; Amal, R.; Marquis, C.P.; Harry, E.J.; Sotiriou, G.A.; Rice, S.A.; Gunawan, C. Nanosilver and the microbiological activity of the particulate solids versus the leached soluble silver. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Siddiqui, R.; Hussain, M.A.; Ahmed, D.; Shah, M.R.; Khan, N.A. Silver nanoparticle conjugation affects antiacanthamoebic activities of amphotericin B, nystatin, and fluconazole. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendiger, E.B.; Padzik, M.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Zyskowska, D.; Grodzik, M.; Pietruczuk-Padzik, A.; Hendiger, J.; Olędzka, G.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles Conjugated with Contact Lens Solutions May Reduce the Risk of Acanthamoeba Keratitis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, T.; Follett, P.A.; Mahmud, J.; Moskovchenko, L.; Salmieri, S.; Allahdad, Z.; Lacroix, M. Silver nanoparticles-essential oils combined treatments to enhance the antibacterial and antifungal properties against foodborne pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 164, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.; Lee, J.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, D.G. Silver nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans through the increase of hydroxyl radicals. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimbela, G.V.; Ngo, S.M.; Fraze, C.; Yang, L.; Stout, D.A. Antibacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3941–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozhin, A.; Batasheva, S.; Kruychkova, M.; Cherednichenko, Y.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Application as Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Szymczak, M.; Maciejewska, M.; Laskowski, Ł.; Laskowska, M.; Ostaszewski, R.; Skiba, G.; Franiak-Pietryga, I. All That Glitters Is Not Silver—A New Look at Microbiological and Medical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, S.; Lozano-Iturbe, V.; García, B.; Andrés, L.J.; Menéndez, M.F.; Rodríguez, D.; Vazquez, F.; Martín, C.; Quirós, L.M. Antibacterial effect of silver nanorings. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, K.; Grudniak, A.M.; Wolska, K.I. Silver nanoparticles as an alternative strategy against bacterial biofilms. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2013, 60, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohanty, S.; Mishra, S.; Jena, P.; Jacob, B.; Sarkar, B.; Sonawane, A. An investigation on the antibacterial, cytotoxic, and antibiofilm efficacy of starch-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Muñoz, R.; Avalos-Borja, M.; Castro-Longoria, E. Ultrastructural analysis of Candida albicans when exposed to silver nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatollahi Mousavi, S.A.; Salari, S.; Hadizadeh, S. Evaluation of Antifungal Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Against Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Microsporum gypseum. Iran J. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Wei, Y.; Syed, F.; Tahir, K.; Taj, R.; Khan, A.U.; Hameed, M.U.; Yuan, Q. Amphotericin B-conjugated biogenic silver nanoparticles as an innovative strategy for fungal infections. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Jose Yacaman, M.; Lopez-Ribot, J. Inhibition of Candida auris Biofilm Formation on Medical and Environmental Surfaces by Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21183–21191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal activity and mode of action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans. BioMetals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kalra, S.K.; Tejan, N.; Ghoshal, U. Nanoparticles based therapeutic efficacy against Acanthamoeba: Updates and future prospect. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 218, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Soomaroo, A.; Anwar, A.; Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Metformin-coated silver nanoparticles exhibit anti-acanthamoebic activities against both trophozoite and cyst stages. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 215, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Ting, E.L.S.; Anwar, A.; Ain, N.U.; Faizi, S.; Shah, M.R.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Antiamoebic activity of plant-based natural products and their conjugated silver nanoparticles against Acanthamoeba castellanii (ATCC 50492). AMB Express 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendiger, E.B.; Padzik, M.; Sifaoui, I.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Rizo-Liendo, A.; Bethencourt-Estrella, C.J.; Nicolás-Hernández, D.S.; Chiboub, O.; Rodríguez-Expósito, R.L.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Potential Preventive Agent against Acanthamoeba Keratitis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Biological properties of “naked” metal nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szerencsés, B.; Igaz, N.; Tóbiás, Á.; Prucsi, Z.; Rónavári, A.; Bélteky, P.; Madarász, D.; Papp, C.; Makra, I.; Vágvölgyi, C.; et al. Size-dependent activity of silver nanoparticles on the morphological switch and biofilm formation of opportunistic pathogenic yeasts. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A. Mechanisms of resistance to antifungal agents: Yeasts and filamentous fungi. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2008, 25, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.S.; Reddy Mudiam, M.K.; Kumar, M.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Singh, S.P.; Prasad, T. Silver nanoparticles induced alterations in multiple cellular targets, which are critical for drug susceptibilities and pathogenicity in fungal pathogen (Candida albicans). Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2647–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, A.; Chi Fung, L.; Anwar, A.; Jagadish, P.; Numan, A.; Khalid, M.; Shahabuddin, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Efects of shape and size of cobalt phosphate nanoparticles against Acanthamoeba castellanii. Pathogens 2019, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, A.; Mungroo, M.R.; Anwar, A.; Sullivan, W.J.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Repositioning of Guanabenz in Conjugation with Gold and Silver Nanoparticles against Pathogenic Amoebae Acanthamoeba castellanii and Naegleria fowleri. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendiger, E.B.; Padzik, M.; Żochowska, A.; Baltaza, W.; Olędzka, G.; Zyskowska, D.; Bluszcz, J.; Jarzynka, S.; Chomicz, L.; Grodzik, M.; et al. Tannic acid-modified silver nanoparticles enhance the anti-Acanthamoeba activity of three multipurpose contact lens solutions without increasing their cytotoxicity. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | [Ag] (ppb) |
|---|---|
| H2O milliQ | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNSs | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNWs | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNRs | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNSs + C. albicans | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNWs + C. albicans | <5 |
| H2O milliQ + AgNRs + C. albicans | <5 |
| Saboureaud | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNSs | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNWs | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNRs | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNSs + C. albicans | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNWs + C. albicans | <5 |
| Saboureaud + AgNRs + C. albicans | <5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Fernández, S.; Lozano-Iturbe, V.; Menéndez, M.F.; Ordiales, H.; Fernández-Vega, I.; Merayo, J.; Vazquez, F.; Quirós, L.M.; Martín, C. A Promising Antifungal and Antiamoebic Effect of Silver Nanorings, a Novel Type of AgNP. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081054
González-Fernández S, Lozano-Iturbe V, Menéndez MF, Ordiales H, Fernández-Vega I, Merayo J, Vazquez F, Quirós LM, Martín C. A Promising Antifungal and Antiamoebic Effect of Silver Nanorings, a Novel Type of AgNP. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(8):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081054
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Fernández, Sara, Victor Lozano-Iturbe, Mª Fe Menéndez, Helena Ordiales, Iván Fernández-Vega, Jesús Merayo, Fernando Vazquez, Luis M. Quirós, and Carla Martín. 2022. "A Promising Antifungal and Antiamoebic Effect of Silver Nanorings, a Novel Type of AgNP" Antibiotics 11, no. 8: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081054
APA StyleGonzález-Fernández, S., Lozano-Iturbe, V., Menéndez, M. F., Ordiales, H., Fernández-Vega, I., Merayo, J., Vazquez, F., Quirós, L. M., & Martín, C. (2022). A Promising Antifungal and Antiamoebic Effect of Silver Nanorings, a Novel Type of AgNP. Antibiotics, 11(8), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081054







