Genomic Analysis of Two MDR Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Spanish Hospital Bearing the blaCTX-M-65 Gene with or without fosA3 in pESI-like Plasmids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Origin of the Isolates, Genome Sequencing and Resistance Phenotypes
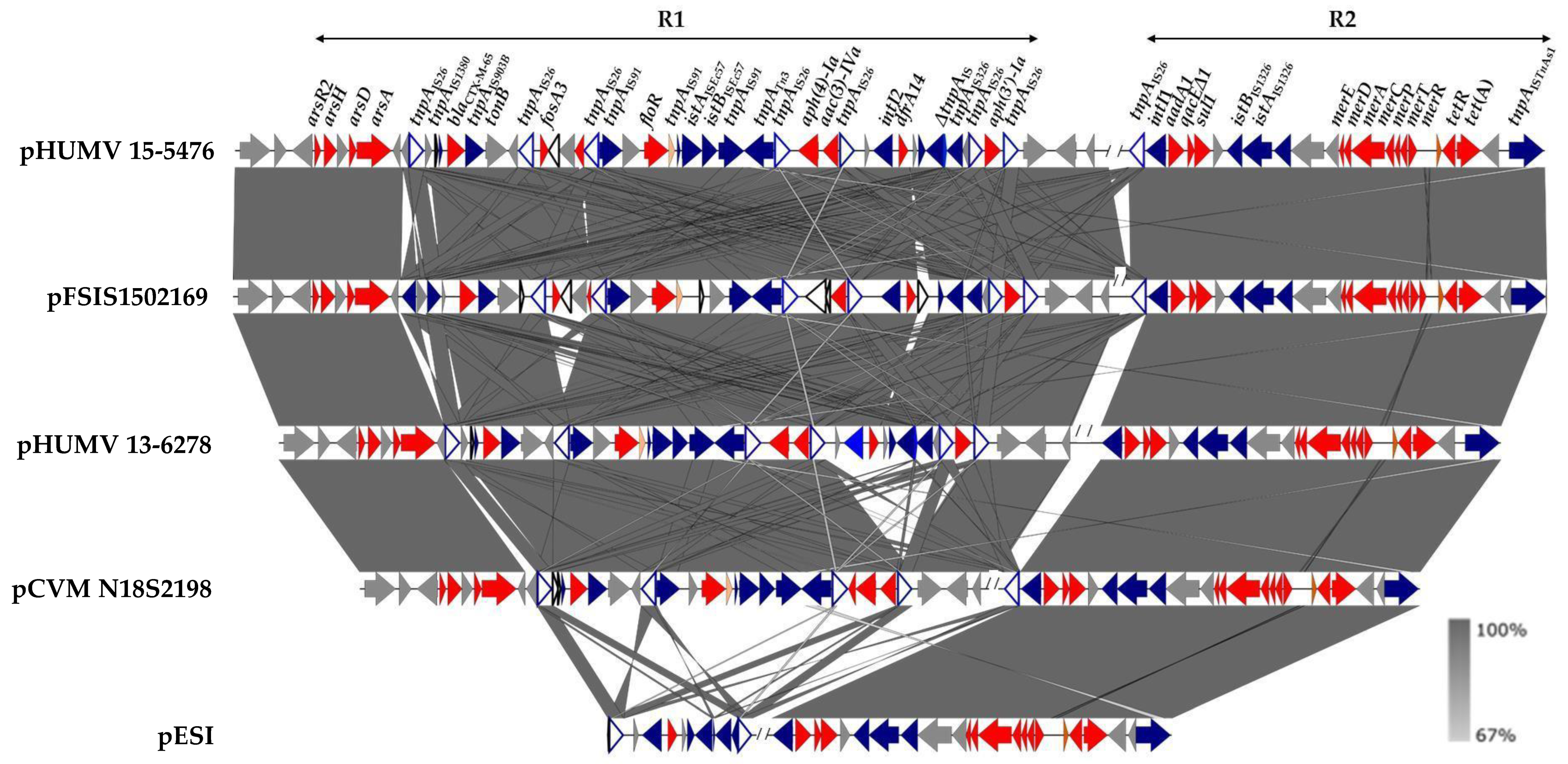
2.2. Genetic Bases of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance
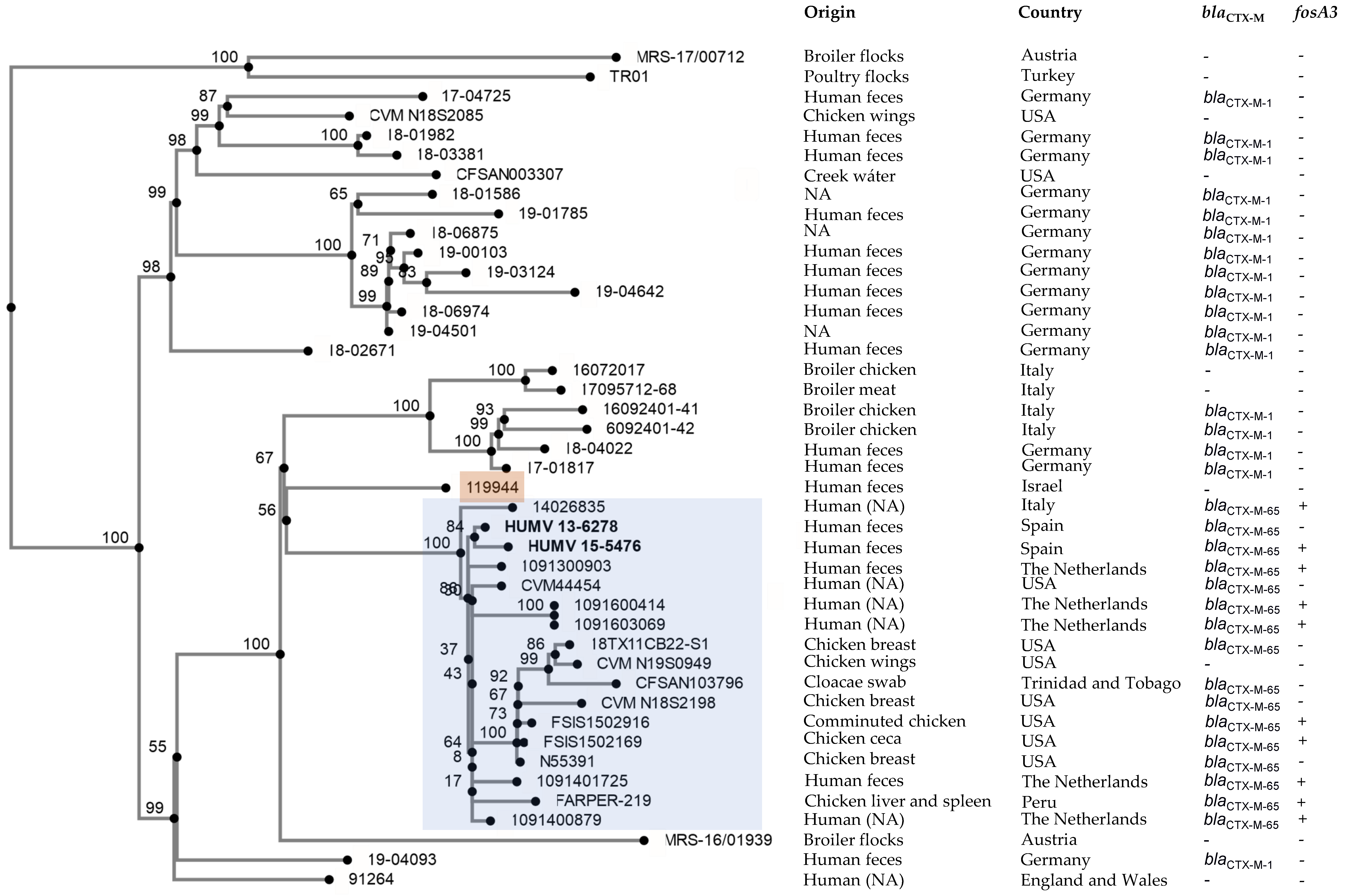
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, E.; Ishida, M.; de Janon, S.; Naushad, S.; Duceppe, M.O.; Gao, R.; Jardim, A.; Chen, J.C.; Tagg, K.A.; Ogunremi, D.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Valinsky, L.; Weinberger, M.; Guy, S.; Jaffe, J.; Schorr, Y.I.; Raisfeld, A.; Agmon, V.; Nissan, I. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis, Israel. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marder Mph, E.P.; Griffin, P.M.; Cieslak, P.R.; Dunn, J.; Hurd, S.; Jervis, R.; Lathrop, S.; Muse, A.; Ryan, P.; Smith, K.; et al. Preliminary Incidence and Trends of Infections with Pathogens Transmitted Commonly Through Food—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 U.S. Sites, 2006–2017. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, I.L.; Heuzenroeder, M.W. A comparison of three molecular typing methods for the discrimination of Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahada, F.; Sugiyama, H.; Chuma, T.; Sueyoshi, M.; Okamoto, K. Genetic analysis of multi-drug resistance and the clonal dissemination of β-lactam resistance in Salmonella Infantis isolated from broilers. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, G.; Tsyba, K.; Steck, N.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Cornelius, A.; Rahav, G.; Grassl, G.A.; Gal-Mor, O. A unique megaplasmid contributes to stress tolerance and pathogenicity of an emergent Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis strain. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Genome Sequence of an Emerging Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis and Genomic Comparison with Other S. Infantis Strains. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.C.; Chen, J.C.; Watkins, L.K.F.; Campbell, D.; Folster, J.P.; Tate, H.; Wasilenko, J.; Van Tubbergen, C.; Friedman, C.R. CTX-M-65 Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Salmonella enterica Serotype Infantis, United States(1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, A.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Feltrin, F.; Alba, P.; Cordaro, G.; Iurescia, M.; Tolli, R.; D’Incau, M.; Staffolani, M.; Di Giannatale, E.; et al. Emergence of a Clonal Lineage of Multidrug-Resistant ESBL-Producing Salmonella Infantis Transmitted from Broilers and Broiler Meat to Humans in Italy between 2011 and 2014. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gymoese, P.; Kiil, K.; Torpdahl, M.; Osterlund, M.T.; Sorensen, G.; Olsen, J.E.; Nielsen, E.M.; Litrup, E. WGS based study of the population structure of Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindermann, D.; Gopinath, G.; Chase, H.; Negrete, F.; Althaus, D.; Zurfluh, K.; Tall, B.D.; Stephan, R.; Nuesch-Inderbinen, M. Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis from Food and Human Infections, Switzerland, 2010-2015: Poultry-Related Multidrug Resistant Clones and an Emerging ESBL Producing Clonal Lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.W.Y.; Mattock, J.; Greig, D.R.; Langridge, G.C.; Baker, D.; Bloomfield, S.; Mather, A.E.; Wain, J.R.; Edwards, A.M.; Hartman, H.; et al. Characterization of a pESI-like plasmid and analysis of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica Infantis isolates in England and Wales. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, H.; Folster, J.P.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, M.; Li, C.; Morales, C.; Tyson, G.H.; Mukherjee, S.; Brown, A.C.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Extended-Spectrum-beta-Lactamase CTX-M-65-Producing Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis Isolates from Humans, Food Animals, and Retail Chickens in the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00488-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallejos-Sanchez, K.; Tataje-Lavanda, L.; Villanueva-Perez, D.; Bendezu, J.; Montalvan, A.; Zimic-Peralta, M.; Fernandez-Sanchez, M.; Fernandez-Diaz, M. Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Infantis Strain Isolated from Broiler Chicken in Peru. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00826-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alba, P.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Carfora, V.; Amoruso, R.; Cordaro, G.; Di Matteo, P.; Ianzano, A.; Iurescia, M.; Diaconu, E.L.; Study Group, E.N.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella Infantis in Europe: Insights into the success of the bacterial host and its parasitic pESI-like megaplasmid. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, E.; Murakami, K.; Shiwa, Y.; Ishige, T.; Ando, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Murakami, S. Phylogenetic and population genetic analysis of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Infantis strains isolated in Japan using whole genome sequence data. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Mourao, J.; Campos, J.; Peixe, L. Salmonellosis: The role of poultry meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, C.G.; Landgraff, C.; Robertson, J.; Pollari, F.; Parker, S.; Nadon, C.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Johnson, R.; Nash, J. Distribution of heavy metal resistance elements in Canadian Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- populations and association with the monophasic genotypes and phenotype. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorilli, E.; Pietrucci, D.; Barco, L.; Ammendola, S.; Petrin, S.; Longo, A.; Mantovani, C.; Battistoni, A.; Ricci, A.; Desideri, A.; et al. A comparative genomic analysis provides novel insights into the ecological success of the monophasic Salmonella serovar 4,[5],12:i. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, X.; Garcia, P.; Garcia, V.; de Toro, M.; Ladero, V.; Heinisch, J.J.; Fernandez, J.; Rodicio, R.; Rodicio, M.R. Genomic analysis and phylogenetic position of the complex IncC plasmid found in the Spanish monophasic clone of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, V.; Montero, I.; Bances, M.; Rodicio, R.; Rodicio, M.R. Incidence and Genetic Bases of Nitrofurantoin Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Two Successful Multidrug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium: Pandemic “DT 104” and pUO-StVR2. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Spieth, J.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Courtney, L.; Porwollik, S.; Ali, J.; Dante, M.; Du, F.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2. Nature 2001, 413, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Tyson, G.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Harrison, L.; Strain, E.; Tran, T.T.; Tillman, G.E.; Dessai, U.; McDermott, P.F.; Zhao, S. Long-Read Sequencing Reveals Evolution and Acquisition of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 777817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, R.; Gonzalez-Alba, J.M.; Galan, J.C. CTX-M Enzymes: Origin and Diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baucheron, S.; Chaslus-Dancla, E.; Cloeckaert, A.; Chiu, C.H.; Butaye, P. High-level resistance to fluoroquinolones linked to mutations in gyrA, parC, and parE in Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates from humans in Taiwan. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kwak, H.S.; Woo, G.J. Characterization of the quinolone resistance mechanism in foodborne Salmonella isolates with high nalidixic acid resistance. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, X.; Fernandez, J.; Hernaez, S.; Rodicio, R.; Rodicio, M.R. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) in Two Clinical Strains of Salmonella enterica Serovar Corvallis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, F.X.; Bertrand, S.; Guesnier, F.; Baucheron, S.; Cloeckaert, A.; Grimont, P.A. Ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella Kentucky in travelers. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1611–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, D.R. An update on the role of nitrofurans in the management of urinary tract infections. Drugs 2001, 61, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalla, D.R.; Olive, P.; Tu, Y.; Fan, M.L. Nitrofurazone-reducing enzymes in E. coli and their role in drug activation in vivo. Can. J. Microbiol. 1975, 21, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandegren, L.; Lindqvist, A.; Kahlmeter, G.; Andersson, D.I. Nitrofurantoin resistance mechanism and fitness cost in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiteway, J.; Koziarz, P.; Veall, J.; Sandhu, N.; Kumar, P.; Hoecher, B.; Lambert, I.B. Oxygen-insensitive nitroreductases: Analysis of the roles of nfsA and nfsB in development of resistance to 5-nitrofuran derivatives in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Fekih, I.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.; Alwathnani, H.A.; Saquib, Q.; Rensing, C.; Cervantes, C. Distribution of Arsenic Resistance Genes in Prokaryotes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.; Saier, M.H. Functional Promiscuity of Homologues of the Bacterial ArsA ATPases. Int. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2010, 187373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.C.; Fu, H.L.; Lin, Y.F.; Rosen, B.P. Pathways of arsenic uptake and efflux. Curr. Top. Membr. 2012, 69, 325–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.C.; Rosen, B.P. New mechanisms of bacterial arsenic resistance. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMillan, E.A.; Wasilenko, J.L.; Tagg, K.A.; Chen, J.C.; Simmons, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Tillman, G.E.; Folster, J.; Jackson, C.R.; Frye, J.G. Carriage and Gene Content Variability of the pESI-Like Plasmid Associated with Salmonella Infantis Recently Established in United States Poultry Production. Genes 2020, 11, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurfluh, K.; Treier, A.; Schmitt, K.; Stephan, R. Mobile fosfomycin resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae-An increasing threat. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y.; Lu, P.L.; Tseng, S.P. Update on fosfomycin-modified genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, G.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Horizontal Transfer of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis Resistance and Virulence Plasmid pESI to the Gut Microbiota of Warm-Blooded Hosts. mBio 2016, 7, e01395-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granda, A.; Riveros, M.; Martínez-Puchol, S.; Ocampo, K.; Laureano-Adame, L.; Corujo, A.; Reyes, I.; Ruiz, J.; Ochoa, T.J. Presence of Extended-Spectrum β-lactamase, CTX-M-65 in Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis Isolated from Children with Diarrhea in Lima, Peru. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2019, 14, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, L.; Cornejo, J.; Zavala, S.; Galarce, N.; Sanchez, F.; Benavides, M.B.; Guzman, M.; Saenz, L. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Virulence Factors and Susceptibility to Antibiotics in Salmonella Infantis Strains Isolated from Chicken Meat: First Findings in Chile. Animals 2020, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.; Khan, A.S.; Adesiyun, A.A.; Georges, K.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N. Genomic comparison of eight closed genomes of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica strains isolated from broiler farms and processing plants in Trinidad and Tobago. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Puchol, S.; Riveros, M.; Ruidias, K.; Granda, A.; Ruiz-Roldan, L.; Zapata-Cachay, C.; Ochoa, T.J.; Pons, M.J.; Ruiz, J. Dissemination of a multidrug resistant CTX-M-65 producer Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis clone between marketed chicken meat and children. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 344, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, G.H.; Li, C.; Harrison, L.B.; Martin, G.; Hsu, C.H.; Tate, H.; Tran, T.T.; Strain, E.; Zhao, S. A Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Infantis Clone is Spreading and Recombining in the United States. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vielva, L.; de Toro, M.; Lanza, V.F.; de la Cruz, F. PLACNETw: A web-based tool for plasmid reconstruction from bacterial genomes. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3796–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcillan-Barcia, M.P.; Redondo-Salvo, S.; Vielva, L.; de la Cruz, F. MOBscan: Automated Annotation of MOB Relaxases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2075, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.; Jones, M.B.; Zhang, Z.; Deatherage Kaiser, B.L.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Fitzgerald, C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. Salmonella serotype determination utilizing high-throughput genome sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Allesoe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A novel web tool for WGS-based detection of antimicrobial resistance associated with chromosomal point mutations in bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the problem of comparing whole bacterial genomes across different sequencing platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drauch, V.; Kornschober, C.; Palmieri, N.; Hess, M.; Hess, C. Infection dynamics of Salmonella Infantis strains displaying different genetic backgrounds—with or without pESI-like plasmid—Vary considerably. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2021, 10, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietsch, M.; Simon, S.; Meinen, A.; Trost, E.; Banerji, S.; Pfeifer, Y.; Flieger, A. Third generation cephalosporin resistance in clinical non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica in Germany and emergence of blaCTX-M-harbouring pESI plasmids. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, V.; Alba, P.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Ballaro, D.; Cordaro, G.; Di Matteo, P.; Donati, V.; Ianzano, A.; Iurescia, M.; Stravino, F.; et al. Colistin Resistance Mediated by mcr-1 in ESBL-Producing, Multidrug Resistant Salmonella Infantis in Broiler Chicken Industry, Italy (2016–2017). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müstak, I.B.; Yardimci, H. Construction and in vitro characterisation of aroA defective (aroAΔ) mutant Salmonella Infantis. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HUMV Isolate a | Patient Sex b/Age | Travel History | Clinical Sample | Resistance Pattern c Antibiotic Resistance Genes d | Chromosome (Size bp) Plasmid e (Size bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13-6278 | M/23 mth | Peru | Feces | [NAL, CIP, PEF], NIT | |
| [gyrA D87Y, parC T57S], [ΔnfsA, ΔnfsB] | Chromosome (4,686,236) | ||||
| [AMP, CTX], CHL, [GEN, TOB, KAN, STR], TET, [SUL, TMP] | |||||
| blaCTX-M-65, floR, [aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia, aph(4)-Ia, aadA1], tet(A), [sul1, dfrA14] | IncFIB (313,645) | ||||
| 15-5476 | M/12 mth | Peru | Feces | [NAL, CIP, PEF], NIT | |
| [gyrA D87Y, parC T57S], [ΔnfsA, ΔnfsB] | Chromosome (4,682,901) | ||||
| [AMP, CTX], CHL [GEN, TOB, KAN, STR], TET, [SUL, TMP], FOS | |||||
| blaCTX-M-65, floR, [aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia, aph(4)-Ia, aadA1], tet(A), [sul1, dfrA14], fosA3 | IncFIB (317,684) |
| Strain a | CTX b | NAL b | CIP b | NIT b | FOS b | HgCl2 | NaAsO2 | Na2HAsO4 | Phenylarsine Oxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HUMV 13-6278 | 32 | 128 | 0.125 | 512 | 0.19 | 64 | 128 | 2048 | 8 |
| HUMV 15-5476 | 32 | >256 | 0.125 | 512 | 512 | 32 | 128 | 512 | 8 |
| LT2 | 4 | 3 | 0.016 | 32 | 0.019 | 4 | 64 | 128 | 0.25 |
| LSP 146/02 | nd | nd | nd | 256 | nd | 32 | 32 | 256 | 0.5 |
| LSP 389/97 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 32 | 64 | 128 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, X.; Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Lozano, J.; Calvo, J.; Rodicio, R.; Rodicio, M.R. Genomic Analysis of Two MDR Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Spanish Hospital Bearing the blaCTX-M-65 Gene with or without fosA3 in pESI-like Plasmids. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060786
Vázquez X, Fernández J, Rodríguez-Lozano J, Calvo J, Rodicio R, Rodicio MR. Genomic Analysis of Two MDR Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Spanish Hospital Bearing the blaCTX-M-65 Gene with or without fosA3 in pESI-like Plasmids. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(6):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060786
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Xenia, Javier Fernández, Jesús Rodríguez-Lozano, Jorge Calvo, Rosaura Rodicio, and M. Rosario Rodicio. 2022. "Genomic Analysis of Two MDR Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Spanish Hospital Bearing the blaCTX-M-65 Gene with or without fosA3 in pESI-like Plasmids" Antibiotics 11, no. 6: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060786
APA StyleVázquez, X., Fernández, J., Rodríguez-Lozano, J., Calvo, J., Rodicio, R., & Rodicio, M. R. (2022). Genomic Analysis of Two MDR Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Spanish Hospital Bearing the blaCTX-M-65 Gene with or without fosA3 in pESI-like Plasmids. Antibiotics, 11(6), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060786








