Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
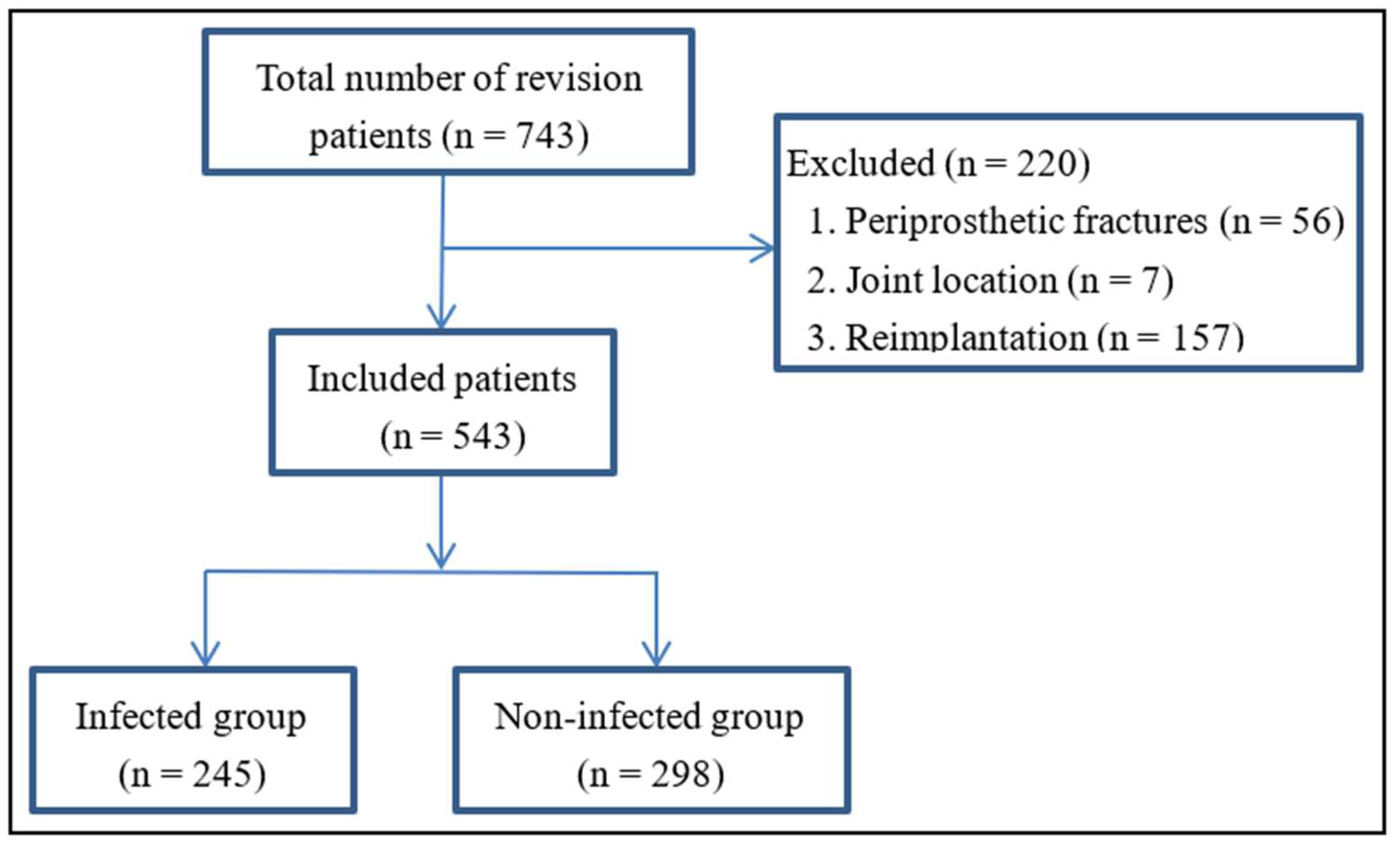
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Diagnostic Definition of Infection and Data Extraction
2.4. Laboratory Evaluations of Tested Markers
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamath, A.F.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Chan, V.; Vail, T.P.; Rubash, H.E.; Berry, D.J.; Bozic, K.J. Quantifying the Burden of Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Shohat, N.; Gehrke, T. Prevention of periprosthetic joint infection: New Guidelines. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, A.; Gramlich, Y.; Rudert, M.; Drees, P.; Hoffmann, R.; Weißenberger, M.; Kutzner, K.P. The projected volume of primary and revision total knee arthroplasty will place an immense burden on future health care systems over the next 30 years. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 29, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, R.S.; Inacio, M.C.; Paxton, E.W. Risk factors associated with deep surgical site infections after primary total knee arthroplasty: An analysis of 56,216 knees. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2013, 95, 75–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, A.; George, J.; Faour, M.; Klika, A.K.; Higuera, C.A. Serum biomarkers in periprosthetic joint infections. Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 7, 5–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehring, T.K.; Odum, S.M.; Berend, K.R.; Jiranek, W.A.; Parvizi, J.; Bozic, K.J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Gioe, T.J. Failure of irrigation and débridement for early postoperative periprosthetic infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marson, B.A.; Deshmukh, S.R.; Grindlay, D.J.C.; Scammell, B.E. Alpha-defensin and the Synovasure lateral flow device for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Shi, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Z. Detecting the presence of bacteria in low-volume preoperative aspirated synovial fluid by metagenomic next-generation sequencing. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shao, H.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Yu, B.Z.; Qu, P.F.; Zhou, Y.X.; Chen, J.Y. Plasma Fibrinogen Exhibits Better Performance Than Plasma D-Dimer in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2019, 101, 13–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohat, N.; Bauer, T.; Buttaro, M.; Budhiparama, N.; Cashman, J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Drago, L.; Gehrke, T.; Marcelino Gomes, L.S.; Goswami, K.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, What is the Definition of a Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) of the Knee and the Hip? Can the Same Criteria be Used for Both Joints?: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S325–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcnally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebse, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection: A practical guide for clinicians. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Kheir, M.M.; Tarabichi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H.R.S.; Tan, T.L.; Parvizi, J. Serum D-Dimer Test Is Promising for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Timing of Reimplantation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2017, 99, 419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Xie, J.; Huang, Q.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pei, F. Plasma Fibrin Degradation Product and D-Dimer Are of Limited Value for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 454–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Xie, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, G.; Huang, Q.; Pei, F. Plasma Fibrinogen and Platelet Count Are Referable Tools for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, G.; Xinxin, Y.; Fan, L.; Shenghong, W.; Yayi, X. Serum Fibrinogen Test Performs Well for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelecki, D.; Walczak, P.; Szostek, M.; Grajek, A.; Rak, S.; Kowalczewski, J. Blood and synovial fluid calprotectin as biomarkers to diagnose chronic hip and knee periprosthetic joint infections. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziuk, T.; Rondon, A.J.; Goswami, K.; Tan, T.L.; Parvizi, J. A Novel Adjunct Indicator of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Platelet Count and Mean Platelet Volume. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirumala, V.; Klemt, C.; Xiong, L.; Chen, W.; Van Den Kieboom, J.; Kwon, Y.-M. Diagnostic Utility of Platelet Count/Lymphocyte Count Ratio and Platelet Count/Mean Platelet Volume Ratio in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Z.; Fu, J.; Chai, W.; Hao, L.-B.; Chen, J.-Y. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a predictor for diagnosis of early Periprosthetic joint infection. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.T.; Zeng, X.; Ford, L. International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision: It’s coming, ready or not. Health Care Manag. 2011, 30, 27–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Chang, C.H.; Chiang-Ni, C.; Hsieh, P.H.; Shih, H.N.; Ueng, S.W.N.; Chang, Y. Rapid analysis of bacterial composition in prosthetic joint infection by 16S rRNA metagenomic sequencing. Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T. International Consensus Group on Periprosthetic Joint I. Definition of periprosthetic joint infection. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Minegishi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Takaso, M. Evaluation of myeloperoxidase in synovial fluid as a biomarker for chronic periprosthetic joint infection. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, L.N.; Moser, K.A.; Schmidt, R.L. D-Dimer Varies Widely Across Instrument Platforms and is Not a Reliable Indicator of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Li, T.; Ye, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W. D-dimer in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, M.; Wolberg, A.S. Fibrinogen and fibrin: An illustrated review. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, C.; Huang, R.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, X. Plasma fibrinogen in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Meng, Z.; Pan, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yongping, C. Plasma Fibrinogen Performs Better Than Plasma d-Dimer and Fibrin Degradation Product in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Determination of Reimplantation Timing. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, K.; Dai, K.; Qu, X.; Yan, M. Serum and Synovial Fluid Interleukin-6 for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, A.; Liang, L.; Jiang, J.; Luo, H.; Deng, W.; Lin, G.; Wu, M.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y. Diagnostic value of blood parameters for community-acquired pneumonia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 64, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgün, D.; Müller, M.; Perka, C.; Winkler, T. The serum level of C-reactive protein alone cannot be used for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections, especially in those caused by organisms of low virulence. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Holinka, J.; Staats, K.; Sevelda, F.; Lass, R.; Kubista, B.; Giurea, A.; Windhager, R. Inferior performance of established and novel serum inflammatory markers in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections. Int. Orthop. 2020, 45, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, J.S.; Hassebrock, J.D.; Christensen, A.L.; Beauchamp, C.P.; Clarke, H.D.; Spangehl, M.J. Screening for Periprosthetic Joint Infections With ESR and CRP: The Ideal Cutoffs. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Infected Group (n = 245) | Non-Infected Group (n = 298) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | |||
| Age, yr | 61.64 ± 13.56 | 63.90 ± 10.70 | 0.059 |
| Female | 117 (47.8) | 180 (60.4) | 0.003 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.47 ± 3.47 | 23.91 ± 3.45 | 0.273 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 60 (24.5) | 112 (37.6) | 0.001 * |
| Diabetes | 29 (11.8) | 23 (7.7) | 0.105 |
| COPD | 3 (1.2) | 4 (1.3) | 0.904 |
| CHD | 3 (1.2) | 11 (3.7) | 0.071 |
| Inflammatory diseases | 18 (7.3) | 15 (5.0) | 0.262 |
| Potential Biomarker | Infected Group (n = 245) | Non-Infected Group (n = 298) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | 19.30 (10.40–44.30) # | 3.07 (1.98–5.32) # | <0.001 * |
| ESR (mm/h) | 61.54 ± 32.68 | 26.46 ± 18.95 | <0.001 * |
| FIB (g/L) | 4.41 ± 1.33 | 2.99 ± 0.77 | <0.001 * |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 14.21 (7.07–27.52) # | 3.56 (2.16–5.89) # | <0.001 * |
| PLT (×109/L) | 242.94 ± 92.23 | 178 ± 65.30 | <0.001 * |
| MLR | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 0.25 ± 0.14 | <0.001 * |
| NLR | 3.21 (2.22–4.43) # | 2.34 (1.75–3.15) # | <0.001 * |
| PLR | 178.90 ± 92.09 | 128.21 ± 66.04 | <0.001 * |
| Biomarker | AUC (95% CI) | Youden Index | Optimal Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | p-Value Compared with CRP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.882 (0.846–0.918) | 0.651 | 7.39 | 79.1% | 86.0% | 82.3% | 83.4% | - |
| ESR (mm/h) | 0.809 (0.736–0.885) | 0.414 | 42.5 | 65.5% | 84.2% | 77.3% | 74.8% | <0.001 * |
| FIB (g/L) | 0.834 (0.791–0.878) | 0.561 | 3.67 | 69.6% | 86.5% | 80.9% | 77.6% | <0.001 * |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.845 (0.803–0.887) | 0.574 | 8.59 | 70.9% | 86.5% | 81.2% | 78.3% | 0.038 * |
| PLT (×109/L) | 0.684 (0.626–0.741) | 0.313 | 201.5 | 61.5% | 69.8% | 62.6% | 68.8% | <0.001 * |
| MLR | 0.686 (0.630–0.742) | 0.332 | 0.30 | 54.1% | 79.1% | 68.0% | 67.7% | <0.001 * |
| NLR | 0.659 (0.601–0.717) | 0.293 | 2.90 | 62.8% | 66.5% | 60.7% | 68.5% | <0.001 * |
| PLR | 0.674 (0.617–0.731) | 0.295 | 126.11 | 72.3% | 57.1% | 58.1% | 71.5% | <0.001 * |
| Tree Depth | Enrolled Marker and Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CRP (5.91 mg/L) | 86.1% | 79.5% | 77.57% | 87.5% | 82.5% |
| 2 | CRP (5.91 mg/L) + ESR (32 mm/h) | 71.8% | 89.9% | 85.4% | 79.5% | 81.8% |
| 3 | CRP (5.91 mg/L) + ESR (32 mm/h) + PLR (131.80) | 58.0% | 66.4% | 58.7% | 65.8% | 62.6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040505
Xu H, Xie J, Zhang S, Wang D, Huang Z, Zhou Z. Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(4):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040505
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hong, Jinwei Xie, Shaoyun Zhang, Duan Wang, Zeyu Huang, and Zongke Zhou. 2022. "Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study" Antibiotics 11, no. 4: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040505
APA StyleXu, H., Xie, J., Zhang, S., Wang, D., Huang, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2022). Potential Blood Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study. Antibiotics, 11(4), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040505







