Gelidiales Are Not Just Agar—Revealing the Antimicrobial Potential of Gelidium corneum for Skin Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
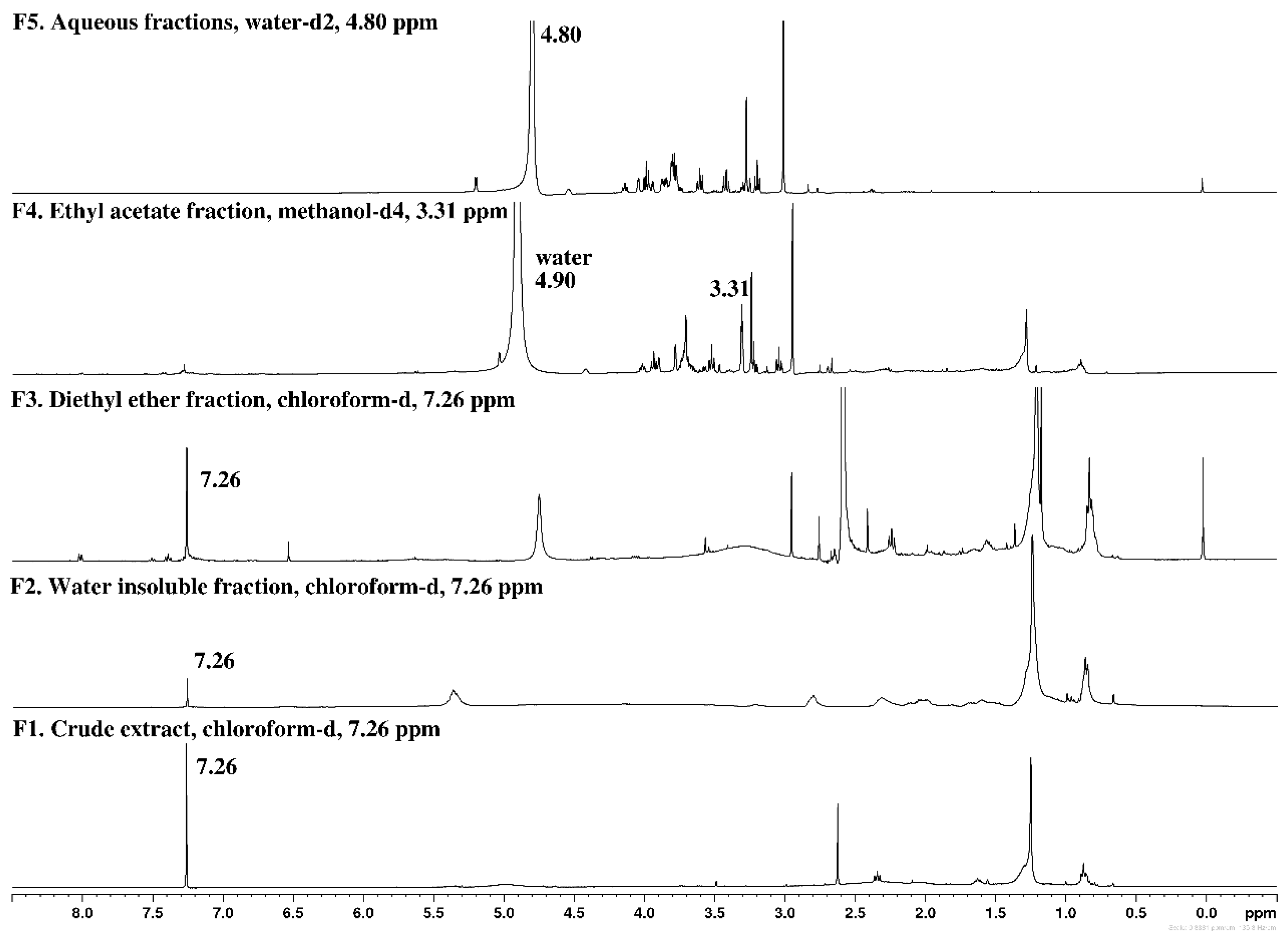
2.1. Chemical Screening by 1H NMR
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Gelidium corneum Fractions
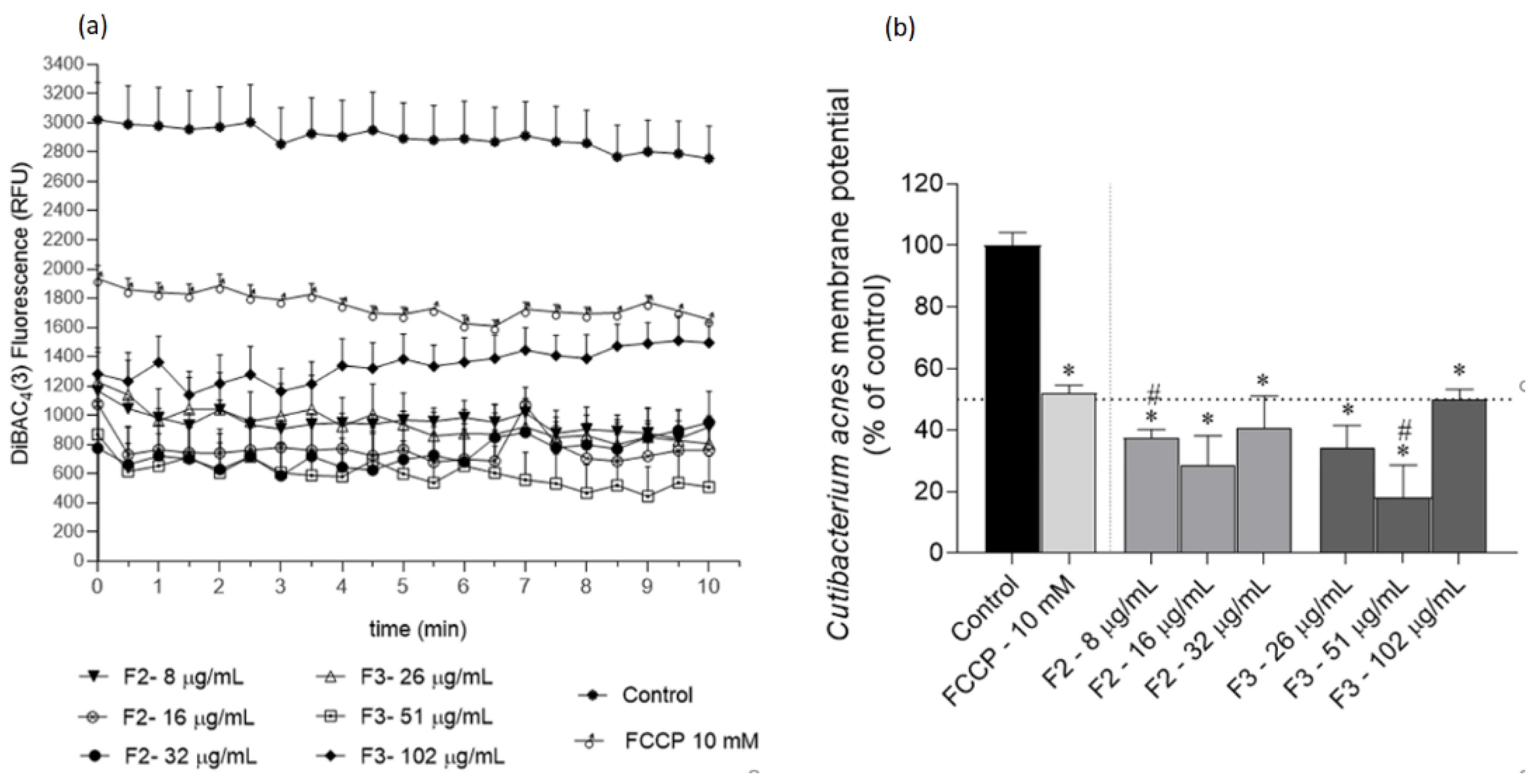
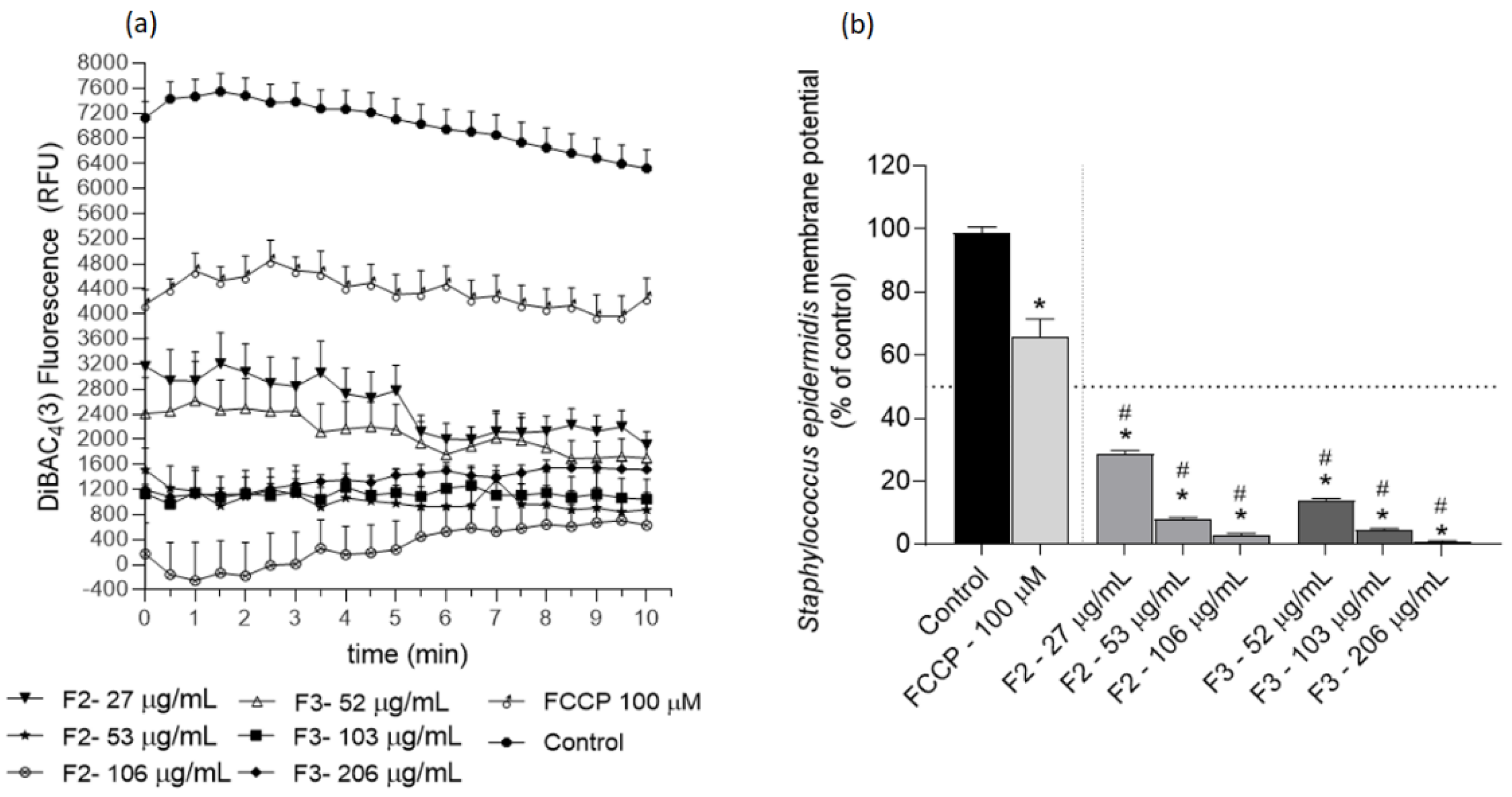
2.3. Effects of Gelidium corneum Fractions on Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis Membrane Potential
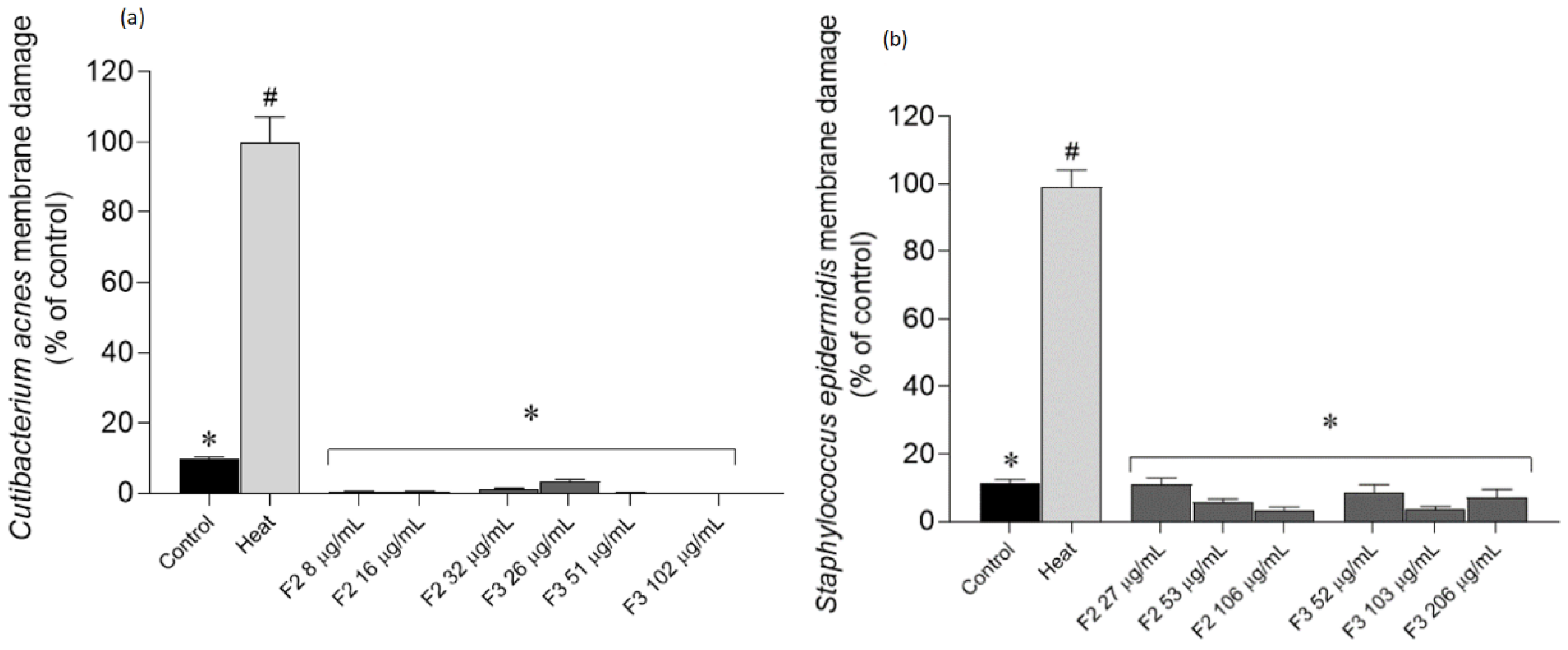
2.4. Effects of Gelidium corneum Fractions on Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis Membrane Integrity
2.5. Potential of Gelidium corneum Fractions to Promote DNA Damage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seaweed Harvest and Sampling
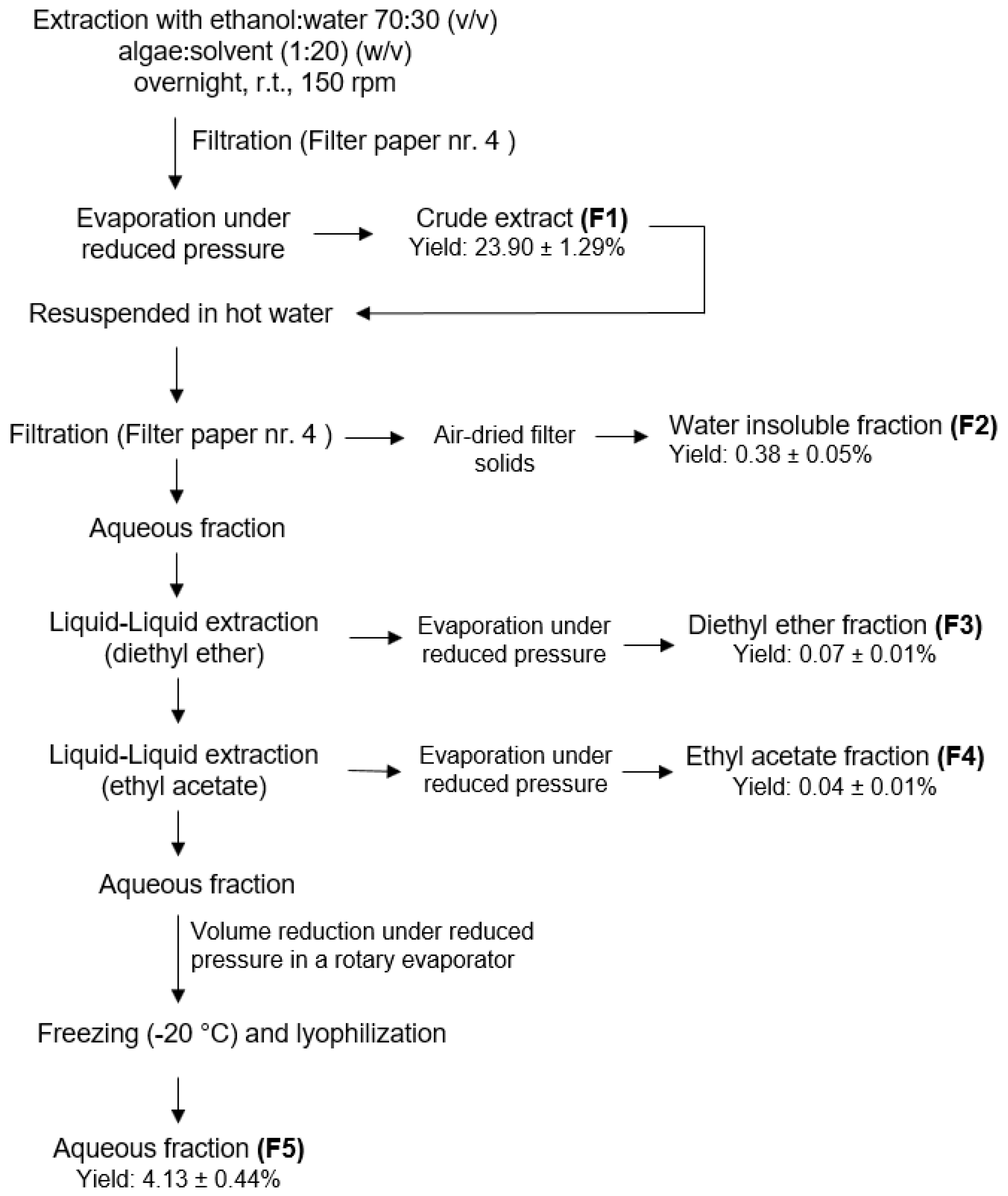
4.2. Extraction Procedure
4.3. Chemical Screening by 1H NMR
4.4. Antimicrobial Activity of Gelidium corneum Fractions against Microorganisms Associated with Skin Disorders
4.5. Mechanisms of Action Underlying the Antimicrobial Activity
4.5.1. Membrane Potential Analysis
4.5.2. Membrane Damage Assay
4.5.3. DNA Damaging Potential
4.6. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, P.A.; Phillips, G.O. 11—The use of hydrocolloids to improve food texture. In Texture in Food; McKenna, B.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 251–274. ISBN 185573673X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical Structures and Bioactivities of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Din, S.M.M.; Alagawany, N.I. Phytochemical Constituents and Anticoagulation Property of Marine Algae Gelidium crinale, Sargassum hornschuchii and Ulva linza. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 35, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, B.Y.; Gürsu, B.Y.; Dağ, I. Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using marine red algae Gelidium corneum. Process Biochem. 2019, 89, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sanz, M.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Ballester, A.R.; Martinez-Abad, A.; Brodkorb, A.; López-Rubio, A. Production of unpurified agar-based extracts from red seaweed Gelidium sesquipedale by means of simplified extraction protocols. Algal Res. 2019, 38, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejón, N.; Parailloux, M.; Izdebska, A.; Lobinski, R.; Fernandes, S.C.M. Valorization of the Red Algae Gelidium sesquipedale by Extracting a Broad Spectrum of Minor Compounds Using Green Approaches. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnelie, M.; Corvec, S.; Timon-David, E.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B. Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis: The unmissable modulators of skin inflammatory response. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournière, M.; Latire, T.; Souak, D.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Bedoux, G. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Cutibacterium acnes: Two Major Sentinels of Skin Microbiota and the Influence of Cosmetics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudel, J.-P.; Auffret, N.; Leccia, M.-T.; Poli, F.; Corvec, S.; Dréno, B. Staphylococcus epidermidis: A Potential New Player in the Physiopathology of Acne? Dermatology 2019, 235, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfriso, R.; Egert, M.; Gempeler, M.; Voegeli, R.; Campiche, R. Revealing the secret life of skin—With the microbiome you never walk alone. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 42, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.C.; Dellavalle, R.; Garner, S. Acne vulgaris. Lancet 2011, 379, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Elliott, A.G.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Ramu, S.; Cooper, M.A. In vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Acne Drugs Against Skin-Associated Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dréno, B.; Pécastaings, S.; Corvec, S.; Veraldi, S.; Khammari, A.; Roques, C. Cutibacterium acnes (Propionibacterium acnes) and acne vulgaris: A brief look at the latest updates. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32 (Suppl. S2), 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaenglein, A.L.; Pathy, A.L.; Schlosser, B.J.; Alikhan, A.; Baldwin, H.E.; Berson, D.S.; Bowe, W.P.; Graber, E.M.; Harper, J.C.; Kang, S.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 945–973.e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The ‘accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Menna, M.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Chemical diversity of bioactive marine natural products: An illustrative case study. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinteus, S.; Lemos, M.F.; Alves, C.; Neugebauer, A.; Silva, J.; Thomas, O.; Botana, L.M.; Gaspar, H.; Pedrosa, R. Marine invasive macroalgae: Turning a real threat into a major opportunity—The biotechnological potential of Sargassum muticum and Asparagopsis armata. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentão, P.; Trindade, P.; Gomes, D.; de Pinho, P.G.; Mouga, T.; Andrade, P.B. Codium tomentosum and Plocamium cartilagineum: Chemistry and antioxidant potential. Food Chem. 2009, 119, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Sousa, S.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Pintado, M.M.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Da Costa, J.P.; Silva, A.M.S.; Duarte, A.C.; et al. Sargassum muticum and Osmundea pinnatifida Enzymatic Extracts: Chemical, Structural, and Cytotoxic Characterization. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Date, Y.; Sakata, K.; Kikuchi, J. Chemical profiling of complex biochemical mixtures from various seaweeds. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cakmak, Y.S.; Kaya, M.; Ozusaglam, M.A. Biochemical composition and bioactivity screening of various extracts from Dunaliella salina, a green microalga. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.J.; Bhatia, N. Oral Antibiotics for Acne. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 22, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, Z.; Gornowicz-Porowska, J.; Sobkowska, D.; Kaszuba, K.; Czajkowski, R. Acne—Therapeutic challenges to the cooperation between a dermatologist and a cosmetologist. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2021, 38, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, H. Oral Antibiotic Treatment Options for Acne Vulgaris. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2020, 13, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Karadag, A.S.; Kayıran, M.A.; Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Parish, L.C. Antibiotic resistance in acne: Changes, consequences and concerns. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 35, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Yoon, J.Y.; Kwon, H.H.; Min, S.; Moon, J.; Suh, D.H. Seeking new acne treatment from natural products, devices and synthetic drug discovery. Derm. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, e1356520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samri, N.; Hsaine, L.; Elkafhi, S.; Khlifi, S.; Etahiri, S. Antimicrobial properties of seven brown algae harvested from the coast of sidi bouzid (El Jadida-Morocco). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metidji, H.; Dob, T.; Mohamed, T.; Krimat, S.; Ksouri, A.; Nouasri, A. In vitro screening of secondary metabolites and evalu-ationof antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of Gelidium sesquipedale Thuret et Bornet red seaweed from Algeria. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar]
- El Wahidi, M.; El Amraoui, B.; El Amraoui, M.; Bamhaoud, T. Screening of antimicrobial activity of macroalgae extracts from the Moroccan Atlantic coast. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2015, 73, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.-S.; Bae, H.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Choi, I.S. In vitro antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of seaweed extracts against acne inducing bacteria, Propionibacterium acnes. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Januário, A.P.; Félix, R.; Félix, C.; Reboleira, J.; Valentão, P.; Lemos, M.F.L. Red Seaweed-Derived Compounds as a Potential New Approach for Acne Vulgaris Care. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, J.; Asally, M. The Microbiologist’s Guide to Membrane Potential Dynamics. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-Y.D.; Prindle, A.; Liu, J.; Süel, G.M. SnapShot: Electrochemical Communication in Biofilms. Cell 2017, 170, 214–214.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prindle, A.; Liu, J.; Asally, M.; Ly, S.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Süel, G.M. Ion channels enable electrical communication in bacterial communities. Nature 2015, 527, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruni, G.N.; Weekley, R.A.; Dodd, B.J.T.; Kralj, J.M. Voltage-gated calcium flux mediates Escherichia coli mechanosensation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9445–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirec, T.; Benarroch, J.M.; Buffard, P.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Asally, M. Electrical Polarization Enables Integrative Quality Control during Bacterial Differentiation into Spores. iScience 2019, 16, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaim, G.; Dimroth, P. ATP synthesis by F-type ATP synthase is obligatorily dependent on the transmembrane voltage. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4118–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strahl, H.; Hamoen, L.W. Membrane potential is important for bacterial cell division. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12281–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-Y.D.; Galera-Laporta, L.; Bialecka-Fornal, M.; Moon, E.C.; Shen, Z.; Briggs, S.P.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Süel, G.M. Magnesium Flux Modulates Ribosomes to Increase Bacterial Survival. Cell 2019, 177, 352–360.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Baek, K.-H. Antibacterial mechanism of the action of Enteromorpha linza L. essential oil against Escherichia coli and Salmonella Typhimurium. Bot. Stud. 2015, 56, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhong, K.; Huang, Y.; Gao, H. A dual antibacterial mechanism involved in membrane disruption and DNA binding of 2R,3R-dihydromyricetin from pine needles of Cedrus deodara against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Antibacterial Activity and Action Mechanism of the Essential Oil from Enteromorpha linza L. against Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Molecules 2016, 21, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Shafay, S.M.; Ali, S.S.; El-Sheekh, M. Antimicrobial activity of some seaweeds species from Red sea, against multidrug resistant bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.-L.; Shi, Y.-H.; Zhao, W.; Hao, G.; Le, G.-W. Interaction of MDpep9, a novel antimicrobial peptide from Chinese tra-ditional edible larvae of housefly, with Escherichia coli genomic DNA. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinteus, S.; Lemos, M.F.; Simões, M.; Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Gaspar, H.; Martins, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Pedrosa, R. Marine invasive species for high-value products’ exploration—Unveiling the antimicrobial potential of Asparagopsis armata against human pathogens. Algal Res. 2020, 52, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial Derivatives of Marine Algae: An Overview of Pharmacological Mechanisms and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.; Soundar, S.; Mangoli, S. DNA damage is a late event in resveratrol mediated inhibition of Escherichia coli. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, X.; Nishiyama, Y.; Tie, D.; Hein, K.Z.; Yamamoto, O.; Morita, E. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of Ougon (Scutellaria root extract) components against pathogenic fungi. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, P.; He, J.; Mackey, V.; Coy, D.H.; He, Q. The antimicrobial peptides and their potential clinical applications. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, L. Studies on antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanism of a novel polysaccharide from Streptomyces virginia H03. Food Control 2010, 21, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmughapriya, S.; Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Selvin, J.; Kiran, G.S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Antimicrobial activity of seaweeds extracts against multiresistant pathogens. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Fan, X.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Niu, R.; Tseng, C. Antibacterial bromophenols from the marine red alga Rhodomela confervoides. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Kiran, G.S.; Selvin, J.; Shakir, C.; Gandhimathi, R.; Lipton, A.P. Antimicrobial potential and seasonality of red algae collected from the southwest coast of India tested against shrimp, human and phytopathogens. Ann. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Alves, C.; Horta, A.; Pinteus, S.; Silva, J.; Culioli, G.; Thomas, O.P.; Pedrosa, R. Antitumor and Antimicrobial Potential of Bromoditerpenes Isolated from the Red Alga, Sphaerococcus coronopifolius. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clementi, E.A.; Marks, L.; Roche-Håkansson, H.; Håkansson, A.P. Monitoring Changes in Membrane Polarity, Membrane Integrity, and Intracellular Ion Concentrations in Streptococcus pneumoniae Using Fluorescent Dyes. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.-P.; Cao, X.-M.; Hao, D.-L.; Zhang, L.-L. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, DNA Damage Protective, Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Activities of Cyperus rotundus Rhizomes Essential Oil against Foodborne Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Fraction | Staphylococcus epidermidis | Cutibacterium acnes |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
| F2 | 53.29 (48.75–57.91) | 16.10 (7.27–23.02) |
| F3 | 102.80 (87.15–122.30) | 51.04 (43.36–59.74) |
| Oxytetracycline | 12.40 (11.22–16.13) | 0.07 (0.05–0.09) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matias, M.; Pinteus, S.; Martins, A.; Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Mouga, T.; Gaspar, H.; Pedrosa, R. Gelidiales Are Not Just Agar—Revealing the Antimicrobial Potential of Gelidium corneum for Skin Disorders. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040481
Matias M, Pinteus S, Martins A, Silva J, Alves C, Mouga T, Gaspar H, Pedrosa R. Gelidiales Are Not Just Agar—Revealing the Antimicrobial Potential of Gelidium corneum for Skin Disorders. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(4):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040481
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatias, Margarida, Susete Pinteus, Alice Martins, Joana Silva, Celso Alves, Teresa Mouga, Helena Gaspar, and Rui Pedrosa. 2022. "Gelidiales Are Not Just Agar—Revealing the Antimicrobial Potential of Gelidium corneum for Skin Disorders" Antibiotics 11, no. 4: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040481
APA StyleMatias, M., Pinteus, S., Martins, A., Silva, J., Alves, C., Mouga, T., Gaspar, H., & Pedrosa, R. (2022). Gelidiales Are Not Just Agar—Revealing the Antimicrobial Potential of Gelidium corneum for Skin Disorders. Antibiotics, 11(4), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040481












